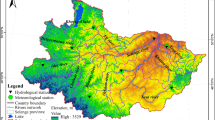
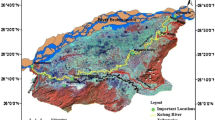
Abstract
Water quality is one of the essential parameters of environmental monitoring; even a slight variation in its characteristics may significantly influence the ecosystem. The water quality of Vembanad Lake is affected by anthropogenic effects such as industrial effluents and tourism. The optical parameters representing water quality, such as diffuse attenuation (Kd), turbidity, suspended particulate matter (SPM), and chlorophyll-a (Chl-a), are considered in this study to evaluate the water quality of Vembanad Lake, Kerala, India. As this lake is regarded as of ecological importance by the Ramsar Convention and has faced severe concerns over recent years, there was a substantial change in the water quality during the lockdowns of the COVID-19 pandemic. This research is aimed at examining the change in water quality using optical data from Sentinel-2 satellites in the ACOLITE processing software from 2016 to 2021. The analyses showed a 2.5% decrease in the values of Kd, whereas SPM and turbidity show a reduction of about 4.3% from the year 2016 to 2021. The flood and the COVID lockdown had an impact on the improvement in the quality of water from 2018 to 2021. The findings indicated that the reduction in industrial activities and tourism had a more significant effect on the improvement in the water quality of the lake. There was no substantial change in the Chl-a until 2020, whereas an average decrease of 12% in Chl-a values was observed throughout 2021. This decrease can be attributed to the reduction in the lake’s hydrological residence time (HRT). Thus, these findings will be a valuable reference to help the government and non-government organizations (NGO) during strategic planning.











Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Abraham, A., & Kundapura, S. (2022a). Evaluating the long-term trends of the climatic variables over three humid tropical basins in Kerala, India. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 15, 811. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-022-10056-y
Abraham, A., & Kundapura, S. (2022b). Spatio-temporal dynamics of land use land cover changes and future prediction using geospatial techniques. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 50(11), 2175–2191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-022-01588-7
Ahmed, U., Mumtaz, R., Anwar, H., Mumtaz, S., & Qamar, A. M. (2020). Water quality monitoring: From conventional to emerging technologies. Water Supply, 20(1), 28–45. https://doi.org/10.2166/WS.2019.144
Alem, A. E., Lhissou, R., Chokmani, K., & Oubennaceur, K. (2021). Remote retrieval of suspended particulate matter in inland waters: Image-based or physical atmospheric correction models? Water, 13(16), 2149. https://doi.org/10.3390/W13162149
Andres, L., Boateng, K., Borja-Vega, C., & Thomas, E. (2018). A review of in-situ and remote sensing technologies to monitor water and sanitation interventions. Water, 10(6), 756. https://doi.org/10.3390/W10060756
Ansper, A., & Alikas, K. (2019). Retrieval of chlorophyll a from Sentinel-2 MSI data for the European Union water framework directive reporting purposes. Remote Sensing. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11010064
Antonini, K., Langer, M., Farid, A., & Walter, U. (2017). SWEET CubeSat – Water detection and water quality monitoring for the 21st century. Acta Astronautica, 140, 10–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ACTAASTRO.2017.07.046
Avtar, R., Kumar, P., Supe, H., Jie, D., Sahu, N., Mishra, B. K., & Yunus, A. P. (2020). Did the COVID-19 lockdown-induced hydrological residence time intensify the primary productivity in lakes? Observational results based on satellite remote sensing. Water, 12(9), 2573. https://doi.org/10.3390/W12092573
Bhuyan, M., Jayaram, C., Menon, N. N., & Joseph, K. A. (2020). Satellite-based study of seasonal variability in water quality parameters in a tropical estuary along the southwest coast of India. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 48, 1265–1276. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12524-020-01153-0/FIGURES/8
Brij, G., & Krishnamurthy, K. (1993). Wetlands of South Asia. In Wetlands of the World (pp. 345–414). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-015-8212-4
Buiteveld, H., Hakvoort, J. H. M., & Donze, M. (1994). Optical properties of pure water. Ocean Optics XII Proceedings of Society Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers, 2258, 174–183. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.190060
