Abstract
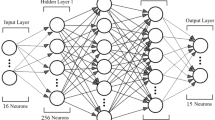
In some developing countries, particularly China, a significant number of individual farmers manage small field scale of cultivated land. However, the existing research on cultivated land quality assessment mainly focuses on large-scale regions, establishing comprehensive index systems from a macro perspective, while lacking evaluations customized to individual farmers, who constitute a crucial component in agricultural production, and a demand-driven field-scale assessment of cultivated land quality. Therefore, we developed a field-scale index system that meets the needs of individual farmers in the black soil region of Northeast China. Additionally, we proposed a machine learning model for field-scale cultivated land quality assessment. The experimental results showed that our model achieved an \({R}^{2}\) value of 0.9660 and an \(RMSE\) of \(1.94\times {10}^{-2}\) under fourfold cross-validation, which represents an improvement of 5.19% and a reduction of 1.13%, respectively, relative to the XGBoost model. Ultimately, we conducted obstacle factor diagnosis, aiming to assist individual farmers in identifying the existing issues in their cultivated land fields. This study not only provides guidance to individual farmers but also addresses the research gap in cultivated land quality assessment by offering an individual farmer demand-driven index system for field-scale studies.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data published in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to the policy of the research project.
References
Ahmed, G. B., Shariff, A. R. M., Balasundram, S. K., & Abdullah, A. F. B. (2016). Agriculture land suitability analysis evaluation based multi criteria and GIS approach. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 37(1), 012044. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/37/1/012044
Akpoti, K., Kabo-bah, A. T., & Zwart, S. J. (2019). Review - Agricultural land suitability analysis: State-of-the-art and outlooks for integration of climate change analysis. Agricultural Systems, 173, 172–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2019.02.013
Alaboz, P., Odabas, M. S., & Dengiz, O. (2023). Soil quality assessment based on machine learning approach for cultivated lands in semi-humid environmental condition part of Black Sea region. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science, 0(0), 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2023.2248002
Albaji, M., & Alboshokeh, A. (2017). Assessing agricultural land suitability in the Fakkeh region. Iran. Outlook on Agriculture, 46(1), 57–65. https://doi.org/10.1177/0030727017690659
Arshad, M. A., & Martin, S. (2002). Identifying critical limits for soil quality indicators in agro-ecosystems. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 88(2), 153–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-8809(01)00252-3
Brabec, E., & Smith, C. (2002). Agricultural land fragmentation: The spatial effects of three land protection strategies in the eastern United States. Landscape and Urban Pla-Nning, 58(2), 255–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-2046(01)00225-0
Chen, G., & Ma, L. (2011). Research on rough set and decision tree method application in evaluation of soil fertility level. In D. Li, Y. Liu, & Y. Chen (Eds.), Comp-uter and Computing Technologies in Agriculture IV (pp. 408–414). Heidelberg: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-18336-2_50
Chen, Y.-D., Wang, H.-Y., Zhou, J.-M., Xing, L., Zhu, B.-S., Zhao, Y.-C., & Chen, X.-Q. (2013). Minimum data set for assessing soil quality in farmland of Northeast China. Pedosphere, 23(5), 564–576. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(13)60050-8
Corbelle-Rico, E., Crecente-Maseda, R., & Santé-Riveira, I. (2012). Multi-scale assessment and spatial modelling of agricultural land abandonment in a European peripheral region: Galicia (Spain), 1956–2004. Land Use Policy, 29(3), 493–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2011.08.008
Dai, H., Yang, Z., Zhang, Y., Li, Q., Liu, K., & Fang, N. (2023). Enrichment characteristics of potential risk elements in the black soil region of Northeast China. Results in Geochemistry, 10, 100021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ringeo.2022.100021
Du, G. M., Yan, J. Q., Zhang, N., & Xu, X. L. (2023). New cognition of cultivated land quality system for the needs of multiple subjects. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 39, 212–222.
