Abstract
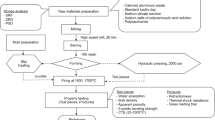
The reuse of industrial waste is an important tool to contribute to the sustainable development of different sectors. It is known that most companies do not have reuse policies, making the final disposal of waste in landfills or even inappropriately. In this context, the objective of this work was to study the reuse of the waste from the production of electrofused alumina in red ceramic. Initially, the electrofused alumina waste was characterized, being subsequently used in ceramic bodies to evaluate the properties of linear shrinkage, water absorption, open porosity and flexural rupture strength. Extruded specimens with dimensions of 120 × 30 × 20 mm3 were produced, being fired at temperatures of 750–1050 ºC. The waste was used in contents of 0–10%, replacing the commercial ceramic masses. The results of mineralogical analysis by XRD, optical microscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and mercury intrusion porosimetry were also evaluated. The waste characterization results show that its use is viable in the production of red ceramic materials. The results obtained in the specimens were also satisfactory, since the waste does not affect flexural strength and increases water absorption and open porosity in acceptable levels. The reason for this is the formation of mullite nucleation due to the clayey mass used and the presence of corundum in the electrofused alumina waste, as proven by XRD and SEM. Through these results, it is possible to conclude that the use of waste is viable for the applications of red ceramic materials.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
ABNT, NBR 7181 - Solo - Análise granulométrica, 2016. /01.080.10; 13.220.99.
ABNT NBR, NBR 15310, 2004. /01.080.10; 13.220.99.
ABNT NBR 15270–1, Componentes cerâmicos. Parte 1: Blocos cerâmicos para alvenaria de vedação - Terminologia e requisitos, Assoc. Bras. Normas Técnicas. (2005). /01.080.10; 13.220.99.
Amaral, L.F., de Carvalho, J. P. R. G., da Silva, B. M., Delaqua, G. C. G., Monteiro, S. N., & Vieira, C. M. F. (2019). Development of ceramic paver with ornamental rock waste. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 8, 599–608 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2018.05.009
Amaral, L.F., Girondi Delaqua, G.C., Nicolite, M., Marvila, M.T, de Azevedo, A.R.G., Alexandre, J., Fontes Vieira, C.M., & Monteiro, S.N. (2020). Eco-friendly mortars with addition of ornamental stone waste - A mathematical model approach for granulometric optimization. Journal of Cleaner Production, 248, 119283 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119283.
Areias, I.O.R., Vieira, C.M.F., & Intorne, A.C. (2017). Incorporação de lodo da estação de tratamento de esgoto ( ETE ) em cerâmica vermelha ( Incorporation of sludge of the sewage treatment station, 63 , 343–349 (2017).
ASSOCIAÇÃO BRASILEIRA DE NORMAS TÉCNICAS - ABNT, Solo — Determinação do limite de plasticidade NBR 7180:2016, 2016. /01.080.10; 13.220.99.
ASSOCIAÇÃO BRASILEIRA DE NORMAS TÉCNICAS - ABNT, Solo — Determinação do limite de liquidez NBR 6459:2016, 2016. /01.080.10; 13.220.99.
ASTM (2018a). Standard Test Methods for Determination of Water Absorption and Associated Properties by Vacuum Method for Pressed Ceramic Tiles and Glass Tiles and Boil Method for Extruded Ceramic Tiles and Non-tile Fired Ceramic Whiteware Products, C 373 (2018).
ASTM (2018b). Standard Test Methods for Flexural Properties of Ceramic Whiteware Materials.
Azevedo, A. R. G., França, B. R., Alexandre, J., Marvila, M. T., Zanelato, E. B., & Xavier, G. C. (2018). Influence of sintering temperature of a ceramic substrate in mortar adhesion for civil construction. Journal of Building Engineering, 19, 342–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2018.05.026
Azevedo, A. R. G., Vieira, C. M. F., Ferreira, W. M., Faria, K. C. P., Pedroti, L. G., & Mendes, B. C. (2020). Potential use of ceramic waste as precursor in the geopolymerization reaction for the production of ceramic roof tiles. Journal of Building Engineering, 29, 101156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2019.101156
Babisk, M. P., Amaral, L.F., da Ribeiro, L. S., Vieira, C.M.F., do Prado, U.S.., Gadioli, M.C.B., Oliveira, M.S., da Luz, F.S., Monteiro, S.N., da Garcia Filho, F. C. (2020). Evaluation and application of sintered red mud and its incorporated clay ceramics as materials for building construction. The Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 9, 2186–2195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2019.12.049.