Caballero, I., Fernández, R., Escalante, O. M., Mamán, L., & Navarro, G. (2020). New capabilities of Sentinel-2A/B satellites combined with in situ data for monitoring small harmful algal blooms in complex coastal waters. Scientific Reports. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-65600-1
Caballero, I., Román, A., Tovar-Sánchez, A., & Navarro, G. (2022). Water quality monitoring with Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8 satellites during the 2021 volcanic eruption in La Palma (Canary Islands). Science of the Total Environment. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2022.153433
Carmichael, W. W., & Boyer, G. L. (2016). Health impacts from cyanobacteria harmful algae blooms: Implications for the North American Great Lakes. Harmful Algae, 54, 194–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.HAL.2016.02.002
Codd, G. A., Morrison, L. F., & Metcalf, J. S. (2005). Cyanobacterial toxins: Risk management for health protection. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 203(3), 264–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TAAP.2004.02.016
Dev, P. J., Sukenik, A., Mishra, D. R., & Ostrovsky, I. (2022). Cyanobacterial pigment concentrations in inland waters: Novel semi-analytical algorithms for multi- and hyperspectral remote sensing data. Science of the Total Environment. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2021.150423
Dogliotti, A. I., Ruddick, K. G., Nechad, B., Doxaran, D., & Knaeps, E. (2015). A single algorithm to retrieve turbidity from remotely-sensed data in all coastal and estuarine waters. Remote Sensing of Environment, 156, 157–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2014.09.020
Falconer, I. R. (1999). An overview of problems caused by toxic blue–green algae (cyanobacteria) in drinking and recreational water. Environmental Toxicology, 14, 5–12. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1522-7278(199902)14:1%3C5::AID-TOX3%3E3.0.CO;2-0
Fettweis, M., Schartau, M., Desmit, X., Lee, B. J., Terseleer, N., Van der Zande, D., Parmentier, K., & Riethmüller, R. (2022). Organic matter composition of biomineral flocs and its influence on suspended particulate matter dynamics along a nearshore to offshore transect. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 127(1), e2021JG006332. https://doi.org/10.1029/2021JG006332
Garg, V., Aggarwal, S. P., & Chauhan, P. (2020). Changes in turbidity along Ganga River using Sentinel-2 satellite data during lockdown associated with COVID-19. Geomatics, Natural Hazards and Risk, 11(1), 1175–1195. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2020.1782482
George, G., Menon, N. N., Abdulaziz, A., Brewin, R. J. W., Pranav, P., Gopalakrishnan, A., Mini, K. G., Kuriakose, S., Sathyendranath, S., & Platt, T. (2021). Citizen scientists contribute to real-time monitoring of lake water quality using 3D printed mini Secchi disks. Frontiers in Water, 3, 40. https://doi.org/10.3389/FRWA.2021.662142/BIBTEX
Gholizadeh, M. H., Melesse, A. M., & Reddi, L. (2016). A comprehensive review on water quality parameters estimation using remote sensing techniques. Sensors, 16(8), 1298. https://doi.org/10.3390/S16081298
HCSL. (2020). Hooghly Cochin Shipyard Limited.
Hope, R. (2011). Clean water is not just a health issue: It is critical for education. University of Oxford. University of Oxford. Retrieved January 7, 2023, from https://www.ox.ac.uk/news/2021-07-26-clean-water-not-just-health-issue-it-critical-education
IOCCG. (2010). Atmospheric correction for remotely-sensed ocean-colour. (M. Wang (ed.)). International Ocean Colour Coordinating Group (IOCCG). https://doi.org/10.25607/OBP-101
IWMI. (2014). Global water demand projections: Past, present and future. Retrieved January 2, 2023, from www.iwmi.org
Jafar-Sidik, M., Gohin, F., Bowers, D., Howarth, J., & Hull, T. (2017). The relationship between suspended particulate matter and turbidity at a mooring station in a coastal environment: Consequences for satellite-derived products. Oceanologia, 59(3), 365–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.OCEANO.2017.04.003
Kari, E., Kratzer, S., Beltrán-Abaunza, J. M., Harvey, E. T., & Vaičiūtė, D. (2016). Retrieval of suspended particulate matter from turbidity – Model development, validation, and application to MERIS data over the Baltic Sea. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 38(7), 1983–2003. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2016.1230289
