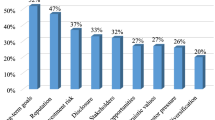
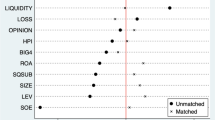
Abstract
China’s cross-border pollution problem has attracted a growing level of attention from the domestic and international community. The elimination of environmental pollution greatly depends on professional environmental protection companies. China’s environmental protection industry has sustained a rapid growth with 26.9% annual growing rate of output value since 2011. To effectively discover the potential investment fields and regions, this study examines the spatial distribution of 53 A-Share Listed Environmental Companies (ASLEC) in China and their 927 subsidiaries. Methods of hot spot analysis, Pearson’s correlation analysis and coarsened exact matching were employed in our paper to reveal the spatial distribution characteristics of environmental protection industry and their main influencing indicators. Results show that ASLEC invested over US$ 13 billion distributed in 210 cities in China in 2017. Treatment of wastewater and municipal solid waste related to traditional water supply, drainage and sanitation are the main businesses of the environmental protection industry in China. This is because these businesses belong to conventional urban municipal works with low technological requirement and high economic return. Therefore, the government should support those environmental protection businesses with fine technology, such as air pollution prevention and industrial waste control. Our study also reveals that there is a strong and positive correlation between municipal indicators and environmental protection investment. This indicates that the municipal works attract much more investment of environmental protection companies than heavy industries. The eastern region of China remains a hot spot for investment whereas the investment in the western region increased significantly in 2017. The potential of future development will be located in the central and western regions. For serious air pollution and large-scale industrial transfer from eastern regions to the central and western regions in China, there is lack of industrialization environmental protection capacity to fulfill the ambitious national pollution reduction target. This opportunity implies to attract more investments from international environmental protection companies.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability and material
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author [Y. Wang] upon reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
AlShebli, B. K., Rahwan, T., & Woon, W. L. (2018). The preeminence of ethnic diversity in scientific collaboration. Nature Communications, 9(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-07634-8.
Analysis of Present Situation and Future Development Trend of China's Environmental Protection Industry in 2017 (CEPI). (2017). China Industrial Information Network. Available online at: http://www.chyxx.com/industry/201712/590548.html. (Accessed 19 May 2019)
Blackwell, M., Iacus, S., King, G., & Porro, G. (2009). Cem: Coarsened exact matching in Stata. The Stata Journal, 9(4), 524–546. https://doi.org/10.1177/1536867x0900900402.
Bruvoll, A. (1998). Taxing virgin materials: An approach to waste problems. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 22(1–2), 15–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0921-3449(97)00040-2.
Catalina, T., Iordache, V., & Caracaleanu, B. (2013). Multiple regression model for fast prediction of the heating energy demand. Energy and Buildings, 57, 302–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2012.11.010.
China Association of Environmental Protection Industry (CAEPI). (2015). Development Index Report of China Environmental Protection Industry 2015. Available online at: http://www.caepi.org.cn/epasp/website/webgl/webglController/view?xh=1521103614566083353600. (Accessed 19 May 2019).
China Association of Environmental Protection Industry (CAEPI). (2016). China Environmental Protection Industry Development Index Report 2016. Available online at: http://www.caepi.org.cn/epasp/website/webgl/webglController/view?xh=1521103455012084561920. (Accessed 19 May 2019).
China Association of Environmental Protection Industry (CAEPI). (2017a). Environmental Industry Climate Index: A Share Listed Environmental Companies (EICl-2017Q1). Available online at: http://www.caepi.org.cn/epasp/website/webgl/webglController/view?xh=1521101964316059629568. (Accessed 19 May 2019).
China Association of Environmental Protection Industry (CAEPI). (2017b). Environmental Industry Climate Index: A Share Listed Environmental Companies (EICl-2017Q2). http://www.caepi.org.cn/epa/resources/pdfjs/web/viewer.html?file=/epa/platform/file/filemanagecontroller/downloadfilebyid/1521102396725060624896. (Accessed 19 May 2019).
China Association of Environmental Protection Industry (CAEPI). (2018). Available online at: http://www.caepi.org.cn/. (Accessed 19 May 2019).
