Abstract
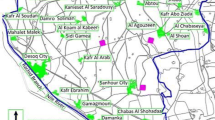
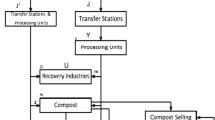
For an efficient management of solid waste across the cities, proper allocation of waste bins has become a subject of paramount importance. At present, most of the cities of developing countries are facing the problem of lack of waste bins in appropriate places. This deficiency in the number of waste bins results in littering habit and increases the number of waste collection points for the local authorities. Large numbers of collection points increase the collection cost and carbon emission in the environment. In this paper, a mixed integer linear programming model has been formulated to determine the total number of bins required in any site considering different factors like multiple types of sources, waste bins and wastes types along with safety and rag-picking. An efficient method has been proposed for the allocation of bins such that the bins are able to provide service to the entire targeted site. The developed model is tested using the data obtained from an Indian city to demonstrate its applicability. The result manifests the effectiveness of the model in terms of reduction in collection points (15%), idling cost (25%) and carbon emission (35%).












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd El-Salam, M. M., & Abu-Zuid, G. I. (2015). Impact of landfill leachate on the groundwater quality: A case study in Egypt. Journal of Advanced Research,6(4), 579–586.
Abdoli, M. A., Rezaei, M., & Hasanian, H. (2016). Integrated solid waste management in megacities. Global Journal of Environmental Science Management,2(3), 289–298.
Ali, S. M., Pervaiz, A., Afzal, B., Hamid, N., & Yasmin, A. (2014). Open dumping of municipal solid waste and its hazardous impacts on soil and vegetation diversity at waste dumping sites of Islamabad city. Journal of King Saud University Science,26(1), 59–65.
Annepu, R. K. (2012). Sustainable solid waste management in India. Department of Earth and Environmental Engineering at Columbia University, pp. 1–189. Retrieved from http://www.seas.columbia.edu/earth/wtert/newwtert/Research/sofos/Sustainable_SWM_India_Final.pdf. Accessed 7 Apr 2016.
Arribas, C. A., Blazquez, C. A., & Lamas, A. N. (2009). Urban solid waste collection system using mathematical modelling and tools of geographic information systems. Waste Management and Research,00, 1–9.
Arti, S., Ayushman, M., & Bhawana, M. (2013). Urban sprawl development and need assessment of landfills for waste disposal: A case study of Bilaspur Municipal Corporation of Chhattisgarh, INDIA. Journal of Environmental Research And Development,7(4), 1718.
Badran, M. F., & El-Haggar, S. M. (2006). Optimization of municipal solid waste management in Port Said, Egypt. Waste Management,26, 534–545.
Bohm, R., Folz, D., Kinnaman, T., & Podolsky, M. (2010). The costs of municipal waste and recycling programs. Resources, Conservation and Recycling,54, 864–871.
Boskovic, G., & Jovicic, N. (2015). Fast methodology to design the optimal collection point locations and number of waste bins: A case study. Waste Management and Research,33(12), 1094–1102.
Census of India. (2011). Provisional Population Totals e India Data Sheet. Office of the Registrar General Census Commissioner, Government of India. Indian Census Bureau. Source: http://censusindia.gov.in/.Accessed 5 Apr 2016.
Central Pollution Control Board. (2017). Management of Municipal Solid Waste. Ministry of Environment and Forests, Delhi, India. Source: http://cpcb.nic.in/uploads/hwmd/MSW_AnnualReviewReport_2015-16.pdf. Accessed 15 Sep 2017.
Chalkias, C., & Lasaridi, K. (2009). A GIS based model for the optimisation of municipal solid waste collection: The case study of Nikea, Athens, Greece. WSEAS Transactions on Environment and Development,5(10), 640–650.
Commission, P. (2014). Report of the task force on waste to energy (volume I). Retrieved from http://planningcommission.nic.in/reports/genrep/rep_wte1205.pdf. Accessed 7 Apr 2016.
Coutinho-rodrigues, J., Tralhão, L., & Alçada-almeida, L. (2012). A multiobjective modeling approach to locate multi-compartment containers for urban-sorted waste. Waste Management, 30, 2418–2429.
Datta, M., & Kumar, A. (2016). Waste dumps and contaminated sites in India—Status and framework for remediation and control. Geo-Chicago 2016 GSP 273 (pp. 664–673).
De, S., & Debnath, B. (2016). Prevalence of health hazards associated with solid waste disposal—A case study of Kolkata, India. Procedia Environmental Sciences,35, 201–208.
Erkut, E., & Tjandra, S. A. (2008). A multicriteria facility location model for municipal solid waste management in North Greece. European Journal of Operational Research,187, 1402–1421.
Gallardo, A., Carlos, M., Peris, M., & Colomer, F. J. (2014). Methodology to design a municipal solid waste generation and composition map: A case study. Waste Management,34(11), 1920–1931.
Gandhe, H. D., & Kumar, A. (2016). Efficient resource recovery options from municipal solid waste: Case study of Patna. India. Current World Environment,11(1), 72–76.
Ghatak, T. K. (2016). Municipal solid waste management in India: A few unaddressed issues. Procedia Environmental Sciences,35, 169–175.
Ghiani, G., Laganà, D., Manni, E., & Triki, C. (2012). Capacitated location of collection sites in an urban waste management system. Waste Management,32(7), 1291–1296.
Ghose, M. K. (2006). A GIS based transportation model for solid waste disposal—A case study on Asansol municipality. Waste Management,26, 1287–1293.
