Abstract
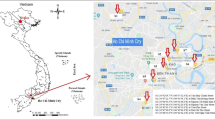
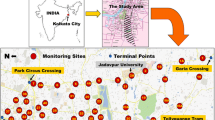
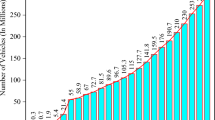
This study attempted to develop a computer-based software for monitoring the traffic noise under heterogeneous traffic condition at the morning peak (MP), off peak (OP), and evening peak (EP) periods of mid-block sections of mid-sized city in India. Traffic noise dataset of 776 (LAeq, 1hr) were collected from 23 locations of Gorakhpur mid-sized city in the state of Uttar Pradesh in India. K-nearest neighbor (K-NN) algorithm was adopted for traffic noise prediction modeling. Moreover, principal component analysis (PCA) technique was used for the dimensionality reduction and to overcome the problem of multi-collinearity. The developed model exhibits R2 value of 0.81, 0.78, and 0.77 in the MP, OP, and EP, respectively, for Leq, and a value of 0.86, 0.80, and 0.84 for L10. The proposed model can predict more than 94% observations within an accuracy of ±3%. Ultimately, a user-friendly noise level calculator named “Traffic Noise Prediction Calculator for Heterogeneous Traffic (TNPC-H)” was developed for the benefit of field engineers and policy planners.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Developed code and computer software is available upon reasonable request to the corresponding author of the manuscript.
References
Abdur-Rouf, K., & Shaaban, K. (2022). Development of prediction models of transportation noise for roundabouts and signalized intersections. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 103, 103174.
Abo-Qudais, S., & Alhiary, A. (2004). Effect of distance from road intersection on developed traffic noise levels. Canadian Journal of Civil Engineering, 31(4), 533–538.
Agarwal, S., & Swami, B. (2011). Comprehensive approach for the development of traffic noise prediction model for Jaipur city. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 172, 113–120.
Akbari, M., Overloop, P. J. V., & Afshar, A. (2011). Clustered K nearest neighbor algorithm for daily inflow forecasting. Water Resources Management, 25(5), 1341–1357.
Ali, S. A., & Tamura, A. (2003). Road traffic noise levels, restrictions and annoyance in Greater Cairo, Egypt. Applied Acoustics, 64(8), 815–823.
AlKheder, S., & Almutairi, R. (2021). Roadway traffic noise modelling in the hot hyper-arid Arabian Gulf region using adaptive neuro-fuzzy interference system. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 97, 102917.
Amiri, M., Bakhshandeh Amnieh, H., Hasanipanah, M., & Mohammad Khanli, L. (2016). A new combination of artificial neural network and K-nearest neighbors models to predict blast-induced ground vibration and air-overpressure. Engineering with Computers, 32(4), 631–644.
Arasan, V. T., & Dhivya, G. (2008). Measuring heterogeneous traffic density. In Proceedings of International Conference on Sustainable Urban Transport and Environment, World Academy of Science, Engineering and technology. Citeseer.
Balderrama, A., Kang, J., Prieto, A., Luna-Navarro, A., Arztmann, D., & Knaack, U. (2022). Effects of façades on urban acoustic environment and soundscape: A systematic review. Sustainability, 14(15), 9670.
Banerjee, D., Chakraborty, S., Bhattacharyya, S., & Gangopadhyay, A. (2008). Evaluation and analysis of road traffic noise in Asansol: An industrial town of eastern India. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 5(3), 165–171.
Besnard, F., Defrance, J., Bérengier, M., Dutilleux, G., Junker, F., Ecotiere, D., Le Duc, E., Baulac, M., Bonhomme, B., & Deparis, J.-P. (2009a). Road noise prediction-2-Noise propagation computation method including meteorological effects (NMPB 2008). SETRA.
Besnard, F., Hamet, J.-F., Lelong, J., Le Duc, E., Guizard, V., Fürst, N., Doisy, S., & Dutilleux, G. (2009b). Road noise prediction 1-Calculating sound emissions from road traffic. SETRA.
Boukhatem, B., Kenai, S., Hamou, A., Ziou, D., & Ghrici, M. (2012). Predicting concrete properties using neural networks(NN) with principal component analysis(PCA) technique. Computers and Concrete, 10(6), 557–573.
Can, A., & Aumond, P. (2018). Estimation of road traffic noise emissions: The influence of speed and acceleration. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 58, 155–171.
Chen, Y., & Hao, Y. (2017). A feature weighted support vector machine and K-nearest neighbor algorithm for stock market indices prediction. Expert Systems with Applications, 80, 340–355.
Cheng, M.-Y., & Hoang, N.-D. (2016). Slope collapse prediction using Bayesian framework with k-nearest neighbor density estimation: Case study in Taiwan. Journal of Computing in Civil Engineering, 30(1), 04014116.
