Abstract
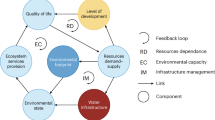
Although very often used, the concept of sustainable development has not yet been perceived pragmatically. Due to its process nature, in this paper, we argue that sustainable development is a process in which the essential feedback loops, or Viability Loops as we name them, in the system in question are kept healthy and functional. This process deals with evolutionary changes with the end point not known in advance. According to this perception, measurement of sustainable development does not make sense. Rather, we should look for the process indicators to monitor systems for sustainable development. The purpose of the paper is to develop a methodology to deal with monitoring systems for sustainable development and its practice in an urban water system. Using a system dynamics approach, the paper adopts a systemic monitoring framework based on the idea of Viability Loops to define process indicators to monitor systems for sustainable development. To illustrate the application of the framework, its practice in the urban water system of Tehran, the capital of Iran, is provided as an example. The example of the urban water supply system of Tehran is given as a case study, albeit with some unavailable data. Here, four typical viability loops are discussed. The results of this application show that the flows of informative signals are lacking. Adopting the process indicators, we can see the gaps between the public perceptions of water abundance, the costs of water provision and energy utilizations, and what is going on in the reality are getting wider. That indicates that the viability loops are not functional enough to produce effective changes to offset the reinforcing mechanisms. The sustainable development of the system is impaired due to the persistence of those reinforcing mechanisms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ASCE Task Committee for Sustainability Criteria: 1998, Sustainability Criteria for Water Resource Systems ASCE, Reston, VA
Ashley R., Hopkinson P. 2002, Sewer systems and performance indicators – into the 21st century Urban Water 4: 123–135
Ashley R.M., Souter N., Butler D., Davies J., Dunkerley J., Hendry S. 1999, Assessment of the sustainability of alternatives for the disposal of domestic sanitary waste Water Science and Technology 39(5): 251–258
Bagheri, A. and Hjorth, P.: 2006, ‘Monitoring for sustainable development: A systemic framework’, International Journal of Sustainable Development (accepted)
Balkema A.J., Preisig H.A., Otterpohl R., Lambert F.J.D. 2002, Indicators for the sustainability assessment of wastewater treatment systems Urban Water 4: 153–161
Bertrand-Krajewski J.L., Barraud S., Chocat B. 2000, Need for improved methodologies and measurements for sustainable management of urban water systems Environmental Impact Assessment Review 20: 323–331
Bossel H. 1999, Indicators for Sustainable Development: Theory, Method, Applications International Institute for Sustainable Development Canada
Bruce, J.P.: 1992, Meteorology and Hydrology for Sustainable Development, Geneva, Switzerland, World Meteorological Organization No. 769, Secretariat of the WMO
Cary, J.: 1998, ‘Institutional innovation in natural resource management in Australia: The triumph of creativity over adversity’, in Abstracts of the Conference Knowledge Generation and Transfer: Implications for Agriculture in the 21st Century, Berkeley, University of California-Berkeley
Crettaz P., Jolliet O., Cuanillon J.M., Orlande S. 1999, Life cycle assessment of drinking water and rainwater for toilet flushing Aqua 48(3): 73–83
Emmerson R.H.C., Morse G.K., Leshter J.N., Edge D.R. 1995, Life-cycle analysis of small-scale sewage treatment processes Journal of the Chartered Institute of Water and Environmental Management 9(3): 317–325
Falkenmark M. 1997, Society’s interaction with the water cycle: A conceptual framework for a more holistic approach Hydrological Sciences Journal 42: 451–466
Falkenmark, M.: 1988, ‘Sustainable development as seen from a water perspective’, in Perspectives of Sustainable Development, Stockholm, Stockholm Studies in Natural Resources Management, No.1, pp. 71–84
Gutierrez-Martin F., Dahab M.F. 1998, Issues of sustainability and pollution prevention in environmental engineering education Water Science and Technology 38: 271–278
Haimes Y.Y. 1992, Sustainable development: A holistic approach to natural resources management Water International 17: 187–192
Hellström D., Jeppsson U., Kärrman E., (2000), A framework for systems analysis of sustainable urban water management Environmental Impact Assessment Review 20: 311–321
