Abstract
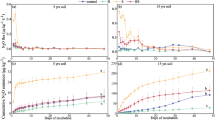
Monitoring and quantification of nutrient movement in soils could help farmers and policy makers to formulate effective nutrient loss reduction strategies and waste management. The study was conducted to monitor and quantify vertical and lateral movements of nitrate-nitrogen (NO3-N), phosphate (PO4) and sulphate-sulphur (SO4-S) in soils around manure dumpsites in Abeokuta, southwest Nigeria. The dumpsites investigated include a flush-type poultry litter, poultry litter mixed with beddings of wood shavings and cattle and pig waste open dumpsites. Soils were sampled at depths of 0–20, 20–40, 40–60 and 60–80 cm and at distances 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 20, 40, 60 and 80 m away from the dumpsites. Soil samples were analysed for some physical and chemical properties and NO3-N, PO4 and SO4-S contents. Results indicated that there were more nutrients in the soil around the poultry manure slurry dumpsite compared with others while the soil pH increased with increase in soil depth, across dump sites. There was evidence of leaching of salts, and this correlated positively with the soil organic matter content (r = 0.41, p < 0.01). The soils were polluted with NO3-N, PO4 and SO4-S as deep as 80-cm depth; these nutrient amounts were higher than the maximum allowable (40, 15 and 7 mg kg−1, respectively) for southwest Nigerian soils. Due to high soil organic matter and for agronomic considerations, the soils are only suitable for cultivation at depths below 40 cm and 8 m away from the dump sites. There was significant pollution of the soils with nitrate, phosphate and sulphate, within 80 m distance from the dump site. This has serious implications for ground water recharges and shallow well sunk around these areas. There is potential risk of NO3-N, PO4 and SO4-S consumption through such water sources.









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Data used for the study can be accessed by contacting the corresponding author.
References
Adepetu, J. A. (1986). Soil Fertility and Fertilizer Requirements in Oyo, Ogun and Ondo States of Nigeria. Federal Development of Agricultural Land Resources, p. 48.
Adetunji, M. T., & Adepetu, J. A. (1989). Sulphur fertilization requirements of Southwestern Nigerian soils. Ife Journal of Agricultural Research, 11, 23–30.
Alves, M. E., & Lavorenti, A. (2004). Sulfate adsorption and its relationships with properties of representative soils of the São Paulo State, Brazil. Geoderma, 118, 89–99.
Amin, M. G. M., Al-Minhaj, A., Bhowmik, B., Deen-Islam, Md., & Islam, N. (2022). Nitrogen and phosphorus leaching and vegetative growth of maize as affected by organic manure application Eurasian. Journal of Soil Science, 11(1), 17–24.
Amin, M. G. M., Bech, T. B., Forslund, A., Hansen, M., Petersen, S. O., & Lægdsmand, M. (2014). Redistribution and persistence of microorganisms and steroid hormones after soil-injection of swine slurry. Science of the Total Environment, 466(467), 1003–1010.
Amin, M. G. M., Karsten, H. D., Veith, T. L., Beegle, D. B., & Kleinman, P. J. A. (2018). Conservation dairy farming impact on water quality in a karst watershed in northeastern US. Agricultural Systems, 165, 187–196.
Azeez, J., Aghorunse, A., Bankole, G., Anamezeonye, M., Adegbite, T., & AbdulAzeez, S. (2021). Soil phosphorus availability indices and saturation ratio as an index of environmental risk assessment. Jordan Journal of Earth and Environmental Sciences., 12(3), 269–274.
Azeez, J. O., Adekunle, I. O., Atiku, O. O., Akande, K. B., & Jamiu-Azeez, S. O. (2009). Effect of nine years of animal waste deposition on profile distribution of heavy metals in Abeokuta, south-western Nigeria and its implication for environmental quality. Waste Management, 29, 2582–2586.
Azeez, J. O., & Van Averbeke, W. (2010a). Nitrogen mineralization potential in a sandy clay loam soil amended with three animal manures. Bioresource Technology, 101, 5645–5651.
Azeez, J. O., & Van Averbeke, W. (2010b). Fate of manure phosphorus in a weathered sandy clay loam soil amended with three animal manures. Bioresource Technology, 101, 6584–6588.
Bloem, E., Haneklaus, S., Sparovek, G., & Schnug, E. (2001). Spatial and temporal variability of sulfate concentration in soils. Communication in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 32, 1391–1403.
Bouyoucos, G. H. (1962). Hydrometer method for making particle size analysis of soils. Agronomy Journal, 54, 464–465.
Cichota, R., Vogeler, I., Bolan, N. S., Clothier, B., & Scotter, D. R. (2004). Sulphate leaching through two contrasting New Zealand soils. Third Australian New Zealand Soils Conference, 5 – 9 December 2004, University of Sydney, Australia.
