Abstract
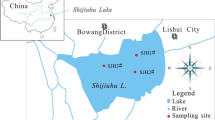
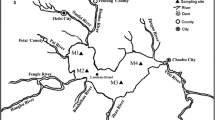
There are few studies on the simultaneous behavior of chromium (Cr), molybdenum (Mo), and tungsten (W) belonging to group VIB of the periodic table. Herein, based on high-resolution dialysis (HR-Peeper) and diffusive gradients in thin films (DGT) technology, the vertical distribution characteristics of DGT-labile and soluble Cr, Mo, and W in two lakes of Nansi Lake (Weishan Lake and Dushan Lake) were analyzed. In addition, the net diffusion fluxes and R-value (CDGT/Csol) were used to evaluate the mobility and release risk of metals at the sediment-water interface. The results showed that the DGT-labile concentrations of the three metal elements (Cr, Mo, and W) in Weishan Lake were higher than those in Dushan Lake, both in overlying water and sediment. This is mainly due to the dredging of the Dushan Lake area, which can permanently remove the polluted sediment in the lake. Meanwhile, the exogenous input is relatively high near the tourist area of Weishan Island. The net diffusion fluxes indicate that the W has a potential release risk of diffusion to the overlying water in Dushan Lake. The release of Cr, Mo, and W is thought to be related to the reductive dissolution of Fe/Mn (hydr)oxides based on Pearson correlation coefficients. The R-values of Cr and W indicate that Cr and W belong to the partial continuity case. The R-value of Mo was lower than the minimum value, meaning that Mo belongs to the single diffusion type and it is difficult for Mo sediments to supply pore water.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Bae, S., Yoon, S., Kaplan, U., Kim, H., Han, S., & Lee, W. (2020). Effect of groundwater ions on removal of hexavalent chromium by Fe(II)-phosphate mineral. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 398(prepublish). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122948
Beutel, M. W., Leonard, T. M., Dent, S. R., & Moore, B. C. (2007). Effects of aerobic and anaerobic conditions on P, N, Fe, Mn, and Hg accumulation in waters overlaying profundal sediments of an oligo-mesotrophic lake. Water Research, 42(8). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.11.027
Bing, H., Zhou, J., Wu, Y., Wang, X., Sun, H., & Li, R. (2016). Current state, sources, and potential risk of heavy metals in sediments of Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Environmental Pollution, 214, 485–496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.04.062
Cai, Y., Wang, B., Pan, F., Fu, Y., Guo, W., Guo, Z., & Liu, H. (2022). Effects of manganese, iron and sulfur geochemistry on arsenic migration in the estuarine sediment of a small river in Xiamen. Southeast China. Environmental Pollution, 293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118570
Cao, Q., Song, Y., Zhang, Y., Wang, R., & Liu, J. (2017). Risk analysis on heavy metal contamination in sediments of rivers flowing into Nansi Lake. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(35), 26910–26918. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4655-8
Chen, C. E., Chen, W., Ying, G. G., Jones, K. C., & Zhang, H. (2015). In situ measurement of solution concentrations and fluxes of sulfonamides and trimethoprim antibiotics in soils using o-DGT. Talanta, 132, 902–908. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2014.08.048
Chen, M., Cui, J., Lin, J., Ding, S., Gong, M., Ren, M., & Tsang, D. C. W. (2018). Successful control of internal phosphorus loading after sediment dredging for 6 years: A field assessment using high-resolution sampling techniques. Science of the Total Environment, 616, 927–936. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.227
Davison, W., Zhang, H., & Grime, G. W. (1994). Performance characteristics of gel probes used for measuring the chemistry of pore waters. Environmental Science Technology, 28(9), 1623–1632. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00058a015
Gao, L., Gao, B., Peng, W., Xu, D., & Yin, S. (2018). Assessing potential release tendency of As, Mo and W in the tributary sediments of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.08.036
Guan, D., Williams, P. N., Luo, J., Zheng, J. L., Xu, H. C., Cai, C., & Ma, L. Q. (2015). Novel precipitated zirconia-based DGT technique for high-resolution imaging of oxyanions in waters and sediments. Environmental Science & Technology, 49(6). https://doi.org/10.1021/es505424m