Feng, T., Zhang, F., Li, C., Qu, Y., & Zhu, F. (2014). Spatial distribution of prime farm-land based on cultivated land quality comprehensive evaluation at county scale. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 30(1), 200–210.
Hoobler, B. M., Vance, G. F., Hamerlinck, J. D., Munn, L. C., & Hayward, J. A. (2003). Applications of land evaluation and site assessment (LESA) and a geographic information system (GIS) in East Park County, Wyoming. Journal of Soil and Water Co-Nservation, 58(2), 105–112.
Hua, Y., Yan, M., & Limin, D. (2011). Land Ecological security assessment for Bai autonomous prefecture of Dali based using PSR model–with data in 2009 as case. Energy Procedia, 5, 2172–2177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2011.03.375
Jin, H., Shi, D., Lou, Y. B., Zhang, J., Ye, Q., & Jiang, N. (2021). Evaluation of the quality of cultivated-layer soil based on different degrees of erosion in sloping farmland with purple soil in China. CATENA, 198, 105048. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2020.105048
Kong, C., Lan, H., Yang, G., & Xu, K. (2016). Geo-environmental suitability assessment for agricultural land in the rural–urban fringe using BPNN and GIS: A case study of Hangzhou. Environmental Earth Sciences, 75(15), 1136. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5956-z
Li, W., & DeJiang, L. (2019). Ecological security evaluation of the cultivated land in Yuxi based on GA-BP neural network. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University, 34(5), 874–883.
Li, Q., & Yan, J. (2012). Assessing the health of agricultural land with energy analysis and fuzzy logic in the major grain-producing region. CATENA, 99, 9–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2012.07.005
Li, X., Wu, K., Zhao, R., Liu, Y., Li, X., & Yang, Q. (2021a). Spatial analysis of cultivated land productivity and health condition: A case study of Gaoping City, China. Land, 10(12), 1296. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10121296
Li, Y., Chang, C., Zhao, Y., Wang, Z., Li, T., Li, J., et al. (2021b). Evaluation system transformation of multi-scale cultivated land quality and analysis of its spatiotemporal variability. Sustainability, 13(18), 10100. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131810100
Li, X., Wu, Q., & Liu, Y. (2023). Spatiotemporal changes of cultivated land system health based on PSR-VOR model—a case study of the two lake plains, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(2), 1629. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20021629
Liu, X. B., Zhang, X. Y., Wang, Y. X., Sui, Y. Y., Zhang, S. L., Herbert, S. J., & Ding, G. (2010). Soil degradation: A problem threatening the sustainable development of agriculture in Northeast China. Plant, Soil and Environment, 56(2), 87–97.
Liu, Y., Li, J., Liu, C., & Wei, J. (2022). Evaluation of cultivated land quality using attention mechanism-back propagation neural network. PeerJ Computer Science, 8, e948. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj-cs.948
Nagy, S., Nagy, K., & Szép, T. (2009). Potential impact of EU accession on common farmland bird populations in Hungary. Acta Ornithologica, 44(1), 37–44. https://doi.org/10.3161/000164509X464867
Niu, S., Lyu, X., Gu, G., Zhou, X., & Peng, W. (2021). Sustainable intensification of cultivated land use and its influencing factors at the farming household scale: A case study of Shandong Province, China. Chinese Geographical Science, 31(1), 109–125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-021-1178-8
Qian, F., Chi, Y., & Lal, R. (2020a). Spatiotemporal characteristics analysis of multifunctional cultivated land: A case-study in Shenyang, Northeast China. Land Degradation & Development, 31(14), 1812–1822. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.3576
Qian, F., Chi, Y., Lal, R., & Lorenz, K. (2020b). Spatio-temporal characteristics of cultivated land fragmentation in different landform areas with a case study in Northeast China. Ecosystem Health and Sustainability, 6(1), 1800415. https://doi.org/10.1080/20964129.2020.1800415
Qian, F., Lal, R., & Wang, Q. (2021a). Land evaluation and site assessment for the basic farmland protection in Lingyuan County, Northeast China. Journal of Cleaner Produ-Ction, 314, 128097. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128097
Qian, F., Wang, W., Wang, Q., & Lal, R. (2021b). Implementing land evaluation and site assessment (LESA system) in farmland protection: A case-study in northeastern China. Land Degradation & Development, 32(7), 2437–2452. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.3922
Qu, Y., Pan, C., & Guo, H. (2021). Factors affecting the promotion of conservation tillage in black soil—The case of Northeast China. Sustainability, 13(17), 9563. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13179563
Raiesi, F. (2017). A minimum data set and soil quality index to quantify the effect of land use conversion on soil quality and degradation in native rangelands of uplan-d arid and semiarid regions. Ecological Indicators, 75, 307–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.12.049
RuiMing, M., RenHui, M., DongMei, H., & WenJu, Y. (2018). Construction of cultivated land quality evaluation system in provincial level based on multilevel indicators. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 34(16), 249–257.
