Abstract
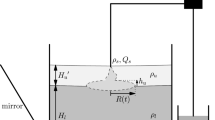
The upward flow of a buoyant plume emanating from a horizontal fissure into a two-layered fluid region is considered. Solutions are computed numerically for a range of fissure widths and water depths. It is shown that for a given fluid depth and fissure size there is a minimum flow rate beneath which no steady solutions exist. At this limiting flow, the fluid detaches from the wall of the fissure via a stagnation point. Solutions exist for all values of flow rate above this minimum. Exact solutions are presented for very large flow rates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Imberger J, Hamblin PF (1982) Dynamics of lakes, reservoirs and cooling ponds. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 14: 153–187
List EJ (1982) Turbulent jets and plumes. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 14: 189–212
Turner JS (2001) Buoyancy effects in fluids. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Schlichting H (1933) Laminare Strahlausbreitung. J Appl Math Mech (ZAMM) 13: 260–263
Savage SB, Chan GKC (1970) The buoyant two-dimensional laminar vertical jet. Q J Mech Appl Math 23(3): 413–430
Morton BR (1959) Forced plumes. J Fluid Mech 5: 151–163
Gangoiti G, Sancho J, Ibarra G, Alonso L, Garcia JA, Navazo M, Durana N, Ilardia JL (1997) Rise of moist plumes from tall stacks in turbulent and stratified atmospheres. Atmos Environ 31(2): 253–269
Janicke U, Janicke L (2001) A three-dimensional plume rise model for dry and wet plumes. Atmos Environ 35(5): 877–890
Morita M, Hirota M (1989) Numerical analysis and experiments of convective heat flow in fire compartment. Fire Sci Technol 9: 11–24
Yu-hong Z, Wen-xin H (2005) Numerical study on the stability and mixing of vertical round buoyant jet in shallow water. Appl Math Mech 26: 92–100
Hunt GR, Kaye NB (2005) Lazy plumes. J Fluid Mech 533: 329–338
Michaux G, Vauquelin O (2008) Solutions for turbulent buoyant plumes rising from circular sources. Phys Fluids 20: 066601 (6 pages)
Bishop SR, Holborn PG, Drysdale DD (1995) Experimental comparison with a compartment fire model. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 22: 235–240
Tuck EO, Goh KHM (1985) Thick waterfalls from horizontal slots. J Eng Maths 19: 341–349
Tuck EO (1987) Efflux from a slit in a vertical wall. J Fluid Mech 176: 253–264
Hocking GC (1992) Flow from a vertical slot into a layer of finite depth. Appl Math Model 16: 300–306
Tricomi FG (1957) Integral equations. Interscience, New York
Tuck EO (1980) Application and solution of Cauchy singular integral equations. In: Anderssen RS et al (eds) The application and numerical solution of integral equations. Sijthoff and Noordhoff, Alpen aan den Rijn, pp 21–50
Glauert H (1926) Aerofoil and airscrew theory. Cambridge University Press, New York
Vanden-Broeck J-M, Tuck EO (1994) Flow near the intersection of a free surface with a vertical wall. Siam J Appl Math 54: 1–13
Christodoulides P, Dias F (2009) Impact of a rising stream on a horizontal plate of finite extent. J Fluid Mech 621: 243–258
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hocking, G.C., Forbes, L.K. Steady flow of a buoyant plume into a constant-density layer. J Eng Math 67, 341–350 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10665-009-9324-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10665-009-9324-9