Abstract
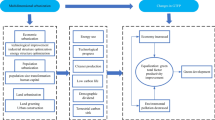
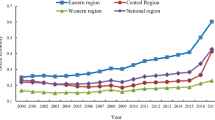
The green use of urban land plays a crucial role in the high-quality development of regional economy. Meanwhile the green total factor productivity is considered an important indicator for measuring high-quality economic development. Based on panel data for 108 cities in the Yangtze River Economic Belt from 2003 to 2018, Spatial Durbin Model and Panel Threshold Model are used in this paper to analyze the impact of urban land scale endowments and land economic endowments on green total factor productivity. The results show that: (1) the green total factor productivity of cities in the Yangtze River Economic Belt ranges from 0.164 to 1.209, which is more than half of the cities achieved growth, and the average value fluctuated up and down during the study period; (2) the expansion of urban land scale significantly inhibits green total factor productivity, while GDP per unit land area promotes green total factor productivity; (3) the spatial correlation exists in urban land use and green total factor productivity, and there is heterogeneity in this impact among regions; (4) there is a threshold effect between urban land use and green total factor productivity, and the effect differs depending on which variables are considered (environmental regulations, average wage, and population density); and (5) under the regulation of urban population density, the influence of the urban land economic benefit on green total factor productivity changes from inhibition to promotion, showing a U-shaped relationship. Finally, we provide some policy suggestions for optimizing land use structures and improving land eco-economic efficiency of the Yangtze River Economic Belt.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Brunnermeier, S. B., & Cohen, M. A. (2003). Determinants of environmental innovation in US manufacturing industries. Journal of Environmental Economics and Management, 45(2), 278–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0095-0696(02)00058-X.
Duro, J. A., Lauk, C., Kastner, T., Erb, K. H., & Haberl, H. (2020). Global inequalities in food consumption, cropland demand and land-use efficiency: A decomposition analysis. Global Environmental Change, 64, 102124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2020.102124.
Dyckhoff, H., & Allen, K. (2001). Measuring ecological efficiency with data envelopment analysis (DEA). European Journal of Operational Research, 132(2), 312–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0377-2217(00)00154-5.
Fetzel, T., Niedertscheider, M., Haberl, H., Krausmann, F., & Erb, K. H. (2016). Patterns and changes of land use and land-use efficiency in Africa 1980–2005: An analysis based on the human appropriation of net primary production framework. Regional Environmental Change, 16, 1507–1520. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-015-0891-1.
Goldsmith, R. W. (2009). A perpetual inventory of national wealth. In Conference on research in income and wealth. Studies in Income and Wealth (pp. 5–74). NBER.
Guan, D. J., He, X. J., He, C. Y., Cheng, L. D., & Qu, S. J. (2020). Does the urban sprawl matter in Yangtze River Economic Belt, China? An integrated analysis with urban sprawl index and one scenario analysis model. Cities, 99, 102611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2020.102611.
Han, B., Ouyang, Z., & Wang, W. (2018). The relationship between regional, industrial organizing levels and ecological economic efficiency. Journal of Cleaner Production, 171(Part 2), 857–866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.09.276
Hansen, B. E. (1999). Threshold effects in non-dynamic panels: Estimation, testing, and inference. Journal of Econometrics, 93(2), 345–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-4076(99)00025-1.
Hansen, G. D., & Prescott, E. C. (2002). Malthus to Solow. American Economic Review, 92(4), 1205–1217. https://doi.org/10.1257/00028280260344731.
Hasan, S. S., Deng, X. Z., Li, Z. H., & Chen, D. D. (2017). Projections of future land use in Bangladesh under the background of baseline, ecological protection and economic development. Sustainability, 9(4), 505. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9040505.
Hou, X. H., Liu, J. M., Zhang, D. J., Zhao, M. J., & Yin, Y. Q. (2021). Effect of landscape-scale farmland fragmentation on the ecological efficiency of farmland use: A case study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(1), 26935–26947. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12523-7.
Huang, D. X., & Chan, R. C. K. (2018). On ‘Land Finance’ in urban China: Theory and practice. Habitat International, 75, 96–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2018.03.002.
Jiang, X., Lu, X., & Gong, M. (2019). Land leasing marketization, industrial structure optimization and urban green total factor productivity: An empirical study based on Hubei province. China Land Science, 33(5), 50–59. https://doi.org/10.11994/zgtdkx.20190418.092049. (In Chinese).
Jin, G., Deng, X. Z., Zhao, X. D., Guo, B. S., & Yang, J. (2018). Spatiotemporal patterns in urbanization efficiency within the Yangtze River Economic Belt between 2005 and 2014. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 28, 1113–1126. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-018-1545-2.
Karakaya, E., Bostan, A., & Özçağ, M. (2019). Decomposition and decoupling analysis of energy-related carbon emissions in Turkey. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(31), 32080–32091. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06359-5.
Lan, X. (2021). Stay inside: China’s economic and political development (pp. 67–68). Shanghai People’s Publishing House. (In Chinese).
