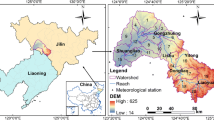
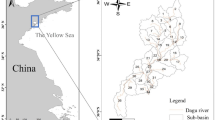
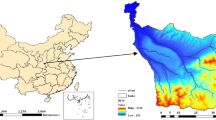
Abstract
Tuojiang River watershed is an economically developed and densely populated area in Sichuan Province (southwest of China), which is also an important tributary of the Yangtze River. Nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) are the main pollutants affecting water quality, but there is still lack of study on the spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of these two pollutants. In this study, the typical non-point source pollution loads in the Tuojiang River watershed are simulated by Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) model, and the spatial autocorrelation method is used to reveal the spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of the pollution loads from the annual average and water periods. Combined with redundancy analysis (RDA) and geographically weighted regression (GWR) analysis, the main driving factors affecting the typical non-point source pollution loads in the Tuojiang River watershed are discussed from the global and local perspectives. The results show that (1) from different water periods, the pollution loads of total nitrogen (TN) and total phosphorus (TP) in three water periods show obviously different, is the highest in the abundant water period, with 323.4 kg/ha and 47.9 kg/ha, followed by the normal water period, with 95.7 kg/ha and 14.1 kg/ha, and the lowest in the dry water period, with 28.4 kg/ha and 4.2 kg/ha. The annual average value of TN pollution load is higher than that of TP, with 447.5 kg/ha and 66.1 kg/ha, respectively; (2) the TN and TP pollution loads are stable on the whole, and the overall level in the middle reaches is higher. The pollution loads of Shifang City and Mianzhu City are higher in all three water periods. (3) Elevation and slope are two main driving factors affecting the TN and TP pollution loads in the Tuojiang River watershed. Therefore, the visualization and quantification of temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of typical non-point source pollution loads in the Tuojiang River watershed are helpful to provide the basis for scientific prevention and control of pollution in the Tuojiang River watershed and are of great significance to promote the sustainable, coordinated, and healthy development of water environment and economy in the watershed.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets and materials used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Arnold, J. G., Srinivasan, R., Muttiah, R. S., & Williams, J. R. (1998). Large area hydrologic modeling and assessment part I: Model development. Journal of the American Water Resources Association., 34(1), 73–89. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1752-1688.1998.tb05961.x
Brunsdon, C., Fotheringham, A. S., & Charlton, M. (1998). Spatial nonstationarity and autoregressive models. Environment and Planning a: Economy and Space., 30(6), 957–973. https://doi.org/10.1068/a300957
Chen, Y. Y., Yu, H., Xiang, Q. S., & Yang, P. (2015). Tuojiang river watershed water environment quality analysis. Sichuan Environment., 34(02), 85–89. https://doi.org/10.14034/j.cnki.schj.2015.02.018. (in Chinese).
Cheng, H., Lin, C., Wang, L., Xiong, J., Peng, L., & Zhu, C. (2020a). The influence of different forest characteristics on non-point source pollution: A case study at Chaohu Basin, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health., 17(5), 1790. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17051790
Cheng, Y. X., Wu, D. S., Bian, Y. (2020b). A systematic approach of determining compensation and allocation for river basin water environment based on total pollutants control. Journal of Environmental Management. 271, 110896. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110896
Ding, Y., Zhao, J. Y., Zhang, J., Fu, Y. C., Peng, W. Q., Chen, Q. C., & Li, Y. Y. (2021). Songhua lake eutrophication of water quality spatial differences and spatial autocorrelation analysis. Environmental Science., 42(05), 2232–2239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110896. (in Chinese).
Du, M., Liu, Q., Luo, B., & Zhang, D. (2016). Evaluation and analysis of present water environment quality of Minjiang & Tuojiang River basins. Sichuan Environment., 35(05), 20–25. https://doi.org/10.14034/j.cnki.schj.2016.05.004. (in Chinese).
