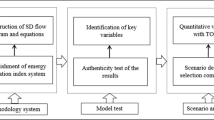
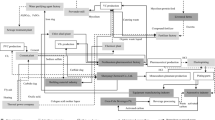
Abstract
As suppliers of basic energy and raw materials, resource-based cities have played an important role in China's induzzstrialization process. However, with the high intensity of resource development and utilization, many resource-based cities are faced with economic and social problems such as resource exhaustion and economic stagnation. How to achieve sustainable development of resource-based cities has become a hot topic both in government and academia in recent times. Zaozhuang City of Shandong Province (Sdzz) was once a famous coal resource-based city in China, but after more than half a century of mining, coal resources have been almost exhausted. Taking Sdzz as an example, based on the theory of complexity, this paper analyzes the development situation of the major industries in Sdzz by using location entropy. On this basis, we use system dynamics to analyze the economic development of Sdzz from the perspectives of resources, environment, population, technology, economy, etc. The research results indicate that prioritizing the development of high-end manufacturing and strengthening financial and technological investment are effective ways to improve the efficiency of Sdzz's economic development. Finally, several constructive countermeasures and suggestions are put forward based on balancing the interests of all parties.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Gwaiz, M., Chao, X., & Wu, Q. O. (2017). Understanding how generation flexibility and renewable energy affect power market competition. Manufacturing and Service Operations Management, 19(1), 114–131. https://doi.org/10.1287/msom.2016.0595
Aflaki, S., & Serguei, N. (2017). Strategic investment in renewable energy sources: The effect of supply intermittency. Manufacturing and Service Operations Management, 19(1), 489–507. https://doi.org/10.1287/msom.2017.0621
Atasu, A., Corbett, C. J., Huang, X., & Toktay, L. B. (2020). Sustainable operations management through the perspective of manufacturing & service operations management. Manufacturing and Service Operations Management, 22(1), 146–157. https://doi.org/10.1287/msom.2019.0804
Babich, V., Lobel, R., Yücel, Ş. (2020). Promoting solar panel investments: Feed-in-tariff vs. tax-rebate policies. Manufacturing and Service Operations Management, 22(6), 1148–1164. https://doi.org/10.1287/msom.2019.0860
Botequilha-Leitão, A., & Díaz-Varela, E. R. (2020). Performance Based Planning of complex urban social-ecological systems: The quest for sustainability through the promotion of resilience. Sustainable Cities and Society, 56, 102089. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2020.102089
Braz, A. C., & de Mello, A. M. (2022). Circular economy supply network management: A complex adaptive system. International Journal of Production Economics, 243, 108317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2021.108317
Bettencourt, L. M. A. (2019). Complex systems modeling of urban development: Understanding the determinants of health and growth across scales. Integrating human health into urban and transport planning. Springer, Cham, 173–197. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-74983-9_10
Chen, X., & Di, G. (2021). A case study on Pingdingshan city: Performance evaluation of and developing approaches to ecological transformation in resource-based cities. Resources and Industry, 23(5), 1–10.
CPC (Central committee and State Council). (2021). The 14th Five Year Plan for National Economic and Social Development and the Long-Range Objectives Through the Year 2035. Beijing: CPC, Central committee and State Council.
Gebetsroither-Geringer, E., Loibl, W. (2016). Urban development simulator: How can participatory data gathering support modeling of complex urban systems. Understanding Complex Urban Systems. Springer, Cham, 33–47.
Hu, X., & Zhang, W. (2018). Institutional evolution and regional economic resilience: A comparison of two resource-depleting cities. Geographical Research, 37(7), 1308–1319.
Huang, T., Li, J., Xu, J., & Liao, X. (2019). Performance evaluation and obstacle factor diagnosis of resource-exhausted urban transformation and development. Journal of Natural Resources, 34(7), 1417–1428.
Innis, H. A. (1931). The economic development of the british overseas empire. Comparative View of Dominion Problems, Canada., 2, 164–166.
Kuai, P., Li, W., Cheng, R., & Cheng, G. (2015). An application of system dynamics for evaluating planning alternatives to guide a green industrial transformation in a resource-based city. Journal of Cleaner Production, 104, 403–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.05.042
Lin, C., Tung, C., & Huang, C. (2006). Elucidating the industrial cluster effect from a system dynamics perspective. Technovation, 26(4), 473–482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.technovation.2004.11.008
Liu, L., Zhu, Y., & Guo, S. (2020). The evolutionary game analysis of multiple stakeholders in the low-carbon agricultural innovation diffusion. Complexity, 2020, 6309545. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/6309545
Luo, F., & Li, W. (2019). Development level of circular economy in Southern Shaanxi Based on system dynamics. Ecological Economics, 35(7), 63–69.
Mabon, L., & Shih, W. (2018). Management of sustainability transitions through planning in shrinking resource city contexts: An evaluation of Yubari City, Japan. Journal of Environmental Policy and Planning, 20(4), 482–498. https://doi.org/10.1080/1523908X.2018.1443004
Meramveliotakis, G., & Manioudis, M. (2021). History, knowledge, and sustainable economic development: the contribution of John Stuart Mill’s grand stage theory. Sustainability, 13(3), 1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031468
Ma, J., Hou, Y., Wang, Z., & Yang, W. (2021). Pricing strategy and coordination of automobile manufacturers based on government inter-vention and carbon emission reduction. Energy Policy, 148, 111919. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2020.111919
Ma, J., Hou, Y., Yang, W., & Tian, Y. (2020). A time-based pricing game in a competitive vehicle market regarding the intervention of car-bon emission reduction. Energy Policy, 142, 111440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2020.111440
Ma, J. (2021). Nonlinear Analysis Methods for Complex Economic and Financial Systems. Beijing Science Press 6.