Chew, C. H., & Lim, K. B. (1994). Facade effects on the traffic noise from the expressway. Applied Acoustics, 41(1), 47–62.
Chhetri, L. (1992). Environmental considerations in development of hill roads. Indian Highways, 20(6).
Chowdhury, S. C., Razzaque, M. M., Helali, M. M., & Bodén, H. (2010). Assessment of noise pollution in Dhaka city. In 17th International Congress on Sound and Vibration, Cairo, Egypt, 2010-07-18-2010-07-22.
Debnath, A., & Singh, P. K. (2018). Environmental traffic noise modelling of Dhanbad township area–A mathematical based approach. Applied Acoustics, 129, 161–172.
Debnath, A., Singh, P. K., & Banerjee, S. (2022). Vehicular traffic noise modelling of urban area—A contouring and artificial neural network based approach. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(26), 39948–39972.
Defrance, J., Salomons, E., Noordhoek, I., Heimann, D., Plovsing, B., Watts, G., Jonasson, H., Zhang, X., Premat, E., & Schmich, I. (2007). Outdoor sound propagation reference model developed in the European Harmonoise project. Acta Acustica united with Acustica, 93(2), 213–227.
Ding, Y. (2013). Noise Reduction Mechanism of Voids within Porous Asphalt Pavement. Southeast University.
Dutilleux, G., Defrance, J., Ecotière, D., Gauvreau, B., Bérengier, M., Besnard, F., & Duc, E. L. (2010). NMPB-routes-2008: The revision of the French method for road traffic noise prediction. Acta Acustica united with Acustica, 96(3), 452–462.
Farooqi, Z. U. R., Sabir, M., Latif, J., Aslam, Z., Ahmad, H. R., Ahmad, I., Imran, M., & Ilić, P. (2020). Assessment of noise pollution and its effects on human health in industrial hub of Pakistan. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27, 2819–2828.
FHWA. (1998). FHWA highway traffic noise prediction model - ROSA P. https://rosap.ntl.bts.gov/view/dot/30259/dot_30259_DS1.pdf
Garg, N., & Maji, S. (2014). A critical review of principal traffic noise models: Strategies and implications. Environmental Impact Assessment Review, 46, 68–81.
Garg, N., Mangal, S., Saini, P., Dhiman, P., & Maji, S. (2015). Comparison of ANN and analytical models in traffic noise modeling and predictions. Acoustics Australia, 43, 179–189.
Givargis, S., & Mahmoodi, M. (2008). Converting the UK calculation of road traffic noise (CORTN) to a model capable of calculating LAeq, 1h for the Tehran’s roads. Applied Acoustics, 69(11), 1108–1113.
Gulliver, J., Morley, D., Vienneau, D., Fabbri, F., Bell, M., Goodman, P., Beevers, S., Dajnak, D., Kelly, F. J., & Fecht, D. (2015). Development of an open-source road traffic noise model for exposure assessment. Environmental Modelling & Software, 74, 183–193.
Haq, M., Islam, M., Ali, M., Haque, M., & Akhand, M. (2012). Status of noise pollution in mixed areas of Dhaka city: A GIS approach. Journal of Environmental Science and Natural Resources, 5(1), 09–17.
Heutschi, K. (2004). SonRoad: New Swiss road traffic noise model. Acta Acustica united with Acustica, 90(3), 548–554.
Hsieh, S.-C. (2021). Prediction of compressive strength of concrete and rock using an elementary instance-based learning algorithm. In Advances in Civil Engineering 2021.
Hunashal, R. B., & Patil, Y. B. (2012). Assessment of noise pollution indices in the city of Kolhapur, India. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 37, 448–457.
Hupeng, W., Kang, J., & Hong, J. (2019). Effects of urban street spatial parameters on sound propagation. Environment and Planning B: Urban Analytics and City Science, 46(2), 341–358.
Hyder, A. A., Ghaffar, A., Sugerman, D. E., Masood, T., & Ali, L. (2006). Health and road transport in Pakistan. Public health, 120(2), 132–141.
Institution, I. S. (1980). Indian Standard, IS-3098, Noise emitted by moving road vehicles, measurement. Indian Standards Institution.
Institution, I. S. (1982). Indian standard ,IS-10399, Noise emitted by stationary road vehicles, methods of measurement. Indian Standards Institution.
Jonasson, H. G. (2007). Acoustical source modelling of road vehicles. Acta Acustica united with Acustica, 93(2), 173–184.
Jónsson, G. B., & Jacobsen, F. (2008). A comparison of two engineering models for outdoor sound propagation: Harmonoise and Nord2000. Acta Acustica united with Acustica, 94(2), 282–289.
Kalaiselvi, R., & Ramachandraiah, A. (2016). Honking noise corrections for traffic noise prediction models in heterogeneous traffic conditions like India. Applied Acoustics, 111, 25–38.