Elken, A. B., Xu, H. L., Ling, H. B., & Bai, Y. (2013). Manas river watershed relationship of spatial distribution of land use and soil type. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences., 41(22), 9275–9280. https://doi.org/10.14034/j.cnki.schj.2016.05.004. (in Chinese).
Fan, M., Xiao, Y. T., Yao, J., Chen, S., & Zhao, L. (2022). Spatial distribution patterns of water environmental pollutions in Tuojiang River basin. Journal of Safety and Environment., 22(03), 1619–1632. https://doi.org/10.13637/j.issn.1009-6094.2021.0435. (in Chinese).
Feng, X. J., Lin, C., Xiong, J. F., Chen, X., Wu, Z. J., & Ma, R. H. (2023). Effects of non-point source pollution on lake nitrogen and phosphorus concentration: A case study of Chaohu Lake watershed. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment., 40(1), 64–75. https://doi.org/10.13254/j.jare.2021.0838. (in Chinese).
Feng, Z. H., Wang, L. Q., Peng, Q., Li, J., Liang, T. (2022). Effect of environmental factors on soil properties under different land use types in a typical basin of the North China Plain.Journal of Cleaner Production. 344, 131084.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131084
Giri, S., Arbab, N. N., Lathrop, R. G. (2019). Assessingthepotential impacts of climate and land use changeonwater fluxes and sediment transportina loosely coupled system.Journal of Hydrology. 57(C): 123955.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.123955
Gou, J. J., Miao, Q. Y., Xu, Z. X., & Duan, Q. Y. (2022). Large scale hydrological model parameter uncertainty analysis of the challenges and comprehensive research framework. Advances in Water Science., 33(02), 327–335. https://doi.org/10.14042/j.cnki.32.1309.2022.02.016. (in Chinese).
Grunwald, S., & Qi, C. (2006). GIS-based water quality modeling in the Sandusky watershed, Ohio, USA. Journal of the American Water Resources Association., 42(4), 957–973. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1752-1688.2006.tb04507.x
Komárková, J., Komárek, O., & Hejzlar, J. (2003). Evaluation of the long term monitoring of phytoplankton assemblages in a canyon-shape reservoir using multivariate statistical methods. Hydrobiologia, 504, 143–157. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:HYDR.0000008514.45771.aa
Li, S., Wang, H. Q., Wang, G. Q., Peng, Y. B., & Han, Z. L. (2020). Study on relationship between non-point source pollution and precipitation in Xiaoqinghe River Watershed. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering., 51(1), 147–158. https://doi.org/10.13928/j.cnki.wrahe.2020.01.017. (in Chinese).
Li, J. L., Sun, R. H., Xiong, M. Q., & Yang, G. C. (2020). Estimation of soil erosion based on the RUSLE model in China. Acta Ecologica Sinica., 40(10), 3473–3485. https://doi.org/10.5846/stxb201903290610. (in Chinese).
Li, W. C., Lei, Q. L., Zhai, L. M., Liu, H. B., Hu, W. L., Liu, S., & Ren, T. Z. (2018). Seasonal changes of the pathways of nitrogen export from an agricultural watershed in China. Environmental Science., 39(12), 5375–5382. https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.201805008. (in Chinese).
Liu, D. D., Bai, L, Qiao, Q., Zhang, Y., Li, X. Y., Zhao, R. N., Liu, J. Y. (2021). Anthropogenic total phosphorus emissions to the Tuojiang River Basin, China.Journal of Cleaner Production. 294, 126325.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126325
Liu, Y., Qi, Y. K., Liu, S. J., & Li, Y. X. (2016). Analysis and control strategy of point source pollution in Qilu Lake watershed. Environmental Science Survey., 35(01), 26–30. https://doi.org/10.13623/j.cnki.hkdk.2016.01.008. (in Chinese).
