Abstract
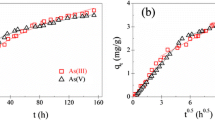
Arsenic (As) in groundwater has become a worldwide concern due to its high toxicity as it is classified as a potent carcinogen, when exposed to drinking water. None of the reported As remediation technologies has so far been reasonably successful in overcoming the constraints encountered during on-field application. This paper evaluated the potential of modifying the well-acclaimed ElectroChemical Arsenic Remediation (ECAR) technique from ‘Batch Scale’ to a ‘Continuous Flow’ operation. The development of this innovative process modification involved a thorough investigation to understand the effects of different process parameters like, iron concentration, pH, dissolved oxygen (DO) and presence of co-occurring solute (PO43−). An indigenously fabricated 50 L continuous ECAR unit exhibited a successful remediation from 604 ppb of As(III) concentration to a value (% removal efficiency greater than 99%) less than the maximum contamination level prescribed by World Health Organization. Powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) and scanning electron microscope (SEM) studies were conducted for iron-arsenic dry sludge to show a highly crystalline nature of the sludge, produced in the process. The experimental results were explored for the formulation of a feed-forward back-propagation artificial neural network (ANN) model to predict the removal efficiency of As from the contaminated water. The experimental outcome of the study justifies the feasibility and significance of the ‘continuous mode’ ECAR system in providing a tangible and sustainable solution towards global As contamination problem.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addy, S. E. A. (2008). Electrochemical Arsenic remediation for rural Bangladesh. Ph.D. dissertation, University of California Berkeley, Berkeley, CA.
Ahmad, J., Goldar, B. N., Misra, S., & Jakaruya, M. (2003). Willingness to pay for arsenic-free, safe drinking water in Bangladesh. Water and Sanitation Programme–South Asia: The World Bank: New Delhi, India.
Ahmed, M., Ahuja, S., Alauddin, M., Hug, S., Lloyd, J., Pfaff, A., Pichler, T., Saltikov, C., Stute, M., & Van Geen, A. (2006). Ensuring safe drinking water in Bangladesh. Science, 314, 5806, 1687–1688.
Ali, I., Khan, T. A., & Asim, M. (2011). Removal of Arsenic from water by electrocoagulation and electrodialysis techniques. Separation & Purification Reviews, 40, 25–42. https://doi.org/10.1080/15422119.2011.542738.
Amrose, S. E., Bandaru, S. R. S., Delaire, C., van Genuchten, C. M., Dutta, A., Debsarkar, A., Orr, C., Roy, J., Das, A., & Gadgil, A. J. (2014). Electro-chemical Arsenic remediation: Field trials in West Bengal. Science of the Total Environment, 539–546.
Amrose, S., Gadgil, A., Srinivasan, V., Kowolik, K., Muller, M., & Huang, J. (2013). Arsenic removal from groundwater using iron electrocoagulation: Effect of charge dosage rate. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, 48, 1019–1030.
Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, American Public Health Association (APHA), 17th edition.
Arienzo, M., Adamo, P., Chiarenzelli, J., Bianco, M. R., & De Martino, A. (2002). Retention of Arsenic on hydrous ferric oxides generated by electrochemical peroxidation. Chemosphere, 48(10), 1009–1018.
Avilés, M., Garrido, S. E., Esteller, M. V., De La Paz, J. S., Najera, C., & Cortés, J. (2013). Removal of groundwater Arsenic using a household filter with iron spikes and stainless steel. Journal of Environmental Management, 131, 103–109.
Balasubramanian, N., & Madhavan, K. (2001). Arsenic removal from industrial effluent through electrocoagulation. Chemical Engineering and Technology, 24(5), 519–521.
Bang, S., Johnson, M. D., Korfiatis, G. P., & Meng, X. (2005a). Chemical reactions between Arsenic and zero-valent iron in water. Water Research, 39(5), 763–770.
Bang, S., Korfiatis, G. P., & Meng, X. G. (2005b). Removal of Arsenic from water by zero-valent iron. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 121(1–3), 61–67.
Barringer, J. L., & Reilly, P. A. (2013). Arsenic in groundwater: A summary of sources and the biogeochemical and hydrogeologic factors affecting arsenic occurrence and mobility. INTECH Open Access Publisher 83–116.