Krishnaraj, A., & Honnasiddaiah, R. (2022). Remote sensing and machine learning based framework for the assessment of spatio-temporal water quality in the Middle Ganga Basin. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(43), 64939–64958. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20386-9
Kulk, G., George, G., Abdulaziz, A., Menon, N., Theenathayalan, V., Jayaram, C., Brewin, R. J. W., & Sathyendranath, S. (2021). Effect of reduced anthropogenic activities on water quality in Lake Vembanad, India. Remote Sensing, 13(9), 1631. https://doi.org/10.3390/RS13091631
Kumar, K. K., & Rajan, P. D. (2012). Fish and fisheries in Vembanad Lake Consolidated report of Vembanad fish count 2008-2011. Retrieved January 3, 2023, from https://www.keralabiodiversity.org/images/2020/Reports/Fish_Fisheries_Vembanad_lake.pdf
Lavigne, H., Ruddick, K., & Vanhellemont, Q. (2022). Monitoring of high biomass Phaeocystis globosa blooms in the Southern North Sea by in situ and future spaceborne hyperspectral radiometry. Remote Sensing of Environment, 282, 113270. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSE.2022.113270
Lee, Z., Carder, K. L., & Arnone, R. A. (2002). Deriving inherent optical properties from water color: A multiband quasi-analytical algorithm for optically deep waters. Applied Optics, 41(27), 5755. https://doi.org/10.1364/ao.41.005755
León, J. G., Beamud, S. G., Temporetti, P. F., Atencio, A. G., Diaz, M. M., & Pedrozo, F. L. (2016). Stratification and residence time as factors controlling the seasonal variation and the vertical distribution of chlorophyll-a in a subtropical irrigation reservoir. International Review of Hydrobiology, 101(1–2), 36–47. https://doi.org/10.1002/IROH.201501811
Leray, S., Engdahl, N. B., Massoudieh, A., Bresciani, E., & McCallum, J. (2016). Residence time distributions for hydrologic systems: Mechanistic foundations and steady-state analytical solutions. Journal of Hydrology, 543, 67–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHYDROL.2016.01.068
Mabit, R., Araújo, C. A. S., Singh, R. K., & Bélanger, S. (2022). Empirical remote sensing algorithms to retrieve SPM and CDOM in Québec coastal waters. Frontiers in Remote Sensing. https://doi.org/10.3389/frsen.2022.834908
Maciel, F. P., Haakonsson, S., Ponce de León, L., Bonilla, S., & Pedocchi, F. (2023). Challenges for chlorophyll-a remote sensing in a highly variable turbidity estuary, an implementation with Sentinel-2. Geocarto International, 38(1), 2160017. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2022.2160017/SUPPL_FILE/TGEI_A_2160017_SM1889.PDF
McCluskey, E., Brewin, R. J. W., Vanhellemont, Q., Jones, O., Cummings, D., Tilstone, G., Jackson, T., Widdicombe, C., Woodward, E. M. S., Harris, C., Bresnahan, P. J., Cyronak, T., & Andersson, A. J. (2022). On the seasonal dynamics of phytoplankton chlorophyll-a concentration in nearshore and offshore waters of Plymouth, in the English Channel: Enlisting the help of a surfer. Oceans, 3(2), 125–146. https://doi.org/10.3390/OCEANS3020011
Mishra, D. R., Narumalani, S., Rundquist, D., & Lawson, M. (2005). Characterizing the vertical diffuse attenuation coefficient for downwelling irradiance in coastal waters: Implications for water penetration by high resolution satellite data. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry & Remote Sensing, 60, 48–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2005.09.003
Mishra, S., & Mishra, D. R. (2012). Normalized difference chlorophyll index: A novel model for remote estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration in turbid productive waters. Remote Sensing of Environment, 117, 394–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2011.10.016
Mitsch, W. J., & Gosselink, J. G. (2000). The value of wetlands: Importance of scale and landscape setting. Ecological Economics, 35(1), 25–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-8009(00)00165-8
Morel, A., & Prieur, L. (1977). Analysis of variations in ocean color. Limnology and Oceanography, 22(4), 709–722. https://doi.org/10.4319/LO.1977.22.4.0709
Nazirova, K., Alferyeva, Y., Lavrova, O., Shur, Y., Soloviev, D., Bocharova, T., & Strochkov, A. (2021). Comparison of in situ and remote-sensing methods to determine turbidity and concentration of suspended matter in the estuary zone of the Mzymta River, Black Sea. Remote Sensing, 13(1), 1–29. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13010143
Nechad, B., Dogliotti, A. I., Ruddick, K. G., & Doxaran, D. (2016). Particulate backscattering and suspended matter concentration retrieval from remote-sensed turbidity in various coastal and. Proceedings of ESA Living Planet Symposium, 2015(May), 9–13.
