Abstract
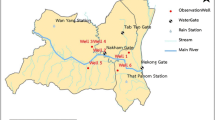
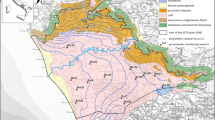
In this paper, a novel approach of modelling time series of nitrate concentrations in drinking water by nonlinear growth functions is proposed. An almost constant increase in the average values of nitrate concentrations occurred at the Vinokovščak wellfield in the county of Varaždin, Croatia, in the period between 1998 and 2013. Our hypothesis was that the time series would be well adjusted to the nonlinear growth function with asymptotic properties after smoothing performed by the moving average method. We used a general growth model which does not have asymptotic properties and the logistic, Gompertz and Richards functions which do have asymptotic properties. Last three growth functions were modified based on the knowledge of a constant presence of basic nitrate concentrations in the drinking water before growth. The fit of growth curves to experimental data was assessed using R 2 and Aikake’s information criterion. The modified growth functions gave the best fit to the smoothed time series of nitrate concentrations with R 2 ranging from 0.9960 to 0.9986.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adhikary, P. P., Chandrasekharan, H., Chakraborty, D., & Kamble, D. (2010). Assessment of groundwater pollution in West Delhi, India using geostatistical approach. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 167(1–4), 599–615. doi:10.1007/s10661-009-1076-5.
Ağca, N., Karanlık, S., & Ödemiş, B. (2014). Assessment of ammonium, nitrate, phosphate, and heavy metal pollution in groundwater from Amik Plain, southern Turkey. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 186(9), 5921–5934. doi:10.1007/s10661-014-3829-z.
Almasri, M. N. (2007). Nitrate contamination of groundwater: a conceptual management framework. Environmental Impact Assessment Review, 27(3), 220–242. doi:10.1016/j.eiar.2006.11.002.
Almasri, M. N., & Kaluarachchi, J. J. (2005). Modular neural network to predict the nitrate distribution in ground water using the on-ground nitrogen loading and recharge data. Environmental Modelling and Software, 20(7), 851–871. doi:10.1016/j.envsoft.2004.05.001.
Arabgol, R., Sartaj, M., & Asghari, K. (2016). Predicting nitrate concentration and its spatial distribution in groundwater resources using support vector machines (SVMs) model. Environmental Modeling and Assessment, 21, 71–82. doi:10.1007/s10666-015-9468-0.
Baba, A., & Tayfur, G. (2011). Groundwater contamination and its effect on health in Turkey. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 183(1–4), 77–94. doi:10.1007/s10661-011-1907-z.
Cole, T. J., Pan, H., & Butler, G. E. (2014). A mixed effects model to estimate timing and intensity of pubertal growth from height and secondary sexual characteristics. Annals of Human Biology, 41(1), 76–83. doi:10.3109/03014460.2013.856472.
Debele, B., Srinivasan, R., Parlange, J., & Y. (2008). Coupling upland watershed and downstream waterbody hydrodynamic and water quality models (SWAT and CE-QUAL-W2) for better water resources management in complex river basins. Environmental Modeling Assessment, 13, 135–153. doi:10.1007/s10666-006-9075-1.
Dokou, Z., Kourgialas, N. N., & Karatzas, G. P. (2015). Assessing groundwater quality in Greece based on spatial and temporal analysis. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187(12), 774. doi:10.1007/s10661-015-4998-0.
Eberhardt, L. L., Breiwick, J. M. (2012). Models for population growth curves. International Scholarly Research Network. ISRN Ecology 2012, Article ID 815016, doi:10.5402/2012/815016.
Ersoy, I. E., Mendes, M., & Keskin, S. (2007). Estimation of parameters of linear and nonlinear growth curve models at early growth stage in California turkeys. Archiv fur Geflugelkunde, 71(4), 175–180.
European Union (EU). (1991). Council Directive 91/676/EEC of 12 December 1991 concerning the protection of waters against pollution caused by nitrates from agricultural sources. Official Journal, L, 375, 0001–0008.
Fan, A. M., & Steinberg, V. E. (1996). Health implications of nitrate and nitrite in drinking water: an update on methemoglobinemia occurrence and reproductive and developmental toxicity. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology, 23(1), 35–43. doi:10.1006/rtph.1996.0006.
Farmani, R., Henriksen, H. J., & Savic, D. (2009). An evolutionary Bayesian belief network methodology for optimum management of groundwater contamination. Environmental Modelling and Software, 24(3), 303–310. doi:10.1016/j.envsoft.2008.08.005.
Fekedulegn, D., Mac Siurtain, M. P., & Colbert, J. J. (1999). Parameter estimation of nonlinear growth models in forestry. Silva Fennica, 33(4), 327–336. doi:10.14214/sf.653.
France, J., Dijkstra, J., & Dhanoa, M. S. (1996). Growth functions and their application in animal science. Annals De Zootechnie, 45(1), 165–174 doi: 10.105/animres:19960637.
Hajhamad, L., & Almasri, M. N. (2009). Assessment of nitrate cosntamination of groundwater using lumped-parameter models. Environmental Modelling and Software, 24(9), 1073–1087. doi:10.1016/j.envsoft.2009.02.014.