Guo, H., Yang, L., Han, X., Dai, J., Pang, X., Ren, M., & Zhang, W. (2019). Distribution characteristics of heavy metals in surface soils from the western area of Nansi Lake, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191(5). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7390-7
Guo, S., Zhang, Y., Xiao, J., Zhang, Q., Ling, J., Chang, B., & Zhao, G. (2021). Assessment of heavy metal content, distribution, and sources in Nansi Lake sediments, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(24), 30929–30942. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12729-9
Han, S., Naito, W., Hanai, Y., & Masunaga, S. (2013). Evaluation of trace metals bioavailability in Japanese river waters using DGT and a chemical equilibrium model. Water Research, 47(14), 4880–4892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.05.025
Harper, M. P., Davison, W., & Tych, W. (2000). DIFS - A modelling and simulation tool for DGT induced trace metal remobilisation in sediments and soils. Environmental Modelling & Software, 15(1), 55–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1364-8152(99)00027-4
He, Y., Guo, C., Lv, J., Hou, S., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Y., & Xu, J. (2018). Predicting trace metal bioavailability to chironomids in sediments by diffusive gradients in thin films. Science of the Total Environment, 636, 134–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.285
Jin, Z. F., Ding, S. M., Sun, Q., Gao, S. S., Fu, Z., Gong, M. D., Lin, J., Wang, D., & Wang, Y. (2019). High resolution spatiotemporal sampling as a tool for comprehensive assessment of zinc mobility and pollution in sediments of a eutrophic lake. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 364, 182–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.09.067
Jobby, R., Jha, P., Yadav, A. K., & Desai, N. (2018). Biosorption and biotransformation of hexavalent chromium Cr(VI) : A comprehensive review. Chemosphere, 207, 255–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.05.050
Jun, L., Hao, Z., Fang-Jie, Z., & William, D. (2010). Distinguishing diffusional and plant control of Cd and Ni uptake by hyperaccumulator and nonhyperaccumulator plants. Environmental science & technology, 44(17). https://doi.org/10.1021/es100371d
Karimian, N., & Cox, F. R. (1978). Adsorption and extractability of molybdenum in relation to some chemical properties of soil 1. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 42(5). https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1978.03615995004200050021x
Kekesi, T., Torok, T. I., & Isshiki, M. (2005). Anion exchange of chromium, molybdenum and tungsten species of various oxidation states, providing the basis for separation and purification in HCl solutions. Hydrometallurgy, 77(1-2), 81–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2004.10.012
Kelly, A. D. R., Lemaire, M., Young, Y. K., Eustache, J. H., Guilbert, C., Molina, M. F., & Mann, K. K. (2013). In vivo tungsten exposure alters B-cell development and increases DNA damage in murine bone marrow. Toxicological Sciences, 131(2), 434–446. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfs324
Li, C., Ding, S., Yang, L., Wang, Y., Ren, M., Chen, M., Fan, X., & Lichtfouse, E. (2019). Diffusive gradients in thin films: Devices, materials and applications. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 17(2), 801–831. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-018-00839-9
Liu, E., Shen, J., Yang, L., Zhang, E., Meng, X., & Wang, J. (2010). Assessment of heavy metal contamination in the sediments of Nansihu Lake Catchment, China. Environmental monitoring and assessment, 161(1-4), 217–227. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0739-y
Ma, X., Li, C., Yang, L., Ding, S., Zhang, M., Zhang, Y., & Zhao, T. (2020). Evaluating the mobility and labile of As and Sb using diffusive gradients in thin-films (DGT) in the sediments of Nansi Lake, China. Science of The Total Environment, 713, 136569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136569
Norgbey, E., Li, Y., Zhu, Y., Nwankwegu, A. S., Bofah-Buah, R., Nuamah, L., & Pu, Y. (2021). Combined use of high-resolution dialysis, diffusive gradient in thin films (DGT) technique, and conventional methods to assess trace metals in reservoir sediments. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 193(8), 469. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09247-z
Pang, X., Dai, J., Hu, X., Song, Z., Yu, C., Chen, L., Zhang, H., Liu, H., Wang, H., Wang, Z., Zhao, X., Zeng, X., & Ren, W. (2018). Background values of soil geochemistry in Shandong Province. Shandong Land and Resources, 34(1), 39–43.
