Abstract
Food production has to be increased in a sustainable way to meet the future global demand. A key position is attributed to developing countries. A deepened understanding of their agricultural regions with specific resource endowments and constraints is therefore crucial. In this study we propose a methodology based on material flux analysis (MFA) to assess the resource potentials and limitations of a Nicaraguan agricultural region. We focus on current regional and farm resource management and explore them under two scenarios. Indicators are nitrogen and the degrees of self-sufficiency (DSS) for energy, and the staples maize and beans. As data is scarce, most information is based on interviews with farmers of four categories and key persons, and on literature.
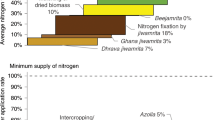
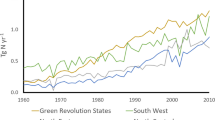
The results show that nitrogen management does not differ considerably among categories. Nitrogen is mined mostly from staple plots. Self-sufficiency for beans is given in an average year. Yet, landless and small farmers neither produce enough maize for autoconsumption, nor are they self-sufficient for firewood. Energy supply is also the core problem of the region, since the DSS is 70%. Soil nitrogen stocks last at most for three more generations. Analyses with the scenario technique show that: (a) Unlimited population growth has serious consequences in the near future e.g. severe shortage of energy and food. (b) Alternative farming systems are possible, but they require reducing the population by a factor 2, and thus the creation of jobs in a Hinterland.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a:
-
year
- C:
-
Celsius
- cap:
-
capita
- DSS:
-
Degree of self-sufficiency as defined in this paper (DSSB = DSS for beans, DSSM = DSS for maize, DSSE = DSS for energy/firewood); e.g. – for instance
- ha:
-
hectare
- kg:
-
kilogram
- km:
-
kilometer
- m.a.s.l.:
-
meters above sea level
- MFA:
-
material flux analysis
- mm:
-
millimeters
- N:
-
nitrogen
References
P. Baccini H.P. Bader (1996) Regionaler Stoffhaushalt Spektrum Akademischer Verlag Heidelberg
P. Baccini P. Brunner (1991) Metabolism of the Antroposphere Springer Verlag Berlin
Baltodano, M.E., Tijerino, D. and Vernooy, R.: 1997, ‘Proceso de identificacio´ n y caracterı´ sticas de la sub-cuenca del rı´ o Calico – San Dionisio, Matagalpa’, in Proyecto CIAT-Laderas Ame´rica Central. Reportes de progreso 1997, Managua, Nicaragua, Centro Internacional de Agricultura Tropical (CIAT).
C. Binder (1996) The Early Recognition of Environmental Impacts of Human Activities in Developing Countries Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETHZ) Zurich, Switzerland
L. Brown (1997) The Agricultural Link: How Environmental Deterioration Could Disrupt Economic Progress Worldwatch Institute Washington, DC, USA
Bundesamt für Landwirtschaft: 2001, www.blw.admin.ch/fakten/statistik/d/tabelle_10.pdf [accessed 10.11.02].
J. Dixon A. Gulliver D. Gibbon (2001) Farming Systems and Poverty Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Bank Rome, Italy and Washington, DC, USA
P. Drechsler L. Gyiele D. Kunze O. Cofie (2001) ArticleTitle`Population density, soil nutrient depletion, and economic growth in sub-Saharan Africa' Ecological Economics 38 251–258 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0921-8009(01)00167-7
E. Elias S. Morse D.G.R. Belshaw (1998) ArticleTitle`Nitrogen and phosphorus balances of Kindo Koisha farms in southern Ethiopia', Agriculture Ecosystems and Environment 71 93–113 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0167-8809(98)00134-0
N. Espinoza R. Vernooy (1998) Las 15 micro-cuencas del Río Calico, San Dionisio, Matagalpa. Mapeo y análisis participativos de los recursos naturales Centro Internacional de Agricultura Tropical (CIAT) Managua, Nicaragua
M. Faist (2001) Ressourceneffizienz in der Aktivität Ernähren Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETHZ) Zurich, Switzerland
G. Fischer M. Shah H. Velthuizen Particlevan F.O. Nachtergaele (2001) Global Agro-ecological Assessment for Agriculture in the 21st Century International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis (IIASA) and Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) Vienna, Austria and Rome, Italy
E.C.R. Folmer P.M.H. Geurts J.R. Francisco (1998) ArticleTitle`Assessment of soil fertility depletion in Mozambique', Agriculture Ecosystems and Environment 71 159–167 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0167-8809(98)00138-8
InstitutionalAuthorNameFood and Agriculture Organization (FAO) (1995) Apoyo a las organizaciones de los pequeños productores para la comercialización de granos básicos. Franja granífera San Ramón-Esquipulas NumberInSeriesVol. 1 + 2 Ministerio Agropecuario y Forestal (MAGFOR)/Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) Managua, Nicaragua
F. Hug (2002) Ressourcenhaushalt alpiner Regionen und deren physiologische Interaktionen mit den Tiefländern im Kontext einer nachhaltigen Entwicklung Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETHZ) Zurich, Switzerland
Instituto Nacional de Estadísticas y Censos (INEC): 2003, www.inec.gob.ni/estadisticas/estadisticas.htm [accessed 10.02.03].