China Association of Environmental Protection Industry (CAEPI). (2018). The Development of China's Environmental Protection Industry Report 2018. Available online at: http://www.caepi.org.cn/epasp/website/webgl/webglController/view?xh=1548321329625036356096. (Accessed 19 May 2019).
China Association of Environmental Protection Industry (CAEPI). (2019). The Development of China's Environmental Protection Industry Report 2019. Available online at: http://www.caepi.org.cn/epasp/website/webgl/webglController/chnlnewsList/W_XXZX_NDFZBG. (Accessed 19 January 2021).
China Association of Environmental Protection Industry (CAEPI). (2020). The Development of China's Environmental Protection Industry Report 2020. Available online at: http://www.caepi.org.cn/epasp/website/webgl/webglController/chnlnewsList/W_XXZX_NDFZBG. (Accessed 19 January 2021).
Duczmal, L., Kulldorff, M., & Huang, L. (2006). Evaluation of spatial scan statistics for irregularly shaped clusters. Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics, 15(2), 428–442. https://doi.org/10.1198/106186006x112396.
Environmental Systems Research Institute (ESRI). (2019). Inc. "ArcGIS Resource Center," Hot Spot Analysis (Getis-Ord Gi*). Available online at: http://desktop.arcgis.com/en/arcmap/. (Accessed 19 May 2019).
Fan, Y., Wu, S., Lu, Y., & Zhao, Y. (2019). Study on the effect of the environmental protection industry and investment for the national economy: An input-output perspective. Journal of Cleaner Production, 227, 1093–1106.
Hong Kong Trade Development Council (HKTDC). (2019). China’s Environmental Market. Available online at: https://hkmb.hktdc.com/en/1X002L45/hktdc-research/China%E2%80%99s-Environmental-Market. (Accessed 19 January 2021).
General Office of the State Council of People's Republic of China (SCPRC). (2016). The 13th five-year plan for ecological and environmental protection. Available online at: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2016-12/05/content_5143290.htm. (Accessed 19 May 2019).
Goovaerts, P., & Jacquez, G. M. (2004). Accounting for regional background and population size in the detection of spatial clusters and outliers using geostatistical filtering and spatial neutral models: the case of lung cancer in Long Island, New York. International Journal of Health Geographics, 3(1), 14.
Hu, B., Shao, S., Fu, Z., Li, Y., Ni, H., Chen, S., & Shi, Z. (2019). Identifying heavy metal pollution hot spots in soil-rice systems: A case study in South of Yangtze River Delta, China. Science of the Total Environment, 658, 614–625.
Iacus, S. M., King, G., & Porro, G. (2011). Multivariate matching methods that are monotonic imbalance bounding. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 106(493), 345–361. https://doi.org/10.1198/jasa.2011.tm09599.
Iacus, S. M., King, G., & Porro, G. (2012). Causal inference without balance checking: Coarsened exact matching. Political analysis, 20(1), 1–24. https://doi.org/10.1093/pan/mpr013.
Jacquez, G. M., & Greiling, D. A. (2003). Local clustering in breast, lung and colorectal cancer in Long Island, New York. International Journal of Health Geographics, 2(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3133/wri924038.
Jia, K., & Chen, S. (2019). Could campaign-style enforcement improve environmental performance? Evidence from China’s central environmental protection inspection. Journal of environmental management, 245, 282–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.05.114.
Johnson, E. L. (1967). Optimality and computation of (σ, S) policies in the multi-item infinite horizon inventory problem. Management Science, 13(7), 475–491. https://doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.13.7.475.
Kulldorff, M. (1997). A spatial scan statistic. Communications in Statistics-Theory and Methods, 26(6), 1481–1496. https://doi.org/10.1080/03610929708831995.
Lezzaik, K., & Milewski, A. M. (2014). A Global Hot Spot Analysis (Getis-Ord Gi*) of Groundwater Storage Change using GRACE Satellite and GIS-Based Spatial Statistical Analysis. In 2014 GSA Annual Meeting in Vancouver, British Columbia.
