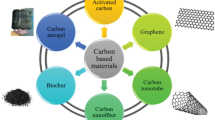
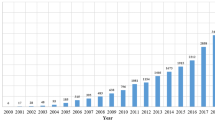
Abstract
Antimony (Sb) has been classified as a high-priority contaminant in the environment. Sb contamination resulting from the use of antimony-containing compounds in industry necessitates the development of efficient methods to remove it from water and wastewater. Adsorption is a highly efficient and reliable method for pollutants removal owing to its availability, recyclability, and low cost. Recently, carbonaceous materials and their applications for the removal of Sb from the aqueous matrices have received special attention worldwide. Herein, this review systematically summarizes the occurrence and exposure of Sb in the environment and on human health, respectively. Different carbon-based adsorbents have been classified for the adsorptive removal of Sb and their adsorption characteristics have been delineated. Recent development in the adsorption performance of the adsorbent materials for improving the Sb removal from the aqueous medium has been outlined. Further, to develop an understanding of the effect of different parameters like pH, competitive ions, and dissolved ions for Sb adsorption and subsequent removal have been discussed. A retrospective analysis of literature was conducted to present the adsorption behavior and underlying mechanisms involved in the removal of Sb using various adsorbents. Moreover, this study has identified emerging research gaps and emphasized the need for developing modified/engineered carbonaceous adsorbents to enhance Sb adsorption from various aqueous matrices.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data use in the current manuscript will be available in public domain and can be provided/shared on request.
References
Abhishek, K., Srivastava, A., Vimal, V., Gupta, A. K., Bhujbal, S. K., Biswas, J. K., Singh, L., Ghosh, P., Pandey, A., Sharma, P., & Kumar, M. (2022). Biochar application for greenhouse gas mitigation, contaminants immobilization and soil fertility enhancement: A state-of-the-art review. Science of The Total Environment, 853, 158562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.158562
Ahmad, M., Lee, S. S., Lim, J. E., Lee, S. E., Cho, J. S., Moon, D. H., & Ok, Y. S. (2014). Speciation and phytoavailability of lead and antimony in a small arms range soil amended with mussel shell, cow bone and biochar: EXAFS spectroscopy and chemical extractions. Chemosphere, 95, 433–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.09.077
Al Ghatta, A., Zhou, X., Casarano, G., Wilton-Ely, J. D., & Hallett, J. P. (2021). Characterization and valorization of humins produced by HMF degradation in ionic liquids: A valuable carbonaceous material for antimony removal. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 9(5), 2212–2223. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c07963
Ambika, S., Kumar, M., Pisharody, L., Malhotra, M., Kumar, G., Sreedharan, V., Singh, L., Nidheesh, P. V., & Bhatnagar, A. (2022). Modified biochar as a green adsorbent for removal of hexavalent chromium from various environmental matrices: Mechanisms, methods, and prospects. Chemical Engineering Journal, 439, 135716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.135716
Ambika, S., Kumar, M., Pisharody, L., Malhotra, M., Kumar, G., Sreedharan, V., Singh, L., Nidheesh, P.V., & Bhatnagar, A. (2022). Modified biochar as a green adsorbent for removal of hexavalent chromium from various environmental matrices: Mechanisms, methods, and prospects. Chemical Engineering Journal, 439, 135716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.135716
Anerao, P., Salwatkar, G., Kumar, M., Pandey, A. & Singh, L. (2022). Physical treatment for biochar modification: opportunities, limitations and advantages. In Engineered Biochar (pp. 49–64). Singapore: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-2488-0_4
Antoniadis, V., Golia, E. E., Liu, Y. T., Wang, S. L., Shaheen, S. M., & Rinklebe, J. (2019). Soil and maize contamination by trace elements and associated health risk assessment in the industrial area of Volos, Greece. Environment International, 124, 79–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.12.053
