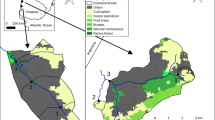
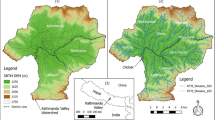
Abstract
The world’s urban population is growing rapidly, and threatening natural ecosystems, especially streams. Urbanization leads to stream alterations, increased peak flow frequencies, and reduced water quality due to pollutants, morphological changes, and biodiversity loss, known as the urban stream syndrome. However, a shift towards recognizing urban streams as valuable natural systems is occurring, emphasizing green infrastructure and nature-based solutions. This study in Uruguay examined water quality in various watersheds with different urbanization levels and socio-environmental characteristics along a precipitation gradient. Using Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and in situ data, we assessed physicochemical parameters, generated territorial variables, and identified key predictors of water quality. We found that urbanization, particularly urban areas, paved areas, and populations without sanitation, significantly influenced water quality parameters. These factors explained over 50% of the variation in water quality indicators. However, the relationship between urbanization and water quality was non-linear, with abrupt declines after specific urban intensity thresholds. Our results illustrate that ensuring sanitation networks and managing green areas effectively are essential for preserving urban stream water quality. This research underscores the importance of interdisciplinary teams and localized data for informed freshwater resource management.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study will be available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Adam, D. (2021). How far will global population rise? Researchers can't agree. Nature, 597, 462–465. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-021-02522-6
Alvareda, E., Lucas, C., Paradiso, M., Piperno, A., Gamazo, P., Erasun, V., Russo, P., Saracho, A., Banega, R., Sapriza, G., & Teixeira de Mello, F. (2020). Water quality evaluation of two urban streams in Northwest Uruguay: Are national regulations for urban stream quality sufficient? Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 192, 661. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08614-6
APHA. (1995). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (19th ed.). New York: American Public Health Association Inc.
APHA. (2017). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (p. 2017). American Public HealthAssociation.
Archer, E. (2013). Estimate permutation p-values for importance metrics. R package version 1.5.2.
Barrios, M., & Teixeira de Mello, F. (2022). Urbanization impacts water quality and the use of microhabitats by fish in subtropical agricultural streams. Environmental Conservation, 49(3), 155–163. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0376892922000200
Benedict, M. A., & McMahon, E. T. (2002). Green infrastructure: Smart conservation for the 21st century. Renewable Resources Journal, 20(3), 12–17.
Benejam, L., Teixeira-de Mello, F., Meerhoff, M., Loureiro, M., Jeppesen, E., & Brucet, S. (2016). Assessing effects of change in land use on size-related variables of fish in subtropical streams. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 73(4), 547–556. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjfas-2015-0025
Bernhard, A. (2010). The nitrogen cycle: Processes, players, and human. Nature Education Knowledge, 2(2), 12.
Booth, D. B., Roy, A. H., Smith, B., & Capps, K. A. (2016). Global perspectives on the urban stream syndrome. Freshwater Science, 35(1), 412–420. https://doi.org/10.1086/684940
Brena, A., Roche, I., & Sommaruga, R. (1999). Montevideo: Correlación entre Densidades y Morfología. ITU, Facultad de Arquitectura de la UDELAR. Estudio Ideograma.
Byrnes, J. E., Gamfeldt, L., Isbell, F., Lefcheck, J. S., Griffin, J. N., Hector, A., Cardinale, B. J., Hooper, D. U., Dee, L. E., & Emmett Duffy, J. (2014). Investigating the relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem multifunctionality: Challenges and solutions. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 5(2), 111–124. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.12143
Capps, K. A., Bentsen, C. N., & Ramírez, A. (2016). Poverty, urbanization, and environmental degradation: Urban streams in the developing world. Freshwater Science, 35(1), 429–435. https://doi.org/10.1086/684945
de Medeiros, G. A., de Lima Tresmondi, A. C. C., de Queiroz, B. P. V., Fengler, F. H., Rosa, A. H., Fialho, J. M., Lopes, R. S., Negro, C. V., dos Santos, L. F., & Ribeiro, A. I. (2017). Water quality, pollutant loads, and multivariate analysis of the effects of sewage discharges into urban streams of Southeast Brazil. Energy, Ecology and Environment, 2, 259–276. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40974-017-0062-y
DINAGUA (2022), Atlas Nacional de Inundaciones y Drenaje Urbano.