Kalansuriya, C., A. Pannila and D. Sonnadara (2015). Traffic composition and variability of road traffic noise levels in the vicinity of Colombo,
Kang, J. (2005). Numerical modeling of the sound fields in urban squares. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 117(6), 3695–3706.
Kang, M.-C., Yoo, D.-Y., & Gupta, R. (2021). Machine learning-based prediction for compressive and flexural strengths of steel fiber-reinforced concrete. Construction and Building Materials, 266, 121117.
Kephalopoulos, S., Paviotti, M., & Anfosso-Lédée, F. (2012). Common noise assessment methods in Europe (CNOSSOS-EU) (p. 180). Publications Office of the European Union.
KrAgh, J. (2001). News and needs in outdoor noise prediction. In Proceedings of the International Congress and Exhibition on Noise Control Engineering.
Krimm, J. (2018). Acoustically effective façades. A+ BE| Architecture and the Built Environment, 16, 1–212.
Kumar, P., Nigam, S., & Kumar, N. (2014). Vehicular traffic noise modeling using artificial neural network approach. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 40, 111–122.
Li, F., Xue, W., Rong, Y., Du, C., Tang, J., & Zhao, Y. (2022). A probability distribution prediction method for expressway traffic noise. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 103, 103175.
Li, T. (2019). A review on physical mechanisms of tire-pavement interaction noise. SAE International Journal of Vehicle Dynamics, Stability, and NVH, 3(10-03-02-0007), 87–112.
Ling, S., Yu, F., Sun, D., Sun, G., & Xu, L. (2021). A comprehensive review of tire-pavement noise: Generation mechanism, measurement methods, and quiet asphalt pavement. Journal of Cleaner Production, 287, 125056.
Lokhande, S. K., Pathak, S. S., Kokate, P. A., Dhawale, S. A., & Bodhe, G. L. (2018). Assessment of heterogeneous road traffic noise in Nagpur. Archives of Acoustics, 43.
McDaniel, R., Shah, A., Dare, T., & Bernhard, R. (2014). Hot mix asphalt surface characteristics related to ride, texture, friction, noise and durability. Institute for Safe, Quiet, and Durable Highways North Central Superpave Center Purdue University.
Mehdi, M. R., Arsalan, M. H., Gazder, U., Kim, M., Seong, J. C., Namdeo, A., & Chang, S. I. (2018). Who is the bigger culprit? Studying impacts of traffic and land use on noise levels in CBD area of Karachi, Pakistan. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 20, 1421–1438.
Mehdi, M. R., Kim, M., Seong, J. C., & Arsalan, M. H. (2011). Spatio-temporal patterns of road traffic noise pollution in Karachi, Pakistan. Environment international, 37(1), 97–104.
Nedic, V., Despotovic, D., Cvetanovic, S., Despotovic, M., & Babic, S. (2014). Comparison of classical statistical methods and artificial neural network in traffic noise prediction. Environmental Impact Assessment Review, 49, 24–30.
Nelson, J. T., Kohler, E., Öngel, A., & Rymer, B. (2008). Acoustical absorption of porous pavement. Transportation Research Record, 2058(1), 125–132.
Nourani, V., Gökçekuş, H., & Umar, I. K. (2020). Artificial intelligence based ensemble model for prediction of vehicular traffic noise. Environmental research, 180, 108852.
Oh, S., Byon, Y.-J., & Yeo, H. (2015). Improvement of search strategy with k-nearest neighbors approach for traffic state prediction. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 17(4), 1146–1156.
Okada, Y., Yoshihisa, K., & Kuno, K. (2010). Simple calculation model for noise propagation in city street canyons based on a diffusion method. Acoustical science and technology, 31(1), 95–101.
Oliveira, M. I. F. and L. T. Silva (2011). "The influence of urban form on facades noise levels."
Pamanikabud, P., Tansatcha, M., & Brown, A. (2008). Development of a highway noise prediction model using an Leq20 s measure of basic vehicular noise. Journal of sound and vibration, 316(1-5), 317–330.
Pamanikabud, P., & Vivitjinda, P. (2002). Noise prediction for highways in Thailand. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 7(6), 441–449.
Pathak, S. S., Lokhande, S. K., Kokate, P., & Bodhe, G. L. (2018). Assessment and prediction of environmental noise generated by road traffic in Nagpur City, India. In Environmental Pollution: Select Proceedings of ICWEES-2016. Springer.
Pathak, V., Tripathi, B., & Mishra, V. K. (2008). Evaluation of traffic noise pollution and attitudes of exposed individuals in working place. Atmospheric Environment, 42(16), 3892–3898.
Peterson, L. E. (2009). K-nearest neighbor. Scholarpedia, 4(2), 1883.