Sangi, M. R., Halstead, M. J., & Hunter, K. A. (2002). Use of the diffusion gradient thin film method to measure trace metals in fresh waters at low ionic strength. Analytica Chimica Acta, 456(2), 241–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0003-2670(02)00012-0
Song, Z., Dong, L., Shan, B., & Tang, W. (2018). Assessment of potential bioavailability of heavy metals in the sediments of land-freshwater interfaces by diffusive gradients in thin films. Chemosphere, 191, 218–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.10.048
Strigul, N., Koutsospyros, A., & Christodoulatos, C. (2009). Tungsten speciation and toxicity: Acute toxicity of mono- and poly-tungstates to fish. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 73(2). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2009.08.016
Sun, Q., Zhang, L., Ding, S., Li, C., Yang, J., Chen, J., & Wang, P. (2015). Evaluation of the diffusive gradients in thin films technique using a mixed binding gel for measuring iron, phosphorus and arsenic in the environment. Environmental Science-Processes & Impacts, 17(3), 570–577. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4em00629a
Tang, W., Duan, S., Shan, B., Zhang, H., Zhang, W., Zhao, Y., & Zhang, C. (2016). Concentrations, diffusive fluxes and toxicity of heavy metals in pore water of the Fuyang River, Haihe Basin. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 127, 80–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.01.013
Wang, L. F., Yang, L. Y., Kong, L. H., Li, S., Zhu, J. R., & Wang, Y. Q. (2014). Spatial distribution, source identification and pollution assessment of metal content in the surface sediments of Nansi Lake, China. Journal Of Geochemical Exploration, 140, 87–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2014.02.008
Wang, W., Wang, S., Chen, J., Jiang, X., & Zheng, B. (2019). Combined use of diffusive gradients in thin film, high-resolution dialysis technique and traditional methods to assess pollution and bioavailability of sediment metals of lake wetlands in Taihu Lake Basin. Science of the Total Environment, 671, 28–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.053
Wang, Y., Ding, S., Gong, M., Xu, S., Xu, W., & Zhang, C. (2016). Diffusion characteristics of agarose hydrogel used in diffusive gradients in thin films for measurements of cations and anions. Analytica Chimica Acta, 945, 47–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2016.10.003
Wang, Y., Ding, S., Shi, L., Gong, M., Xu, S., & Zhang, C. (2017). Simultaneous measurements of cations and anions using diffusive gradients in thin films with a ZrO-Chelex mixed binding layer. Analytica Chimica Acta, 972, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2017.04.007
Wei, T., Guan, D., Fang, W., & Luo, J. (2018). Theory and application of diffusive gradients in thin-films (DGT) in the environment III: Theoretical basis and application potential in phytoavailability assessment. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 35(7), 841–849. https://doi.org/10.11654/jaes.2018-0341
WHO. (2008). Guidelines for Drinking-water. IWA Publishing.