Safitri, S., Wikantika, K., Riqqi, A., Deliar, A., & Sumarto, I. (2021). Spatial allocation based on physiological needs and land suitability using the combination of ecological footprint and SVM (case study: Java Island, Indonesia). ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 10(4), 259. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10040259
Sarmadian, F., Keshavarzi, A., Rooien, A., Zahedi, G., Javadikia, H., & Iqbal, M. (n.d.). Support vector machines based-modeling of land suitability analysis for rainfed agriculture. Journal of Geosciences and Geomatics.
Sengupta, S., Mohinuddin, Sk., Arif, M., Sengupta, B., & Zhang, W. (2022). Assessment of agricultural land suitability using GIS and fuzzy analytical hierarchy process approach in Ranchi District, India. Geocarto International, 37(26), 13337–13368. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2022.2076925
Shen, C., Wang, Y., Zhao, L., Xu, X., Yang, X., & Liu, X. (2019). Characteristics of material migration during soil erosion in sloped farmland in the black soil region of Northeast China. Tropical Conservation Science, 12, 1940082919856835. https://doi.org/10.1177/1940082919856835
Shi, T., & Xu, X. (2016). Extraction and validation of abandoned farmland parcel in typical counties of Chongqing. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engin-Eering, 32(24), 261–267.
Song, W., Zhang, H., Zhao, R., Wu, K., Li, X., Niu, B., & Li, J. (2022). Study on cultivated land quality evaluation from the perspective of farmland ecosystems. Ecologic-Al Indicators, 139, 108959. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108959
Sun, Z., You, L., & Müller, D. (2018). Synthesis of agricultural land system change in China over the past 40 years. Journal of Land Use Science, 13(5), 473–479. https://doi.org/10.1080/1747423X.2019.1571120
Sun, X. B., Kong, X. B., Zhang, Q. P., Wen, L. Y., & Liao, Y. B. (2020). Evaluation of inherent quality and dynamic quality of cultivated land based on comprehensive characteristics of indexes. Transations of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 36, 254–265.