Crowther, J., Kay, D., & Wyer, M. D. (2002). Faecal-indicator concentrations in waters draining lowland pastoral catchments in the UK: Relationships with land use and farming practices. Water Research, 36(7), 1725–1734.
Gerba, C. P., & Smith, J. E. (2005). Sources of pathogenic microorganisms and their fate during land application of wastes. Journal of Environmental Quality, 34, 42–48.
ILMM policy. (2015). Draft national integrated livestock manure management (ILMM) policy, Ministry of Fisheries and Livestock, Government of the people’s republic of Bangladesh. Available at [Access date: 26.12.2020].
Jackson, M. L. (1973). Soil chemical analysis practice Hall Inc. 86–92. New York: Englewood Cliffs.
Kokulan, V., Akinremi, O. O., & Moulin, A. P. (2022a). The seasonality of nitrate and phosphorus leaching from manure and chemical fertilizer added to a chernozemic soil in Canada. Journal of Environmental Quality, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1002/jeq2.20399
Kokulan, V., Ige, D., & Akinremi, O. O. (2022b). Agri-environmental implications of N and P based manure application to perennial and annual cropping systems. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 122, 205–218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-021-10187-w
Ksheem, A. M., Bennett, J. M., Antille, D. L., & Raine, S. R. (2015). Towards a method for optimized extraction of soluble nutrients from fresh and composted chicken manures. Waste Management, 45, 76–90.
Lehrsch, G. A., & Kincaid, D. C. (2007). Compost and manure effects on fertilized corn silage and nitrogen uptake under irrigation. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 38, 2131–2147.
Mclean, E. O. (1982). Methods of soil analysis, part 2. In A. Klute, G. S. Campbell, & R. D. Jackson (Eds.), Soil pH and lime requirement (pp. 199–224). American Society of Agronomy.
Mohamed, M. N., Wellen, C., Parsons, C. T., Taylor, W. D., Arhonditsis, G., Chomicki, K. M., Boyd, D., Weidman, P., Mundle, S. O. C., Van Cappellen, P., Sharpley, A. N., & Haffner, D. G. (2019). Understanding and managing the re-eutrophication of Lake Erie: knowledge gaps and research priorities. Freshwater Science, 38, 675–691. https://doi.org/10.1086/705915
Nair, V. D. (2014). Soil phosphorus saturation ratio for risk assessment in land use systems. Frontiers in Environmental Science. Mini Review, 2(6), 1–4. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2014.00006
Nelson, D. W., & Sommer, L. E. (1996) Total carbon, organic carbon, and organic matter. In: Spark, D.L., Ed., Method of Soil Analysis, Part 3, American Society of Agronomy, 34, 961–1010.
Norring, N. P., & Jørgensen, E. (2009). Eutrophication and agriculture in Denmark: 20 years of experience and prospects for the future. In: Eutrophication in Coastal Ecosystems. Developments in Hydrobiology. Andersen, J.H., Conley, D.J. (Eds.). Vol 207. Springer, Dordrecht. pp. 65–70.
Sainju, U. M. (2017). Determination of nitrogen balance in agroecosystems. MethodsX, 4, 199–208.
Schindler, D. W., Hecky, R. E., & McCullough, G. K. (2012). The rapid eutrophication of Lake Winnipeg: Greening under global change. Journal of Great Lakes Research, 38, 6–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jglr.2012.04.003
Tian, Y. Q., Gong, P., Radke, J. D., & Scarborough, J. (2002). Spatial and temporal modeling of microbial contaminants on grazing farmlands. Journal of Environmental Quality, 31(3), 860–869.
Williams, M. R., King, K. W., Duncan, E. W., Pease, L. A., & Penn, C. J. (2018). Fertilizer placement and tillage effects on phosphorus concentration in leachate from fine-textured soils. Soil and Tillage Research, 178, 130–138.
Xia, L., Lam, S. K., Yan, X., & Chen, D. (2017). How does recycling of livestock manure in agroecosystems affect crop productivity, reactive nitrogen losses, and carbon balance? Environmental Science & Technology, 51, 7450–7457.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jamiu Oladipupo Azeez conceived, planned and supervised the execution of the research. He also wrote the manuscript. Ganiyu Olawale Bankole supervised the field works and laboratory analyses. He also did the data analysis and proofread the manuscript drafts. Justice Omonigho did the implementation of the field works, laboratory analyses and data entry under the supervision of Azeez and Bankole.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All authors have read, understood, and have complied as applicable with the statement on “Ethical responsibilities of authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Azeez, J.O., Bankole, G.O. & Omonigho, J. Vertical and lateral movements of nitrate, phosphate and sulphate in soils around manure dumpsites and the potential environmental implications. Environ Monit Assess 195, 907 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11520-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11520-2