Borisova, M. Z., Struchkov, N. F., & Vinkurov, G. G. (2019). Evaluation of the content of corundum in the wear-resistant coating applied by wire arc metallization of a powder wire with fireproof additives. Procedia Structural Integrity, 20, 48–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prostr.2019.12.114
Carvalho, R. S., da Silva, V. J., da Nóbrega, R. B., Lira, H. L., & Santana, L. N. L. (2020). Fabrication and characterization of dielectric ceramics using alumina and aluminosilicates. Cerâmica, 66, 56–64. https://doi.org/10.1590/0366-69132020663772808
Castro, R. H. R., & Gouvêa, D. (2003). Efeito do íon Mn como aditivo na transição de fase da alumina. Cerâmica, 49, 55–60. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0366-69132003000100012
Chen, X., Zheng, W., Zhang, J., Liu, C., Han, J., Zhang, L., & Liu, C. (2020). Enhanced thermal properties of silica-based ceramic cores prepared by coating alumina/mullite on the surface of fused silica powders. Ceramics International, 46, 11819–11827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.01.216
Conconi, M. S., Morosi, M., Maggi, J., Zalba, P. E., Cravero, F., & Rendtorff, N. M. (2019). Thermal behavior (TG-DTA-TMA), sintering and properties of a kaolinitic clay from Buenos Aires Province, Argentina. Cerâmica, 65, 227–235. https://doi.org/10.1590/0366-69132019653742621
Da Silva Ribeiro, L., Babisk, M.P.., Do Prado, U.S., Monteiro, S.N., & Vieira, C.M.F. (2015). Incorporation of in natura and calcined red muds into clay ceramic. Materials Research, 18, 279–282. https://doi.org/10.1590/1516-1439.372014.
de Souza, C. C., Delaqua, G. C. G., Vieira, C. M. F., Monteiro, S. N., & da Luz, F. S. (2019). Evaluation of solid waste from H2S removal process in natural gas treatment incorporated into red ceramic. Materials Research, 22, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-5373-MR-2019-0129
de Azevedo, A.R.G., Alexandre, J., Zanelato, E.B., Marvila, M.T. (2017) Influence of incorporation of glass waste on the rheological properties of adhesive mortar. Construction and Building Materials 148 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.04.208.
de Azevedo, A.R.G., Alexandre, J., Pessanha, L.S.P., da Manhães R. S. T., de Brito, J., Marvila, M.T. (2019) Characterizing the paper industry sludge for environmentally-safe disposal. Waste Management, 95, 43–52 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2019.06.001.
Delaqua, G.C.G., Marvila, M.T., Souza, D., Rodriguez, R.S.J., Colorado, H.A., Vieira, C.M.F. (2020). Evaluation of the application of macrophyte biomass Salvinia auriculata Aublet in red ceramics. Journal of Environmental Management, 275, 111253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111253
Domínguez, E., Dondi, M., Etcheverry, R., Recio, C., & Iglesias, C. (2016). Genesis and mining potential of kaolin deposits in Patagonia (Argentina). Applied Clay Science, 131, 44–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2015.12.031
Dondi, M., Guarini, G., Raimondo, M., & Zanelli, C. (2009). Recycling PC and TV waste glass in clay bricks and roof tiles. Waste Management, 29, 1945–1951. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2008.12.003
França, B. R., Azevedo, A. R. G., Monteiro, S. N., Da Costa, F., Filho, G., Marvila, M. T., Alexandre, J., & Zanelato, E. B. (2018). Durability of soil-Cement blocks with the incorporation of limestone residues from the processing of marble. Materials Research., 21, 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-5373-MR-2017-1118
Girondi, G. D., Marvila, M.T., Azevedo, A.R.G., Souza, C.C., Souza, D., Brito, J., Vieira, C.M.F. (2020). Recycling potential of powdered cigarette waste in the development ofceramic materials. The Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management , 22, 955–965. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-020-01058-
Jang, H., Lim, Y.-T., Kang, J.-H., So, S., & So, H. (2018). Influence of calcination and cooling conditions on pozzolanic reactivity of paper mill sludge. Construction and Building Materials, 166, 257–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.01.119
Jordán, M. M., Meseguer, S., Pardo, F., & Montero, M. A. (2015). Properties and possible ceramic uses of clays from lignite mine spoils of NW Spain. Applied Clay Science, 118, 158–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2015.09.015