Bagherifam, S., Brown, T. C., Fellows, C. M., & Naidu, R. (2019). Bioavailability of arsenic and antimony in terrestrial ecosystems: A review. Pedosphere, 29(6), 681–720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2019.106348
Bai, Y., Tang, X., Sun, L., Yin, W., Hu, G., Liu, M., & Gong, Y. (2021). Application of iron-based materials for removal of antimony and arsenic from water: Sorption properties and mechanism insights. Chemical Engineering Journal, 431, 134143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.134143
Baskar, A. V., Bolan, N., Hoang, S. A., Sooriyakumar, P., Kumar, M., Singh, L., Jasemizad, T., Padhye, L.P., Singh, G., Vinu, A., & Sarkar, B. (2022). Recovery, regeneration and sustainable management of spent adsorbents from wastewater treatment streams: A review. Science of the Total Environment, 822, 153555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153555
Bolan, N., Hoang, S. A., Beiyuan, J., Gupta, S., Hou, D., Karakoti, A., Joseph, S., Jung, S., Kim, K. H., Kirkham, M. B., & Kua, H. W. (2022a). Multifunctional applications of biochar beyond carbon storage. International Materials Reviews, 67(2), 150–200. https://doi.org/10.1080/09506608.2021.1922047
Bolan, N., Kumar, M., Singh, E., Kumar, A., Singh, L., Kumar, S., Keerthanan, S., Hoang, S. A., El-Naggar, A., Vithanage, M., & Sarkar, B. (2022). Antimony contamination and its risk management in complex environmental settings: A review. Environment International, 158, 106908. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2021.106908
Cai, F., Ren, J., Tao, S., & Wang, X. (2016). Uptake, translocation and transformation of antimony in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings. Environmental Pollution, 209, 169–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2015.11.033
Calugaru, I. L., Neculita, C. M., Genty, T., & Zagury, G. J. (2019). Removal efficiency of As (V) and Sb (III) in contaminated neutral drainage by Fe-loaded biochar. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26, 9322–9332. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04381-1
Chai, W. S., Cheun, J. Y., Kumar, P. S., Mubashir, M., Majeed, Z., Banat, F., ..., & Show, P. L. (2021). A review on conventional and novel materials towards heavy metal adsorption in wastewater treatment application. Journal of Cleaner Production, 296, 126589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126589
Chen, Y., Guo, X., Zhao, Y., & Chen, J. (2014). Adsorption behavior of Sb(V) on Fe-Mn binary oxide: Effect of ionic strength and co-existing anions. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 280, 29–35.
Chen, W., Lin, Z., Chen, Z., Weng, X., Owens, G., & Chen, Z. (2022). Simultaneous removal of Sb (III) and Sb (V) from mining wastewater by reduced graphene oxide/bimetallic nanoparticles. Science of The Total Environment, 836, 155704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155704
Chen, H., Gao, Y., El-Naggar, A., Niazi, N. K., Sun, C., Shaheen, S. M., Hou, D., Yang, X., Tang, Z., Liu, Z., & Hou, H. (2022a). Enhanced sorption of trivalent antimony by chitosan-loaded biochar in aqueous solutions: Characterization, performance and mechanisms. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 425, 127971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127971
Cheng, K., Wu, Y. N., Zhang, B., & Li, F. (2020). New insights into the removal of antimony from water using an iron-based metal-organic framework: Adsorption behaviors and mechanisms. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 602, 125054. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.125054
Cheng, M., Fang, Y., Li, H., & Yang, Z. (2022). Review of recently used adsorbents for antimony removal from contaminated water. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(18), 26021–26044. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18653-w
Cooper, R. G., & Harrison, A. P. (2009). The exposure to and health effects of antimony. Indian journal of occupational and environmental medicine, 13(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5278.50716
Cui, X., Ni, Q., Lin, Q., Khan, K. Y., Li, T., Khan, M. B., He, Z., & Yang, X. (2017). Simultaneous sorption and catalytic oxidation of trivalent antimony by Canna indica derived biochars. Environmental Pollution, 229, 394–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.06.005