Nechad, B., Ruddick, K. G., & Neukermans, G. (2009). Calibration and validation of a generic multisensor algorithm for mapping of turbidity in coastal waters. Remote Sensing of the Ocean, Sea Ice, and Large Water Regions 2009, 7473(September), 74730H. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.830700
Nechad, B., Ruddick, K. G., & Park, Y. (2010). Calibration and validation of a generic multisensor algorithm for mapping of total suspended matter in turbid waters. Remote Sensing of Environment, 114(4), 854–866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2009.11.022
Ngoc, D. D., Loisel, H., Vantrepotte, V., Xuan, H. C., Minh, N. N., Verpoorter, C., Meriaux, X., Minh, H. P. T., Thi, H. L., Hong, H. L. V., & Van, T. N. (2020). A simple empirical band-ratio algorithm to assess suspended particulate matter from remote sensing over coastal and inland waters of Vietnam: Application to the VNREDSat-1/NAOMI sensor. Water, 12(9), 2636. https://doi.org/10.3390/W12092636
Parthasarathy, K. S. S., & Deka, P. C. (2022). Spatio-temporal classification and prediction of land use and land cover change for the Vembanad Lake system, Kerala: A machine learning approach. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(57), 86220–86236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17257-0
Pereira-Sandoval, M., Ruescas, A., Urrego, P., Ruiz-Verdú, A., Delegido, J., Tenjo, C., Soria-Perpinyà, X., Vicente, E., Soria, J., & Moreno, J. (2019). Evaluation of atmospheric correction algorithms over Spanish inland waters for Sentinel-2 multi spectral imagery data. Remote Sensing, 11(12), 1469. https://doi.org/10.3390/RS11121469
Remani, K. N., Jayakumar, P., & Jalaja, T. K. (2010). Environmental problems and management aspects of Vembanad Kol wetlands in south west coast of India. Nature Environment and Pollution Technology.
REMSEM. (2022). ACOLITE manual. Retrieved June 12, 2022, from https://github.com/acolite/acolite/releases/download/20221114.0/acolite_manual_20221114.0.pdf
Ritchie, J. C., Schiebe, F. R., & McHenry, J. R. (1976). Remote sensing of suspended sediments in surface waters. Journal of American Society of Photogrammetry, 42(12).
Ritchie, J. C., Zimba, P. V., & Everitt, J. H. (2003). Remote sensing techniques to assess water quality. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 69(6), 695–704. https://doi.org/10.14358/PERS.69.6.695
Schewe, J., Heinke, J., Gerten, D., Haddeland, I., Arnell, N. W., Clark, D. B., Dankers, R., Eisner, S., Fekete, B. M., Colón-González, F. J., Gosling, S. N., Kim, H., Liu, X., Masaki, Y., Portmann, F. T., Satoh, Y., Stacke, T., Tang, Q., Wada, Y., & Kabat, P. (2014). Multimodel assessment of water scarcity under climate change. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 111(9), 3245–3250. https://doi.org/10.1073/PNAS.1222460110/SUPPL_FILE/SAPP.PDF
Sravanthi, N., Ramana, I. V., Ali, Y., Ashraf, M., Ali, M. M., & Narayana, A. C. (2013). An algorithm for estimating suspended sediment concentrations in the coastal waters of India using remotely sensed reflectance and its application to coastal environments. International Journal of Environmental Research, 7(4), 841–850.