Ma R, Cheng K, Guo YY, Liu XQ, Li L, Niu Y (2020) Study on spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of agricultural non-point source nitrogen pollution in Shiwen River Basin based on SWAT model. Soil And Water Conservation In China. 07: 61–64. https://doi.org/10.14123/j.cnki.swcc.2020.0172. (in Chinese)
Marco, D. M., Mario, S., Massimiliano, Z., & Fabrizio, F. (2020). Understanding dominant controls on streamflow spatial variability to set up a semi-distributed hydrological model: The case study of the Thur catchment. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences., 24(3), 1319–1345. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-24-1319-2020
Mondal, A., Khare, D., Kundu, S., Meena, P. K., Mishra, P. K., & Shukla, R. (2014). Impact of climate change on future soil erosion in different slope, land use, and soil-type conditions in a part of the Narmada River Basin, India. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering., 20(6), C5014003. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0001065
Monika, S., Hans-Peter, B., & Ruth, S. (2009). Modeling the contribution of point sources and non-point sources to Thachin River water pollution. Science of the Total Environment., 407(17), 4902–4915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.05.007
Nikolic, G., Spalevic, V., Curovic, M., Khaledi Darvishan, A., Skataric, G., Pajic, M., Kavian, A., & Tanaskovik, V. (2018). Variability of soil erosion intensity due to egetation cover changes: Case study of Orahovacka Rijeka, Montenegro. Notulae Botanicae Horti Agrobotanici Cluj-Napoca., 47(1), 237–248. https://doi.org/10.15835/nbha47111310
Qiao, S. S., Wu, L., & Peng, M. L. (2018). Simulation of runoff, sediment, nitrogen and phosphorus loss on bare loess sloping land using simulated rainfall. Research of Environmental Sciences., 31(10), 1728–1735. https://doi.org/10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2018.05.05. (in Chinese).
Rallapalli, S., Ajit, P. S., Kunal, D., Chirag, G. (2020). An evidence based integrated watershed modelling system to assess the impact of non-point source pollution in the riverine ecosystem.Journal of Cleaner Production. 246(C): 118963.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118963
Santhi, C., Arnold, J. G., Williams, J. R., Dugas, W. A., Srinivasan, R., & Hauck, L. M. (2001). Validation of the SWAT model on a large river basin with point and nonpoint sources. Journal of the American Water Resources Association., 37, 1169–1188. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1752-1688.2001.tb03630.x
Sun, W. Y., Shao, Q. Q., Liu, J. Y., & Zhai, J. (2014). Assessing the effects of land use and topography on soil erosion on the Loess Plateau in China. Catena, 121, 151–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2014.05.009
Wang, H., Xu, Y. L., Zhang, Q., Lin, C. W., Zhai, L. M., Liu, H. T., & Pu, B. (2020). Emission characteristics of nitrogen and phosphorus in a typical agricultural small watershed in Tuojiang river basin. Environmental Science., 41(10), 4547–4554. https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.202003213. (in Chinese).
Wang, W. Z., Cheng, Y., Ao, T. Q., & Li, X. D. (2018). Simulation of non-point source pollution in Gulin River watershed based on SWAT model. China Rural Water and Hydropower., 10, 32-36+42. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1007-2284.2018.10.007. (in Chinese).
Wang, X. Y., Qin, F. L., Ou, Y., & Xue, Y. F. (2008). SWAT-based simulation on non-point source pollution in the Northern watershed of Miyun reservoir. Journal of Agro-Environment Science., 27(3), 1098–1105. (in Chinese).
Wei, W. H., Hassan, M., Che, Y., Peng, Q. K., Su, Y., & Xie, B. (2019). Spatio-temporal characteristics and source apportionment of water pollutants in upper reaches of Maotiao River, Southwest of China, from 2003 to 2015. Journal of Environmental Informatics., 37(2), 93–106. https://doi.org/10.3808/jei.201900415
Wu, D., & Wang, Y. H. (2014). Dynamic performance evaluation of water resources management in seven river basin of China. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin., 23(01), 32–38. https://doi.org/10.11870/cjlyzyyhj201401005. (in Chinese).