Ma, J., & Xu, T. (2023). Optimal strategy of investing in solar energy for meeting the renewable portfolio standard requirement in America. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 74(1), 181–194. https://doi.org/10.1080/01605682.2022.2032427
Ma, J., & Ren, N. (2016). Complexity and Hopf bifurcation analysis on a kind of fractional-order IS-LM macroeconomic system. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, 26(11), 1650181. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218127416501819
Ma, J., Si, F., Zhang, Q., & Wang, Z. (2024). Impact of extended warranty service on product pricing in online direct retailers’ competitive market. Energy Economics, 129(1), 107217.
Sun, T., Lu, Y., & Cheng, L. (2020). Implementation effect, long-term mechanism and industrial upgrading of resource-exhausted cities. China Industrial Economics, 7, 98–116.
Tang, J., & Chen, J. (2011). A game analysis of resource depletion from the perspective of prisoner dilemma. Management World, 7, 173–174.
Tao, J., Zhou, X., & Liu, Y. (2018). The Breaking Changes of resource-exhausted Cities. People’s Forum, 4, 86–88.
Tian, S., Li, X., Yang, J., & Guo, J. (2023). Spatiotemporal evolution of pseudo human settlements: Case study of 36 cities in the three provinces of Northeast China from 2011 to 2018. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 25, 1742–1772. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-022-02120-0
Tian, Y., Zhao, L., & Zhu, M. (2022). dynamic game of the dual-channel supply chain under a carbon subsidy policy. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos 32(15), 2250223. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218127422502236
Tonts, M., Plummer, P., & Lawrie, M. (2012). Socio-economic wellbeing in Australian mining towns: A comparative analysis. Journal of Rural Studies, 28(3), 288–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrurstud.2011.10.006
Wang, C. J., Qu, Y. Y., & Wu, X. L. (2019). A study on Economic-Population contraction governance in Resource-exhausted cities: a realistic analysis based on the reality analysis of resource-exhausted cities in Heilongjiang Province. Macroeconomic Research, 8, 156–169.
Wu, T., Zhang, N., Gui, L., & Wu, W. (2018). Sustainable endogenous growth model of multiple regions: Reconciling OR and economic perspectives. European Journal of Operational Research, 269(1), 218–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2017.10.040
Wu, Q., Zhu, M., & Guo, P. (2019). Research on the performance evaluation of resource-based economic transformation based on decoupling theory. Economic Problems, 6, 127–134.
Wu, W., Zhou, J., Niu, J., & Lv, H. (2021). Study on coupling between mineral resources exploitation and the mining ecological environment in Shanxi Province. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 23, 13261–13283. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-020-01209-8
Qi, L., Zhou, Y., Li, F., Li, X., & Zhang, J. (2017). Research on the order degree of circular economy system in Industrial park: Based on the perspective of complex network structure entropy. Science and Technology Management Research, 22, 242–247.
Yu, H., Wang, W., Yang, B., & Li., C. (2019). Evolutionary game analysis of the stress effect of cross-regional transfer of resource-exhausted enterprises. Complexity, 2019, 7652430. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/7652430
Zakeri, G., Pritchard, G., Bjorndal, M., & Bjorndal, E. (2019). Pricing wind: A revenue adequate, cost recovering uniform price auction for electricity markets with intermittent generation. Informs Journal on Optimization, 1(1), 35–48. https://doi.org/10.1287/ijoo.2018.0002
Zhu, Y., Luo, Y., Chen, J. Wan, Q. (2023). Industrial transformation efficiency and sustainable development of resource-exhausted cities: a case study of Daye City, Hubei province, China. Environment, Development and Sustainability. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-023-03269-y
ZMG (Zaozhuang Municipal Government). (2020). Proposal of zaozhuang municipal committee of the communist party of China on the formulation of the 14th Five-Year plan for national economic and social development of zaozhuang and The 2035 vision goal. Zaozhuang, Zaozhuang municipal government.
ZMG (Zaozhuang Municipal Government). (2018). Special planning of zaozhuang on kinetic energy conversion in information technology industry (2018–2022). Zaozhuang, Zaozhuang Municipal Government.
ZMG (Zaozhuang Municipal Government). (2011). The Zaozhuang’s plan on resource city transformation and sustainable development (2010–2020). Zaozhuang, Zaozhuang Municipal Government.
ZMG (Zaozhuang Municipal Government). (2018). Zaozhuang modern financial industry development regulations (2018–2022). Zaozhuang, Zaozhuang Municipal Government.
Acknowledgements
We thank the reviewers and associate editor for their careful reading and helpful comments on the revision of paper. The research was supported by the Tianjin Planning Leading Group Office of Philosophy and Social Sciences under Grant (Number TJYJ21-001) and the Innovation Fund of Tianjin University. The Tianjin Planning Leading Group Office of Philosophy and Social Sciences under Grant (Number TJYJ21-001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, J., Zhang, B., Liu, L. et al. Sustainable development research of resource-exhausted cities based on system dynamics: a case study of Sdzz. Environ Dev Sustain (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-024-04839-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-024-04839-4