Abstract
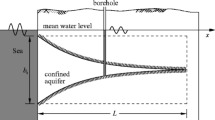
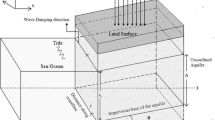
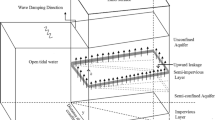
The groundwater response to tidal forcing is described by Laplace’s equation for the hydraulic head subject to appropriate boundary conditions. A previous solution to this problem based on long-wave and shallow-aquifer approximations is extended to higher-order and a general solution scheme, automated in Mathematica, is described. The solution can, in principle, be extended to arbitrary order, but is restricted to a detailed study of the properties of the solution when truncated to sixth-order. These results show that the mean water table height increases throughout the aquifer to a steady inland height elevated above mean sea level. The phase shift of the fluctuations and the asymmetry of the pore drainage process are investigated using Fourier analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Philip J (1973) Periodic nonlinear diffusion: an integral relation and its physical consequences. Aust J Phys 26: 513–519
Nielsen P (1990) Tidal dynamics of the water table in beaches. Water Resour Res 26(9): 2127–2134
Austin MJ, Masselink G (2006) Swash-groundwater interaction on a steep gravel beach. Cont Shelf Res 26: 2503–2519. doi:10.1016/j.csr.2006.07.031
Cartwright N, Li L, Nielsen P (2004) Response of the salt-freshwater interface in a coastal aquifer to a wave-induced groundwater pulse: field observations and modelling. Adv Water Resour 27: 297–303. doi:10.1016/j.advwatres.2003.12.005
Horn DP (2006) Measurements and modelling of beach groundwater flow in the swash-zone: a review. Cont Shelf Res 26: 622–652. doi:10.1016/j.csr.2006.02.001
Li L, Barry DA, Parlange J, Pattiaratchi CB (1997) Beach water table fluctuations due to wave run-up: capillarity effects. Water Resour Res 33: 925–945
Li L, Barry D, Cunningham C, Stagnitii F, Parlange J-Y (2000) A two-dimensional analytical solution of groundwater responses to tidal loading in an estuary and ocean. Adv Water Resour 23: 825–833. doi:10.1016/S0309-1708(00)00016-6
Li L, Dong P, Barry DA (2002) Tide-induced water table fluctuations in coastal aquifers bounded by rhythmic shorelines. J Hydraul Eng 128(10): 925–933
Trefry MG, Svensson TJA, Davis GB (2007) Hypoaigic influences on groundwater flux to a seasonally saline river. J Hydrol 335: 330–353
Ataie-Ashtiani B, Volker RE, Lockington DA (1999) Tidal effects on sea water intrusion in unconfined aquifers. J Hydrol 216: 17–31. doi:10.1016/S0022-1694(98)00275-3
Protano G, Riccobono F, Sabatini G (2000) Does salt water intrustion constitute a mercury contamination risk for coastal fresh water aquifers?. Environ Pollut 110: 451–458
Smiles DE, Stokes AN (1976) Periodic solutions of a nonlinear diffusion equation used in groundwater flow theory: examination using a Hele-Shaw model. J Hydrol 31: 27–35
Knight JH (1981) Steady periodic flow through a rectangular dam. Water Resour Res 17(4): 1222–1224
Glover RE (1959) The pattern of fresh-water flow in a coastal aquifer. J Geophys Res 64: 457–459
Robinson C, Li L, Barry D (2007) Effect of tidal forcing on a subterranean estuary. Adv Water Resour 30(4): 851–865. doi:10.1016/j.advwatres.2006.07.006
Westbrook SJ, Rayner JL, Davis GB, Clement TP, Bjerg PL, Fisher SJ (2005) Interaction between shallow groundwater, saline surface water and contaminant discharge at a seasonally and tidally forced estuarine boundary. J Hydrol 302: 255–269. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2004.07.007
International Symposium on Water Resources and the Urban Environment, Review of analytical studies of tidal groundwater flow in coastal aquifer systems
Artiles W, Kraenkel RA (2007) An exact equation for the free surface of a fluid in a porous medium. SIAM J Appl Math 67(3): 619–629. doi:10.1137/050644835
Lanyon J, Eliot E, Clarke D (1982) Groundwater level variation during semidiurnal spring tidal cycles on a sandy beach. Aust J Mar Freshw Res 33: 377–400
Li L, Barry DA, Stagnitti F, Parlange JY, Jeng DS (2000) Beach water table fluctuations due to spring-neap tides: moving boundary effects. Adv Water Resour 23: 817–824. doi:10.1016/S0309-1708(00)00017-8
Bear J (1972) Dynamics of fluids in porous media. American Elsevier Publishing Company Inc., New York
Ataie-Ashtiani B, Volker RE, Lockington DA (2001) Tidal effects on groundwater dynamics in unconfined aquifers. Hydrol Process 15: 655–669
Teo HT, Jeng DS, Seymour BR, Barry DA, Li L (2003) A new analytical solution for water table fluctuations in coastal aquifers with sloping beaches. Adv Water Resour 26: 1239–1247. doi:10.1016/j.advwatres.2003.08.004
Parlange J, Stagnitti F, Starr J, Braddock R (1984) Free-surface flow in porous media and periodic solution of the shallow-flow approximation. J Hydrol 70(1–4): 251–263. doi:10.1016/0022-1694(84)90125-2
Jeng D-S, Seymour B, Barry D, Li L, Parlange J-Y (2005) New approximation for free surface flow of groundwater: capillarity correction. Adv Water Resour 28: 1032–1039. doi:10.1016/j.advwatres.2004.05.012
Turner IL, Coates BP, Acworth RI (1996) The effects of tides and waves on water-table elevations in coastal zones. Hydrogeol J 4: 51–69. doi:10.1007/s100400050090
Mao X, Enot P, Barry D, Li L, Binley A, Jeng D (2006) Tidal influence on behaviour of a coastal aquifer adjacent to a low-relief estuary. J Hydrol 327(1–2): 110–127. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2005.11.030
Blyth MG, Vanden-Broeck JM (2008) Free-surface flow over a trapped bubble. IMA J Appl Math 73: 803–814
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roberts, M.E., Trefry, M.G., Fowkes, N. et al. Water-table response to tidal forcing at sloping beaches. J Eng Math 69, 291–311 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10665-010-9407-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10665-010-9407-7