Ling-yun, H., et al. (2013). Research on the effect of china’s environmental protection investment to the environmental protection industry development. Soft Science, 27, 37–41 (in Chinese with English abstract).
MacQueen, J. (1967). Some methods for classification and analysis of multivariate observations. Proceedings of the Fifth Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability, 1967, 281–297.
Ministry of Ecology and Environmental of People's Republic of China (MEEPRC), (2017). Bulletin on China's Ecological Environment 2017. Available online at: http://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/sthjzk/zghjzkgb/201805/P020180531534645032372.pdf. (Accessed 19 May 2019).
National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). (2017). China city statistical yearbook 2017. . China: China Statistics Press.
Parchomenko, A., & Borsky, S. (2018). Identifying phosphorus hot spots: A spatial analysis of the phosphorus balance as a result of manure application. Journal of Environmental Management., 214, 137–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.01.082.
Schikuta, E., & Erhart, M. (1997). The BANG-clustering system: Grid-based data analysis. In International Symposium on Intelligent Data Analysis. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg https://doi.org/10.1007/bfb0052867
Shunze, W., et al. (2014). The fourth comprehensive analysis report of national environmental protection related industries. China Environmental Protection Industry., 8, 4–17 (in Chinese).
Tianyancha. (2018). Available online at: www.tianyancha.com. (Accessed 19 May 2018).
Williams, S. (1996). Pearson's correlation coefficient. The New Zealand medical journal, 109(1015), 38. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.32388/y3qecy
Wu, Y., Sheng, J., & Huang, F. (2015). China’s future investments in environmental protection and control of manufacturing industry: lessons from developed countries. Natural Hazards, 77(3), 1889–1901. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-015-1681-2.
Xepapadeas, A., & de Zeeuw, A. (1999). Environmental policy and competitiveness: The Porter hypothesis and the composition of capital. Journal of Environmental Economics and Management, 37(2), 165–182. https://doi.org/10.1006/jeem.
Xu, X., & Zhang, T. (2020). Spatial-temporal variability of PM2. 5 air quality in Beijing, China during 2013–2018. Journal of Environmental Management, 262, 110263 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110263
Yunze, M. A. (2011). Problems and solutions facing environmental protection industry in China. Energy Procedia, 5, 275–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2011.03.049.
Zeng, D., Chang, W., & Chen, H. (2004). A comparative study of spatio-temporal hotspot analysis techniques in security informatics. In Proceedings. The 7th International IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (IEEE Cat. No. 04TH8749) (pp. 106–111). IEEE https://doi.org/10.1109/itsc.2004.1398880
Zhang, C., Weng, S., & Bao, J. (2020). The changes in the geographical patterns of China’s tourism in 1978–2018: Characteristics and underlying factors. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 30(3), 487–507.
Zhang, J., & Shang, J. (2010). Research on developing environmental protection industry based on TRIZ theory. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 2, 1326–1334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2010.10.143.
Zhang, Q., Jiang, X., Tong, D., Davis, S. J., Zhao, H., Geng, G., & Ni, R. (2017). Transboundary health impacts of transported global air pollution and international trade. Nature, 543(7647), 705–709. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature21712.
Zhao, J., Zhao, X., Ren, Y., & Wang, M. (2020). The Impact of Environmental Finance Development on the Growth of Environmental Protection Industry. In 2020 International Conference on Social Science, Economics and Education Research (SSEER 2020) (pp. 257–262). Atlantis Press.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [Grants # 41871211, 41571522] and the National Key Research and Development Program of China [Grant # 2018YFC0213600]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LL and YW conceived and designed the research, performed model simulations and data analysis and wrote the manuscript in collaboration with JZ and GZ. Moreover, YW, GM and JZ designed the framework of geospatial hot spot analysis of ASLEC to the environmental pollution treated ratio. ZW, YS and TX collected the data from Tianyancha database. MJS and GZ whose native language is English checked language and grammar usage in manuscripts. All authors suggested analysis, interpreted the data, discussed their implications and contributed to the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, LC., Wang, Y., Mao, G. et al. Spatial characteristic of environmental protection businesses: a study of A-Share Listed Environmental Companies in China. Environ Dev Sustain 23, 18598–18617 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01395-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01395-z