Abstract
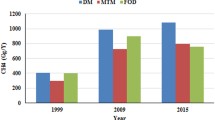
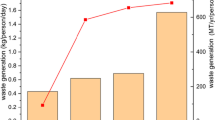
The study reported herein presents the methane generation potential from municipal solid waste (MSW) generated in Kanpur city using four established methods, namely: the IPCC Default Method (DM), EPER Germany, The IPCC First Order Decay (FOD) method, and the Modified Triangular Method (MTM). Results revealed that the average maximum and minimum emissions with respect to total MSW generated and considered over the study period were obtained in the IPCC Default Method (19.17Gg/year) and the MTM (1.00Gg/year), respectively. Furthermore, the sensitivity analysis carried out revealed that the MTM method is the least uncertain method in predicting the methane emissions. Energy generation using the Yedla method and the Stoichiometric method was also carried out, highlighting the potential for energy recovery using methane emissions. The total energy generation potential using the Yedla method over the entire study period was determined to be 924 TJ, with an increased potential of 30% between the periods of 2022 to 2031. According to the study, there exists significant potential for effectively managing the greenhouse gas emissions from open dumpsite by harnessing the methane produced and using it for energy generation.

Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
All the data used in this study is available in this paper.
Code availability
No commercial software was used for this study.
References
Alrbai, M., Abubaker, A. M., Ahmad, A. D., Al-Dahidi, S., Ayadi, O., Hjouj, D., & Al-Ghussain, L. (2022). Optimization of energy production from biogas fuel in a closed landfill using artificial neural networks: A case study of Al Ghabawi Landfill, Jordan. Waste Management, 150, 218–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2022.07.011
Amirmahani, N., Sadeghi, S., Yazdanpanah, G., Tayebiyan, A., Nasiri, A., & Malakootian, M. (2020). Estimating methane gas generation rate from Kerman City landfill using LandGEM software. International Journal of Environment and Waste Management, 26(4), 520–530. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJEWM.2020.110399
Araiza-Aguilar, J. A., Rojas-Valencia, M. N., & Aguilar-Vera, R. A. (2020). Forecast generation model of municipal solid waste using multiple linear regression. Global Journal of Environmental Science and Management, 6(1), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.22034/GJESM.2020.01.01
Baghanam, A. H., Vakili, A. T., Nourani, V., Dąbrowska, D., & Soltysiak, M. (2022). AI-based ensemble modeling of landfill leakage employing a lysimeter, climatic data and transfer learning. Journal of Hydrology, 612, 128243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.128243
Berger, K. U. (2015). On the current state of the Hydrologic Evaluation of Landfill Performance (HELP) model. Waste Management, 38, 201–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.01.013
Cakir, A. K., Gunerhan, H., & Hepbasli, A. (2016). A comparative study on estimating the landfill gas potential: Modeling and analysis. Energy Sources, Part a: Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects, 38(16), 2478–2486. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2015.1039670
Chandra, S., & Ganguly, R. (2023). Assessment of landfill gases by LandGEM and energy recovery potential from municipal solid waste of Kanpur city, India. Heliyon, 9(4). Article ID e15187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15187
Chakma, S., Vaishya, R. C., & Yadav, A. K. (2014). Modeling chemical compositions of municipal solid waste. Environmental Geotechnics, 3(2), 65–77. https://doi.org/10.1680/envgeo.13.00082
Chakraborty, M., Sharma, C., Pandey, J., Singh, N., & Gupta, P. K. (2011). Methane emission estimation from landfills in Delhi: A comparative assessment of different methodologies. Atmospheric Environment, 45(39), 7135–7142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2011.09.015
Chalvatzaki, E., & Lazaridis, M. (2010). Estimation of greenhouse gas emissions from landfills: Application to the Akrotiri landfill site (Chania, Greece). Global NEST Journal, 12(1), 108–116. Available online at https://journal.gnest.org/sites/default/files/Journal%20Papers/108-116_681_Lazaridis_12-1.pdf
Chen, D. M. C., Bodirsky, B. L., Krueger, T., Mishra, A., & Popp, A. (2020). The world’s growing municipal solid waste: Trends and impacts. Environmental Research Letters, 15(7), 074021. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/ab8659
Choden, Y., & Sharma, M. P. (2019). Greenhouse gas estimation from municipal solid waste dump site in Roorkee (Uttrakhand), India. International Journal of Research in Environmental Studies, 6(2019), 39–46. Available online at http://www.bluepenjournals.org/ijres/pdf/2019/September/Choden_and_Sharma.pdf