Chakraborti, D., Das, B., Rahman, M. M., Chowdhury, U. K., Biswas, B., Goswami, A. B., et al. (2009). Status of groundwater Arsenic contamination in the state of West Bengal, India: A 20-year study report, May 2009. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.200700517.
Chen, X. M., Chen, G. H., & Yue, P. L. (2000). Separation of pollutants from restaurant waste water by electrocoagulation. Separation and Purification Technology, 19(1–2), 65–76.
Cheng, W., Xu, J., Wang, Y., Xu, X., & Li, J. (2015). Dispersion-precipitation synthesis nanosized magnetic iron oxide for efficient removal of arsenite in water. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 445, 93–101.
Choong, T. S., Chuah, T. G., Robiah, Y., Koay, F. G., & Azni, I. (2007). Arsenic toxicity, health hazards and removal techniques from water: An overview. Desalination, 217(1), 139–166.
Çiftçi, T. D., & Henden, E. (2015). Nickel/nickel boride nanoparticles coated resin: A novel adsorbent for As (III) and As (V) removal. Powder Technology, 269, 470–480.
Dixit, S., & Hering, J. G. (2003). Comparison of As(V) and As(III) sorption onto iron oxide minerals: Implications for Arsenic mobility. Environmental Science and Technology, 37, 4182–4189.
Ekici, B. B., & Aksoy, U. T. (2010). Prediction of building energy consumption by using artificial neural networks. AdvEng Soft, 41(2), 141–147.
Emamjomeh, M. M., & Sivakumar, M. (2009). Review of pollutants removed by electrocoagulation and electrocoagulation/flotation processes. Journal of Environmental Management, 90, 1663–1679.
Farrell, J., Wang, J. P., O’Day, P., & Conklin, M. (2001). Electrochemical and spectroscopic study of arsenate removal from water using zero-valent iron media. Environmental Science and Technology, 35(10), 2026–2032.
Ferguson, J. F., & Gavis, J. (1972). Review of Arsenic cycle in natural waters. Water Research, 6(11), 1259–1274.
Garelick, H., & Jones, H. (2008). Mitigating Arsenic pollution::Bridging the gap between knowledge and practice. Chemistry International pp 7–12.
Ghosh (Nath), S., Debsarkar, A., & Dutta, A. (2019). Technology alternatives for decontamination of Arsenic rich groundwater- a critical review. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 13, 277–303.
Hansen, H. K., Nunez, P., Raboy, D., Schippacasse, I., & Grandon, R. (2007). Electrocoagulation in wastewater containing Arsenic: Comparing different process designs. Electrochimica Acta, 52, 3464–3470.
Hiemstra, T., & Van Riemsdijk, W. H. (1999). Surface structural ion adsorption modelling of competitive binding of oxyanions by metal (hydr)oxides. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 210(1), 182–193.
Hingston, F. J., Posner, A. M., & Quirk, J. P. (1993). Competitive adsorption of negatively charged ligands on oxide surfaces. Discussions of the Faraday Society, 52, 334–342.
Hoque, B. A., Hoque, M. M., Ahmed, T., Islam, S., Azad, A. K., Ali, N., et al. (2004). Demand-based water options for Arsenic mitigation: An experience from rural Bangladesh. Public Health, 118(1), 70–77.
Hossain, M. A., Sengupta, M. K., Ahamed, S., Rahman, M. M., Mondal, D., Lodh, D., et al. (2005). Ineffectiveness and poor reliability of Arsenic removal plants in West Bengal, India. Environmental Science and Technology, 39(11), 4300–4306.
Jin, X., She, Q., Ang, X., & Tang, C. Y. (2012). Removal of boron and Arsenic by forward osmosis membrane: Influence of membrane orientation and organic fouling. Journal of Membrane Science, 389, 182–187.
Kabir, A., & Howard, G. (2007). Sustainability of Arsenic mitigation in Bangladesh: Results of a functionality survey. International Journal of Environmental Health Research, 17, 207–218.
Kapaj, S., Peterson, H., Liber, K., & Bhattacharya, P. (2006). Human health effects from chronic Arsenic poisoning—a review. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, 41, 2399–2428.
Kim, M. J., Nriagu, J., & Haack, S. (2002). Arsenic species and chemistry in groundwater of south-east Michigan. Environmental Pollution, 120(2), 379–390.
Kumar, P. R., Chaudhari, S., Khilar, K. C., & Mahajan, S. P. (2004). Removal of Arsenic from water by electrocoagulation. Chemosphere, 55(9), 1245–1252.
