Abstract
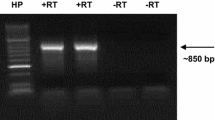
Polish apple cvs: ‘Ligol’, ‘Odra’ and ‘Primula’ served for studies of self-incompatibility. Basing on available sequence data, a new set of primers upstream and downstream of the hypervariable (HV) region of apple S-RNases were designed. Using the RT-PCR method, cDNA was amplified on RNA isolated from styles. PCR products were cloned and sequenced. A new trans-generic S-RNase allele, designated as Skb (GenBank accession no. EU443101), was discovered in cvs ‘Odra’ and ‘Primula’. Nucleotide sequence alignment revealed that Skb-RNase shows 98% identity to SaucS19-RNase from Sorbus aucuparia and 97% identity to CmonS17-RNase from Crataegus monogyna. The occurrence of extensive intergeneric hybridization among extant Pyrinae is considered since the deduced amino acid sequence of Skb-RNase from M. × domestica showed higher similarity to CmonS17 from C. monogyna, SaucS19-RNase from S. aucuparia, St from Malus transitoria, S5-RNase and S3-RNase from Pyrus pyrifolia, and S40-RNase from P. ussuriensis than to S-alleles from Malus × domestica and all of them are grouped in the same cluster of phylogenetic tree. In respect to extremely high similarities between aforementioned S-RNases it could be possible that these alleles existed before the separation of Malus, Pyrus, Sorbus and Crataegus genera. Within Malus, the Skb-RNase from M. × domestica and St-RNase from M. transitoria show 100% identity of the HV region at the deduced amino acid level, suggesting that these S-RNases diverged more recently than the other Malus S-RNases. In ‘Ligol’, the agronomically most important cultivar in Poland, the S2 and S9 were identified.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold K, Bordoli L, Kopp J, Schwede T (2006) The SWISS-MODEL workspace: a web-based environment for protein structure homology modelling. Bioinformatics 22:195–201
Banno K, Kumashiro K, Tateishi S, Takamizawa M, Kiura Y, Tokuhisa F, Tanabe K (1993) Breeding of intergeneric hybrids between Japanese pear and the apple. J Jpn Soc Hort Sci 62(1):138–139
Broothaerts W (2003) New findings in apple S-genotype analysis resolve previous confusion and request the re-numbering of some S-alleles. Theor Appl Genet 106:703–714
Broothaerts W, Janssens GA, Proost P, Broekaert WF (1995) cDNA cloning and molecular analysis of two self-incompatibility alleles from apple. Plant Mol Biol 27:499–511
Campbell CS, Evans RC, Morgan DR, Dickinson TA, Arsenault MP (2007) Phylogeny of subtribe Pyrinae (formerly the Maloideae, Rosaceae): limited resolution of a complex evolutionary history. Pl Syst Evol 266:119–145
Clamp M, Cuff J, Searle SM, Barton GJ (2004) The Jalview Java alignment editor. Bioinformatics 2004(20):426–427
Entani T, Iwano M, Shiba H, Che FS, Isogai A, Takayama S (2003) Comparative analysis of the self-incompatibility (S-) locus region of Prunus mume: identification of a pollen-expressed F-box gene with allelic diversity. Genes Cells 8:203–213
Evans RC, Campbell CS (2002) The origin of the apple subfamily (Rosaceae: Maloideae) is clarified by DNA sequence data from duplicated GBSSI genes. Amer J Bot 89:1478–1484
Felsenstein J (1989) PHYLIP—phylogeny inference package (version 3.2). Cladistics 5:164–166
Golz JF, Su V, Clarke AE, Newbigin E (1999) A molecular description of mutations affecting the pollen components of the Nicotiana alata S locus. Genetics 152:1123–1135