Choudhary, A., Kumar, A., & Kumar, S. (2020). National municipal solid waste energy and global warming potential inventory: India. Journal of Hazardous, Toxic, and Radioactive Waste, 24(4), 06020002. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HZ.2153-5515.0000521
CPCB. (2021). Annual report on solid waste management (2020–21), CPCB, Delhi. Available online at https://cpcb.nic.in/uploads/MSW/MSW_AnnualReport_2020-21.pdf . [Accessed on 27th June 2023 at 3.35 PM]
da Silva, N. F., Schoeler, G. P., Lourenco, V. A., de Souza, P. L., Caballero, C. B., Salamoni, R. H., & Romani, R. F. (2020). First order models to estimate methane generation in landfill: A case study in south Brazil. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 8(4), 104053. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104053
Delgado, M., López, A., Esteban-García, A. L., & Lobo, A. (2022). The importance of particularising the model to estimate landfill GHG emissions. Journal of Environmental Management, 325, 116600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.116600
Đidelija, M., Kulo, N., Mulahusić, A., Tuno, N., & Topoljak, J. (2022). Segmentation scale parameter influence on the accuracy of detecting illegal landfills on satellite imagery. A case study for Novo Sarajevo. Ecological Informatics, 70, 101755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoinf.2022.101755
Du, M., Peng, C., Wang, X., Chen, H., Wang, M., & Zhu, Q. (2017). Quantification of methane emissions from municipal solid waste landfills in China during the past decade. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 78, 272–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.04.082
Fallahizadeh, S., Rahmatinia, M., Mohammadi, Z., Vaezzadeh, M., Tajamiri, A., & Soleimani, H. (2019). Estimation of methane gas by LandGEM model from Yasuj municipal solid waste landfill Iran. Methods X, 6, 391–398.
Fjelsted, L., Christensen, A. G., Larsen, J. E., Kjeldsen, P., & Scheutz, C. (2019). Assessment of a landfill methane emission screening method using an unmanned aerial vehicle mounted thermal infrared camera–A field study. Waste Management, 87, 893–904. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.05.031
Ghinea, C., Drăgoi, E. N., Comăniţă, E. D., Gavrilescu, M., Câmpean, T., Curteanu, S. I. L. V. I. A., & Gavrilescu, M. (2016). Forecasting municipal solid waste generation using prognostic tools and regression analysis. Journal of environmental management, 182, 80–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVMAN.2016.07.026
Ghosh, P., Shah, G., Chandra, R., Sahota, S., Kumar, H., Vijay, V. K., & Thakur, I. S. (2019). Assessment of methane emissions and energy recovery potential from the municipal solid waste landfills of Delhi, India. Bioresource Technology, 272, 611–615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.10.069
Gollapalli, M., & Kota, S. H. (2018). Methane emissions from a landfill in north-east India: Performance of various landfill gas emission models. Environmental Pollution, 234, 174–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.11.064
Govindan, S. S., & Agamuthu, P. (2014). Quantification of landfill methane using modified Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change’s waste model and error function analysis. Waste Management & Research, 32(10), 1005–1014. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X14552551
Hoklis, C., & Sharp, A. (2014). Comparison of GHG emission from municipal solid waste management technology in selected cities in Cambodia. In Advanced Materials Research (Vol. 931, pp. 645–649). Trans Tech Publications Ltd. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.931-932.645
IPCC. (2006). Guidelines for national greenhouse gas inventories. http://www.ipccnggipigesorjp/public/2006gl. [Accessed on 30th September; 7.30 PM]
Jensen, J. E., & Pipatti, R. (2002). CH4 Emissions from solid waste disposal, background papers. In IPCC Expert Meetings on Good Practice Guidance and Uncertainty Management in National Greenhouse Gas Inventories, Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)-National Greenhouse Gas Inventories Programme (NGGIP), IGES, Hayama, Japan (pp. 419–465). Available online at https://www.ipccnggip.iges.or.jp/public/gp/bgp/5_1_CH4_Solid_Waste.pdf ; Accessed on 2nd August 2022 at 10.22 AM
Karimi, N., Ng, K. T. W., & Richter, A. (2021). Prediction of fugitive landfill gas hotspots using a random forest algorithm and Sentinel-2 data. Sustainable Cities and Society, 73, 103097. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2021.103097
Kaushal, A., & Sharma, M. P. (2016). Methane emission from Panki open dump site of Kanpur, India. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 35, 337–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2016.07.014