Karkach, A. S. (2006). Trajectories and models of individual growth. Demographic Research, 15(12), 347–400. doi:10.4054/DemRes.2006.15.12.
Kebreab, E., Schulin-Zeuthen, M., Lopez, S., Soler, J., Dias, R. S., de Lange, C. F. M., & France, J. (2007). Comparative evaluation of mathematical functions to describe growth and efficiency of phosphorus utilization in growing pigs. Journal of Animal Science, 85(1), 2498–2507. doi:10.2527/jas.2006-738.
Khamis, A., Ismail, Z., Heron, K., & Mohammed, A. T. (2005). Nonlinear growth models for modelling oil palm yield growth. Journal of Mathematics and Statistics, 1(3), 225–233.
Koya, P. R., & Goshu, A. T. (2013). Generalized mathematical model for biological growths. Open Journal of Modelling and Simulation, 1, 42–53. doi:10.4236/ojmsi.2013.14008.
Kundu, M. C., & Mandal, B. (2009). Agricultural activities influence nitrate and fluoride contamination in drinking groundwater of an intensively cultivated district in India. Water, Air & Soil Pollution, 198(1–4), 243–252. doi:10.1007/s11270-008-9842-5.
Mao, X., Prommer, H., Barry, D. A., Langevin, C. D., Panteleit, B., & Li, L. (2006). Tree-dimensional model for multi-component reactive transport with variable density groundwater flow. Environmental Modelling and Software, 21(5), 615–628. doi:10.1016/j.envsoft.2004.11.008.
Mastrocicco, M., Colombani, N., Castaldelli, G., & Jovanovic, N. (2010). Monitoring and modeling nitrate persistence in a shallow aquifer. Water, Air & Soil Pollution, 217(1–4), 83–93. doi:10.1007/s11270-010-0569-8.
McLay, C. D. A., Dragten, R., Sparling, G., & Sevarajah, N. (2001). Predicting groundwater nitrate concentrations in a region of mixed agricultural land use: a comparison of three approaches. Environmental Pollution, 115(2), 191–204. doi:10.1016/S0269-7491(01)00111-7.
Motulsky, H. J., & Christopoulos, A. (2003). Fitting models to biological data using linear and nonlinear regression: a practical guide to curve fitting. USA: Oxford University Press.
Mousavi, S. F., & Amiri, M. J. (2012). Modelling nitrate concentration of groundwater using adaptive neural-based fuzzy inference system. Soil and Water Research, 7(2), 73–83.
Nemčić-Jurec, J., Konjačić, M., & Jazbec, A. (2013). Monitoring of nitrates in drinking water from agricultural and residential areas of Podravina and Prigorje (Croatia). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185(11), 9509–9520. doi:10.1007/s10661-013-3269-1.
Newbold, P., Carlson, W. L., & Thorne, B. (2003). Statistics for business and economics (Fifth ed.). New Jersey: Prentice Hall.
Rammig, A., Bebi, P., Bugmann, H., & Fahse, L. (2007). Adapting a growth equation to model tree regeneration in mountain forests. European Journal of Forest Research, 126(1), 49–57. doi:10.1007/s10342-005-0088-0.
Reddy, A. G. S., Kumar, K. N., Rao, D. S., Rao, S. S. (2009). Assessment of nitrate contamination due to groundwater pollution in north eastern part of Anantapur District,
Richards, F. J. (1959). A flexible growth function for empirical use. Journal of Experimental Botany, 10, 290–300. doi:10.1093/jxb/10.2.290.
Sedmak, R., & Scheer, L. (2012). Modelling of tree diameter growth using growth functions parameterised by least squares and Bayesian methods. Journal of Forest Science, 58(6), 245–252.
Smith, J. T., Bowes, M. J., & Clarke, R. T. (2010). Are groundwater nitrate concentrations reaching a turning point in some chalk aquifers? Science of the Total Environment, 408(20), 4722–4732. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.07.001.
Tompić, T., Dobša, J., Legen, S., Tompić, N., & Medić, H. (2011). Modeling the growth patterns of in-season and off-season Ross 308 broiler breeder flocks. Poultry Science, 90(12), 2879–2887. doi:10.3382/ps.2010-01301.
Tait, N. G., Daviso, R. M., & Leharne, D. N. (2008). Borehole optimization system (BOS)—a case study assessing options for abstraction of urban groundwater in Nottingham, UK. Environmental Modelling and Software, 23(5), 611–621. doi:10.1016/j.envsoft.2007.09.001.
Urumović, K. (1991). O kvartnom vodonosnom kompleksu na području Varaždina. Zagreb: Geološki vjesnik, 24.
Urumović, K. (1991). Hidrogeološki uvjeti Varaždinskog vodonosnika. Zagreb: Geološki vjesnik, 43.
Winsor, C. P. (1932). The Gompertz curve as a growth curve. Proceedings of National Academy Science, 18(1), 1–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.18.1.1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dobša, J., Kovač, I. Nonlinear Growth Models for Modelling Time Series of Groundwater Nitrate Concentrations. Environ Model Assess 23, 175–184 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10666-017-9565-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10666-017-9565-3