Abstract
Food manufacturing is an important value-adding sector of both local economies and the global economy in terms of job creation, food security and participatory community development, among others. Along with highly relevant issues on energy consumption, unsustainable land-use patterns, waste generation associated with the industry, social issues in terms of health and safety of food products are part of the larger sustainability concerns. While maintaining economic stability at the firm level, there is a need to develop a sustainable manufacturing strategy that addresses competitiveness and sustainability. Emerging concerns for sustainable manufacturing are circulating, but focusing on a particular industry remains a gap. Thus, this paper attempts to formulate a sustainable manufacturing strategy and then to map this strategy to established best practices. The main departure of this work is: (1) identifying the content strategy of sustainable manufacturing strategy for food manufacturing firms, (2) determining the most relevant best practice that would largely address the content strategy and (3) providing guidelines for food manufacturing decision-makers and policy-makers in strategy formulation that aims to enhance the sustainability of their manufacturing firms. A fuzzy analytic hierarchy process–technique for order of preference by similarity to ideal solution (AHP–TOPSIS) approach is used to formulate the strategy and then rank the best practices. A case study is carried out in the Philippines, and results show the content strategy and total quality management is the best practice that supports the sustainability of food manufacturing firms followed by resource and material efficiency approaches.



Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
18 June 2018
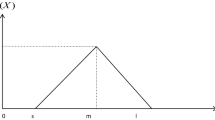
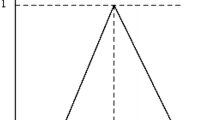
Unfortunately, the below equations have been published incorrectly in the original publication. The correct equations are provided below:
References
Abdul Rashid, S. H., Evans, S., & Longhurst, P. (2008). A comparison of four sustainable manufacturing strategies. International Journal of Sustainable Engineering, 1(3), 214–229.
Balasubramanian, D., Kher, D., Dinesh, M., Madan, G., Shekharan, G., & Venkatesh, V. G. (2015). Factors influencing successful implementation of green manufacturing. AIMS International Journal of Management, 9(1), 1–16.
Baltazar, M. E., Jardim, J., Alves, P., Silva, J. (2014). Air transport performance and efficiency: MCDA vs. DEA approaches. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 111, 790–799.
Barreto, L. V., Anderson, H. C., Anglin, A., & Tomovic, C. L. (2010). Product lifecycle management in support of green manufacturing: Addressing the challenges of global climate change. International Journal of Manufacturing Technology and Management, 19(3/4), 294–305.
Brundtland, G. H. (1987). Report of the world commission on environment and development: Our common future. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Chase, R., & Aquilano, N. (1992). Production and operations management (6th ed.). Toronto: Irwin Publishing.
Chen, C.-T. (2000). Extensions of the TOPSIS for group decision-making under fuzzy environment. Fuzzy Sets Systems, 114(1), 1–9.
Clelland, I. J., Dean, T. J., & Douglas, T. J. (2000). Stepping towards sustainable business: An evaluation of waste minimization practices in US manufacturing, 30(3), 107–124.
Crosby, P. B. (1987). Quality process improvement principles and strategic goals. Washington, DC: Management College (course materials). Department of the Navy. San Jose, CA: Philip Crosby Associates, Inc.
Department of Trade and Industry. (2017). Securing the future of Philippine industries. http://industry.gov.ph/category/manufacturing/. Accessed 21 March 2017.
Ehrenfeld, D. (2005). Sustainability: Living with the imperfections. Conservation Biology, 19(1), 33–35.
Elkington, J. (1994). Towards the sustainable corporation: Win–win–win business strategies for sustainable development. California Management Review, 36(2), 90–100.
ETBPP. (1996). Saving money through waste minimisation: Raw material use. Environmental Technology Best Practice Programme.
Forster, A. (2011). Sustainability: Best practices in the food industry. UW-L Journal of Undergraduate Research, 16, 1–9.
Global Environmental Management Initiative (GEMI). (1994). Environmental reporting in a total quality management framework. http://gemi.org/resources/REP_105.pdf. Accessed 21 March 2017.
Hallgren, M., & Olhager, J. (2006). Quantification in manufacturing strategy: A methodology and illustration. International Journal of Production Economics, 104(1), 113–124.
Howarth, G., & Hadfield, M. (2006). A sustainable product design model. Materials and Design, 27(10), 1128–1133.
Huang, K. S. (2003). Food manufacturing productivity and its economic implications. Electronic report from the Economic Research Service, United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), Technical bulletin number 1905.
Hwang, C. L., Yoon, K. (1981). Multiple attribute decision making: Methods and applications. New York: Springer.