Kaza, S., Yao, L., Bhada-Tata, P., & Van Woerden, F. (2018). What a waste 2.0: A global snapshot of solid waste management to 2050 (urban development series) (Washington, DC: World Bank). https://doi.org/10.1596/978-1-4648-1329-0
Kumar, S., Nimchuk, N., Kumar, R., Zietsman, J., Ramani, T., Spiegelman, C., & Kenney, M. (2016). Specific model for the estimation of methane emission from municipal solid waste landfills in India. Bioresource Technology, 216, 981–987. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.06.050
Majdinasab, A., Zhang, Z., & Yuan, Q. (2017). Modelling of landfill gas generation: A review. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio/technology, 16, 361–380. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-017-9425-2
Mehra, A., & Bhargava, A. (2020). Sustainable Municipal Solid Waste Management-A case study of Kanpur, India. Journal of New Developments in Chemistry, 3(1), 12–22. https://doi.org/10.14302/issn.2377-2549.jndc-20-3516
MoEF. (2016). The solid waste management rules, 2016. Available online at https://cpcb.nic.in/uploads/MSW/SWM_2016.pdf . [Accessed on 27th June 2023at 3.21 PM]
MoEF. (2019). The National Clean Air Program, 2019. Available online at https://moef.gov.in/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/NCAP_Report.pdf. [Accessed on 27th June 2023 at 3.40 PM]
Moghadam, M. A., Feizi, R., Panahi Fard, M., Haghighi Fard, N. J., Omidinasab, M., Faraji, M., & Shenavar, B. (2021). Estimating greenhouse emissions from sanitary landfills using Land-GEM and IPCC model based on realistic scenarios of different urban areas: A case study of Iran. Journal of Environmental Health Science and Engineering, 19(1), 819–830. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-021-00649-2
Majhi, B. K., & Jash, T. (2016). Estimation of landfill gas generation from Dhapa landfill in Kolkata. Indian Journal of Environmental Protection, 36(5), 353–363.
MONARE. (2022). Renewable purchase obligations. Available online at https://rpo.gov.in/Home/Objective [Accessed on 27th June 2023 at 4.00 PM]
Mor, S., Ravindra, K., De Visscher, A., Dahiya, R. P., & Chandra, A. (2006). Municipal solid waste characterization and its assessment for potential methane generation: A case study. Science of the Total Environment, 371(1–3), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2006.04.014
Mou, Z., Scheutz, C., & Kjeldsen, P. (2015). Evaluation and application of site-specific data to revise the first-order decay model for estimating landfill gas generation and emissions at Danish landfills. Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association, 65(6), 686–698. https://doi.org/10.1080/10962247.2015.1008653Myers,S.S.(2009).Globalenvironmentalchange:Thethreattohumanhealth(Vol.181).WorldwatchInstitute
Myers, S. S. (2009). Global environmental change: the threat to human health (Vol. 181). World Watch Institute.
Nath, S., & Siddiqui, A. R. (2018). Distribution and moisture content of municipal solid waste in different wards of Kanpur city. India. the Pharma Innovation Journal, 7(7), 989–992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2016.07.014
Njoku, P. O., Odiyo, J. O., Durowoju, O. S., & Edokpayi, J. N. (2018). A review of landfill gas generation and utilisation in Africa. Open Environmental Sciences, 10(1), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.2174/1876325101810010001
Nozarpour, A., & Tavakoli, O. (2023). Evaluation of biogas production rate and leachate treatment in landfill through a water-energy Nexus framework for integrated waste management. Energy Nexus, 100218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nexus.2023.100218
Prayas (Energy Group). (2021, July). ‘Electricity Consumption Patterns’, part of blog-series on smart meter data collected under the eMARC initiative, Available online at https://energy.prayaspune.org/our-work/article-and-blog/electricity-consumption-patterns#:~:text=On%20an%20average%2C%20the%20household,and%20205%20kWh%20in%20Gonda. [Accessed on 17th August 11.40 PM]
Rafey, A., & Siddiqui, F. Z. (2023). Modelling and simulation of landfill methane model. Cleaner Energy Systems, 100076. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cles.2023.100076
Ramprasad, C., Teja, H. C., Gowtham, V., & Vikas, V. (2022). Quantification of landfill gas emissions and energy production potential in Tirupati Municipal solid waste disposal site by LandGEM mathematical model. MethodsX, 9, 101869. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mex.2022.101869
Rana, R., Choudhary, A., Yangzom, K., & Kumar, K. (2022). Estimation of methane generation from municipal solid waste of Mohali landfill site. In Advances in construction materials and sustainable environment (pp. 585–595). Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-6557-8_48