Kundu, P., Debsarkar, A., Mukherjee, S., & Kumar, S. (2013). Artificial neural network modelling in biological removal of organic carbon and nitrogen for the treatment of slaughterhouse wastewater in a batch reactor. Environmental Technology. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2013.866698.
Lackovic, J. A., Nikolaidis, N. P., & Dobbs, G. M. (2000). Inorganic Arsenic removal by zero-valent iron. Environmental Engineering Science, 17(1), 29–39.
Lakshmanan, D., Clifford, D. A., & Samanta, G. (2009). Ferrous and ferric ion generation during iron electrocoagulation. Environmental Science and Technology, 43(10), 3853–3859.
Li, L., van Genuchten, C. M., Addy, S. E. A., Yao, J., Gao, N., & Gadgil, A. J. (2012). Modeling As(III) oxidation and removal with iron electrocoagulation in groundwater. Environmental Science and Technology, 46, 12038–12045.
Liu, F., De Cristofaro, A., & Violante, A. (2001). Effect of pH, phosphate and oxalate on the adsorption/desorption of arsenate on/from goethite. Soil Science, 166(3), 197–208.
Macedonio, F., & Drioli, E. (2008). Pressure-driven membrane operations and membrane distillation technology integration for water purification. Desalination, 223(1–3), 396–409.
Maji, S. K., Pal, A., & Pal, T. (2008). As removal from real-life groundwater by adsorption on laterite soil. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 151(2–3), 811–820.
Manning, B. A., & Goldberg, S. (1996a). Modelling arsenate competitive adsorption on kaolinite, montmorillonite and illite. Clays and Clay Minerals, 44(5), 609–623.
Manning, B. A., & Goldberg, S. (1996b). Modeling competitive adsorption of arsenate with phosphate and molybdate on oxide minerals. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 60(1), 121–131.
Meng, X., Bang, S., & Korfiatis, G. P. (2000). Effects of silicate, sulfate, and carbonate on arsenic removal by ferric chloride. Water Research, 34(4), 1255–1261.
Meng, X., Koratis, G. P., Jing, C., & Christodoulatos, C. (2001). Redox transformations of arsenic and iron in water treatment sludge during aging and TCLP extraction. Environmental Science and Technology, 35(17), 3476–3481.
Mukherjee, A., Sengupta, M. K., Hossain, M. A., Ahamed, S., Das, B., & Nayak, B. (2006). Arsenic contamination in groundwater: A global perspective with emphasis on the Asian scenario. Journal of Health, Population and Nutrition, 24(2), 142–163.
Ng, K. S., Ujang, Z., & Le-Clech, P. (2004). Arsenic removal technologies for drinking water treatment. Reviews in Environmental Science & Biotechnology, 3, 43–53.
Nidheesh, P. V., & Singh, T. S. A. (2017). Arsenic removal by electrocoagulation process: Recent trends and removal mechanis. Chemosphere, 181, 418–432.
Ortega, A., Oliva, I., Contreras, K. E., González, I., Cruz-Díaz, M. R., & Rivero, E. P. (2017). Arsenic removal from water by hybrid electro-regenerated anion exchange resin/electrodialysis process. Separation and Purification Technology, 184, 319–326.
Parga, J. R., Cocke, D. L., Valenzuela, J. L., Gomes, J. A., Kesmez, M., Irwin, G., et al. (2005). Arsenic removal via electrocoagulation from heavy metal contaminated groundwater in la Comarca Lagunera Mexico. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 124, 247–254.
Phillips, D. H., Sen Gupta, B., Mukhopadhyay, S., & Sen Gupta, A. K. (2018). Arsenic and fluoride removal from contaminated drinking water with Haix-Fe-Zr and Haix-Zr resin beads. Journal of Environmental Management, 215, 132–142.
Rahman, S., Kim, K., Saha, S. K., Swaraz, A. M., & Paul, D. K. (2014). A novel approach utilizing bio-organisms. Journal of Environmental Management, 134, 175–185.
Rahman, M. M., Naidu, R., & Bhattacharya, P. (2009). Arsenic contamination in groundwater in the South East Asia region. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 31, 9–21.
Raven, K. P., Jain, A., & Loeppert, R. H. (1998). Arsenite and arsenate adsorption on ferrihydrite: Kinetics, equilibrium, and adsorption envelopes. Environmental Science and Technology, 32(3), 344–349.