Gupta, N., Yadav, K. K., & Kumar, V. (2015). A review on current status of municipal solid waste management in India. Journal of Environmental Sciences,37, 206–217.
Hazra, T., & Goel, S. (2009). Solid waste management in Kolkata, India: Practices and challenges. Waste Management,29(1), 470–478.
Hemmelmayr, V. C., Doerner, K. F., Hartl, R. F., & Vigo, D. (2014). Models and algorithms for the integrated planning of bin allocation and vehicle routing in solid waste management. Transportation Science,48(1), 103–120.
Kaushal, R., Varghese, G., & Chabukdhara, M. (2012). Municipal solid waste management in india-current state and future challenges: A review. International Journal of Engineering Science and Technology,4(04), 1473–1489.
Khan, D., & Samadder, S. R. (2016). Allocation of solid waste collection bins and route optimisation using geographical information system: A case study of Dhanbad City. India. Waste Management & Research,34(7), 666–676.
Kumar, V., & Pandit, R. K. (2013). Problems of solid waste management in Indian cities. International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications,3(3), 1–9.
Mehr, M. N., & Mcgarvey, R. G. (2017). Planning solid waste collection with robust optimization: Location-allocation, receptacle type, and service frequency. Advances in Operations Research. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/2912483. Accessed 16 Jan 2018.
Ministry of Environment and Forests (MoEF). (2010). Report of the committee to evolve road map on management of wastes in India (pp. 1–54). Retrieved from http://www.moef.nic.in/downloads/public-information/Roadmap-Mgmt-Waste.pdf. Accessed 5 Aug 2016.
Ministry of Urban Development. (2016a). MUNICIPAL SOLID WASTE part I: An overview. Central Public Health and Environmental Engineering Organisation (CPHEEO) (pp. 1–96). Retrieved from http://moud.gov.in/pdf/57f1e55834489Book03.pdf. Accessed 5 Nov 2017.
Ministry of Urban Development. (2016b). MUNICIPAL SOLID WASTE part II: The manual. Central Public Health & Environmental Engineering Organisation (pp. 1–604). Retrieved from http://cpheeo.nic.in/WriteReadData/Cpheeo_SolidWasteManagement2016/Manual.pdf. Accessed 5 Nov 2017.
National Institute of Urban Affairs. (2015). Urban solid waste management in Indian cities (pp. 1–44). Retrieved from https://pearl.niua.org/sites/default/files/books/GP-IN3_SWM.pdf. Accessed 17 Nov 2017.
Nguyen, T. T. T., & Wilson, B. G. (2010). Fuel consumption estimation for kerbside municipal solid waste (MSW) collection activities. Waste Management and Research,28, 289–297.
Purkayastha, D., Majumder, M., & Chakrabarti, S. (2015). Collection and recycle bin location-allocation problem in solid waste management: A review. Pollution,1(2), 175–191.
Rada, E. C., Ragazzi, M., & Fedrizzi, P. (2013). Web-GIS oriented systems viability for municipal solid waste selective collection optimization in developed and transient economies. Waste Management,33(4), 785–792.
Rathore, P., & Sarmah, S. P. (2018). Allocation of bins in urban solid waste logistics system. In Harmony search and nature inspired optimization algorithms (pp. 485–495). Singapore: Springer.
Rathore, P., & Sarmah, S. P. (2019). Modeling transfer station locations considering source separation of solid waste in urban centers: A case study of Bilaspur city, India. Journal of Cleaner Production,211, 44–60.
Steuer, B., Ramusch, R., Part, F., & Salhofer, S. (2017). Analysis of the value chain and network structure of informal waste recycling in Beijing, China. Resources, Conservation and Recycling,117, 137–150.
Sukholthaman, P., & Sharp, A. (2016). A system dynamics model to evaluate effects of source separation of municipal solid waste management: A case of Bangkok, Thailand. Waste Management,52, 50–61.
Tavares, G., Zsigraiova, Z., Semiao, V., & Carvalho, M. G. (2009). Optimisation of MSW collection routes for minimum fuel consumption using 3D GIS modelling. Waste Management,29(3), 1176–1185.
Upadhyay, V., Jethoo, A. S., & Poonia, M. P. (2012). Solid waste collection and segregation: A case study of MNIT campus, Jaipur. International Journal of Engineering and Innovative Technology,1(3), 144–149.
United Nations. (2014). World Urbanization Prospects: The 2014 Revision. Department of Economic and Social Affairs, United Nations Publications. Source: http://esa.un.org/unpd/wup/highlights/wup2014-highlights.pdf. Accessed 19 Sep 2017.
Vuji, G., Jovi, N., Redži, N., Jovi, G., Batini, B., Stanisavljevi, N., et al. (2010). A fast method for the analysis of municipal solid waste in developing countries—Case study of Serbia. Environmental Engineering and Management Journal,9(8), 1021–1029.
Zamorano, M., Molero, E., Grindlay, A., Rodríguez, M. L., Hurtado, A., & Calvo, F. J. (2009). A planning scenario for the application of geographical information systems in municipal waste collection: A case of Churriana de la Vega (Granada, Spain). Resources, Conservation and Recycling,54, 123–133.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the support of Bilaspur Municipal Corporation for providing the necessary data and having discussions over the present situation and the feasibility of the proposed model. The author also acknowledges the effort of reviewer’s for their valuable suggestion in order to increase the standard of the article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rathore, P., Sarmah, S.P. & Singh, A. Location–allocation of bins in urban solid waste management: a case study of Bilaspur city, India. Environ Dev Sustain 22, 3309–3331 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-019-00347-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-019-00347-y