Sun, L., Yu, Y., Petropoulos, E., Cui, X., & Wang, S. (2023). Long-term manure amendment sustains black soil biodiversity by mitigating acidification induced by chemical N fertilization. Microorganisms, 11(1), 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11010064
Taghizadeh-Mehrjardi, R., Nabiollahi, K., Rasoli, L., Kerry, R., & Scholten, T. (2020). Land suitability assessment and agricultural production sustainability using machine learning models. Agronomy, 10(4), 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10040573
Tan, Y., Chen, H., Lian, K., & Yu, Z. (2020). Comprehensive evaluation of cultivated land quality at county scale: A case study of Shengzhou, Zhejiang Province, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(4), 1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17041169
Tang, H., Niu, J., Niu, Z., Liu, Q., Huang, Y., Yun, W., et al. (2023). System cognition and analytic technology of cultivated land quality from a data perspective. Land, 12(1), 237. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12010237
Vasu, D., Srivastava, R., Patil, N. G., Tiwary, P., Chandran, P., & Kumar Singh, S. (2018). A comparative assessment of land suitability evaluation methods for agricultural land use planning at village level. Land Use Policy, 79, 146–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2018.08.007
Wang, D., Shen, Y., Zhao, Y., He, W., Liu, X., Qian, X., & Lv, T. (2020). Integrated assessment and obstacle factor diagnosis of China’s scientific coal production capacity based on the PSR sustainability framework. Resources Policy, 68, 101794. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2020.101794
Wang, H., Yang, S., Wang, Y., Gu, Z., Xiong, S., Huang, X., et al. (2022a). Rates and causes of black soil erosion in Northeast China. CATENA, 214, 106250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2022.106250
Wang, H., Zhang, C., Yao, X., Yun, W., Ma, J., Gao, L., & Li, P. (2022b). Scenario simulation of the tradeoff between ecological land and farmland in black soil region of Northeast China. Land Use Policy, 114, 105991. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2022.105991
Xu, X. Z., Xu, Y., Chen, S. C., Xu, S. G., & Zhang, H. W. (2010). Soil loss and conservation in the black soil region of Northeast China: A retrospective study. Environm-Ental Science & Policy, 13(8), 793–800. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsci.2010.07.004
Xu, W., Jin, X., Liu, J., & Zhou, Y. (2020). Impact of cultivated land fragmentation on spatial heterogeneity of agricultural agglomeration in China. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 30(10), 1571–1589. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-020-1800-1
Xu, F., Shao, Y., Xu, B., Li, H., Xie, X., Xu, Y., & Pu, L. (2023). Evaluation and zoning of cultivated land quality based on a space–function–environment. Land, 12(1), 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12010174
Yang, H., Wang, H., Fu, G., Yan, H., Zhao, P., & Ma, M. (2017). A modified soil water deficit index (MSWDI) for agricultural drought monitoring: Case study of Songnen Plain, China. Agricultural Water Management, 194, 125–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2017.07.022
Yu, J., Wang, Z., Meixner, F. X., Yang, F., Wu, H., & Chen, X. (2010). Biogeochemical characterizations and reclamation strategies of saline sodic soil in Northeastern China. CLEAN Soil, Air, Water, 38(11), 1010–1016. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201000276
Zhao, C., Zhou, Y., Jiang, J., Xiao, P., & Wu, H. (2021). Spatial characteristics of cultivated land quality accounting for ecological environmental condition: A case study in hilly area of northern Hubei province, China. Science of the Total Environment, 774, 145765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145765
Zhou, Z., Wang, L., Chen, Q., Luo, J., Zhao, X., Zhang, S., et al. (2023). Abandoned land identification in karst mountain area based on time series SAR characteristics at geo-parcels scale. Journal of Mountain Science, 20(3), 792–809. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-021-7281-6
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Agricultural Bureau of Gannan County for its valuable assistance in data collection.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2021YFD1500104-2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H. S.: conceptualization, formal analysis, supervision, and project administration. Z. Y.: study design, methodology, data curation, validation, and original draft preparation. X. L.: formal analysis, methodology, and original draft preparation. Y. H.: supervision and validation. M. G.: review and editing. X. L.: study design. Y. Y.: data curation. X. M.: validation. L. Z.: original draft preparation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Disclaimer
All authors have read, understood, and complied as applicable with the statement on “Ethical responsibilities of Authors” as found in the Instructions for Authors and are aware that with minor exceptions, no changes can be made to author-ship once the paper is submitted.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, H., Yang, Z., Li, X. et al. Assessment of the cultivated land quality in the black soil region of Northeast China based on the field scale. Environ Monit Assess 195, 1508 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-12099-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-12099-4