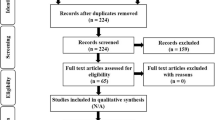
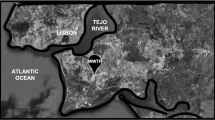
Abstract
The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of possible endocrine disruptors in surface and wastewater using a cell proliferation assay in an estrogen-responsive cell line (MCF-7). This study was conducted in the Sinos River (Brazil). The residual water was collected from a Pilot Treatment Plant (using Typha domingensis) and surface waters of the Luis Rau stream, the Sinos River, and the Water Treatment Station (WTS). After exposures (24–120 h), a Sulforhodamine B assay was performed to determine the proliferation rate. The higher increase in proliferation rate was observed with the Luiz Rau stream and the sewage treated by macrophytes in a flotation filter. The results from WTS water remained with a proliferation rate similar to the negative control at all times, suggesting that the conventional treatment is partially effective for the withdrawal of endocrine-disrupting agents. The study demonstrated the efficiency of the MCF-7 line in assessing endocrine disruption caused by wastewater and surface water samples. Our results indicate that conventional water treatment can partially remove the polluting load of endocrine disruptors, minimizing their environmental and public health impacts. Besides, it demonstrates the need to expand sanitary services to improve the population’s quality of life.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Almazrouei, B., Islayem, D., Alskafi, F., Catacutan, M. K., Amna, R., Nasrat, S., Sizirici, B., & Yildiz, I. (2023). Steroid hormones in wastewater: Sources, treatments, environmental risks, and regulations. Emerging Contaminants, 9(2), 100210.
APHA. (2005). Standard methods of water and wastewater (21st ed., pp. 2–61). Washington, DC.: American Public Health Association.
Argolo, A. S., Gomes, G., & Bila, D. M. (2023). (Anti)estrogenic activity impacted by complex environmental matrices: A DOM and multiphase distribution approach. Chemosphere, 310, 136917.
Bergmann, A. J., Simon, E., Schifferli, A., Schönborn, A., & Vermeirssen, E. L. M. (2020). Estrogenic activity of food contact materials—evaluation of 20 chemicals using a yeast estrogen screen on HPTLC or 96-well plates. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 412, 4527–4536.
Bernardelli, J. K. B., Liz, M. V., Belli, T. J., Lobo-Recio, M. A., Lapolli, F. R. (2015). Removal of estrogens by activated sludge under different conditions using batch experiments. Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 32, 421–432.
Bianchi, E., Lessing, G., Brina, K. R., Angeli, L., Andriguetti, N. B., Peruzzo, J. R. S., Nascimento, C. A., Spilki, F. R., Ziulkosi, A. L., & Silva, L. B. (2017). Monitoring the genotoxic and cytotoxic potential and the presence of pesticides and hydrocarbons in water of the Sinos River Basin, Southern Brazil. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 72, 321–334.
Cho, H., Ryu, C. S., Lee, S., Adeli, Z., Meupea, B., Kim, Y., Kim, Y. J. (2022). Endocrine-disrupting potential and toxicological effect of para-phenylphenol on Daphnia magna. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 243, 113965.
Coello-Garcia, T., Curtis, T. P., Mrozik, W., & Davenport, R. J. (2019). Enhanced estrogen removal in activated sludge processes through the optimization of the hydraulic flow pattern. Water Research, 164, 114905.
Conselho Estadual do Meio Ambiente–CONSEMA. (2006). Conselho Estudal. Estado do Rio Grande do Sul. Secretaria do Meio Ambiente, Resolução Conseman, n. 128.
El-Bassyouni, G., Eldera, S. S., Kenawy, S. H., & Hamzawy, E. M. A. (2020). Hydroxyapatite nanoparticles derived from mussel shells for in vitro cytotoxicity test and cell viability. Heliyon, 6(6), e04085.
Etteieb, S., Kawachi, A., Han, J., Tarhouni, J., Isoda, H. (2015). Bioanalytical tests for assessing cytotoxicity and estrogenicity effects of treated wastewater on mammalian cell lines. Energy Procedia, 74, 874–885.