Probst, W. (2010). New techniques in noise prediction. Proceedings of 20th international Congress on acoustics, ICA.
Probst, W., & Huber, B. (2010). Accuracy and precision in traffic noise prediction. In Proceedings of conference Internoise.
Quiñones-Bolaños, E. E., Bustillo-Lecompte, C. F., & Mehrvar, M. (2016). A traffic noise model for road intersections in the city of Cartagena de Indias, Colombia. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 47, 149–161.
Ranpise, R. B., Tandel, B., & Singh, V. A. (2021). Development of traffic noise prediction model for major arterial roads of tier-II city of India (Surat) using artificial neural network. Noise Mapping, 8(1), 172–184.
Rasmussen, R. O., Bernhard, R. J., Sandberg, U., & Mun, E. (2007). The little book of quieter pavements, United States. Federal Highway Administration. Office of Pavement Technology.
Sagar, T. V., & Rao, G. N. (2006). Noise pollution levels in Visakhapatnam city (India). Journal of Environmental Science and Engineering, 48(2), 139.
Saunders, R., S. Samuels, R. Leach and A. Hall (1983). An evaluation of the UK DoE traffic noise prediction method
Shukla, A. K., Jain, S. S., Parida, M., & Srivastava, J. B. (2009). Performance of FHWA model for predicting traffic noise: A case study of Metropolitan city, Lucknow (India). Transport, 24(3), 234–240.
Singh, D., Francavilla, A. B., Mancini, S., & Guarnaccia, C. (2021a). Application of machine learning to include honking effect in vehicular traffic noise prediction. Applied Sciences, 11(13), 6030.
Singh, D., Upadhyay, R., Pannu, H. S., & Leray, D. (2021b). Development of an adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system based vehicular traffic noise prediction model. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 12, 2685–2701.
Smith, B. L., Williams, B. M., & Oswald, R. K. (2002). Comparison of parametric and nonparametric models for traffic flow forecasting. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 10(4), 303–321.
Steele, C. (2001). A critical review of some traffic noise prediction models. Applied acoustics, 62(3), 271–287.
Tang, S. K., & Piippo, K. (2011). Sound fields inside street canyons with inclined flanking building façades. In Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics 161ASA. Acoustical Society of America.
Tang, S. K., & Tong, K. (2004). Estimating traffic noise for inclined roads with freely flowing traffic. Applied acoustics, 65(2), 171–181.
Tansatcha, M., Pamanikabud, P., Brown, A., & Affum, J. (2005). Motorway noise modelling based on perpendicular propagation analysis of traffic noise. Applied acoustics, 66(10), 1135–1150.
Thomas, P., Van Renterghem, T., De Boeck, E., Dragonetti, L., & Botteldooren, D. (2013). Reverberation-based urban street sound level prediction. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 133(6), 3929–3939.
To, W., Ip, R. C., Lam, G. C., & Yau, C. T. (2002). A multiple regression model for urban traffic noise in Hong Kong. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 112(2), 551–556.
Vijay, R., Kori, C., Kumar, M., Chakrabarti, T., & Gupta, R. (2014). Assessment of traffic noise on highway passing from urban agglomeration. Fluctuation and Noise Letters, 13(04), 1450031.
Watts, G. (2005). Harmonoise prediction model for road traffic noise.
Yamamoto, K. (2010). Road traffic noise prediction model “ASJ RTN-Model 2008”: Report of the research committee on road traffic noise. Acoustical Science and Technology, 31(1), 2–55.
Yu, B., Song, X., Guan, F., Yang, Z., & Yao, B. (2016). k-Nearest neighbor model for multiple-time-step prediction of short-term traffic condition. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 142(6), 04016018.
Zheng, Z., & Su, D. (2014). Short-term traffic volume forecasting: A k-nearest neighbor approach enhanced by constrained linearly sewing principle component algorithm. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 43, 143–157.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank IMPRINT India, who realized the dangers posed by noise pollution and supported our group’s initiatives to work in the field of noise pollution by providing financial backing. Because of this, we have amassed a plethora of data, and the Transportation Engineering Department, IIT BHU has established a national center for the evaluation of traffic noise.
Funding
The research is funded by IMPRINT India under domain of Sustainable habitat whose objective is to make assessment of road traffic noise propagation; plotting of horizontal and vertical profile of noise signature; survey of community response; and analysis of data for model development for three Indian mid-sized cities of Kanpur, Varanasi, and Gorakhpur having similar traffic and geophysical conditions and noise enviroscape with a view to propose suggestions for noise mitigation in urban planning. The project and sanction no. is 4583.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
All the authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chouksey, A.K., Kumar, B., Parida, M. et al. Heterogeneous road traffic noise modeling at mid-block sections of mid-sized city in India. Environ Monit Assess 195, 1349 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11924-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11924-0