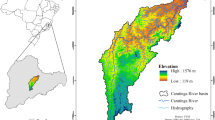
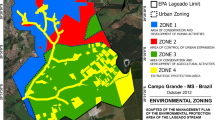
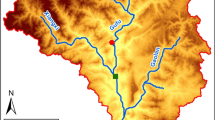
Abstract
In southwestern Tunisia, the intense exploitation of the natural resources (soil, water, hydrocarbons, etc.) bears unrecoverable consequences on the local environment. In fact, the harsh climate conditions, the expansion of irrigated areas (date plantation and greenhouses) and the overexploitation of water resources in these ecologically fragile lands increase understandably desertification in the Kebili field. The field observations in the study indicate that the sustainability of natural resources is threatened, besides increasing soil salinization and water degradation. The used water quality indexes (BCWQI, OWQI and WAWQI) indicate that more than 55% of the samples are unsuitable for domestic consumption and irrigation purposes. The contamination of the CI water and the agricultural lands by crude mature organic matter is confirmed by the elevated concentrations of organic compounds that range between 1.8 and 16 mg/L in the sampled waters, while they reach the 80 mg/L in the surface horizon in the oases in Mazraa Neji and Oum El Fareth areas. The sensitivity of the study area to different processes of land degradation is evaluated by two multi-criteria models (MEDALUS and IMDPA), which indicate high to very high risks of environmental degradation in the study area with an average geometric mean of 1.67 and 2.8, respectively. Given the potential relevance of the contamination and its long-term impacts on the healthy environmental functioning, this paper outlines the main baselines aspects, the rehabilitation measures and the decontamination actions that should be taken in account in the planning of the most adopted management projects.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
The software used in this manuscript is ArcGIS 10.1 clearly described at https://www.esri.com/news/arcnews/spring12articles/introducing-arcgis-101.html
References
Abad, J. R. S., Nohegar, A., Zehtabian, G., Khosravi, H., & Gholami, H. (2016). Study of desertification status based on a sub-IMDPA model for a case study in YazdArdakan plain Iran. International Journal of Forest, Soil and Erosion (IJFSE), 6(3), 73–81.
Abha, S. & Singh, C.S. (2012). Hydrocarbon pollution: Effects on living organisms, remediation of contaminated environments and effects of heavy metals co-contamination on bioremediation. In L. Romero-Zeron (Ed.) Introduction to enhanced oil on recovery (EOR) processes and bioremediation of oil contaminated sites (pp. 186–206). InTech Publisher. ISBN: 978-953-51-0629-6.
Akbari, M., Ownegh, M., Asgari, H., Sadoddin, A., & Khosravi, H. (2016). Desertifcation risk assessment and management program. Global Journal of Environmental Science and Management, 2, 365–380. https://doi.org/10.22034/gjesm.2016.02.04.006.
Akrout, D., Ahmadi, R., Mercier, E., & Montacer, M. (2012). Natural hydrocarbon accumulation related to formation overpressured interval; Study case is the Saharan platform (southern Tunisia). Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 5, 849–857.
Akujuru, V.A. (2014). A framework for determining the compensable value of damages due to contamination to wetlands in the Niger Delta of Nigeria. University of Salford, School of the Built Environment. 367.
Anoliefo, G. O., & Vwioko, D. F. (1994). Effects of spent lubricating oil on the growth of Capsicum annum. L. and Lycopersicon esculetum Miller. Environmental Pollution, 88, 361–374.
Ayers, R.S., & Westcot , D.W. (1999). The water quality in agriculture, 2nd. Campina Grande: UFPB, Studies FAO Irrigation and drainage. 29.
Basso, F., Bove, E., Dumontet, S., Ferrara, A., Pisante, M., Quaranta, G., & Taberner, M. (2000). Evaluating environmental sensitivity at the basin scale through the use of geographic information systems and remotely sensed data: An example covering the Agri basin (Southern Italy). CATENA, 40, 19–25.
Mohammed, B. H. A., Saïdi, M., & Soussi, M. (2015). Organic geochemistry of paleozoic source rocks in the chott basin Southern Tunisia. Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE). https://doi.org/10.2118/175830-MS.
Ben Hassine, H. (2005). Effets de la nappe phréatique sur la salinisation dessols de cinq périmètres irrigués en Tunisie. Étude et Gestion des Sols., 12, 281–300.
Ben Hassine, H., Ben Slimane, A., Mlawah, M., Albouchi, L., & Gandouzi, A. (2016a). An assessment of the impact of underground water level on soil salinity and date palms production. International Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 6, 1059–1066.