Ferraz, M., Bauer, A. L., Valiati, V. H., & Schulz, U. H. (2020). Microplastic concentrations in raw and drinking water in the Sinos River. Southern Brazil. Water, 12(11), 3115.
Furtado, C. M., & von Mühlen, C. (2015). Endocrine disruptors in water filters used in the Rio dos Sinos Basin region, Southern Brazil. Brazilian Journal of Biology, 75, 85–90.
Giulivo, M., Alda, M. L., Capri, E., & Barceló, D. (2016). Human exposure to endocrine disrupting compounds: Their role in reproductive systems, metabolic syndrome and breast cancer. A Review. Environmental Research, 151, 251–264.
Goldoni, A., Golfeto, C., Teixeira, J. B., Blumm, G., Wihelm, C. M., Telöken, F., Bianchi, E., Schmitt, J. L., Gehlen, G., Rodrigues, M. A. S., & Silva, L. B. (2014). Cytotoxic and genotoxic evaluation and chemical characterization of sewage treated using activated sludge and a floating emergent-macrophyte filter in a municipal wastewater treatment plant: A case study in Southern Brazil. Environmental Earth Sciences, 72, 1503–1509.
Gomes, G., Argolo, A. S., Felix, L. C., & Bila, D. M. (2023). Interferences in the yeast estrogen screen (YES) assay for evaluation of estrogenicity in environmental samples, chemical mixtures, and individual substances. Toxicology in Vitro, 88, 105551.
Hu, C., Bai, Y., Li, J., Sun, B., & Chen, L. (2023). Endocrine disruption and reproductive impairment of methylparaben in adult zebrafish. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 171, 113545.
Ismanto, A., Hadibarata, T., Kristanti, R. A., Maslukah, L., Safinatunnajah, N., & Kusumastuti, W. (2022). Endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) in environmental matrices: Occurrence, fate, health impact, physio-chemical and bioremediation technology. Environmental Pollution, 302, 119061.
Kabir, E. R., Rahman, M. S., & Rahman, I. (2015). A review on endocrine disruptors and their possible impacts on human health. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 40(1), 241–258.
Körner, W., Spengler, P., Bolz, U., Schuller, W., Hanf, V., & Metzger, J. W. (2001). Substances with estrogenic activity in effluents of sewage treatment plants in southwestern Germany. 2. Biological Analysis. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 20, 2142–2151.
Lei, B., Peng, W., Li, W., Yu, Y., & Wang, Y. (2016). Diethylstilbestrol at environmental levels affects the development of early life stage and target gene expression in Japanese Medaka (Oryzias latipes). Ecotoxicology, 25, 563–573.
Leusch, F. D., Khan, S. J., Gagnon, M. M., Quayle, P. Trinh, T., Coleman, H., Rawson, C., Chapman, H. F., Blair, P., Nice, H., Reitsema, T. (2014). Assessment of wastewater and recycled water quality: a comparison of lines of evidence from in vitro, in vivo and chemical analyses. Water Research, 50, 420–431.
Lu, Y. S., Yang, S. L., Gou, C. L., Wang, X. L., Wen, X., He, X., Guo, X., Yu, J., & Qian, Y. (2022). Integrated metabolomics and transcriptomics analysis reveals new biomarkers and mechanistic insights on atrazine exposures in MCF-7 cells. Exotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 232, 113244.
Machado, A. B., Rodrigues, G. Z. P., Souza, F. G., Linden, R., Osorio, D. M. (2018). Environmental assessment of a stream located in Novo Hamburgo, RS. Geama, 4(2),31–35.
Matin, O., Scholze, M., Ermeler, S., McPhie, J., Bopp, S. K., Kienzler, A., Parissis, N., & Kortenkamp, A. (2021). Ten years of research on synergisms and antagonisms in chemical mixtures: A systematic review and quantitative reappraisal of mixture studies. Environment International, 146, 106206.
Metcalfe, C. D., Bayen, S., Desrosiers, M., Muñoz, G., Suavé, S., & Yargeau, V. (2022). An introduction to the sources, fate, occurrence and effects of endocrine disrupting chemicals released into the environment. Environmental Research, 207, 112658.