Wu, Z., Jiang, X., Wang, S., Zhao, L., Jiao, L., Chen, J., Cai, Q., Wang, K., & Yao, C. (2021). Mobilization and geochemistry of nutrients in sediment evaluated by diffusive gradients in thin films: Significance for lake management. Journal of Environmental Management, 292. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVMAN.2021.112770
Wu, Z., Jiao, L., Wang, S., & Xu, Y. (2016). Multi-metals measured at sediment-water interface (SWI) by diffusive gradients in thin films (DGT) technique for geochemical research. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 70(2), 429–437. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-015-0184-1
Wu, Z., & Wang, S. (2017). Release mechanism and kinetic exchange for phosphorus (P) in lake sediment characterized by diffusive gradients in thin films (DGT). Journal of Hazardous Materials, 331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.02.024
Xu, D., Wu, W., Ding, S., Sun, Q., & Zhang, C. (2012). A high-resolution dialysis technique for rapid determination of dissolved reactive phosphate and ferrous iron in pore water of sediments. Science of The Total Environment, 421, 245–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.01.062
Xu, J., Zhang, J., Huo, S., Xi, B., He, Z., & Xu, Y. (2017). High-resolution profiles of trace metals assessed by DGT techniques in lake sediment porewaters. Environmental Earth Sciences, 76(8). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6642-5
Xu, N., Braida, W., Christodoulatos, C., & Chen, J. (2013). A review of molybdenum adsorption in soils/bed sediments: Speciation, mechanism, and model applications. Soil & Sediment Contamination, 22(8), 912–929. https://doi.org/10.1080/15320383.2013.770438
Yang, P., & Wang, S. (2021). Sorption and speciation of molybdate in soils: Implications for molybdenum mobility and availability. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 408. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2020.124934
Yin, H. B., Cai, Y. J., Duan, H. T., Gao, J. F., & Fan, C. X. (2014). Use of DGT and conventional methods to predict sediment metal bioavailability to a field inhabitant freshwater snail (Bellamya aeruginosa) from Chinese eutrophic lakes. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 264, 184–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.11.030
You, N., Feng, Z. M., Wang, Y., Fan, H. T., & Sun, T. (2018). Carbon nanodot aqueous binding phase-based diffusive gradients in thin films device for measurement of dissolved copper and lead species in the aquatic environment. Analyst, 143(22), 5568–5577. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8an00612a
Yuan, H., Tai, Z., Li, Q., & Liu, E. (2020). In-situ, high-resolution evidence from water-sediment interface for significant role of iron bound phosphorus in eutrophic lake. Science of The Total Environment, 706(C). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136040
Zhang, C., Ding, S., Xu, D., Tang, Y., & Wong, M. H. (2014). Bioavailability assessment of phosphorus and metals in soils and sediments: A review of diffusive gradients in thin films (DGT). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 186(11), 7367–7378. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3933-0
Zhang, M., Li, C., Yang, L., Ding, S., Ma, X., Zhang, Y., & Zhao, T. (2020). Application of DGT/DIFS combined with BCR to assess the mobility and release risk of heavy metals in the sediments of Nansi Lake. China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 42(11), 3765–3778. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00638-8
Zhuang, W., & Gao, X. (2013). Acid-volatile sulfide and simultaneously extracted metals in surface sediments of the southwestern coastal Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea: Concentrations, spatial distributions and the indication of heavy metal pollution status. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 76(1-2), 128–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2013.09.016
Acknowledgements
I would like to express my gratitude to the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42177385) for its support of this research, as well as my lab mates and teachers for their continued support and encouragement to carry out this research.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42177385).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Jin Wang, Liyuan Yang, Dan Shi. Methodology: Jin Wang. Formal analysis and investigation: Jin Wang. Writing—original draft preparation: Jin Wang, Danshi. Writing—review and editing: Jin Wang, Dan Shi, Xin Ma, Liyuan Yang, Shiming Ding, Enfeng Liu. Funding acquisition: Enfeng Liu. Resources: Liyuan Yang. Supervision: Liyuan Yang.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Shi, D., Ma, X. et al. Application of high-resolution techniques in the assessment of the mobility of Cr, Mo, and W at the sediment-water interface of Nansi Lake, China. Environ Monit Assess 195, 980 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11567-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11567-1