Instituto Nicaragüense de Fomento Municipal (INIFOM): 2002, www.inifom.gob.ni/Caracter/Informacion/Matagalpa/SanDionisio.htm [accessed 04.09.02].
InstitutionalAuthorNameIntergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) (2001) Climate Change 2001: Impacts Adaptation and Vulnerability, Technical Summary Cambridge University Press Cambridge, UK
E. Leemann R. Scheidegger (2002) Mapa general SUSULI Micro-Cuenca del Río Calíco Municipio San Dionisio, 2000 Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETHZ) Zurich, Switzerland
D.B. Müller (1998) Modellierung Simulation und Bewertung des regionalen Holzhaushaltes Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETHZ) Zurich, Switzerland
InstitutionalAuthorNameNitlapán-UCA (1995) Diagnóstico de la producción agropecuaria en el interior del país. Análisis de Encuesta Rural 1995 Universidad Centroamericana (UCA) Managua, Nicaragua
H. Pagel J. Enzmann H. Mutscher (1982) Pflanzennährstoffe in tropischen Böden–ihre Bestimmung und Bewertung Deutscher Landwirtschaftsverlag Berlin Berlin, Germany
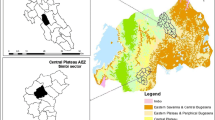
F. Pfister (2003) Resource potentials and limitations of a Nicaraguan agricultural region Switzerland, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETHZ) Zurich
P. Pinstrup-Andersen R. Pandya-Lorch (1994) Alleviating Poverty, Intensifying Agriculture and Effectively Managing Natural Resources International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI) Washington, DC, USA,
P. Pinstrup-Andersen R. Pandya-Lorch M.W. Rosegrant (1997) The World Food Situation: Recent Developments Emerging Issues and Long-Term Prospects, Food Policy Report International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI) Washinton, DC, USA
M. Redle (1999) Kies- und Energiehaushalt urbaner Regionen in Abhängigkeit der Siedlungsentwicklung Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETHZ) Zurich, Switzerland
S. Rivas (2000) Ein agro-ökologisches regionalisiertes Modell zur Analyse des Brennholzversorgungssystems in Entwicklungsländern Institut für Energiewirtschaft und rationelle Energieanwendung, Universität Stuttgart Stuttgart, Germany
InstitutionalAuthorNameSecretaría Técnica de la Presidencia (SETEC) (2001) Estrategia reforzada de crecimiento económico y reducción de pobreza Secretaría Técnica de la Presidencia (SETEC), Gobierno de Nicaragua Managua, Nicaragua
L.C. Smith A.E. El Obeid H.H. Jensen (2000) ArticleTitle`The geography and causes of food insecurity in developing countries' Agricultural Economics 22 199–215
United Nations Development Programme (UNDP): 2000, El Desarrollo Humano en Nicaragua 2000, http://www.pnud.org.ni/idhnicaragua/index.htm [accessed 10.04.01].
H. Bosch ParticleVan den J.N. Gitari V.N. Ogaro S. Maobe J. Vlaming (1998) ArticleTitle`Monitoring nutrient flows and economic performance in African farming systems (NUTMON). III. Monitoring nutrient flows and balances in three districts in Kenya', Agriculture Ecosystems and Environment 71 53–80
B. Steiger ParticleVon P. Baccini (1990) Regionale Stoffbilanzierung von landwirtschaftlichen Böden mit messbarem Ein- und Austrag Bericht 38 des Nationalen Forschungsprogramms “Boden” Liebefeld-Bern, Switzerland
C.C. Webster P.N. Wilson (Eds) (1998) Agriculture in the Tropics Blackwell Science Oxford, UK
InstitutionalAuthorNameWorld Energy Council (WEC)/Food Agriculture Organization (FAO) (1999) The Challenge of Rural Energy Poverty in Developing Countries World Energy Council (WEC)/Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) London, UK
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Readers should send their comments on this paper to: BhaskarNath@aol.com within 3 months of publication of this issue.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pfister, F., Baccini, P. Resource Potentials and Limitations of A Nicaraguan Agricultural Region. Environ Dev Sustain 7, 337–361 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-004-7318-3
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-004-7318-3