De Boeck, M., Kirsch-Volders, M., & Lison, D. (2003). Cobalt and antimony: Genotoxicity and carcinogenicity. Mutation Research/fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis, 533(1–2), 135–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2003.07.012
Diquattro, S., Garau, G., Mangia, N. P., Drigo, B., Lombi, E., Vasileiadis, S., & Castaldi, P. (2020). Mobility and potential bioavailability of antimony in contaminated soils: Short-term impact on microbial community and soil biochemical functioning. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 196, 110576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110576
Diquattro, S., Castaldi, P., Ritch, S., Juhasz, A. L., Brunetti, G., Scheckel, K. G., ..., & Lombi, E. (2021). Insights into the fate of antimony (Sb) in contaminated soils: Ageing influence on Sb mobility, bioavailability, bioaccessibility and speciation. Science of The Total Environment, 770, 145354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145354
Dong, S., Dou, X., Mohan, D., Pittman, C. U., Jr., & Luo, J. (2015). Synthesis of graphene oxide/schwertmannite nanocomposites and their application in Sb (V) adsorption from water. Chemical Engineering Journal, 270, 205–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.01.071
Filella, M., Belzile, N., & Lett, M. C. (2007). Antimony in the environment: A review focused on natural waters. III. Microbiota Relevant Interactions. Earth-Science Reviews, 80(3–4), 195–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2006.09.003
Fort, M., Grimalt, J. O., Querol, X., Casas, M., & Sunyer, J. (2016). Evaluation of atmospheric inputs as possible sources of antimony in pregnant women from urban areas. Science of the Total Environment, 544, 391–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.11.095
Frengstad, B., Skrede, A. K. M., Banks, D., Krog, J. R., & Siewers, U. (2000). The chemistry of Norwegian groundwaters: III. The distribution of trace elements in 476 crystalline bedrock groundwaters, as analysed by ICP-MS techniques. Science of the Total environment, 246(1), 21–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(99)00413-1
Guo, W., Fu, Z., Wang, H., Liu, S., Wu, F., & Giesy, J. P. (2018). Removal of antimonate (Sb (V)) and antimonite (Sb (III)) from aqueous solutions by coagulation-flocculation-sedimentation (CFS): Dependence on influencing factors and insights into removal mechanisms. Science of the Total Environment, 644, 1277–1285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.034
He, M., Wang, X., Wu, F., & Fu, Z. (2012). Antimony pollution in China. Science of the Total Environment, 421, 41–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.06.009
He, X., Min, X., & Luo, X. (2017). Efficient removal of antimony (III, V) from contaminated water by amino modification of a zirconium metal–organic framework with mechanism study. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 62(4), 1519–1529. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jced.7b00010
He, M., Wang, N., Long, X., Zhang, C., Ma, C., Zhong, Q., & Shan, J. (2019). Antimony speciation in the environment: Recent advances in understanding the biogeochemical processes and ecological effects. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 75, 14–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2018.05.023
Herath, I., Vithanage, M., & Bundschuh, J. (2017). Antimony as a global dilemma: Geochemistry, mobility, fate and transport. Environmental Pollution, 223, 545–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.01.057
Hu, X., He, M., Li, S., & Guo, X. (2017). The leaching characteristics and changes in the leached layer of antimony-bearing ores from China. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 176, 76–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2016.01.009
Hu, X., You, S., Li, F., & Liu, Y. (2022). Recent advances in antimony removal using carbon-based nanomaterials: A review. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 16(4), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-021-1482-7
Hua, L., Wu, C., Zhang, H., Cao, L., Wei, T., & Guo, J. (2021). Biochar-induced changes in soil microbial affect species of antimony in contaminated soils. Chemosphere, 263, 127795. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127795