Godron DA (1874) De l’hybridité dans le genre Sorbier. Revue des Sc Nat 4:443–447
Guex N, Peitsch MC (1997) SWISS-MODEL and the Swiss-PdbViewer: an environment for comparative protein modelling. Electrophoresis 18:2714–2723
Hauck NR, Yamane H, Tao R, Iezzoni AF (2006) Accumulation of nonfunctional S-haplotypes results in the breakdown of gametophytic self-incompatibility in tetraploid Prunus. Genetics 172:1191–1198
Horiuchi H, Yanai K, Takagi M, Yano K, Wakabayashi E, Sanda A, Mine S, Ohgi K, Irie M (1998) Primary structure of a base nonspecific ribonuclease from Rhizopus niveus. J Biochem 103:408–418
Hua ZH, Kao T-h (2006) Identification and characterization of components of a putative Petunia S-locus F-box containing E3 ligase complex involved in S-RNase-based self-incompatibility. Plant Cell 18:2531–2553
Hua ZH, Kao T-h (2008) Identification of major lysine residues of S 3-RNase of Petunia inflata involved in ubiquitin–26S proteasome-mediated degradation in vitro. Plant J 54:1094–1104
Hua ZH, Fields A, Kao Th (2008) Biochemical models for S-RNase-based self-incompatibility. Mol Plant 1(4):575–585
Ide H, Kimura M, Arai M, Funatsu G (1991) The complete amino acid sequence of ribonuclease from the seeds of bitter gourd (Momordica charantia). FEBS Lett 284:161–164
Ikeda K, Igic B, Ushijima K, Yamane H, Hauck NR, Nakano R, Sassa H, Iezzoni AF, Kohn JR, Tao R (2004) Primary structural features of the S haplotype-specific F-box protein, SFB, in Prunus. Sex Plant Reprod 16:235–243
Ioerger TR, Clark AG, Kao T-H (1990) Polymorphism at the selfincompatibility locus in Solanaceae predates speciation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:9732–9735
Irie M (1997) Structures and functions of ribonucleases. Yakugaku Zasshi 117(9):561–582
Ishimizu T, Norioka S, Kanai M, Clarke AE, Sakiyama F (1996) Location of cysteine and cystine residues in S-ribonucleases associated with gametophytic self-incompatibility. Eur J Biochem 242:627–635
Ishimizu T, Shinkawa T, Sakiyama F, Norioka S (1998) Primary structural features of rosaceous S-RNases associated with gametophytic self-incompatibility. Plant Mol Biol 37:931–941
Janssens GA, Goderis IJ, Broekaert WF, Broothaerts W (1995) A molecular method for S allele identification in apple based on allele-specific PCR. Theor Appl Genet 91:691–698
Jost W, Bak H, Glund K, Terpstra P, Beintema JJ (1991) Amino acid sequence of an extracellular, phosphate-starvation-induced ribonuclease from cultured tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) cells. Eur J Biochem 198:1–6
Kato S, Mukai Y (2004) Allelic diversity of S-RNase at the self-incompatibility locus in natural flowering cherry populations (Prunus lannesiana var. speciosa). Heredity 92:249–256
Kawata Y, Sakiyama F, Hayashi F, Kyogoku Y (1989) Identification of two essential histidine residues of ribonuclease T2 from Aspergillus oryzae. Eur J Biochem 187:255–262
Kawata Y, Sakiyama F, Tamaoki H (1998) Amino acid sequence of ribonuclease T2 from Aspergillus oryzae. Eur J Biochem 176:683–697
Kurihara H, Nonaka T, Mitsui Y, Ohgi K, Irie M, Nakamura KT (1996) The crystal structure of ribonuclease Rh from Rhizopus niveus at 2.0 Å resolution. J Mol Biol 255:310–320
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2007) ClustalW and ClustalX version 2. Bioinformatics 23(21):2947–2948
