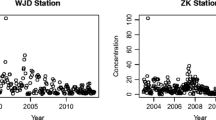
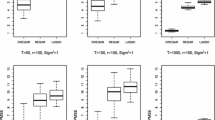
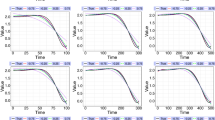
Abstract
In environmental studies, regression analysis is frequently performed. The classical approach is the ordinary least squares method which consists in minimizing the sum of the squares of the residuals. However, this method relies on strong assumptions that are not always satisfied. In environmental data, the response variable often contains outliers and errors can be heteroscedastic. This can have significant effects on parameter estimation. To solve this problem, the weighted M-estimation was developed. It assumes a parametric function for the variance, and, estimates alternately and robustly, mean and variance parameters. However, this method is limited to the independent errors case, and is not applicable to time series data. Therefore, we introduce a new estimation procedure which adapts the weighted M-estimation to environmental time series data, while selecting optimal value for the tuning parameter present in the M-estimation. We compare the efficiency of our procedure on simulated data to other usual regression methods. Our estimation procedure outperforms the other methods providing estimates with lower biases and mean squared errors. Finally, we illustrate the proposed method using an air quality dataset from Beijing. This method has been implemented in the R package RlmDataDriven.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bianco, A., Boente, G., & Di Rienzo, J. (2000). Some results for robust GM-based estimators in heteroscedastic regression models. Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference, 89(1-2), 215–242.
Bickel, P.J. (1978). Using residuals robustly I: Tests for heteroscedasticity, nonlinearity. The Annals of Statistics, 6(2), 266–291.
Box, G.E., & Hill, W.J. (1974). Correcting inhomogeneity of variance with power transformation weighting. Technometrics, 16(3), 385–389.
Carroll, R.J., & Ruppert, D. (1982). Robust estimation in heteroscedastic linear models. The Annals of Statistics, 10(2), 429–441.
Chan, C.K., & Yao, X. (2008). Air pollution in mega cities in China. Atmospheric Environment, 42(1), 1–42.
Croux, C. (1994). Efficient high-breakdown M-estimators of scale. Statistics & Probability Letters, 19(5), 371–379.
Davidian, M., & Carroll, R.J. (1987). Variance function estimation. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 82(400), 1079–1091.
Evin, G., Kavetski, D., Thyer, M., & Kuczera, G. (2013). Pitfalls and improvements in the joint inference of heteroscedasticity and autocorrelation in hydrological model calibration. Water Resources Research, 49(7), 4518–4524.
Giltinan, D.M. (1983). Bounded influence estimation in heteroscedastic linear modelS. Ph.D. thesis, Citeseer.
Huber, P.J. (1973). Robust regression: Asymptotics, conjectures and Monte Carlo. The Annals of Statistics, 1(5), 799–821.
Huber, P.J. (1981). Robust statistics. New york, Chichester, Brisbane. Toronto, Singapore: John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Hyslop, N.P., Trzepla, K., & White, W.H. (2015). Assessing the suitability of historical pm2. 5 element measurements for trend analysis. Environmental Science & Technology, 49(15), 9247–9255.
Jiang, Y., Wang, Y.G., Fu, L., & Wang, X. (2019). Robust estimation using modified huber’s functions with new tails. Technometrics, 61(1), 111–122.
Jiang, Y., Wang, Y.G., Fu, L., & Wang, X. (2019). Robust estimation using modified huber’s functions with new tails. Technometrics, 61(1), 111–122.
Knibbs, L.D., van Donkelaar, A., Martin, R.V., Bechle, M.J., Brauer, M., Cohen, D.D., Cowie, C.T., Dirgawati, M., Guo, Y., Hanigan, I.C., & et al. (2018). Satellite-based land-use regression for continental-scale long-term ambient pm2. 5 exposure assessment in australia. Environmental Science & Technology, 52 (21), 12445–12455.
Liang, X., Zou, T., Guo, B., Li, S., Zhang, H., Zhang, S., Huang, H., & Chen, S.X. (2015). Assessing Beijing’s PM2. 5 pollution: Severity, weather impact, APEC and winter heating. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 471(2182), 20150257.
McCullagh, P., & Nelder, J.A. (1989). Generalized Linear Models. vol. 37, CRC press.
Newey, W.K., & West, K.D. (1987). A simple, positive semi-definite, heteroskedasticity and autocorrelation consistent covariance matrix. Econometrica, 55(3), 703–708. http://www.jstor.org/stable/1913610.
Pope, C.A. III, Burnett, R.T., Thun, M.J., Calle, E.E., Krewski, D., Ito, K., & Thurston, G.D. (2002). Lung cancer, cardiopulmonary mortality, and long-term exposure to fine particulate air pollution. Jama, 287(9), 1132–1141.
R Core Team. (2018). R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. https://www.R-project.org/.
Rousseeuw, P.J., & Leroy, A.M. (2005). Robust Regression and Outlier Detection. vol. 589, John wiley & sons.
Stefanski, L.A., Carroll, R.J., & Ruppert, D. (1986). Optimally hounded score functions for generalized linear models with applications to logistic regression. Biometrika, 73(2), 413– 424.
Van Donkelaar, A., Martin, R.V., Spurr, R.J., & Burnett, R.T. (2015). High-resolution satellite-derived pm2. 5 from optimal estimation and geographically weighted regression over north america. Environmental Science & Technology, 49(17), 10482– 10491.
Wang, N., Wang, Y.G., Hu, S., Hu, Z.H., Xu, J., Tang, H., & Jin, G. (2018). Robust regression with data-dependent regularization parameters and autoregressive temporal correlations. Environmental Modeling & Assessment, 23(6), 1–8.
Wang, Y.G., Lin, X., Zhu, M., & Bai, Z. (2007). Robust estimation using the Huber function with a data-dependent tuning constant. Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics, 16(2), 468–481.
White, H. (1980). A heteroskedasticity-consistent covariance matrix estimator and a direct test for heteroskedasticity. Econometrica, 48(4), 817–838. http://www.jstor.org/stable/1912934.
Wu, E.M.Y., & Kuo, S.L. (2012). Air quality time series based garch model analyses of air quality information for a total quantity control district. Aerosol and Air Quality Research, 12(3), 331–343.
Zhao, J., & Wang, J. (2009). Robust testing procedures in heteroscedastic linear models. Communications in Statistics–Simulation and Computation ® , 38(2), 244–256.
Zheng, M., Salmon, L.G., Schauer, J.J., Zeng, L., Kiang, C.S., Zhang, Y., & Cass, G.R. (2005). Seasonal trends in PM2. 5 source contributions in Beijing, China. Atmospheric Environment, 39(22), 3967–3976.
Acknowledgements
The work was carried out during the visit of Aurelien Callens to the School of Mathematical Science, Queensland University of Technology, Brisbane, Australia.
Funding
This research was partially funded by the Australian Research Council project (DP160104292). Liya Fu’s research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (11871390), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. xjj2017180), the Natural Science Basic Research Plan in Shaanxi Province of China (2018JQ1006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Callens, A., Wang, YG., Fu, L. et al. Robust Estimation Procedure for Autoregressive Models with Heterogeneity. Environ Model Assess 26, 313–323 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10666-020-09730-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10666-020-09730-w