Xiao, Y. T., Fan, M., Yao, J., Liang, X. Y., Cai, C., Wang, Y. Z., & Tu, W. G. (2023). Spatial and temporal characteristics of pollution loads in Tuojiang River watershed located in Sichuan Province, Southwest of China. Environment, Development and Sustainability. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-023-03147-7
Xu, J., Wang, Y. G., Chen, Y., Tong, H. J., Yao, W., & Hui, B. (2020). Temporal and spatial variation of surface water environmental quality in the Tuojiang River watershed of the upper Yangtze river. Earth Science., 45(06), 1937–1947. https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2020.012. (in Chinese).
Yao, J., Fan, M., Xiao, Y. T., Liang, X. Y., Cai, C., & Wang, Y. Z. (2023). Spatial-temporal characteristics of corrected total phosphorus pollution loads from agricultural non-point sources in Tuojiang River watershed, Sichuan Province of southwestern China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research., 30(14), 42192–42213. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11356-023-25244-W
Ye, K. M., Meng, M. S., Zhang, L. S., Yao, Z. P., Xue, H., Cheng, P. X., & Zhang, D. P. (2020). Songhua river watershed nitrogen in time and space distribution characteristics and source of analytical research. Research of Environmental Sciences., 33(04), 901–910. https://doi.org/10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2020.02.04. (in Chinese).
Zeng, Z., Luo, W. G., Wang, Z., & Yi, F. C. (2021). Water pollution and its causes in the Tuojiang River Basin, China: An artificial neural network analysis. Sustainability., 13(2), 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13020792
Zhang, F. W., Li, H. Q., Yi, L. B., Luo, F. L., Zhang, G. R., Wang, C. Y., Yang, Y. S., & Li, Y. N. (2022). Spatial response of topsoil organic carbon, total nitrogen, and total phosphor content of alpine meadows to grassland degradation in the Sanjiangyuan National Park. Acta Ecological Sinica., 42(14), 5586–5592. https://doi.org/10.5846/stxb202106111566. (in Chinese).
Zhang, M. J., Chen, C. H., & Guo, G. G. (2020). Spatial and temporal variation characteristics of water quality in Tuojiang River Basin ( Zigong City) from 2013 to 2018. Sichuan Environment., 39(02), 128–132. https://doi.org/10.14034/j.cnki.schj.2020.02.020. (in Chinese).
Zhang, Q., Shen, J. Q., Sun, F. H. (2021). Spatiotemporal differentiation of coupling coordination degree between economic development and water environment and its influencing factors using GWR in China’s province.Ecological Modelling. 462,109794.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2021.109794
Zhang, W., Sun, F. Y., Liu, M., & Li, C. L. (2017). Quantifying the relationships of impact factors on non-point source pollution using the boosted regression tree algorithm. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies., 26(1), 403–411. https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/64381
Zhao, W. W., Wei, H., Jia, L. Z., Daryanto, S., Zhang, X., & Liu, Y. X. (2018). Soil erodibility and its influencing factors on the Loess Plateau of China: A case study in the Ansai watershed. Solid Earth., 9(6), 1507–1516. https://doi.org/10.5194/se-9-1507-2018
Ziadat, F. M., & Taimeh, A. Y. (2013). Effect of rainfall intensity, slope, land use and antecedent soil moisture on soil erosion in an arid environment. Land Degradation & Development., 24(6), 582–590. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.2239
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the editors and reviewers for fundamental improvement of this manuscript.
Funding
This study is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 72003158, 41601088), Tuojiang River Watershed High-quality Development Research Center (TJGZL2022-06), and Key Research and Development Projects of Sichuan Science and Technology Plan (No. 2019YFS0057).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Yuanzhe Wang and Min Fan. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Yuanzhe Wang, was revised by Min Fan, Jing Yao, and Lele Zhou. The figures and tables of the manuscript were revised by Can Cai and Nanlan Zhong. The resubmitted manuscript was revised by Chunlin Hua.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Hua, C., Fan, M. et al. Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of typical pollution loads based on SWAT model across Tuojiang River watershed located in Sichuan Province, Southwest of China. Environ Monit Assess 195, 865 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11481-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11481-6