Ben Hassine, H., Ben Slimane, A., Mlawah, M., Albouchi, L., & Gandouzi, A. (2016) An assessment of the impact of underground water level on soil salinity.
Besser, H., & Hamed, Y. (2019). Causes and risk evaluation of oil and brine contamination in the lower cretaceous continental intercalaire aquifer in the Kebili region of southern Tunisia using chemical fingerprinting techniques. Environmental Pollution, 253, 412–423.
Besser, H., Mokadem, N., Redhouania, B., Hadji, R., Hamad, O., & Hamed, Y. (2018). Groundwater mixing and geochemical assessment of low enthalpy resources in the geothermal field of Southwestern Tunisia. Euro-Mediterranean Journal for Environmental Integration. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41207-018-0055-z.
Besser, H., Mokadem, N., Redhouania, B., Rhimi, N., Khelifi, F., Ayadi, Y., et al. (2017). GIS based model evaluation of groundwater quality and estimation of soil salinization and land degradation risks in arid Mediterranean site (SW Tunisia). Arabian Journal of Geosciences. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-3148-0.
Besser, H., Redhouania, B., Bedoui, S., Ayadi, Y., Khelifi, F., & Hamed, Y. (2019). Geochemical, isotopic and statistical monitoring of groundwater quality: Assessment of the potential environmental impacts of the highly polluted CI water in Southwestern Tunisia. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 153, 144–155.
Brown, R. M., McClelland, N. I., Deininger, R. A., & Tozer, R. G. (1970). A water quality index-do we dare. Water Sew Works, 117, 339–343.
Burazer, M., & Burazer, N. (2017). Geophysical and geochemical investigation of hydrocarbon subsurface contamination. In August 31st to September 2nd 15th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology, Rhodes, Greece.
Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment (CCME) (2001) Canadian Water Quality Guidelines for the Protection of Aquatic Life: CCME Water Quality Index 1.0. Technical Report, Canadian Council of Ministers of the environment Winnipeg, MB, Canada.
Chauhan, A., & Singh, S. (2010). Evaluation of Ganga water for drinking purpose by water quality index at Rishikesh, Uttarakhand, India. Report Opinion, 9, 53–71.
Cheng, J. L., Shi, Z., & Zhu, Y. W. (2007). Assessment and mapping of environmental quality in agricultural soils of Zhejiang Province, China. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 19, 50–64.
C.R.D.A. (2015). Commissariat Regional du developpement agricole : Kébili en chiffres. Rapport Interne. 71–81.
C.R.D.A. (2017). Commissariat Regional du developpement agricole : Kébili en chiffres. Rapport Interne. 108–117.
Cude, C. G. (2001). Oregon water quality index: A tool for evaluating water quality management effectiveness. Journal of American Water Resource Association, 37, 125–137.
Dahoua, L., Yakovitch, S. V., Hadji, R., & Farid, Z. (2018). Landslide susceptibility mapping using analytic hierarchy process method in bba-bouira region, case study of east-west highway, NE Algeria. In A. Kallel, M. Ksibi, D. H. Ben, & N. Khélifi (Eds.), Recent advances in environmental science from the euro-mediterranean and surrounding regions (pp. 1837–1840). Cham: Springer.
Demdoum, A., Hamed, Y., Feki, M., Hadji, R., & Djebbar, M. (2014). Multi-tracer investigation of groundwater in El Eulma Basin (northwestern Algeria), North Africa. Arabian Journal of Geosciences , 8, 3321–3333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1377-z.
Dunnette, D. A. (1979). A geographically variable water quality index used in Oregon. Journal of the Water Pollution Control Federation, 51, 53–61.
Edmunds, W. M., Guendouz, A. H., Mamou, A., Shand, P., & Zouari, K. (2003). Groundwater evolution in the continental intercalaire aquifer of southern Algeria and Tunisia; Trace element and isotopic indicators. Applied Geochemistry, 18, 805–822. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0883-2927(02)00189-0.
Eilers, R.G., & Eilers, W.D. (1996). Soil degradation risk indicator: soil salinity risk component. Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada, Report n° 16, M.M. Fitzgerald, University of Manitoba, 27.
El Sayed, S. M. (2013). Spatial assessment of desertification in north Sinai using modified MEDLAUS model. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 6, 4647–4659.
Emmanuel, O. I., Douglason, G. O., & Felicia, N. A. (2006). The effect of oil spillage on crop yield and farm income in Delta State. Nigeria. Journal of Central European Agriculture, 7, 7.
Ferchichi, A. (1996). Etude climatique en Tunisie présahrienne. MEDIT., 8, 46–53.