Elmore, A. J., & Kaushal, S. S. (2008). Disappearing headwaters: Patterns of stream burial due to urbanization. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 6, 308–312. https://doi.org/10.1890/070101
Fortmann-Roe, S. (2015). Consistent and clear reporting of results from diverse modeling techniques: The A3 method. Journal of Statistical Software, 66(7), 1–23 http://www.jstatsoft.org/v66/i07/
Frantzeskaki, N. (2019). Seven lessons for planning nature-based solutions in cities. Environmental Science & Policy, 93, 101–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsci.2018.12.033
Gao, M., Chen, B., Xu, Y., & Li, D. (2023). Heterogeneous impacts of global land urbanization on land-use structure from economic and technological perspectives. Ecological Indicators, 147, 109955. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.109955
Gay, E. T., Martin, K. L., Caldwell, P. V., Emanuel, R. E., Sanchez, G. M., & Suttles, K. M. (2023). Riparian buffers increase future baseflow and reduce peakflows in a developing watershed. Science of The Total Environment, 862, 160834. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.160834
Grimm, N. B., Faeth, S. H., Golubiewski, N. E., Redman, C. L., Wu, J., Bai, X., & Briggs, J. M. (2008). Global change and the ecology of cities. Science, 319, 756–760. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1150195
House, M. A., Ellis, J. B., Herricks, E. E., Hvitved-Jacobsen, T., Seager, J., Lijklema, L., Aaldeink, H., & Clifforde, I. T. (1993). Urban drainage-impacts on receiving water quality. Water Science and Technology, 27(12), 117.
IDEUY, 2018. Infraestructura de datos espaciales de Uruguay, consulted in 2023 in https://visualizador.ide.uy/ideuy/core/load_public_project/ideuy/. Accessed July 2023.
INE. (2011). Instituto Nacional de Estadística. Resultados del Censo de Población 2011: población, crecimiento y estructura por sexo y edad. https://www.gub.uy/instituto-nacional-estadistica/datos-y-estadisticas/estadisticas/censo-2011. Accessed July 2023.
Johnson, R. C., Jin, H. S., Carreiro, M. M., & Jack, J. D. (2013). Macroinvertebrate community structure, secondary production and trophic-level dynamics in urban streams affected by non-point-source pollution. Freshwater Biology, 58(5), 843–857. https://doi.org/10.1111/fwb.12090
Kantamaneni, K., Li, Q., Wu, H., Zhu, M., Apostolopoulou, A., Xu, W., Kenawy, I., Rajendran, L. P., Rice, L., Jimenez-Bescos, C., Panneer, S., & Pushparaj, R. R. B. (2023). Towards a combined physical and social evaluation of climate vulnerability in coastal urban megacities. Water, 15(4), 712. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15040712
Koroleff, F. (1970). Direct determination of ammonia in natural waters as indophenol blue. In Information on techniques and methods for seawater analysis (pp. 19–22).