Hellström D., Kärrman E. 1997, Exergy analysis and nutrient flows of various sewerage systems Water Science and Technology 35(9): 135–144
Hjorth, P. and Bagheri, A.: 2006, ‘Navigating towards sustainable development: A system dynamics approach’, Futures 38(1), 74–92
Holling, C.S.: 2000, ‘Theories for sustainable futures’, Conservation Ecology 4(2), 7. [Online] URL: http://www.consecol.org/vol4/iss2/art7/
Holmberg, J.: 1995, Socio-Ecological Principles and Indicators for Sustainability, Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Physical Resource Theory, Göteborg, Sweden, Chalmers University of Technology & University of Göteborg
Holmberg J., Robèrt K.H., Eriksson K.E. 1996, Socio-ecological principles for sustainability in: Costanza R., Olmlan S., Martinez-Alier J., (eds), Getting Down to Earth – Practical Applications of Ecological Economics International Society of Ecological Economics Island Press, Washington
Huang G.H., Xia J. 2001, Barriers to sustainable water-quality management Journal of Environmental Management 61: 1–23
Kandiah A., 1990, Water-quality management for sustainable agricultural development Natural Resources Forum 14: 22–29
Kundzewicz Z.W. 1997, Water resources for sustainable development Hydrological Science Journal 42: 467–780
Loucks D.P., 1997, Quantifying trends in system sustainability Hydrological Science Journal 42: 513–530
Loucks D.P., 2000, Sustainable water resources management Water International 25(1): 3–10
Lundin M., Bengtsson M., Molander S., 2000, Life cycle assessment of wastewater systems: Influence of system boundaries and scale on calculated environmental loads Environmental Science and Technology 34: 180–186
Lundin M., Morrison G.M., 2002, A life cycle assessment based procedure for development of environmental sustainability indicators for urban water systems Urban Water 4: 145–152
Meadows D.H., Meadows D.L., Randers J. 2004, Limits to Growth – The 30-Year Update Chelsea Green White River Junction, VT
Niu W.Y., Harris W.M. 1996, China: The forecast of its environmental situation in 21st century Journal of Environmental Management 47: 101–114
Pearce D.W., 1993 Blueprint 3: Measuring Sustainable Development Earthscan London
Peet J., Bossel H. 2000, An ethics-based systems approach to indicators of sustainable development International Journal of Sustainable Development 3(3): 221–238
Plate E.J. 1993, Sustainable development of water resources: A challenge to science and engineering Water International 18: 84–93
Ròbert K.H., Daly H., Hawken P., Holmberg J., 1997 A compass for sustainable development International Journal of Sustainable Development and World Ecology 4: 79–92
Robèrt K.H., 2000, Tools and concepts for sustainable development, how do they relate to a general framework for sustainable development, and to each other? Journal of Cleaner Production 8: 243–254
Roelveld P.J., Klapwijk A., Eggles P.G., Rulkens W.H., van Starkenburg W., 1997, Sustainability of municipal wastewater treatment Water Science and Technology 35(10): 221–228
Simonovic S.P., 1996a, Decision support system for sustainable management of water resources: 1 General principles Water International 21: 223–232
Simonovic S.P., 1996b, Decision support system for sustainable management of water resources: 2 Case studies Water International 21: 233–244
Sonesson U., Björklund A., Carlsson M., Dalemo M., 2000, Environmental and economic analysis for biodegradable waste Resources Conservation and Recycling 28: 29–53
Suzuki M., 1998, A look at technology’s role in sustainable water management Water Quality International 5: 9–16
Tehran Water & Waste Water Company: 2001, Activities Report: Past, Now, Future Ministry of Energy, Tehran, Iran
Tillman A.M., Lundström H., Svingby M. 1998, Life cycle assessment of municipal waste water systems International Journal of LCA 3(3): 145–157
Xia J., Hu B. 1997, A grey system model for predicting trend change of urban wastewater load Journal of Environmental Hydrology 5: 1–10
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to gratefully acknowledge the Swedish Institute for its financial support, Somayeh Sima, Reza Roozbahani, and Younes Gharbali Moghaddam for provision of necessary data, and also the editor and the anonymous reviewer for their helpful suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
BAGHERI, A., HJORTH, P. A FRAMEWORK FOR PROCESS INDICATORS TO MONITOR FOR SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT: PRACTICE TO AN URBAN WATER SYSTEM. Environ Dev Sustain 9, 143–161 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-005-9009-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-005-9009-0