Abstract
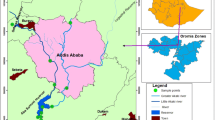
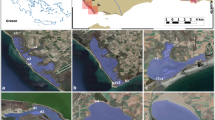
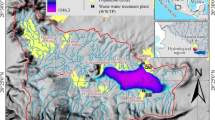
Physicochemical properties and total content of potentially toxic metals (Pb, Zn, As, Cd and Cu) in sediment and surface water samples from the pit lakes of the abandoned Pb mine were determined to assess the contamination level, and to evaluate the impact of the past mining activities on their quality. The results of the metallic trace elements in water samples gave high concentrations especially for Pb, Cd and As, which makes these lakes unusable neither for irrigation nor for drinking water supply. In addition to some statistical analyses, the geoaccumulation index (Igeo), potential ecological risk \((E_{\text{r}}^{\text{i}} )\), and other pollution indices were applied to assess pollution levels of sediments. The obtained values of Igeo and the comparison with the sediment quality guidelines reveals a high Pb contamination especially for the lakes located near next to the tailings. As for the \(E_{\text{r}}^{\text{i}}\), it shows an extreme contamination by As in some studied lakes. The correlation results showed that Pb and As are from different sources. In fact, the tailings could represent the most important source of Pb, while the As can be related to lithogenic or anthropogenic sources.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahim, G., & Parker, R. (2008). Assessment of heavy metal enrichment factors and the degree of contamination in marine sediments from Tamaki Estuary, Auckland, New Zealand. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 136(1–3), 227–238.
Adriano, D. (2001). Trace Elements in the Terrestrial Environment Springer-Verlag, New York,. 18-20.
Aggett, J., & Aspell, A. (1980). Arsenic contamination in an apple orchard. Environmental Pollution Series A, Ecological and Biological, 22(1), 39–46.
Amade, E. (1965). Les gisements de plomb de Zeïda et de Boumia. Notes & Mém. Serv. géol. Maroc, 181, 175–184.
Amrani, A., EL wartiti, M., Marini, A., Zahraoui, M., & Naitza, L. (2006). Analyse du dynamisme morphogénétique du bassin de la haute et moyenne moulouya (maroc) par couplage d’imagerie landsat et du modèle numérique de terrain Télédétection. Télédétection, 5(4), 379–391.
Antizar-Ladislao, B., Mondal, P., Mitra, S., & Sarkar, S. K. (2015). Assessment of trace metal contamination level and toxicity in sediments from coastal regions of West Bengal, Eastern part of India. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 101(2), 886–894.
Basta, N. T., Pantone, D., & Tabatabai, M. (1993). Path analysis of heavy metal adsorption by soil. Agronomy Journal, 85(5), 1054–1057.
Bouzekri, S., El Hachimi, M. L., Touach, N., El Fadili, H., & ElMahi, M. (2019). The study of metal (As, Cd, Pb, Zn and Cu) contamination in superficial stream sediments around of Zaida mine (High Moulouya-Morocco). Journal of African Earth Sciences, 154, 49–58.
Eary, L. E. (1999). Geochemical and equilibrium trends in mine pit lakes. Applied Geochemistry, 14(8), 963–987.
El Azhari, A., Rhoujjati, A., El Hachimi, M. L., & Ambrosi, J.-P. (2017). Pollution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the soil-plant system and the sediment-water column around a former Pb/Zn-mining area in NE Morocco. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 144, 464–474.
El Azhari, A., Rhoujjati, A., & Hachimi, M. L. E. (2016). Assessment of heavy metals and arsenic contamination in the sediments of the Moulouya River and the Hassan II Dam downstream of the abandoned mine Zeïda (High Moulouya, Morocco). Journal of African Earth Sciences, 119, 279–288.
El Hachimi, M. L., Bouabdli, A., & Fekhaoui, M. (2013). Les rejets miniers de traitement: caractérisation, capacité polluante et impacts environnementaux, mine Zeïda, mine Mibladen, Haute Moulouya (Maroc). Environnement & Technique, 323, 32–42.
El Hachimi, M., El Founti, L., Bouabdli, A., Saidi, N., Fekhoui, M., & Tassé, N. (2007). Pb et As dans des eaux alcalines minières: contamination, comportement et risques (mine abandonnée de Zeïda, Maroc). Revue des Sciences de l’eau/Journal of Water Science, 20(1), 1–13.
El Hachimi, M. L., El Hanbali, M., Fekhaoui, M., Bouabdli, A., ElFounti, L., & Saïdi, N. (2005). Impact d’un site minier abandonné sur l’environnement: cas de la mine de Zeïda (Haute Moulouya, Maroc). Bulletin de l’institut Scientifique, Rabat, Section Sciences de la Terre, 27, 93–100.