Isaksson, R. (2006). Total quality management for sustainable development: Process based system models. Business Process Management Journal, 12(5), 632–645.
Kaufmann, A., & Gupta, M. M. (1985). Introduction to fuzzy arithmetic: Theory and applications. New York, NY: Van Nostrand Reinhold Company.
Kleindorfer, P., Singhal, K., & Van Wassenhove, L. (2005). Sustainable operations management. Production and Operation Management, 14(4), 482–492.
Klöpffer, W. (1997). Life cycle assessment: From the beginning to the current state. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 4(4), 223–228.
Kroyer, G. T. (1995). Impact of food processing on the environment—An overview. LWT Food Science and Technology, 28(6), 547–552.
Langemeyer, J., Gómez-Baggethun, E., Haase, D., Scheuer, S., Elmqvist, T. (2016). Bridging the gap between ecosystem service assessments and land-use planning through Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA). Environmental Science & Policy, 62, 45–56.
León-Bravo, V., Caniato, F., Caridi, M., & Johnsen, T. (2017). Collaboration for sustainability in the food supply chain: A multi-stage study in Italy. Sustainability, 9, 1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9071253.
Liker, J. K. (2004). The Toyota way: 14 management principles from the world’s greatest manufacturer. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
Luthra, S., Mangla, S. K., Xu, L., & Diabat, A. (2016). Using AHP to evaluate barriers in adopting sustainable consumption and production initiatives in a supply chain. International Journal of Production Economics, 181, 342–349.
Mani, V., Agrawal, R., & Sharma, V. (2014). Supplier selection using social sustainability: AHP based approach in India. International Strategic Management Review, 2(2), 98–112.
Mastrocinque, E., Coronado Mondragon, A., & Hogg, P. (2016). Manufacturing technology selection in the supply chain context by means of fuzzy-AHP: A case study in the high performance textile industry. ARPN Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences, 11(1), 240–246.
Meyer, P., Olteanu, A.-L. (2013). Formalizing and solving the problem of clustering in MCDA. European Journal of Operational Research, 227(3), 494–502.
Mikhailov, L., & Tsvetinov, P. (2004). Evaluation of services using a fuzzy hierarchy process. Applied Soft Computing, 5(1), 23–33.
Morteza, Z., Reza, F. M., Seddiq, M. M., Sharareh, P., & Jamal, G. (2016). Selection of the optimal tourism site using the ANP and fuzzy TOPSIS in the framework of integrated coastal zone management: A case of Qeshm Island. Ocean and Coastal Management, 130, 179–187.
Naudé, W., & Szirmai, A. (2012). The importance of manufacturing in economic development: Past, present and future perspectives. UNU-MERIT working papers, Maastricht Economic and Social Research Institute on Innovation and Technology (UNU-MERIT) and Maastricht Graduate School of Governance (MGSoG) (pp. 1–65).
Ocampo, L., & Clark, E. (2015a). A sustainable manufacturing strategy framework: The convergence of two fields. Asian Academy of Management Journal, 20(2), 29–57.
Ocampo, L., & Clark, E. (2015b). A simulation-based fuzzy analytic network process approach in developing sustainable manufacturing strategy. Management and Production Engineering Review, 6(2), 32–39.
Ocampo, L. A., & Clark, E. E. (2017). Integrating sustainability and manufacturing strategy into a unifying framework. International Journal of Social Ecology and Sustainable Development, 8(1), 1–16.
Ocampo, L., Clark, E., & Promentilla, M. A. (2016). Computing sustainable manufacturing index with fuzzy analytic hierarchy process. International Journal of Sustainable Engineering, 9(5), 305–314.
Ocampo, L. A., Clark, E. E., Tanudtanud, K. V. G., Ocampo, C. O. V., Impas, C. G., Sr., Vergara, V. G., et al. (2015). An integrated sustainable manufacturing strategy framework using fuzzy analytic network process. Advances in Production Engineering and Management, 10(3), 125–139.
Ocampo, L., & Promentilla, M. A. (2016). Development of a sustainable manufacturing strategy using analytic network process (ANP). International Journal of Business and Systems Research, 10(2–4), 262–290.
Ohno, T. (1978). Toyota production system—Beyond management of large-scale production. Tokyo: Diamond Publishing.
Paul, I. D., Bhole, G. P., & Chaudhari, J. R. (2014). A review on green manufacturing: It’s important, methodology and its application. Procedia Materials Science, 6, 1644–1649.
Promentilla, M. A. B., Aviso, K. B., & Tan, R. R. (2014). A group fuzzy analytic network process to prioritize low carbon energy systems in the Philippines. Energy Procedia, 61, 808–811.