Marchler-Bauer A, Anderson JB, Cherukuri PF, DeWeese-Scott C, Geer LY, Gwadz M, He S, Hurwitz DI, Jackson JD, Ke Z, Lanczycki CJ, Liebert CA, Liu C, Lu F, Marchler GH, Mullokandov M, Shoemaker BA, Simonyan V, Song JS, Thiessen PA, Yamashita RA, Yin JJ, Bryant SH (2005) CDD: a conserved domain database for protein classification. Nucleic Acids Res 33:D192–D196
Matsumoto S, Kitahara K (2000) Discovery of a new self-incompatibility allele in apple. HortScience 35:1329–1332
Matsumoto S, Suzuki M, Kitahara K, Soejima J (2000) Possible involvement of a new S-gene ‘St-RNase’ (accession no. AB035928) in the wild apple possessing high similarity to the ‘S3-’ and ‘S5-RNase’ in the Japanese pear. Plant Physiol 122:620
Matsumoto S, Kitahara K, Komatsu H, Soejima J (2001) A functional S-allele, ‘Sg’, in the wild apple possessing a single amino acid, S-RNase ‘Sg’-RNase’, different from ‘Sg-RNase’ in Malus × domestica cultivars. J Hortic Sci Biotechnol 76(2):163–166
Matsuura T, Sakai H, Unno M, Ida K, Sato M, Sakiyama F, Norioka S (2001) Crystal structure at 1.5-Å resolution of Pyrus pyrifolia pistil ribonuclease responsible for gametophytic self-incompatibility. J Biol Chem 276(48):45261–45269
McClure BA, Franklin-Tong V (2006) Gametophytic self-incompatibility: understanding the cellular mechanisms involved in “self” pollen tube inhibition. Planta 224:233–245
McGinnis S, Madden TL (2004) BLAST: at the core of a powerful and diverse set of sequence analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 32:20–25
Nelson-Jones EB, Briggs D, Smith AG (2002) The origin of intermediate species of the genus Sorbus. Theor Appl Genet 105:953–963
Norioka N, Norioka S, Ohnishi Y, Ishimizu T, Oneyama C, Nakanishi T, Sakiyama F (1996) Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequences of cDNAs encoding S-allele specific stylar RNases in a self-incompatible cultivar and its self-compatible mutant of Japanese pear, Pyrus pyrifolia Nakai. J Biochem 120:335–345
Oddou-Muratorio S, Petit RJ, Guerroue BL, Guesnet D, Demesure B (2001) Pollen- versus seed-mediated gene flow in a scattered forest tree species. Evolution 55:1123–1135
Ohgi K, Horiuchi H, Watanabe H, Iwama M, Takagi M, Irie M (1992) Role of Asp51 and GlulO5 in the enzymatic activity of a ribonuclease from Rhizopus niveus. J Biochem 113:219–224
Ohgi K, Iwama M, Ogawa Y, Hagiwara C, Ono E, Kawaguchi R, Kanazawa C, Irie M (1996) Enzymatic activities of several K108 mutants of ribonuclease (RNase) Rh isolated from Rhizopus niveus. Biol Pharm Bull 19:1080–1082
Ortega E, Bošković RI, Sargent DJ, Tobutt KR (2006) Analysis of S-RNase alleles in almond (Prunus dulcis): characterization of new sequences, resolution of synonyms and evidence of intragenic recombination. Mol Genet Genomics 276:413–426
Potter D, Eriksson T, Evans RC, Oh S, Smedmark JEE, Morgan DR, Kerr M, Robertson KR, Arsenault M, Dickinsos TA, Campbell CS (2007) Phylogeny and classification of Rosaceae. Pl Syst Evol 266:5–43
Przybyla AA, Kantorowicz-Bąk M (2005) New Polish cultivars of apples. Proc of Int Sc Conf Environmentally Friendly Fruit Growing 222:15–19
Qiao H, Wang F, Zhao L, Zhou J, Lai Z, Zhang Y, Robbins TP, Xue Y (2004a) The F-box protein AhSLF-S2 controls the pollen function of S-RNase-based self-incompatibility. Plant Cell 16:2307–2322
Qiao H, Wang F, Zhao L, Zhou J, Huang J, Zhang Y, Xue Y (2004b) The F-box protein AhSLF-S2 physically interacts with S-RNases that may be inhibited by the ubiquitin/26S proteasome pathway of protein degradation during compatible pollination in Antirrhinum. Plant Cell 16:582–595
