Abstract
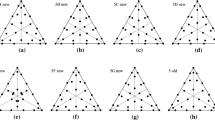
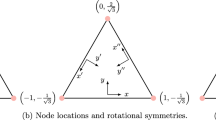
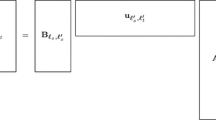
The cornerstone of nodal spectral-element methods is the co-location of the interpolation and integration points, yielding a diagonal mass matrix that is efficient for time-integration. On quadrilateral elements, Legendre–Gauss–Lobatto points are both good interpolation and integration points; on triangles, analogous points have not yet been found. In this paper, a promising set of points for the triangle that were only available for polynomial degree N ≤ 5 are used. However, the derivation of these points is generalized to obtain degree N ≤ 7 points, which are referred to as cubature points because their selection is based on their integration accuracy. The diagonal-mass-matrix (DMM) triangular-spectral-element (TSE) method based on these points can be used for any set of equations and any type of domain. Because these cubature points integrate up to order 2N along the element boundaries and yield a diagonal mass matrix, they allow the triangular spectral elements to compete with quadrilateral spectral elements in terms of both accuracy and efficiency, while offering more geometric flexibility in the choice of grids. It is shown how to implement this DMM TSE for a variety of applications involving elliptic and hyperbolic equations on different domains. The DMM TSE method yields comparable accuracy to the exact integration (non-DMM) TSE method, while being far more efficient for time-dependent problems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Patera AT (1984) A spectral element method for fluid dynamics—laminar flow in a channel expansion. J Comp Phys 54:468–488
Solin P, Segeth K, Dolezel I (2003) Higher-order finite element methods. Chapman and Hall/CRC Press
Sherwin SJ, Karniadakis GE (1995) A triangular spectral element method; applications to the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations. Comp Meth Appl Mech Eng 123:189–229
Hesthaven JS (1998) From electrostatics to almost optimal nodal sets for polynomial interpolation in a simplex. SIAM J Num Anal 35:655–676
Taylor MA, Wingate BA, Vincent RE (2000) An algorithm for computing Fekete points in the triangle. SIAM J Num Anal 38:1707–1720
Warburton T, Pavarino LF, Hesthaven JS (2000) A pseudo-spectral scheme for the incompressible Navier–Stokes equations using unstructured nodal elements. J Comp Phys 164:1–21
Giraldo FX, Warburton T (2005) A nodal triangle-based spectral element method for the shallow water equations on the sphere. J Comp Phys 207:129–150
Cohen G, Joly P, Roberts JE, Tordjman N (2001) Higher order triangular finite elements with mass lumping for the wave equation. SIAM J Num Anal 38:2047–2078
Taylor MA, Wingate BA (2000) A generalized diagonal mass matrix spectral element method for non-quadrilateral elements. Appl Num Math 33:259–265
Helenbrook B (2004) Polynomial bases suitable for mass lumping on triangles. Int Conf Spectral and High-Order Methods (ICOSAHOM).
Cohen G, Joly P, Tordjman N (1995). Higher order triangular finite elements with mass lumping for the wave equation. In: Cohen G, Becahe E, Joly P, Roberts JE (eds). Proc. 3rd Int. Conf. on Mathematical and Numerical Aspects of Wave Propagation. SIAM, Philadelphia
Mulder WA (2001) Higher-order mass-lumped finite elements for the wave equation. J Comp Acoust 9:671–680
Komatitsch D, Martin R, Tromp J, Taylor MA, Wingate BA (2001) Wave propagation in 2-D elastic media using a spectral element method with triangles and quadrangles. J. Comp. Acoustics 9:703–718
Cools R, Rabinowitz P (1993) Monomial cubature rules since Stroud: a compilation. J Comp and Appl Math 48:309–326
Lyness J, Cools R (1994) A survey of numerical cubature over triangles. Appl Math 48:127–150
Cools R (1997) Constructing cubature formulae: the science behind the art. Acta Numerica 6:1–54
Cools R (1999) Monomial cubature rules since Stroud: a compilation—part 2. J Comp Appl Math 112:21–27
Cools R (2003) An encyclopaedia of cubature formulas. J Complexity 19:445–453. Online database located at http://www.cs.kuleuven.ac.be/~nines/research/ecf/ecf.html
Lyness J, Jespersen D (1975) Moderate degree symmetric quadrature rules for the triangle. J Inst Math Appl 15:19–32
Wandzura S, Xiao H (2003) Symmetric quadrature rules on a triangle. Comp Math Appl 45:1829–1840
Taylor MA, Wingate BA, Bos LP (2006) A cardinal function algorithm for computing multivariate quadrature points. SIAM J Num Anal (to appear)
Proriol J (1957) Sur une famille de polynomes á deux variables orthogonaux dans un triangle. C R Acad Sci Paris 257:2459
Dubiner M (1991) Spectral methods on triangles and other domains. J Scientific Comp 6:345–390
Karniadakis GE, Sherwin SJ (1999) Spectral/hp element methods for CFD, Oxford Univ Press
Taylor M, Tribbia J, Iskandarani M (1997) The spectral element method for the shallow water equations on the sphere. J Comp Phys 130:92–108
Boyd J (1996). The erfc-log filter and the asymptotics of the Euler and Vandeven sequence accelerations. In: Ilin AV, Scottv LR (eds). Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Spectral and High Order Methods. Houston Journal of Mathematics, Houston Texas, 267–276
Maday Y, Patera AT (1987). Spectral element methods for the incompressible Navier Stokes equations. In: Noor AK, Oden JT, (eds). state of the art surveys on computational mechanics. ASME, New York, 71–143
Williamson DL, Drake JB, Hack JJ, Jakob R, Swarztrauber PN (1992) A standard test set for numerical approximations to the shallow water equations in spherical geometry. J Comp Phys 102:211–224
Karniadakis GE, Israeli M, Orszag SA (1991) High-order splitting methods for the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations. J Comp Phys 97:414–443
Giraldo FX (2005) Semi-implicit time-integrators for a scalable spectral element atmospheric model. Quart J Roy Meteorol Soci 131:2431–2454
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giraldo, F.X., Taylor, M.A. A diagonal-mass-matrix triangular-spectral-element method based on cubature points. J Eng Math 56, 307–322 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10665-006-9085-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10665-006-9085-7