Abstract
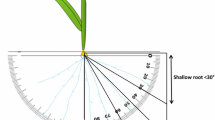
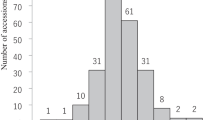
In order to gain a better understanding of the complex root traits observed in previous studies using a mapping population derived from a Bala × Azucena cross, an experiment was conducted growing plants in agar-filled Perspex chambers with the aim of identifying quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for both seminal root morphology (SRM) and gravitropic response. A total of four main effect QTLs were detected for SRM (a measurement of the degree of a wavy/curly seminal root phenotype); two were located on chromosome 2, one at the top of chromosome 3 and one on chromosome 11. Two main effect QTLs were detected for the gravitropic response (the degree of bending of the growing seminal root when subjected to a 90° rotation); one on chromosome 6 and 1 on chromosome 11. As well as main effect QTLs, an epistatic interaction was observed for each of the traits. For SRM an interaction was detected between the top and the bottom of chromosome 4. For the gravitropic response an interaction was observed between a location on chromosome 6 and 11. Both these interactions were confirmed by analysis of variance using marker classes and the epistatic gravitropic response was also confirmed using a pair of near isogenic lines. All the SRM QTLs detected in this experiment co-localise with root growth QTLs (root penetration or morphology) detected previously in the mapping population. This information could prove valuable in attempts to identify candidate genes for these potentially valuable QTLs because we could postulate that the underlying genes should be involved in the pathway of gravity detection, signal transduction or the growth response to gravity.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BA:
-
Bending angle
- RIL:
-
Recombinant inbred line
- RINIL:
-
Recombinant inbred near isogenic line
- SRM:
-
Seminal root morphology
References
Blancaflor EB, Fasano JM, Gilroy S (1998) Mapping the functional roles of cap cells in the response of arabidopsis primary roots to gravity. Plant Physiol 116:213–222. doi:10.1104/pp.116.1.213
Cairns JE, Audebert A, Townend J, Price AH, Mullins CE (2004) Effect of soil mechanical impedance on root growth of two rice varieties under field drought stress. Plant Soil 267:309–318. doi:10.1007/s11104-005-0134-1
Chen R, Guan C, Boonsirichai K, Masson PH (2002) Complex physiological and molecular processes underlying root gravitropism. Plant Mol Biol 49:305–317. doi:10.1023/A:1015294711391
Debi BR, Mushika J, Taketa S, Miyao A, Hirochika H, Ichii M (2003) Isolation and characterization of a short lateral root mutant in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Sci 165:895–903. doi:10.1016/S0168-9452(03)00293-0
Debi BR, Chhun T, Taketa S, Tsurumi S, Xia K, Miyao A et al (2005) Defects in root development and gravity response in the aem1 mutant of rice are associated with reduced auxin efflux. J Plant Physiol 162:678–685. doi:10.1016/j.jplph.2004.09.012
MacMillan K, Emrich K, Piepho H, Mullins CE, Price AH (2006) Assessing the importance of genotype × environment interaction for root traits in rice using a mapping population II: conventional QTL analysis. Theor Appl Genet 113:953–964. doi:10.1007/s00122-006-0357-4
Müller A, Guan C, Gälweiler L, Tänzler P, Huijser P, Marchant A, Parry G, Bennett M, Wisman E, Palme K (1998) AtPIN2 defines a locus of Arabidopsis for root gravitropism control. EMBO J 17:6903–6911
Perrin RM, Young L, Narayana Murthy UM, Harrison BR, Wang Y, Will JL, Masson PH (2005) Gravity signal transduction in primary roots. Ann Bot 96:737–743
Price AH, Tomos AD (1997) Genetic dissection of root growth in rice (Oryza sativa L.). II: mapping quantitative trait loci using molecular markers. Theor Appl Genet 95:143–152
Price AH, Tomos AD, Virk DS (1997) Genetic dissection of root growth in rice (Oryza sativa L.) I: a hydroponic screen. Theor Appl Genet 95:132–142
Price AH, Steele KA, Moore BJ, Barraclough PB, Clark LJ (2000) A combined RFLP and AFLP linkage map of upland rice (Oryza sativa L.) used to identify QTLs for root-penetration ability. Theor Appl Genet 100:49–56
Price AH, Steele KA, Moore BJ, Jones RGW (2002) Upland rice grown in soil-filled chambers and exposed to contrasting water-deficit regimes. II. Mapping quantitative trait loci for root morphology and distribution. Field Crops Res 76:25–43
Shen Y, Jiang H, Jin J, Zhang Z, Xi B, He Y, Wang G, Wang C, Qian L, Li X, Yu Q, Liu H, Chen D, Gao J, Huang H, Shi T, Yang Z (2004) Development of genome-wide DNA polymorphism database for map-based cloning of rice genes. Plant Physiol 135:1198–1205
Swarup R, Friml J, Marchant A, Ljung K, Sandberg G, Palme K, Bennett M (2001) Localization of the auxin permease AUX1 suggests two functionally distinct hormone transport pathways operate in the Arabidopsis root apex. Genes Dev 15:2648–2653
Wang DL, Zhu J, Li ZK, Paterson AH (1999a) Mapping QTLs with epistatic effects and QTL × environment interactions by mixed linear model approaches. Theor Appl Genet 99:1255–1264
Wang DL, Zhu J, Li ZK, Paterson AH (1999b) User manual for QTLMapper version 1.0. Texas A & M University, College Station
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by a BBSRC grant (BB/C509931/1). The RINILs were generated in BBSRC grant P11790.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Norton, G.J., Price, A.H. Mapping of quantitative trait loci for seminal root morphology and gravitropic response in rice. Euphytica 166, 229–237 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-008-9833-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-008-9833-z