LeSage, J. P., & Pace, R. K. (2008). Spatial econometric modeling of origin-destination flows. Journal of Regional Science, 48(5), 941–967. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9787.2008.00573.x.
Li, B., & Wu, S. (2017). Effects of local and civil environmental regulation on green total factor productivity in China: A spatial Durbin econometric analysis. Journal of Cleaner Production, 153, 342–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.10.042.
Li, W., Feng, T., & Hao, J. (2009). The evolving concepts of land administration in China: Cultivated land protection perspective. Land Use Policy, 26(2), 262–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2008.02.008.
Lin, G. C. S., & Yi, F. (2013). Urbanization of capital or capitalization on urban land? Land development and local public finance in urbanizing China. Urban Geography, 32(1), 50–79. https://doi.org/10.2747/0272-3638.32.1.50.
Liu, S. Y. (2019). The structure and changes of China’s land system. China Agricultural Economic Review, 11(3), 471–488. https://doi.org/10.22459/CYRD.07.2018.22.
Liu, X., & Yin, X. (2010). Spatial externalities and regional income inequality: Evidence from China’s prefecture-level data. Frontiers of Economics in China, 5, 325–338. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11459-010-0016-1.
Liu, Z. J., Huang, H. Q., Werners, S. E., & Yan, D. (2016). Construction area expansion in relation to economic-demographic development and land resource in the Pearl River Delta of China. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 26, 188–202. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-016-1262-7.
Liu, Y., Zhang, Z., & Zhou, Y. (2018). Efficiency of construction land allocation in China: An econometric analysis of panel data. Land Use Policy, 74, 261–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2017.03.030.
Liu, Y. L., Zhang, X. H., Pan, X. Y., Ma, X. X., & Tang, M. Y. (2020). The spatial integration and coordinated industrial development of urban agglomerations in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Cities, 104, 102801. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2020.102801.
Loganathan, N., Mursitama, T., Pillai, L., Khan, A., & Taha, R. (2020). The effects of total factor of productivity, natural resources and green taxation on CO2 emissions in Malaysia. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(36), 45121–45132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10291-4
Lu, X., Chen, D., Kuang, B., Zhang, C., & Cheng, C. (2020). Is high-tech zone a policy trap or a growth drive? Insights from the perspective of urban land use efficiency. Land Use Policy, 95, 104583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2020.104583.
Luo, Q. L., Zhou, J. F., Li, Z. G., & Yu, B. L. (2020). Spatial differences of ecosystem services and their driving factors: A comparation analysis among three urban agglomerations in China’s Yangtze River Economic Belt. Science of the Total Environment, 725, 138452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138452.
Mao, X. Y., Huang, X. J., Song, Y. Y., Zhu, Y., & Tan, Q. C. (2020). Response to urban land scarcity in growing megacities: Urban containment or inter-city connection? Cities, 96, 102399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2019.102399.
Patel, S. K., Verma, P., & Singh, G. (2019). Agricultural growth and land use land cover change in peri-urban India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191(9), 600. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7736-1.
Qiu, S., Wang, Z., & Geng, S. (2021). How do environmental regulation and foreign investment behavior affect green productivity growth in the industrial sector? An empirical test based on Chinese provincial panel data. Journal of Environmental Management, 287, 112282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112282.
Rehfeld, K. M. (2007). Integrated product policy and environmental product innovations: An empirical analysis. Ecological Economics, 61(1), 91–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2006.02.003.
Ryan-Collins, J., Lloyd, T., & Macfarlane, L. (2017). Rethinking the economics of land and housing. University of Chicago Press.
Samie, A., Abbas, A., Azeem, M. M., Hamid, S., Iqbal, M. A., Hasan, S. S., & Deng, X. Z. (2020). Examining the impacts of future land use/land cover changes on climate in Punjab Province, Pakistan: Implications for environmental sustainability and economic growth. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27, 25415–25433. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08984-x
Sbardella, A., Pugliese, E., & Pietronero, L. (2017). Economic development and wage inequality: A complex system analysis. PLoS ONE, 12(9), e0182774. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0182774
Schaltegger, S., & Sturm, A. (1990). Ökologische Rationalität (German/in English: Environmental rationality). Die Unternehmung, 4(4), 117–131.
She, Y., Liu, Y. B., Jiang, L., & Yuan, H. X. (2019). Is China’s River Chief Policy effective? Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 220, 919–930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.02.031.
