Abstract
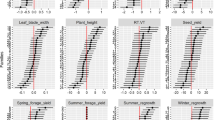
Coffea canephora Pierre breeding in Côte d’Ivoire is based on indirect reciprocal recurrent selection (RRSi) using the Congolese and Guinean populations. In practice, the genotypes of each population (78 Congolese genotypes and 100 Guinean genotypes) are tested with several testers from the reciprocal population: two Guinean and three Congolese testers. These testers are heterozygous as C. canephora is a strictly outcrossing species. After a first cycle of RRSi, we judged the efficiency of these testers for yield, susceptibility to coffee leaf rust (SCLR) and hundred bean weight (HBW). All the testers discriminated the tested genotypes highly significantly (P < 0.01), even though differences were found in the degrees of discrimination. For yield and SCLR, no interaction between tested genotypes and testers was observed and correlations between test values obtained from different testers were significant or highly significant. Furthermore, test values of tested genotypes could be used to predict the yield and SCLR of between-population (BP) hybrids. Prediction was always more accurate with the best tester than with the mean of several testers. As opposed to yield and SCLR, HBW showed significant interactions between tested genotypes and testers and HBW of hybrids could not be predicted from the test value of the genotypes. We conclude that only one reciprocal tester can be used in the next cycles of RRSi applied to C. canephora. This will allow either a reduced cost of selection or increased selection intensity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baudouin L, Baril C, Clément-Demanges A et al (1997) Recurrent selection of tropical tree crops. Euphytica 96:101–114
Berthaud J (1980) L’incompatibilité chez Coffea canephora : méthode de test et déterminisme génétique. Café Cacao Thé 24:267–274
Berthaud J (1986) Les ressources génétiques pour l’amélioration des caféiers africains diploïdes. Evaluation de la richesse génétique des populations sylvestres et de ses mécanismes organisateurs. Conséquences pour l’application. Orstom, Paris (FRA), 379 pp
Capot J (1977) L’amélioration du caféier Robusta en Côte d’Ivoire. Café Cacao Thé 21:233–244
Charcosset A, Lefort-Buson M, Gallais A (1990) Use of top-cross designs for predicting performance of maize single cross hybrids. Maydica 35:23–27
Charcosset A, Bonnisseau B, Touchebeuf O et al (1998) Prediction of maize hybrid silage performance using marker data: comparison of several models for specific combining ability. Crop Sci 38:38–44
Comstock RE, Robinson HF, Harvey PH (1949) A breeding procedure designed to make the maximum use of both general and specific combining ability. Agron J 41:360–367
Darrah LL, Eberhart SA, Penny LH (1972) A maize breeding methods study in Kenya. Crop Sci 12:605–608
Flachenecker C, Frisch M, Falke KC, Melchinger AE (2006) Genetic drift and selection effects of modified recurrent full-sib selection programs in two F2 populations of European flint maize. Theor Appl Genet 113:1113–1120
Gallais A (1978) Amélioration des populations, méthodes de sélection et création de variétés. III. Bases théoriques de la sélection récurrente réciproque. Ann Amélioration des Plantes 28:637–666
Gallais A (1990a) Application of the concepts of test value and varietal value to the study of genetic advance in recurrent selection : a synthesis. Euphytica 48:197–209
Gallais A (1990b) Théorie de la sélection en amélioration des plantes. Masson, Paris, 588 pp
Gouesnard B, Panouillé A, Dupin M, Boyat A (1996) Evaluation of three grain maize composites developed from broad-base synthetics by divergent selection on three complementary testers. Agronomie 16:187–193
Groos C, Oury FX, Sourdille P et al (2001) Selection of molecular markers for prediction of heterosis with an application to wheat. In: Gallais A, Dillman C, Goldringer I (eds) Quantitative genetics and breeding methods: the way ahead. INRA, Paris, 221–230