Rezaei-Moghaddam, K., & Karami, E. (2008). A multiple criteria evaluation of sustainable agricultural development models using AHP. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 10(4), 407–426.
Ribeiro, F., Ferreira, P., Araújo, M. (2013). Evaluating future scenarios for the power generation sector using a Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA) tool: The Portuguese case. Energy, 52, 126–136.
Rothenberg, S., Pil, F. K., & Maxwell, J. (2001). Lean, green, and the quest for superior environmental performance. Production and Operations Management, 10(3), 228–243.
Saaty, T. L. (1980). The analytic hierarchy process. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
Schmidheiny, S. (1992). Changing course: A global business perspective on development and the environment. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Schmidt-Bleek, F. (1996). Factor 10 with its MIPS and ecological rucksacks as measurement tools.
Seliger, G., Kim, H.-J., Kernbaum, S., & Zettl, M. (2008). Approaches to sustainable manufacturing. International Journal of Sustainable Manufacturing, 1(1–2), 58–77.
Shingo, S. (1981). Study of ‘TOYOTA’ production system from industrial engineering viewpoint. Portland, OR: Productivity Press.
Singh, R. P., & Nachtnebel, H. P. (2016). Analytical hierarchy process (AHP) application for reinforcement of hydropower strategy in Nepal. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 55, 43–58.
Singian, M. R. C. (2014). Booming Philippine food processing industry provides opportunities for U.S. ingredients. USDA Foreign Agricultural Service. https://gain.fas.usda.gov/Recent%20GAIN%20Publications/Food%20Processing%20Ingredients_Manila_Philippines_2-12-2014.pdf. Accessed 21 March 2017.
Siva, V., Gremyr, I., Bergquist, B., Garvare, R., Zobel, T., & Isaksson, R. (2016). The support of quality management to sustainable development: A literature review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 138, 148–157.
Skinner, W. (1969). Manufacturing—Missing link in corporate strategy. Brighton, MA: Harvard Business Review.
Stroufe, R. (2003). Effects of environmental management systems on environmental management practices and operations. Production and Operations Management, 12(3), 416–431.
Sundharam, V. N., Sharma, V., & Thangaiah, I. S. T. (2013). An integration of BSC and AHP for sustainable growth of manufacturing industries. International Journal of Business Excellence, 6(1), 77–92.
Tan, X., Liu, D., & Li, C. (2008). A decision-making framework model of cutting tool selection for green manufacturing and its application. Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Systems, 7(2), 257–260.
Tari, J. J., & Molina-Azorín, J. F. (2010). Integration of quality management and environmental management systems: Similarities and the role of the EFQM model. The TQM Journal, 22(6), 687–701.
Thokala, P., Devlin, N., Marsh, K., Baltussen, R., Boysen, M., Kalo, Z., et al. (2016). Multiple criteria decision analysis for health care decision making—an introduction: Report 1 of the ISPOR MCDA emerging good practices task force. Value in Health, 19(1), 1–13.
Tsai, W.-H., & Chou, W.-C. (2009). Selecting management systems for sustainable development in SMEs: A novel hybrid model based on DEMATEL, ANP, and ZOGP. Expert Systems with Applications, 36(2), 1444–1458.
Tseng, M. L., Lin, Y. H., Chiu, A. S. F., & Liao, J. C. H. (2008). Using FANP approach on selection of competitive priorities based on cleaner production implementation: A case study in PCB manufacturer, Taiwan. Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy, 10(1), 17–29.
Veisi, H., Liaghati, H., & Alipour, A. (2016). Developing an ethics-based approach to indicators of sustainable agriculture using analytic hierarchy process (AHP). Ecological Indicators, 60, 644–654.
Voss, C., & Clutterbuck, D. (1989). Just-in-time: A global status report. Bedford: IFS Publications.
Worrell, E., Bernstein, L., Roy, J., Price, L., & Harnisch, J. (2009). Industrial energy efficiency and climate change mitigation. Energy Efficiency, 2, 109–123.
Yuce, B., & Mastrocinque, E. (2016). A hybrid approach using the bees algorithm and fuzzy-AHP for supplier selection. In P. Samui (Ed.), Handbook of research on advanced computational techniques for simulation-based engineering (pp. 171–194). Hersey, PA: IGI Global.
Zadeh, L. A. (1965). Fuzzy sets. Information and Control, 8(3), 338–353.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ocampo, L.A. Applying fuzzy AHP–TOPSIS technique in identifying the content strategy of sustainable manufacturing for food production. Environ Dev Sustain 21, 2225–2251 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-018-0129-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-018-0129-8