El Hachimi, M. L., Fekhaoui, M., El Abidi, A., & Rhoujatti, A. (2014). Contamination des sols par les métaux lourds à partir de mines abandonnées: Le cas des mines Aouli-Mibladen-Zeïda au Maroc. Cahiers Agricultures, 23(3), 213–219.
Emberger, A. (1965). Eléments pour une synthèse métallogénique du district plombifère de la Haute Moulouya. Notes & Mém. Serv. géol. Maroc, 181, 205–244.
Fall, C. (2008). Etude de la qualité de l’eau de robinet et de celle de la nappe phréatique dans les différentes Communes d’Arrondissement du département de Guédiawaye, Dakar. Sénégal, P61.
Fuge, R., Paveley, C. F., & Holdham, M. T. (1989). Heavy metal contamination in the Tanat Valley, North Wales. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 11(3–4), 127–135.
Guitián, F., & Carballas, T. (1976). Técnicas de análisis de suelos (soil analysis techniques). Pico Sacro: Santiago de Compostela.
Guo, W., Liu, X., Liu, Z., & Li, G. (2010). Pollution and potential ecological risk evaluation of heavy metals in the sediments around Dongjiang Harbor, Tianjin. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 2, 729–736.
Iavazzo, P., Ducci, D., Adamo, P., Trifuoggi, M., Migliozzi, A., & Boni, M. (2012). Impact of past mining activity on the quality of water and soil in the High Moulouya Valley (Morocco). Water, Air, and Soil pollution, 223(2), 573–589.
Jung, M. (1995). Environmental contamination of heavy metals in soils, plants, waters and sediments in the vicinity of metalliferous mine in Korea. Unpublished PhD thesis, University of London, pp. 189–317.
Jung, M. C. (2001). Heavy metal contamination of soils and waters in and around the Imcheon Au–Ag mine, Korea. Applied Geochemistry, 16(11–12), 1369–1375.
Jung, M. C., & Thornton, I. (1996). Heavy metal contamination of soils and plants in the vicinity of a lead-zinc mine, Korea. Applied Geochemistry, 11(1–2), 53–59.
Jung, M. C., & Thornton, I. (1997). Environmental contamination and seasonal variation of metals in soils, plants and waters in the paddy fields around a Pb–Zn mine in Korea. Science of the Total Environment, 198(2), 105–121.
Kribi, S. (2005). Décomposition des matières organiques et stabilisation des métaux lourds dans les sédiments de dragage. These de doctorat, Ecole des Mines d’Albi.
Krzywinski, M., & Altman, N. (2014). Points of significance: Visualizing samples with box plots. Berlin: Nature Publishing Group.
Laghlimi, M., Baghdad, B., Moussadak, R., El Hadi, H., Bouabdli, A., & Bouaziz, S. (2015). Characterization of soil Heavy Metal Contamination in the Abandoned mine of Zaida (High Moulouya, Morocco). The International Journal of Earth Sciences, 3(3), 1–3.
Lee, C. G., Chon, H.-T., & Jung, M. C. (2001). Heavy metal contamination in the vicinity of the Daduk Au–Ag–Pb–Zn mine in Korea. Applied Geochemistry, 16(11–12), 1377–1386.
Li, F., Li, G., & Ji, J. (2011). Increasing magnetic susceptibility of the suspended particles in Yangtze River and possible contribution of fly ash. CATENA, 87(1), 141–146.
Lions, J. (2004). Étude hydrogéochimique de la mobilité depolluants inorganiques dans des sédiments de curage mis en dépôt: Expérimentations, études in situ et modélisation. Thèse de doctorat, École Nationale Supérieure des mines de Paris.
MacDonald, D. D., Ingersoll, C. G., & Berger, T. (2000). Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 39(1), 20–31.
Makhoukh, M., Sbaa, M., Berrahou, A., & Vanclooster, M. (2011). Contribution à l’étude de l’impact d’un site minier abandonné dans la haute Moulouya sur la qualité de l’Oued Moulouya, Maroc. Afrique Science: Revue Internationale des Sciences et Technologie, 7(3), 33–48.
Merrington, G., & Alloway, B. (1994). The transfer and fate of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn from two historic metalliferous mine sites in the UK. Applied Geochemistry, 9(6), 677–687.
Müller, G. (1969). Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal, 2, 108–118.
N. M. (2015). Norme Marocaine sur la qualité Eaux. Recueil des textes juridiques relatifs aux ressources en eau au Maroc, Vol. 1. Ministère délégué auprès du Ministre de l’Energie, des Mines, de l’Eau et de l’Environnement.
Ngadi, M. (1995). Précipitations et écoulements dans le bassin versant de la Moulouya (Maroc). Thèse de Doctorat Université Montpellier III, France, 333p.