Kottek, M., Grieser, J., Beck, C., Rudolf, B., & Rubel, F. (2006). World map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification updated. Meteorologische Zeitschrift, 15(3), 259–263. https://doi.org/10.1127/0941-2948/2006/0130
Lammers, R. W., Dell, T. A., & Bledsoe, B. P. (2020). Integrating stormwater management and stream restoration strategies for greater water quality benefits. Journal of Environmental Quality, 49, 569–581. https://doi.org/10.1002/jeq2.20047
Lane, C. R., Creed, I. F., Golden, H. E., Leibowitz, S. G., Mushet, D. M., Rains, M. C., Wu, Q., D’Amico, E., Alexander, L. C., Ali, G. A., Basu, N. B., Bennett, M. G., Christensen, J. R., Cohen, M. J., Covino, T. P., DeVries, B., Hill, R. A., Jencso, K., Lang, M. W., et al. (2023). Vulnerable waters are essential to watershed resilience. Ecosystems, 26(1), 1–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-021-00737-2
Ledford, S. H., & Lautz, L. K. (2015). Floodplain connection buffers seasonal changes in urban stream water quality. Hydrological Processes, 29(6), 1002–1016. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.10210
Li, G., Fang, C., Li, Y., Wang, Z., Sun, S., He, S., Qi, W., Bao, C., Ma, H., Fan, Y., Feng, Y., & Liu, X. (2022). Global impacts of future urban expansion on terrestrial vertebrate diversity. Nature Communications, 13(1), 1628. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-29324-2
Liaw, A., & Wiener, M. (2002). Classification and regression by randomForest. R News, 2(3), 18–22 https://CRAN.R-project.org/doc/Rnews/
Lucas, C., Aguilera-Betti, I., Muñoz, A. A., Puchi, P., Sapriza, G., Profumo, L., Maxwell, R. S., & Venegas-González, A. (2022). Cross-continental hydroclimate proxies: Tree-rings in Central Chile reconstruct historical streamflow in Southeastern South American rivers. Progress in Physical Geography: Earth and Environment, 46(3), 458–480. https://doi.org/10.1177/03091333211067466
Marques, P., & Cunico, A. (2023). Integrating the influence of untreated sewage into our understanding of the urban stream syndrome. Freshwater Science, 42(2), 195–203. https://doi.org/10.1086/724823
Marshall, S., Pettigrove, V., Carew, M., & Hoffmann, A. (2010). Isolating the impact of sediment toxicity in urban streams. Environmental Pollution, 158(5), 1716–1725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2009.11.019
Martins, R. T., Couceiro, S. R., Melo, A. S., Moreira, M. P., & Hamada, N. (2017). Effects of urbanization on stream benthic invertebrate communities in Central Amazon. Ecological Indicators, 73, 480–491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.10.013
McMichael, A. J. (2000). The urban environment and health in a world of increasing globalization: Issues for developing countries. Bulletin of the World Health Organization, 78, 1117–1126.
Meyer, J. L., Paul, M. J., & Taulbee, W. K. (2005). Stream ecosystem function in urbanizing landscapes. Journal of the North American Benthological Society, 24(3), 602–612. https://doi.org/10.1899/04-021.1
Moi, D. A., & Teixeira de Mello, F. (2022). Cascading impacts of urbanization on multitrophic richness and biomass stock in neotropical streams. Science of The Total Environment, 806, 151398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151398
Moran, S., Perreault, M., & Smardon, R. (2019). Finding our way: A case study of urban waterway restoration and participatory process. Landscape and Urban Planning, 191, 102982. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2016.08.004
Müller, R., & Wiedemann, F. (1955). Die Bestimmung des Nitrats in Wasser. Jahrbuch fur Wasserchem und Wasserreinigungstech Verlag Chemie, 12, 247–271.
Murphey, J., & Riley, J. P. (1962). Phosphorus analysis procedure. Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2, 413–426.
MVOT (2018). Ministerio de Vivienda y Ordenamiento Territorial. Informal settlements, area obtained from the Neighborhood Improvement Program, spatial data of Irregular Settlements 2018, consulted in 2023 in https://sit.mvotma.gub.uy/js/chs/. Accessed July 2023.
OSE. (2018). Obras Sanitarias del Estado, consulted in 2023 in https://gisdev.ose.com.uy/visor. Accessed July 2023.