Mlynarcikova, A., Havranek, T., & Fickova, M. (2013). Effects of endocrine disruptors bisphenol A and di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate in a combination with 17β-estradiol on apoptosis-related genes in the MCF-7 breast cancer cell line. Toxicology Letters, 221, S106.
Morgan, M., Deoraj, A., Felty, Q., & Roy, D. (2017). Environmental estrogen-like endocrine disrupting chemicals and breast cancer. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, 457, 89–102.
Naime, R., & Garcia, A. C. (2005). Aplicação de enraizadas no tratamento de efluentes agroindustriais. Revista Tecnologia e Tendências, 1(2), 10–20.
Norman, M. A., Feng, W., Zhu, G., Hossain, M. B., Chen, Y., Zhang, H., & Sun, J. (2022). Bioaccumulation and potential human health risks of metals in commercially important fishes and shellfishes from Hangzhou Bay China. Scientific Reports, 12, 4634.
Orellana, E. A., & Kasinski, A. L. (2016). Sulforhodamine B (SRB) Assay in cell culture to investigate cell proliferation. Bio-protocol, 6(21), e1984.
Park, S. U., & Choi, J. (2007). Cytotoxicity, genotoxicity and ecotoxicity assay using human cell and environmental species for the screening of the risk from pollutant exposure. Environment International, 33(6), 817–822.
Pauwels, B., Korst, A. E. C., de Pooter, C. M. J., et al. (2003). Comparison of the sulforhodamine B assay and the clonogenic assay for in vitro chemoradiation studies. Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology, 51, 221–226.
Peteffi, G. P., Fleck, J. D., Kael, I. M., Rosa, D. C., Antunes, M. V., & Linden, R. (2018). Ecotoxicological risk assessment due to the presence of bisphenol A and caffeine in surface waters in the Sinos River Basin-Rio Grande do Sul-Brazil. Brazilian Journal of Biology, 79, 712–712.
Picinini, J., Oliveira, R. F., Garcia, A. L. H., DA Silva, G. N., Sebben, V. C., De Souza, G. M. S., Dias, J.F., Corrêa, D.S., Da Silva, J. (2022). In vitro genotoxic and mutagenic effects of water samples from Sapucaia and Esteio streams (Brazil) under the influence of different anthropogenic activities. Mutation Research/Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis, 878, 503484.
Rio Grande Do Sul. Resolução No 149, de 1 de julho de 2014. [Aprova o enquadramento das águas superficiais da Bacia Hidrográfica do Rio dos Sinos]. Diário Oficial [do] estado do Rio Grande do Sul, Poder Executivo, Porto Alegre, RS, ano 72, No 125, p 89, 7 de jul. 2014
Rodrigues, G. Z. P., Finkler, M., Garcia, A. L. H., & Gehlen, G. (2020). Evaluation of transgenerational effects caused by metals as environmental pollutants in Daphnia magna. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 192, 755.
Rodrigues, G. Z. P., Machado, A. B., Finkler, M., Berleze, D. B., & Gehlen, G. (2020). Environmental assessment of Luiz Rau stream (Brazil) utilizing Allium cepa test. Ciência e Natura, 42(e76), 1–15.
Rodrigues, G. Z. P., Staudt, L. B. M., Moreira, M. G., Santos, T. G., Souza, M. S., Lúcio, C. J., Panizzon, J., Kayser, A. L., Bonan, C. D., Oliveira, D. L., & Gehlen, G. (2020). Histopathological, genotoxic, and behavioral damages induced by manganese (II) in adult zebrafish. Chemosphere, 244, 125550.
Simões, L. A. R., Dalzochio, T., Goldoni, A., Souza, M. S., Rodrigues, G. Z. P., Petry, I. E., Gehlen, G., & Silva, L. B. (2019). Micronucleus test in fish for in situ evaluation of the Sinos River water quality, in Brazil. Ciência e Natura, 41, e38.