Hallauer AR, Miranda JB (1988) Quantitative genetics in maize breeding. 2nd edn. Iowa State University Press, Ames, Iowa, pp 468
Horner ES, Chapman WH, Lundy HW, Lutrick MC (1973) Comparison of three methods of recurrent selection in maize. Crop Sci 13:485–498
Landi P, Frascaroli E (1995) Response to modified reciprocal recurrent selection in two maize synthetics. Crop Sci 35:791–797
Lashermes P, Couturon E, Charrier A (1994) Doubled haploids of Coffea canephora : development, fertility and agronomic characteristics. Euphytica 74:149–157
Leroy T, Montagnon C, Charrier A, Eskes AB (1993) Reciprocal recurrent selection applied to Coffea canephora Pierre. I. Characterization and evaluation of breeding populations and value of intergroup hybrids. Euphytica 67:113–125
Leroy T, Montagnon C, Cilas C et al (1994) Reciprocal recurrent selection applied to Coffea canephora Pierre. II. Estimation of genetic parameters. Euphytica 74:121–128
Menz Rademacher MA, Hallauer AR, Russell WA (1999) Comparative response of two reciprocal recurrent selection methods in BS21 and BS22 maize populations. Crop Sci 39:89–97
Montagnon C (2000) Optimisation des gains génétiques dans le schéma de sélection récurrente réciproque de Coffea canephora Pierre. Thèse de doctorat, Ecole Nationale Supérieure Agronomique (Montpellier), 133 pp
Montagnon C, Cilas C, Leroy T, Yapo A, Charmetant P (2000) Genotype-location interactions for Coffea canephora yield in the Ivory Coast. Agron 20:101–109
Montagnon C, Guyot B, Cilas C, Leroy T (1998) Genetic parameters of several biochemical compounds from green coffee, Coffea canephora. Plant Breed 117:576–578
Montagnon C, Leroy T, Kebe I, Eskes AB (1994) Importance of coffee leaf rust and factors involved in field evaluation of the resistance of Coffea canephora in Côte d’Ivoire. Café Cacao Thé 38:103–112
Oury FX, Brabant P, Bérard P, Pluchard P (2000) Predicting hybrid value in bread wheat : biometric modelling based on a « top-cross » design. Theor Appl Genet 100:96–104
Rawlings JO, Thompson DL (1962) Performance level as criterion for the choice of maize testers. Crop Sci 2:217–220
Russell WA, Eberhart SA, Vega UA (1973) Recurrent selection for specific combining ability for yield in two maize populations. Crop Sci 13:257–261
Russell WA, Eberhart SA (1975) Hybrid performance of selected maize lines from reciprocal recurrent selection and testcross selection programs. Crop Sci 15:1–4
Russell WA, Blackburn DJ, Lamkey KR (1992) Evaluation of a modified reciprocal recurrent selection procedure for maize improvement. Maydica 37:61–67
Schumann DEW, Bradley RA (1959) The comparison of the sensitivities of similar experiments : model II of the analysis of variance. Biometrics 15:405–416
Walejko RN, Russell WA (1977) Evaluation of recurrent selection for specific combining ability in two open pollinated maize cultivars. Crop Sci 17:647–651
Wricke G (1965) Die erfassung der wechselwirkung zwischen genotyp und umwelt bei quantitativen eigenschaften. J Plant Breed 53:266–343
Zambezi BT, Horner ES, Martin FG (1986) Inbred lines as testers for general combining ability in maize. Crop Sci 26:908–910
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work is the result of a cooperation between the Centre National de Recherche Agronomique of Côte d’Ivoire (CNRA) and the Centre International de Recherche Agronomique pour le Développement (CIRAD).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Montagnon, C., Leroy, T., Cilas, C. et al. Heterozygous genotypes are efficient testers for assessing between-population combining ability in the reciprocal recurrent selection of Coffea canephora . Euphytica 160, 101–110 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-007-9561-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-007-9561-9