Kavas, T. (2006). Use of boron waste as a fluxing agent in production of red mud brick. Building and Environment, 41, 1779–1783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2005.07.019
Kovářík, T., Rieger, D., Kadlec, J., Křenek, T., Kullová, L., Pola, M., Bělský, P., Franče, P., & Říha, J. (2017). Thermomechanical properties of particle-reinforced geopolymer composite with various aggregate gradation of fine ceramic filler. Construction and Building Materials., 143, 599–606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.03.134
Marvila, M. T., Alexandre, J., Azevedo, A. R. G., Zanelato, E. B., Xavier, G. C., & Monteiro, S. N. (2019a). Study on the replacement of the hydrated lime by kaolinitic clay in mortars. Advances in Applied Ceramics, 118, 373–380. https://doi.org/10.1080/17436753.2019.1595266
Marvila, M.T., Azevedo, A.R.G., Alexandre, J., Zanelato, E.B., Azeredo, N.G., Simonassi, N.T., Monteiro, S.N. (2019b). Correlation between the properties of structural clay blocks obtained by destructive tests and Ultrasonic Pulse Tests. The Journal of Building Engineering, 26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2019.100869.
Menezes, R. R., Marques, L. N., Santana, L. N. L., Kiminami, R. H. G. A., Neves, G. A., & Ferreira, H. S. (2010). Uso de resíduo da produção de alumina eletrofundida na produção de blocos e telhas cerâmicos. Cerâmica, 56, 244–249. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0366-69132010000300006
Monteiro, S. N., Silva, F. A. N., & Vieira, C. M. F. (2006). Microstructural evaluation of a clay ceramic incorporated with petroleum waste. Applied Clay Science, 33, 171–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2006.04.005
Monteiro, S.N., Soares, R., Vieira, C.M.F. (2004). Comparison of roofing tile clay ceramic bodies from Campos dos Goytacazes, Brazil. Silicate Industriels 69(11–12), 103–109.
NBR 15270-2, NBR 15270: Componentes cerâmicos ― blocos e tijolos para alvenaria, Parte 2: Métodos de ensaios, Rio Janeiro. (2017).
Pardo, F., Jordan, M. M., & Montero, M. A. (2018). Ceramic behaviour of clays in Central Chile. Applied Clay Science, 157, 158–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2018.02.044
Silva, M. C. A., Leão, V. A., & Reis, E. L. (2021). Incorporation of quartzite fines in the production of red ceramics. Journal of Cleaner Production, 288, 125098. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125098
Sun, Y., Li, Y., Zhang, L., Shen, Y., & Sun, J. (1973). Formation mechanism of Ti(C, N) solid solution in Al-brown fused alumina refractory at K in flowing N2. Ceramics International, 46(2020), 2654–2660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.09.250
Vieira, C. M. F., Soares, T. M., & Monteiro, S. N. (2003). Massas cerâmicas para telhas: Características e comportamento de queima. Cerâmica, 49, 245–250. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0366-69132003000400009
Vieira, C. M. F., de Souza, E. T. A., & Monteiro, S. N. (2004). Efeito da incorporação de chamote no processamento e microestrutura de cerâmica vermelha. Cerâmica, 50, 254–260. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0366-69132004000300013
Vieira, C. M. F., Morais, A. S. C., Monteiro, S. N., & Delaqua, G. C. G. (2016). Teste industrial de cerâmica vermelha incorporada com resíduo de vidro de lâmpada fluorescente. Cerâmica, 62, 376–385. https://doi.org/10.1590/0366-69132016623642035
Zhao, P., Zhang, H., Gao, H., Zhu, Y., Yu, J., Chen, Q., & Zhao, H. (2018). Separation and characterisation of fused alumina obtained from aluminium-chromium slag. Ceramics International, 44, 3590–3595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.11.073
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Brazilian agencies: CNPq, proc. No. 301634/ 2018.1, and FAPERJ, proc. No. E-26/202.773/2017, for supporting this investigation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nicolite, M., Delaqua, G.C.G., Marvila, M.T. et al. Reuse of wastes from the production of electrofused alumina in red ceramics. Environ Dev Sustain 25, 669–685 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-02075-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-02075-8