Skehan, P., Storeng, R., Scudiero, D., Monks, A., McMahon, J., Vistica, D., Warren, J. T., Bokesch, H., Kenney, S., & Boyd, M. R. (1990). New colorimetric cytotoxicity assay for anticancer-drug screening. Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 82(13), 1107–1112.
Tang, Y., Yin, M., Yang, W., Zhong, Y., Mo, L., Liang, Y., Ma, X., & Sun, X. (2019). Emerging pollutants in water environment: Occurrence, monitoring, fate, and risk assessment. Water Environment Research, 91(10), 984–991.
Tao, Y., Li, Z., Yang, Y., Jiao, Y., Qu, J., Wang, Y., & Zhang, Y. (2022). Effects of common environmental endocrine-disrupting chemicals on zebrafish behavior. Water Research, 208, 117826.
Trintinaglia, L., Bianchi, E., Silva, L. B., Nascimento, C. A., Spilki, F. R., & Ziulkoski, A. L. (2015). Cytotoxicity assays as tools to assess water quality in the Sinos river basin. Brazilian Journal of Biology, 75(2), S75–S80.
Vajrabhaya, L. O., & Korsuwannawong, S. (2018). Cytotoxicity evaluation of a Thai herb using tetrazolium (MTT) and sulforhodamine B (SRB) assays. J Anal Sci Technol, 9, 15.
Vázquez-Tapia, I., Salazar-Martínez, T., Acosta-Castro, M., Meléndez-Castolo, K.A., Mahlknecht, J., Cervantes-Avilés, P., Capparelli, M.V., Mora, A. (2022). Occurrence of emerging organic contaminants and endocrine disruptors in different water compartments in Mexico – a review. Chemosphere, 136285.
Viganó, L., Benfenati, E., Cauwenberge, A., Eidem, J. K., Erratico, C., Goksoyr, A., Maggioni, S., Kloas, W., Mandich, A., & Urbatzka, R. (2008). Estrogenicity profile and estrogenic compounds determined in river sediments by chemical analysis, ELISA and yeast assays. Chemosphere, 73, 1078–1089.
Villalobos, M., Olea, N., Brotons, J. A., Olea-Serrano, M. F., Ruiz de Almodovar, J. M., & Pedraza, V. (1995). The E-screen assay: a comparison of different MCF7 cell stocks. Environmental Health Perspectives, 103(9), 844–850.
Wang, S., Wang, Z., Wang, X., Qu, J., Li, F., Ji, C., & Wu, H. (2023). Histopathological and transcriptomic analyses reveal the reproductive endocrine-disrupting effects of decabromodiphenyl ethane (DBDPE) in mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Science of the Total Environment, 862, 160724.
Yang, G., Nowsheen, S., Aziz, K., & Georgakilas, A. G. (2013). Toxicity and adverse effects of Tamoxifen and other anti-estrogen drugs. Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 139(3), 392–404.
Zhang, H., Yang, X., Zhang, H., Li, X., Zhang, Z., Hou, L., Wang, Z., Niu, Q., & Wang, T. (2018). Neurotrophins and cholinergic enzyme regulated by calpain-2: New insights into neuronal apoptosis induced by polybrominated diphenyl ether-153. Toxicology Letters, 291, 29–38.
Funding
CAPES (Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel) and Feevale University. The study received financial support from CAPES (Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel) and CNPq (National Council for Scientific and Technological Development).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Marina Griebeler Moreira and Gabriela Zimmermann Prado Rodrigues participated in the study methodology, but also in the preparation and editing of the main text. Diego Araújo da Silva and Eloisa Bianchi assisted in all methodological processes. Günther Gehlen and Ana Luiz Ziulkoski conducted the entire study and participated in the final revision of the text.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All authors have read, understood, and complied as applicable with the statement on the “Ethical responsibilities of Authors” as found in the Instructions for Authors.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Moreira, M.G., Rodrigues, G.Z.P., da Silva, D.A. et al. Differences in MCF-7 response to endocrine disruptors in waste, superficial, and treated water from Southern Brazil. Environ Monit Assess 195, 1539 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-12109-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-12109-5