Staehr, S. U., Van der Zande, D., Staehr, P. A. U., & Markager, S. (2022). Suitability of multisensory satellites for long-term chlorophyll assessment in coastal waters: A case study in optically-complex waters of the temperate region. Ecological Indicators, 134, 108479. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ECOLIND.2021.108479
Stumpner, E. B., Bergamaschi, B. A., Kraus, T. E. C., Parker, A. E., Wilkerson, F. P., Downing, B. D., Dugdale, R. C., Murrell, M. C., Carpenter, K. D., Orlando, J. L., & Kendall, C. (2020). Spatial variability of phytoplankton in a shallow tidal freshwater system reveals complex controls on abundance and community structure. Science of the Total Environment, 700, 134392. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2019.134392
Tilstone, G. H., Land, P. E., Pardo, S., Kerimoglu, O., & Van der Zande, D. (2023). Threshold indicators of primary production in the north-east Atlantic for assessing environmental disturbances using 21 years of satellite ocean colour. Science of the Total Environment, 854, 158757. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2022.158757
Toming, K., Kutser, T., Uiboupin, R., Arikas, A., Vahter, K., & Paavel, B. (2017). Mapping water quality parameters with Sentinel-3 ocean and land colour instrument imagery in the Baltic Sea. Remote Sensing, 9(10), 1070. https://doi.org/10.3390/RS9101070
UN WWDR. (2022). The United Nations World Water Development Report 2022: Groundwater: Making the invisible visible. In United Nations World Water. UNESCO. Retrieved August 7, 2022, from https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000380721
Vanhellemont, Q. (2019). Adaptation of the dark spectrum fitting atmospheric correction for aquatic applications of the Landsat and Sentinel-2 archives. Remote Sensing of Environment, 225, 175–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSE.2019.03.010
Vanhellemont, Q. (2023). Evaluation of eight band SuperDove imagery for aquatic applications. Optics Express, 31(9), 13851–13874. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.483418
Vanhellemont, Q., & Ruddick, K. (2016a). ACOLITE processing for Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8: Atmospheric correction and aquatic applications. Ocean Optics Conference.
Vanhellemont, Q., & Ruddick, K. (2016b). ACOLITE For Sentinel-2: Aquatic applications of MSI imagery. 2016 ESA Living Planet Symposium, 740. Retrieved September 9, 2022, from https://odnature.naturalsciences.be/downloads/publications/vanhellemontruddick_esa_lps2016_coastalapplications_final_header.pdf
Vanhellemont, Q., & Ruddick, K. (2018). Atmospheric correction of metre-scale optical satellite data for inland and coastal water applications. Remote Sensing of Environment, 216, 586–597. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSE.2018.07.015
Vanhellemont, Q., & Ruddick, K. (2021). Atmospheric correction of Sentinel-3/OLCI data for mapping of suspended particulate matter and chlorophyll-a concentration in Belgian turbid coastal waters. Remote Sensing of Environment, 256, 112284. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSE.2021.112284
Vinita, J., Revichandran, C., & Manoj, N. T. (2017). Suspended sediment dynamics in Cochin estuary, West Coast, India. Journal of Coastal Conservation, 21(1), 233–244. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11852-017-0494-8/TABLES/1
Wetlands International. (2014). Wetlands: Why should I care ? Ramsar Fact Sheet. Retrieved April 4, 2022, from http://www.ramsar.org/sites/default/files/documents/library/factsheet1_why_should_i_care_0.pdf
Yang, H., Kong, J., Hu, H., Du, Y., Gao, M., & Chen, F. (2022). A review of remote sensing for water quality retrieval: Progress and challenges. Remote Sensing, 14(8), 1770. https://doi.org/10.3390/RS14081770
Yunus, A. P., Masago, Y., & Hijioka, Y. (2020). COVID-19 and surface water quality: Improved lake water quality during the lockdown. Science of the Total Environment, 731, 139012. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2020.139012
Zhang, Y., Pulliainen, J. T., Koponen, S. S., & Hallikainen, M. T. (2003). Water quality retrievals from combined Landsat TM data and ERS-2 SAR data in the Gulf of Finland. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 41(3), 622–629. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2003.808906
Zwart, J. A., Sebestyen, S. D., Solomon, C. T., & Jones, S. E. (2017). The influence of hydrologic residence time on lake carbon cycling dynamics following extreme precipitation events. Ecosystems, 20(5), 1000–1014. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10021-016-0088-6
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the Department of Water Resources and Ocean Engineering, National Institute of Technology Karnataka, Mangaluru, India, for providing infrastructural support. Also, the authors would like to acknowledge the ESA for open-access data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Participation of Parthasarathy Kulithalai Shiyam Sundar includes conceptualization, data collection, analyzing the results, and writing of the article. Participation of Subrahmanya Kundapura includes supervision, reviewing, and editing of the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The authors confirm that this article is original research and has not been published or presented previously in any journal or conference in any language (in whole or in part).
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sundar, P.K.S., Kundapura, S. Spatiotemporal variation in the water quality of Vembanad Lake, Kerala, India: a remote sensing approach. Environ Monit Assess 195, 1097 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11746-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11746-0