Richards FM, Wyckoff HW (1971) Bovine pancreatic ribonuclease. In: Boyer PD (ed) The enzymes, 4th edn. Academic Press, New York, pp 647–806
Richman AD, Kohn JR (1996) Learning from rejection: the evolutionary biology of single-locus incompatibility. Trends Ecol Evol 11:497–502
Robertson KR, Phipps JB, Rohrer JR, Smith PG (1991) A synopsis of genera of the Maloideae (Rosaceae). Syst Bot 16:376–394
Sassa H, Nishio T, Kowyama Y, Hirano T, Koba T, Ikehashi H (1996) Self-incompatibility (S) alleles of the Rosaceae encode members of a distinct class of the T2/S ribonuclease superfamily. Mol Gen Genet 250:547–557
Sassa H, Kakui H, Miyamoto M, Suzuki Y, Hanada T, Ushijima K, Kusaba M, Hirano H, Koba T (2007) S locus F-box Brothers: multiple and pollen-specific F-box genes with S haplotype-specific polymorphisms in apple and Japanese pear. Genetics 175:1869–1881
Sax K (1931) The origin and relationships of the Pomoideae. J Arnold Arbor 12:3–22
Sax K (1932) Chromosome relationships in the Pomoideae. J Arnold Arbor 13:363–367
Schwede T, Kopp J, Guex N, Peitsch MC (2003) SWISS-MODEL: an automated protein homology-modeling server. Nucleic Acids Res 31:3381–3385
Shimura I, Ito Y, Seike K (1983) Intergeneric hybrid between Japanese pear and quince. J Jpn Soc Hort Sci 52:243–249
Sonneveld T, Tobutt KR, Vaughan SP, Robbins TP (2005) Loss of pollen-S function in two self-compatible selections of Prunus avium is associated with deletion/mutation of an S haplotype-specific F-box gene. Plant Cell 17:37–51
Šurbanovsky N, Tobutt KR, Konstantinović M, Maksimović SargentDJ, Stefanović V, Ortega E, Bošković R (2007) Self-incompatibility of Prunus tenella and evidence that reproductively isolated species of Prunus have different SFB alleles coupled with an identical S-RNase allele. Plant J 50:723–724
Sutherland BG, Tobutt KR, Robbins TP (2008) Trans-specific S-RNase and SFB alleles in Prunus self-incompatibility haplotypes. Mol Genet Genomics 279:95–106
Tanaka N, Arai J, Inokuchi N, Koyama T, Ohgi K, Irie M, Nakamura KT (2000) Crystal structure of a plant ribonuclease, RNase LE. J Mol Biochem 298:859–873
Tsai D-S, Lee H-S, Post LC, Kreiling KM, Kao T-H (1992) Sequence of an S-protein of Lycopersicon peruvianum and comparison with other solanaceous S-proteins. Sex Plant Reprod 5:256–263
Ushijima K, Sassa H, Tao R, Yamane H, Dandekar AM, Gradziel TM, Hirano H (1998) Cloning and characterization of cDNAs encoding S-RNases from almond (Prunus dulcis): primary structural features and sequence diversity of the S-RNases in Rosaceae. Mol Gen Genet 260:261–268
Vieira J, Morales-Hojas R, Santos RAM, Vieira CP (2007) Different positively selected sites at the gametophytic self-incompatibility pistil S-RNase gene in the Solanaceae and Rosaceae (Prunus, Pyrus, and Malus). J Mol Evol 65:175–185
Westwood MN, Lombard PB, Bjornstad HO (1989) Pear on ‘Winter Banana’ interstem with M. 26 apple rootstock as a compatible combination. HortScience 24:765–767
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Warsaw University of Life Sciences—SGGW, Grant No. 504-10-04020011.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bokszczanin, K., Palucha, A. & Przybyla, A.A. Description of a new trans-generic Skb-RNase allele in apple. Euphytica 166, 83–94 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-008-9839-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-008-9839-6