Roy, A., van Genuchten, C. M., Mookherje, E. I., Debsarkar, A., & Dutta, A. (2019). Concrete stabilization of arsenic-bearing iron sludge generated from an electrochemical arsenic remediation plant. Journal of Environmental Management, 233, 141–150.
Ryden, J. C., Syers, J. K., & Tillman, R. W. (1987). Inorganic anion sorption and interactions with phosphate sorption by hydrous ferric oxide gel. European Journal of Soil Science, 38(2), 211–217.
Sharma, V. K., & Sohn, M. (2009). Aquatic arsenic: toxicity, speciation, transformations, and remediation. Environment International, 35, 743–759.
Smedley, P. L., & Kinniburgh, D. G. (2002). A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Applied Geochemistry, 17(5), 517–568.
Song, P., Yang, Z., Xu, H., Huang, J., Yang, X., & Wang, L. (2014). Investigation of influencing factors and mechanism of antimony and arsenic removal by electrocoagulation using Fe–Al electrodes. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 53, 12911–12919.
Stumm, W., & Lee, G. (1961). Oxygenation of ferrous iron. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 53(2), 143–146.
Su, C. M., & Puls, R. W. (2001). Arsenate and arsenite removal by zerovalent iron: Kinetics, redox transformation, and implications for in situ groundwater remediation. Environmental Science and Technology, 35(7), 1487–1492.
Thirunavukkarasu, O. S., Viraraghavan, T., & Subramanian, K. S. (2003). Arsenic removal from drinking water by iron oxide-coated sand. Water, Air, and Soil pollution, 142(1–4), 95–111.
vanGenuchten, C. M., Addy, S. E. A., Pena, J., & Gadgil, A. J. (2012). Removing arsenic from synthetic groundwater with iron electrocoagulation: And Fe and arsenic K-edge EXAFS study. Environmental Science & Technology, 46, 986–994.
van Genuchten, M. C., Pena, J., Amrose, S. E., & Gadgil, A. J. (2014). Structure of Fe(III) precipitates generated by the electrolytic dissolution of Fe(0) in the presence of groundwater ions Author links open overlay panel. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 127, 285–304.
Vik, E. A., Carlson, D. A., Eikum, A. S., & Gjessing, E. T. (1984). Electrocoagulation of potable water. Water Research, 18(11), 1355–1360.
Vitre, R. D., Belzilel, N., & Tessier, A. (1991). Speciation and adsorption of arsenic on diagenetic iron oxyhydroxides. Limnology and Oceanography, 36(7), 1480–1485.
Wan, W., Pepping, T. J., Banerji, T., Chaudhari, S., & Giammar, D. E. (2011). Effects of water chemistry on arsenic removal from drinking water by electrocoagulation. Water Research, 45, 384–392.
Wang, L., & Giammar, D. E. (2015). Effects of pH, dissolved oxygen, and aqueous ferrous iron on the adsorption of arsenic to lepidocrocite. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 448, 331–338.
Waychunas, G. A., Rea, B. A., Fuller, C. C., & Davis, J. A. (1993). Surface chemistry of ferrihydrite 1 EXAFS studies of the geometry of co-precipitated and adsorbed arsenate. GeochimicaEtCosmochimicaActa, 57(10), 2251–2269.
WHO. (1993). Guidelines for drinking-water quality: Recommendations (Vol. 1). Geneva: The World Health Organization.
WHO. (2008). Guidelines for drinking water quality: Recommendations, incorporating the first and second addenda (Vol. 1). Geneva: World Health Organization.
Yarlagadda, S., Gude, V. G., Camacho, L. M., Pinappu, S., & Deng, S. (2011). Potable water recovery from Arsenic, U, and F contaminated ground waters by direct contact membrane distillation process. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 192, 1388–1394.
Acknowledgements
Authors are thankful to the Environmental Engineering Division, Department of Civil Engineering, Jadavpur University and Indian Institute of Science Education and Research, Bhopal for their technical assistance and advice and University Grants Commission, India for the financial aid.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghosh (Nath), S., Debsarkar, A., Dutta, A. et al. Delivering Arsenic-free Drinking Water-Made Practically Possible: Continuous Scale Electrochemical Arsenic Remediation Process Furnished, based on Experimental Studies and ANN Simulation. Environ Dev Sustain 23, 13087–13112 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-020-01200-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-020-01200-3