Song, M. L., Ma, X. W., Shang, Y. P., & Zhao, X. (2020). Influences of land resource assets on economic growth and fluctuation in China. Resources Policy, 68, 101779. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2020.101779
Sun, Y. T., & Liu, K. (2016). Proximity effect, preferential attachment and path dependence in inter-regional network: A case of China’s technology transaction. Scientometrics, 108(1), 201–220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-016-1951-0
Tikoudis, I., Farrow, K., Mebiame, R. M., & Oueslati, W. (2021). Beyond average population density: Measuring sprawl with density-allocation indicators. Land Use Policy, 112, 105832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2021.105832
Tone, K. (2001). A slacks-based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis. European Journal of Operational Research, 130(3), 498–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0377-2217(99)00407-5
Ullah, K. M., & Mansourian, A. (2015). Evaluation of land suitability for urban land-use planning: Case study Dhaka city. Transactions in GIS, 20(01), 20–37. https://doi.org/10.1111/tgis.12137
Visser, O. (2017). Running out of farmland? Investment discourses, unstable land values and the sluggishness of asset making. Agriculture and Human Values, 34, 185–198. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10460-015-9679-7
Wang, Q., & Zeng, G. (2020). Spatial organization of innovation in the oil equipment manufacturing industry: Case of Dongying, China. Chinese Geographical Science, 30, 324–339. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-019-1092-5
Wang, M., Pang, S., Ikram, H., Hmani, I., Li, C., & He, Z. (2020a). Toward sustainable development: How does technological innovation drive the increase in green total factor productivity? Sustainable Development, 29, 217–227. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.2142
Wang, M., Xu, M., & Ma, S. (2022). The effect of the spatial heterogeneity of human capital structure on regional green total factor productivity. Structural Change and Economic Dynamics, 59, 463–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.strueco.2021.09.018
Wang, Z., Xu, X., Wang, H., & Meng, S. (2020b). Does land reserve system improve quality of urbanization? Evidence from China. Habitat International, 106(54), 102291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2020.102291
Xie, R., Yao, S., Han, F., & Fang, J. (2019). Land finance, producer services agglomeration, and green total factor productivity. International Regional Science Review, 42(5–6), 550–579. https://doi.org/10.1177/0160017619836.
Xu, Z., Zhang, J. J., Zhang, Z. F., Li, C., & Wang, K. (2020). How to perceive the impacts of land supply on urban management efficiency: Evidence from China’s 315 cities. Habitat International, 98, 102145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2020.102145.
Xue, D., Li, Y., Fayyaz, A., Draz, M. U., Chandio, A. A., Ahmad, M., & Amin, W. (2022). Empirical investigation of urban land use efficiency and influencing factors of the Yellow River basin Chinese cities. Land Use Policy, 117, 106117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2022.106117.
Yang, K., Chen, B. M., Du, H. L., & Tang, X. M. (2011). The contribution of cultivated land occupation by construction to China’s economic growth. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 21, 897. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-011-0888-8.
Yu, M., & Deng, X. (2021). The inheritance of marketization level and regional human capital accumulation: Evidence from China. Finance Research Letters, 43, 102268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.frl.2021.102268.
Yu, B., & Su, Y. (2020). Research on the impact of industrial structure adjustment on land use efficiency and spillover effect: An empirical analysis based on PSDM model and PTR model. China Land Science, 34(11), 57–66. https://doi.org/10.11994/zgtdkx.20201030.141639. (In Chinese).
Zabihi, H., Ahmad, A., Vogeler, I., Said, M. N., Golmohammadi, M., Golein, B., & Nilashi, M. (2015). Land suitability procedure for sustainable citrus planning using the application of the analytical network process approach and GIS. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 117, 114–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2015.07.014.
Zhang, J. (2008). Estimation of China’s provincial capital stock (1952–2004) with applications. Journal of Chinese Economic and Business Studies, 6, 177–196. https://doi.org/10.1080/14765280802028302.
Zhang, J., Lu, G., Skitmore, M., & Ballesteros-Pérez, P. (2021). A critical review of the current research mainstreams and the influencing factors of green total factor productivity. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28, 35392–35405. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14467-4.
Zhang, B., Yu, L., & Sun, C. (2022). How does urban environmental legislation guide the green transition of enterprises? Based on the perspective of enterprises’ green total factor productivity. Energy Economics, 110, 106032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2022.106032.
Zhou, K., Wu, J. X., Fan, J., & Liu, H. (2022). Drivers of regional environmental pollution load and zoning control: A case study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Chinese Geographical Science, 32, 31–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-022-1257-5.
Zou, H., & Ma, X. (2021). Identifying resource and environmental carrying capacity in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China: The perspectives of spatial differences and sustainable development. Environment Development and Sustainability, 23(10), 14775–14798. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01271-w.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the editors and the reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions.
Funding
This work was supported by Humanities and Social Sciences Foundation of the Ministry of Education of China (No. 22YJA790030), and by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China University of Geosciences (Wuhan) (CUG2642022006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KG contributed to conceptualization, methodology, writing—original draft preparation, data collection, software and revising, formal analysis, validation. SL contributed to supervision, validation, writing—reviewing and editing. JB contributed to writing—reviewing and editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. There is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service and/or company that could be construed as influencing the position presented in, or the review of, the manuscript entitled.
Consent to publish
All authors agreed to publish.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, K., Li, S. & Bai, J. How does urban land use impact green total factor productivity? Evidence from 108 cities in the Yangtze River Economic Belt of China. Environ Dev Sustain (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-023-04439-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-023-04439-8