Huang, Z., Lai, Z., Zhu, D., Wang, H., Zhao, C., Ruan, G., & Du, F. (2021). Electrospun graphene oxide/MIL-101 (Fe)/poly (acrylonitrile-co-maleic acid) nanofiber: A high-efficient and reusable integrated photocatalytic adsorbents for removal of dye pollutant from water samples. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 597, 196–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.04.020
Ilgen, A. G., Foster, A. L., & Trainor, T. P. (2012). Role of structural Fe in nontronite NAu-1 and dissolved Fe (II) in redox transformations of arsenic and antimony. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 94, 128–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2012.07.007
Ji, J., Xu, S., Ma, Z., & Mou, Y. (2022). Optimisation of preparation conditions and removal mechanism for trivalent antimony by biochar-supported nano zero-valent iron. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 26, 102240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2021.102240
Jia, M., Hu, J. W., Luo, J., Duan, S. M., Li, Z. B., & Liu, C. (2013). Comparison study on adsorption and removal of antimony from acidic aqueous solution by activated carbons and machine-made charcoal. Advanced Materials Research, 779, 1600–1606. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.779-780.1600
Jia, X., Zhou, J., Liu, J., Liu, P., Yu, L., Wen, B., & Feng, Y. (2020). The antimony sorption and transport mechanisms in removal experiment by Mn-coated biochar. Science of the Total Environment, 724, 138158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138158
Kumar, A. S. K., Jiang, S. J., & Tseng, W. L. (2015). Effective adsorption of chromium (VI)/Cr (III) from aqueous solution using ionic liquid functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes as a super sorbent. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 3(13), 7044–7057. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TA06948J
Kumar, P., Bansal, V., Kim, K. H., & Kwon, E. E. (2018). Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) as futuristic options for wastewater treatment. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 62, 130–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2017.12.051
Kumar, M., Xiong, X., Sun, Y., Yu, I. K., Tsang, D. C., Hou, D., Gupta, J., Bhaskar, T., & Pandey, A. (2020a). Critical review on biochar-supported catalysts for pollutant degradation and sustainable biorefinery. Advanced Sustainable Systems, 4(10), 1900149. https://doi.org/10.1002/adsu.201900149
Kumar, M., Xiong, X., Wan, Z., Sun, Y., Tsang, D. C., Gupta, J., Gao, B., Cao, X., Tang, J., & Ok, Y. S. (2020). Ball milling as a mechanochemical technology for fabrication of novel biochar nanomaterials. Bioresource Technology, 312, 123613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123613
Kumar, M., Ambika, S., Hassani, A., & Nidheesh, P. V. (2022a). Waste to catalyst: Role of agricultural waste in water and wastewater treatment. Science of The Total Environment, 858, 159762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.159762
Kumar, M., Sridharan, S., Sawarkar, A.D., Shakeel, A., Anerao, P., Mannina, G., Sharma, P., & Pandey, A. (2022b). Current research trends on emerging contaminants pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs): A comprehensive review. Science of The Total Environment, 859, 160031. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.160031
Lahermo, P., Tarvainen, T., Hatakka, T., Backman, B., Juntunen, R., Kortelainen, N., & Suomela, P. (2002). A thousand wells - the physical and chemical quality of Finnish well waters in 1999. Research report 155, Geological Research Center, 1-92. https://urn.fi/URN:NBN:fi-fe2014120247956. Accessed on Nov 2022
Lan, B., Wang, Y., Wang, X., Zhou, X., Kang, Y., & Li, L. (2016). Aqueous arsenic (As) and antimony (Sb) removal by potassium ferrate. Chemical Engineering Journal, 292, 389–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.02.019
Lapo, B., Demey, H., Carchi, T., & Sastre, A. M. (2019). Antimony removal from water by a chitosan-Iron (III)[ChiFer (III)] biocomposite. Polymers, 11(2), 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11020351