Gargi, C. (2015). Evaluating environmental sensitivity of arid and semiarid regions in Northeastern Rajasthan India. Geographical Review, 105, 441–451.
Hachicha, M., & Ben Aissa, I. (2014). Managing salinity in Tunisian oases. Journal of Life Sciences, 8, 775–782.
Hakanson, L. (1980). An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution controla sedimentological approach. Water Resources, 14, 975–1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8.
Hamad, A., Hadji, R., Bâali, F., Besser, H., Redhaounia, B., Zighmi, K., et al. (2018). Conceptual model for karstic aquifers by combined analysis of GIS, chemical, thermal, and isotopic tools in Tuniso-Algerian transboundary basin. Arabian Journal of Geosciences. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3773-2.
Hamed, Y., Ahmadi, R., Hadji, R., Mokadem, N., Ben Dhia, H., & Ali, W. (2014). Groundwater evolution of the continental intercalaire aquifer of southern Tunisia and a part of southern Algeria: Use of geochemical and isotopic indicators. Desalination and Water Treatment, 52, 1990–1996. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2013.806221.
Hamed, Y., Ahmadi, R., Demdoum, A., Bouri, S., Gargouri, I., Dhia, H. B., et al. (2014). Use of geochemical, isotopic, and age tracer data to develop models of groundwater flow: A case study of Gafsa mining basin-Southern Tunisia. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 100, 418–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2014.07.012.
Hamed, Y., Awad, S., & Ben Sâad, A. (2013) Nitrate contamination in groundwater in the Sidi Aïch-Gafsa Oasis region, Southern Tunisia. Environmental Earth Sciences Journal. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2445-5.
Hamed, Y. (2015). Les ressources hydriques en Tunisie et impact des changements climatiques. Editions europeennes universitaires, ISBN 978–9938–12–961–8
Hamed, Y., Hadji, R., Redhaounia, B., Zighmi, K., Bâali, B., & El Gayar, A. (2018). Climate impact on surface and groundwater in North Africa: a global synthesis of findings and recommendations. Euro-Mediterranean Journal for Environmental Integration, 3, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41207-018-0067-8.
Hostert, P., Röder, A., Hill, J., Udelhoven, T., & Tsiourlis, G. (2003). Retrospective studies grazing-induced land degradation: A case study in central Crete Greece. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 24, 4019–2024.
Hu, S., Niu, Z., Chen, Y., Li, L., & Zhang, H. (2017). Global wetlands: Potential distribution, wetland loss, and status. The Science of the Total Environment, 586, 319–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.02.001.
Hulme, M., & Kelly, M. (1993). Exploring the links between desertification and climate change. Environment Science and Policy for Sustainable Development, 35, 4–44.
Ibeji, C. C. G., & Chikaire, J. U. (2016). Consequences of environmental pollution on agricultural productivity in developing countries: A Case of Nigeria. International Journal of Agricultural and Food Research, 5, 1–2.
Kadović, R., Bohajar, Y. A. M., Perović, V., Simić, S. B., Todosijević, M., Tošić, S., et al. (2016). Land sensitivity analysis of degradation using MEDALUS model: Case study of Deliblato Sands Serbia. Archives of Environmental Protection, 42(4), 114–124. https://doi.org/10.1515/aep-2016-0045.
Kauppi, S., Sinkkonen, A., & Romantschuk, M. (2011). Enhancing bioremediation of diesel-fuel-contaminated soil in a boreal climate: Comparison of biostimulation and bioaugmentation. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 65, 359–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2010.10.011.
Khosravi, H., Zehtabian, G. R., Ahmadi, H., & Azarnivand, H. (2014). Hazard assessment of desertification as a result of soil and water recourse degradation in Kashan Region Iran. Desert, 19, 45–55.
Kosmas, C., Kirkby, M. J., & Geeson, N. (1999). Medalus Project: Mediterranean Desertification and Land Use. Manual on KEY INDICATORS of Desertification and Mapping Environmentally Sensitive Areas. Brussels: Publication of European Union.
Lahlaoi, H., Rhinane, H., Hilali, A., Lahssini, S., & Moukrim, S. (2017). Desertification assessment using MEDALUS model in watershed Oued El Maleh Morocco. Geosciences, 7, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences7030050.
Lamqadem, A. A., Pradhan, B., Saber, H., & Rahimi, A. (2018). Desertification sensitivity analysis using MEDALUS model and GIS: A case study of the Oases of Middle Draa Valley Morocco. Sensors. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18072230.