Parkinson, J., Tayler, K., & Mark, O. (2007). Planning and design of urban drainage systems in informal settlements in developing countries. Urban Water Journal, 4(3), 137–149. https://doi.org/10.1080/15730620701464224
Parr, T. B., Smucker, N. J., Bentsen, C. N., & Neale, M. W. (2016). Potential roles of past, present, and future urbanization characteristics in producing varied stream responses. Freshwater Science, 35(1), 436–443. https://doi.org/10.1086/685030
Paul, J. P., & Meyer, J. L. (2001). Streams in the urban landscape. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 32, 333–365. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.32.081501.114040
R Development Core Team. (2020). R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing.
Rieck, L. O., & Sullivan, S. (2022). Ecological impacts of altered stream hydrogeomorphic characteristics extend beyond the channel boundary: Evidence from urban streams of Columbus, OH, United States. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 10, 817289. https://doi.org/10.3389/fevo.2022.817289
Rockström, J., Steffen, W., Noone, K., Persson, Å., Chapin, F. S., Lambin, E. F., Lenton, T. M., Scheffer, M., Folke, C., Schellnhuber, H. J., Nykvist, B., de Wit, C. A., Hughes, T., van der Leeuw, S., Rodhe, H., Sörlin, S., Snyder, P. K., Costanza, R., Svedin, U., et al. (2009). A safe operating space for humanity. Nature, 461(7263), 472–475. https://doi.org/10.1038/461472a
Scoggins, M., Booth, D. B., Fletcher, T., Fork, M., Gonzalez, A., Hale, R. L., Hawley, R. J., Roy, A. H., Bilger, E. E., Bond, N., Burns, M. J., Hopkins, K. G., Macneale, K. H., Martí, E., McKay, S. K., Neale, M. L., Paul, M. J., Rios-Touma, B., Russell, K. L., et al. (2022). Community-powered urban stream restoration: A vision for sustainable and resilient urban ecosystems. Freshwater Science, 41(3), 404–419. https://doi.org/10.1086/721150
Suárez, B., Barrios, M., & Teixeira de Mello, F. (2022). Macroinvertebrates’ response to different land use in lowland streams from Uruguay: Use of artificial substrates for biomonitoring. Neotropical Biodiversity, 8(1), 136–146. https://doi.org/10.1080/23766808.2022.2049178
Tesitore, G., & Teixeira de Mello, F. (2023). A humped pattern of standing fish biomass in lowland subtropical streams as a response to a gradient of environmental degradation, species richness and season. Hydrobiologia, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-023-05255-x
Torremorell, A., Hegoburu, C., Brandimarte, A. L., Rodrigues, E. H. C., Pompeo, M., da Silva, S. C., Moschini-Carlos, V., Caputo, L., Fierro, P., Mojica, J. I., Matta, A. L. P., Donato, J. C., Jiménez-Pardo, P., Molinero, J., Ríos-Touma, B., Goyenola, G., Iglesias, C., López-Rodríguez, A., Meerhoff, M., et al. (2021). Current and future threats for ecological quality management of South American freshwater ecosystems. Inland Waters, 11(2), 125–140. https://doi.org/10.1080/20442041.2019.1608115
Ungerovich, M., Barreiro, M., & Masoller, C. (2021). Influence of Madden–Julian Oscillation on extreme rainfall events in Spring in southern Uruguay. International Journal of Climatology, 41(5), 3339–3351. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.7022
United Nations, 2018. World urbanization prospects. The 2018 revision. Highlights. Available online at: https://population.un.org/wup/Publications/. Accessed 16 Sept 2023.