Pellet, R. (1963). La laverie-pilote de flottation de Plomb Moulouya. Mines et Géologie, 21–22, 135–143.
Pestana, M. H. D., Formoso, M. L., & Teixeir, E. C. (1997). Heavy metals in stream sediments from copper and gold mining areas in southern Brazil. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 58(2–3), 133–143.
Ping, L., Zhao, H.-J., Wang, L.-L., Liu, Z.-H., Wei, J.-L., Wang, Y.-Q., et al. (2011). Analysis of heavy metal sources for vegetable soils from Shandong Province, China. Agricultural Sciences in China, 10(1), 109–119.
Pueyo, M., Lopez-Sanchez, J., & Rauret, G. (2004). Assessment of CaCl2, NaNO3 and NH4NO3 extraction procedures for the study of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn extractability in contaminated soils. Analytica Chimica Acta, 504(2), 217–226.
Qian, J., Shan, X.-Q., Wang, Z.-J., & Tu, Q. (1996). Distribution and plant availability of heavy metals in different particle-size fractions of soil. Science of the Total Environment, 187(2), 131–141.
Raynal, R. (1961). Plaines et piedmonts du bassin de la Moulouya (Maroc Oriental). Étude Géomorphologique, 615, 74.
Razo, I., Carrizales, L., Castro, J., Díaz-Barriga, F., & Monroy, M. (2004). Arsenic and heavy metal pollution of soil, water and sediments in a semi-arid climate mining area in Mexico. Water, Air, and Soil pollution, 152(1–4), 129–152.
Rodriguez, J. A., Nanos, N., Grau, J. M., Gil, L., & Lopez-Arias, M. (2008). Multiscale analysis of heavy metal contents in Spanish agricultural topsoils. Chemosphere, 70(6), 1085–1096.
Schmitt, J.-M. (1976). Sédimentation, paléoaltération, géochimie et minéralisation en plomb de la série triasique de Zeida. Maroc: Haute Moulouya.
Serpaud, B., Al-Shukry, R., Casteignau, M., & Matejka, G. (1994). Adsorption des métaux lourds (Cu, Zn, Cd et Pb) par les sédiments superficiels d’un cours d’eau: rôle du pH, de la température et de la composition du sédiment. Revue des sciences de l’eau/Journal of Water Science, 7(4), 343–365.
Sigg, L., Behra, P., & Stumm, W. (2000). Chimie des milieux aquatiques: Chimie des eaux naturelles et des interfaces dans l’environnement (3rd ed.). Paris: Dunod.
Smedley, P., & Kinniburgh, D. (2002). A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Applied Geochemistry, 17(5), 517–568.
Suresh, G., Ramasamy, V., Meenakshisundaram, V., Venkatachalapathy, R., & Ponnusamy, V. (2011). Influence of mineralogical and heavy metal composition on natural radionuclide concentrations in the river sediments. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 69(10), 1466–1474.
Taylor, K. G., & Boult, S. (2007). The role of grain dissolution and diagenetic mineral precipitation in the cycling of metals and phosphorus: A study of a contaminated urban freshwater sediment. Applied Geochemistry, 22(7), 1344–1358.
Thornton, I. (1980). Geochemical aspects of heavy metal pollution and agriculture in England and Wales. Reference Book, Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food, 326, 105–125.
Ujević, I., Odžak, N., & Barić, A. (2000). Trace metal accumulation in different grain size fractions of the sediments from a semi-enclosed bay heavily contaminated by urban and industrial wastewaters. Water Research, 34(11), 3055–3061.
Wong, C., Renshaw, C., Feng, X., & Sturup, S. (2002). New Hampshire apple orchards as a source of arsenic contamination. In AGU spring meeting abstracts.
World Health Organization. (2004). Guidelines for drinking-water quality (Vol. 1). Geneva: World Health Organization.
Xiaoling, M., Zuo, H., Tian, M., Zhang, L., Meng, J., Zhou, X., et al. (2016). Assessment of heavy metals contamination in sediments from three adjacent regions of the Yellow River using metal chemical fractions and multivariate analysis techniques. Chemosphere, 144, 264–272.
Yao, Q., Wang, X., Jian, H., Chen, H., & Yu, Z. (2015). Characterization of the particle size fraction associated with heavy metals in suspended sediments of the Yellow River. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 12(6), 6725–6744.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bouzekri, S., El Fadili, H., El Hachimi, M.L. et al. Assessment of trace metals contamination in sediment and surface water of quarry lakes from the abandoned Pb mine Zaida, High Moulouya-Morocco. Environ Dev Sustain 22, 7013–7031 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-019-00525-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-019-00525-y