Mokadem, N., Demdoum, A., Hamed, Y., Bouri, S., Hadji, R., Boyce, A., et al. (2016). Hydrogeochemical and stable isotope data of Groundwater of a multi-aquifer system: Northern Gafsa basin - Central Tunisia. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 114, 174–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2015.11.010.
Muller, G. (1996). Index of geo-accumulation in sediments of the Rhine river. GeoJournal, 2, 108–118.
Mtimet, A. (2001). Soils of Tunisia. Soil resources of southern and eastern Mediterranean countries Bari. CIHEAM, 34, 243–262.
Ncibi, K., Chaar, H., Hadji, R., Baccari, N., Sebai, A., Khlifi, F., et al. (2020). A GIS-based statistical model for assessing groundwater susceptibility index in shallow aquifer in Central Tunisia Sidi Bouzid basin. Arabian Journal of Geosciences. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-5112-7.
O.S.S. (2003). Observatoire du Sahara et du Sahel: Systeme aquifere du Sahara Septentrional. Gestion commune d’un bassin transfrontiere. Synthesis Report, Tunis. Tunisia La Houile Blanche, 5, 128–133.
Omar, Z., Bouajila, A., Bouajila, J., Rahmani, R., Besser, H., & Hamed, Y. (2019). Spectroscopic and Chromatographic Characterization of the Composition of Organic Matter in Arid Salt-Affected Soils Under Different Vegetation Cover, Southeastern Tunisia (Gabes and Medenine). Advances in Science, Technology & Innovation. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01452-0_74.
Rezouga, N., Mohammed, B. H. A., & SaïdiBouaziz, M. I. (2012). Geochemical correlation and migration studies of the south eastern part of Tunisia. SPE International. https://doi.org/10.2118/150832-MS.SPE150832.
Rown RM, McCleiland NJ, Deiniger RA, & O’Connor MFA (1972) Water quality index – crossing the physical barrier. In S H Jenkis (Ed), Proceedings in International Conference on water pollution Research Jerusalem, 6, 787–797.
Sepehr, A., Hassanli, A. M., Ekhtesasi, M. R., & Jamali, J. B. (2007). Quantitative assessment of desertification in South of Iran using MEDALUS method. Journal of Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 134, 243–254.
Shakeriana, N., Zehtabianb, G. R., Azarnivandc, H., & Khosravi, H. (2011). Evaluation of desertification intensity based on soil and water criteria in Jarghooyeh region. Desert, 16, 23–32.
Swezey, C. S. (1996). Structural controls on quaternary depocentres within the Chotts Trough region of southern Tunisia. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 22, 335–347.
Tomlinson, D. C., Wilson, J. C., Harris, C. R., & Jeffery, D. W. (1980). Problems in the assessment of heavy metals in estuaries and the formation pollution index. Helgoland Marine Research, 33, 566–575.
Tyagi, S., Sharma, B., Singh, P., & Dobhal, R. (2013). Water quality assessment in terms of water quality index. American Journal of Water Resources, 3, 34–48. https://doi.org/10.12691/ajwr-1-3-3.
Wijitkosum, S. (2016). The impact of land use and spatial changes on desertification risk in degraded areas in Thailand. Sustainable Environment Research. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.serj.2015.11.004.
Yang, J., & Prince, S. D. (2000). Remote sensing of savanna vegetation changes in eastern Zambia 1972–1989. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 21, 301–312.
Zammouri, M., Siegfried, T., El Fahem, T., Kriâa, S., & Kinzelbach, W. (2007). Salinization of groundwater in the Nefzaoua oases region, Tunisia: Results of a regional scale hydrogeologic approach. Hydrogeology Journal, 15, 1357–1375.
Zighmi, K., Hadji, R., & Hamed, Y. (2019). GIS-based approaches for the landslide susceptibility prediction in setif region (NE Algeria). Geotechnical and Geological Engineering, 37, 359–374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-018-0615-7.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the technical staff of CRDA-Kebili, GC-Gabes and of Borj Cedria for their helpful assistance during analysis and their fruitful discussions. The authors are grateful, as well, for the insightful comments and the valuable feedback offered by the reviewers.
Funding
No finding was received for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
We attest that all authors contributed significantly to the creation of this manuscript and we confirm that the manuscript has been read and approved by all named authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that this research was not supported by any profitable company or organization and there is no conflict of interest related to it.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Besser, H., Hamed, Y. Environmental impacts of land management on the sustainability of natural resources in Oriental Erg Tunisia, North Africa. Environ Dev Sustain 23, 11677–11705 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-020-01135-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-020-01135-9