Valderrama, J. C. (1981). The simultaneous analysis of total nitrogen and total phosphorus in natural waters. Marine Chemistry, 10(2), 109–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-4203(81)90027-X
Varuolo-Clarke, A. M., Williams, A. P., Smerdon, J. E., Ting, M., & Bishop, D. A. (2022). Influence of the South American low-level jet on the austral summer precipitation trend in Southeastern South America. Geophysical Research Letters, 49(9), e2021GL096409. https://doi.org/10.1029/2021GL096409
Vidal, C., Lozoya, J. P., Tesitore, G., Goyenola, G., & Teixeira de Mello, F. (2021). Incidence of watershed land use on the consumption of meso and microplastics by fish communities in uruguayan lowland streams. Water, 13(11), 1575. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13111575
Vidal, N., Loureiro, M., Hued, A. C., Eguren, G., & Teixeira de Mello, F. (2018). Female masculinization and reproductive success in Cnesterodon decemmaculatus (Jenyns, 1842) (Cyprinodontiforme: Poeciliidae) under anthropogenic impact. Ecotoxicology, 27, 1331–1340. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-018-1985-6
Walsh, C. J. (2000). Urban impacts on the ecology of receiving waters: A framework for assessment, conservation and restoration. Hydrobiologia, 431(2-3), 107–114. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004029715627
Walsh, C. J., Fletcher, T. D., Bos, D. G., & Imberger, S. J. (2015). Restoring a stream through retention of urban stormwater runoff: A catchment-scale experiment in a social–ecological system. Freshwater Science, 34(3), 1161–1168. https://doi.org/10.1086/682422
Walsh, C. J., Fletcher, T. D., & Ladson, A. R. (2005). Stream restoration in urban catchments through re-designing stormwater systems: Looking to the catchment to save the stream. Journal of the North American Benthological Society, 24, 690–705. https://doi.org/10.1899/04-020.1
Wei, C.-L., Rowe, G. T., Escobar-Briones, E., Boetius, A., Soltwedel, T., Caley, M. J., Soliman, Y., Huettmann, F., Qu, F., Yu, Z., Pitcher, C. R., Haedrich, R. L., Wicksten, M. K., Rex, M. A., Baguley, J. G., Sharma, J., Danovaro, R., MacDonald, I. R., Nunnally, C. C., et al. (2010). Global patterns and predictions of seafloor biomass using Random Forests. PLoS One, 5, e15323. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0015323
Wiederkehr, F., Wilkinson, C. L., Zeng, Y., Yeo, D. C., Ewers, R. M., & O'Gorman, E. J. (2020). Urbanisation affects ecosystem functioning more than structure in tropical streams. Biological Conservation, 249, 108634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2020.108634
Wong, C. H., Barton, G. W., & Barford, J. P. (2003). The nitrogen cycle and its application in wastewater treatment. The Handbook of Water and Wastewater Microbiology (ed. D. Mara, N. Horan), 427-440.
Acknowledgements
This work was carried out by our working group belonging to the Núcleo Interdisciplinario Agua y Ciudad. We thank Sofía Rameau, Nicolás Rezzano, Matías Santa Cruz for their help in sampling, as well as Claudia Fosalba for the water nutrient analysis from the Department of Ecology and Environmental Management, Universidad de la República, CURE.
Funding
This work was supported by the Universidad de la República—Espacio Interdisciplinario and Comisión Sectorial de Investigación Cientifica (CSIC). FTM, EA, and CL also were supported by PEDECIBA and SNI.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Franco Teixeira de Mello: funding acquisition, conceptualization, investigation, methodology, writing—original draft, data curation, formal analysis, visualization, writing—review and editing. Pablo Sierra: funding acquisition, conceptualization, investigation, methodology, writing —original draft, data curation, visualization, writing—review and editing. Dieison A. Moi: formal analysis, visualization, writing—review and editing. Jimena Alonso, Christine Lucas, Elena Alvareda, María Soledad Andrade, Lucía Urtado: investigation, methodology, visualization, writing—review and editing. Jimena Alvarez, Lucía Arimon, Bárbara Suárez: investigation, methodology, data curation, visualization, writing—review and editing. Adriana Piperno: funding acquisition, conceptualization, investigation, methodology, writing—original draft, data curation, visualization, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Consent to participate
All authors consent to participate in this research.
Consent for publication
All authors consent to publish this research.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Teixeira de Mello, F., Sierra, P., Moi, D.A. et al. Effects of urbanization and accessibility to sanitation services on water quality in urban streams in Uruguay. Environ Monit Assess 196, 185 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-024-12365-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-024-12365-z