Rana, R., Ganguly, R., & Kumar Gupta, A. (2017). Evaluation of solid waste management in satellite towns of Mohali and Panchkula-India. Journal of Solid Waste Technology and Management, 43(4), 280–294. https://doi.org/10.5276/JSWTM.2017.280
Scarlat, N., Motola, V., Dallemand, J. F., Monforti-Ferrario, F., & Mofor, L. (2015). Evaluation of energy potential of municipal solid waste from African urban areas. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 50, 1269–1286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.05.067
Scharff, H., & Jacobs, J. (2006). Applying guidance for methane emission estimation for landfills. Waste Management, 26(4), 417–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2005.11.015
Sharma, A., Ganguly, R., & Gupta, A. K. (2018). Matrix method for evaluation of existing solid waste management system in Himachal Pradesh, India. Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management, 20(3), 1813–1831. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-018-0703-z
Sharma, A., Ganguly, R., & Gupta, A. K. (2019). Characterization and energy generation potential of municipal solid waste from nonengineered landfill sites in Himachal Pradesh, India. Journal of Hazardous, Toxic, and Radioactive Waste, 23(4), 04019008. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HZ.2153-5515.0000442
Singh M., (2015). Waste disposal management and resource generation: A case study of Kanpur Metropolis. International Journal of Interdisciplinary Research in Science Society and Culture, 1(1),
Singh, S. K., Anunay, G., Rohit, G., Shivangi, G., & Vipul, V. (2016). Greenhouse gas emissions from landfills: A case of NCT of Delhi, India. Journal of Climatology & Weather Forecasting, 1–6. https://doi.org/10.4172/2332-2594.1000157
Singh, C. K., Kumar, A., & Roy, S. S. (2018). Quantitative analysis of the methane gas emissions from municipal solid waste in India. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-21326-9
Singh, D., Chavan, D., Pandey, A. K., Periyaswami, L., & Kumar, S. (2021). Determination of landfill gas generation potential from lignocellulose biomass contents of municipal solid waste. Science of The Total Environment, 785, 147243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147243
Srivastava, A. N., & Chakma, S. (2020). Quantification of landfill gas generation and energy recovery estimation from the municipal solid waste landfill sites of Delhi, India. Energy Sources, Part A: Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2020.1754970
Tolaymat, T. M., Green, R. B., Hater, G. R., Barlaz, M. A., Black, P., Bronson, D., & Powell, J. (2010). Evaluation of landfill gas decay constant for municipal solid waste landfills operated as bioreactors. Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association, 60(1), 91–97. https://doi.org/10.3155/1047-3289.60.1.91
Vu, H. L., Ng, K. T. W., & Richter, A. (2017). Optimization of first order decay gas generation model parameters for landfills located in cold semi-arid climates. Waste Management, 69, 315–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.08.028
Yedla, S. (2005). Modified landfill design for sustainable waste management. International Journal of Global Energy Issues, 23(1), 93–105. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJGEI.2005.006412
Zhao, H., Themelis, N., Bourtsalas, A., & McGillis, W. R. (2019). Methane emissions from landfills. Columbia University. https://secureservercdn.net/198.71, 233.
Zia, H., & Devadas, V. (2007). Municipal solid waste management in Kanpur, India: obstacles and prospects. Management of Environmental Quality: An International Journal, 18(1), 89–108. https://doi.org/10.1108/14777830710717749
Zia, H., & Devadas, V. (2008). Urban solid waste management in Kanpur: Opportunities and perspectives. Habitat International, 32(1), 58–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2007.08.001
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the different researchers whom the authors have referred, authorities of Kanpur Municipal Corporation (KMC), Kanpur Development Authority (KDA) for their help with suitable data utilized in the analysis. The authors are also thankful to the editor and reviewers for their comments for improvement of the manuscript. No financial assistance was received for the study
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SC: conceptualization, data collection and analysis, initial draft of manuscript. RG: conceptualization, supervision, draft manuscript writing and editing. DP: writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chandra, S., Ganguly, R. & Parmar, D. Assessment of gas generation and energy recovery from municipal solid waste in Kanpur city, India. Environ Monit Assess 195, 1107 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11727-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11727-3