Leng, Y., Guo, W., Su, S., Yi, C., & Xing, L. (2012). Removal of antimony (III) from aqueous solution by graphene as an adsorbent. Chemical Engineering Journal, 211, 406–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.09.078
Li, Y., Du, Q., Liu, T., Peng, X., Wang, J., Sun, J., Wang, Y., Wu, S., Wang, Z., Xia, Y., & Xia, L. (2013a). Comparative study of methylene blue dye adsorption onto activated carbon, graphene oxide, and carbon nanotubes. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 91(2), 361–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2012.07.007
Li, Z. B., Hu, J. W., Duan, S. M., Huang, X. F., Jia, M., Wang, Y., Liu, C., & Luo, J. (2013b). A study on adsorption kinetics of antimony onto coconut shell activated carbon. Advanced Materials Research, 788, 471–475. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.788.471
Li, J., Wang, Q., Oremland, R. S., Kulp, T. R., Rensing, C., & Wang, G. (2016). Microbial antimony biogeochemistry: Enzymes, regulation, and related metabolic pathways. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 82(18), 5482–5495. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01375-16
Li, L., Liao, L., Wang, B., Li, W., Liu, T., Wu, P., Xu, Q., & Liu, S. (2022). Effective Sb (V) removal from aqueous solution using phosphogypsum-modified biochar. Environmental Pollution, 301, 119032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119032
Li, J., Zheng, B., He, Y., Zhou, Y., Chen, X., Ruan, S., ..., & Tang, L. (2018). Antimony contamination, consequences and removal techniques: A review. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 156, 125–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.03.024
Liu, R., Xu, W., He, Z., Lan, H., Liu, H., Qu, J., & Prasai, T. (2015). Adsorption of antimony (V) onto Mn (II)-enriched surfaces of manganese-oxide and FeMn binary oxide. Chemosphere, 138, 616–624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.07.039
Liu, Z., Chen, Z., & Yu, F. (2019). Enhanced thermal conductivity of microencapsulated phase change materials based on graphene oxide and carbon nanotube hybrid filler. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 192, 72–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2018.12.014
Liu, D., Yang, L., Chen, Z., Zou, G., Hou, H., Hu, J., & Ji, X. (2020a). Ultra-stable Sb confined into N-doped carbon fibers anodes for high-performance potassium-ion batteries. Science Bulletin, 65(12), 1003–1012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2020.03.019
Liu, J., Wei, X., Ren, S., Qi, J., Cao, J., Wang, J., Wan, Y., Liu, Y., Zhao, M., Wang, L., & Xiao, T. (2022). Synergetic removal of thallium and antimony from wastewater with jacobsite-biochar-persulfate system. Environmental Pollution, 304, 119196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119196
Liu, H., Dong, W., Wang, H., Lu, L., Ruan, Q., Tan, Y. S., ..., & Yang, J. K. (2020b). Rewritable color nanoprints in antimony trisulfide films. Science Advances, 6(51), eabb7171. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abb7171
Loni, P. C., Wu, M., Wang, W., Wang, H., Ma, L., Liu, C., Song, Y., & Tuovinen, O. H. (2020). Mechanism of microbial dissolution and oxidation of antimony in stibnite under ambient conditions. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 385, 121561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121561
Long, X., Wang, X., Guo, X., & He, M. (2020). A review of removal technology for antimony in aqueous solution. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 90, 189–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2019.12.008
Long, X., Wang, T., & He, M. (2022). Simultaneous removal of antimony and arsenic by nano-TiO2-crosslinked chitosan (TA-chitosan) beads. Environmental Technology, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2022.2048084
López-García, I., Rivas, R. E., & Hernández-Córdoba, M. (2011). Use of carbon nanotubes and electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry for the speciation of very low amounts of arsenic and antimony in waters. Talanta, 86, 52–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2011.07.105
Luo, X. F., Yang, C. H., Peng, Y. Y., Pu, N. W., Ger, M. D., Hsieh, C. T., & Chang, J. K. (2015). Graphene nanosheets, carbon nanotubes, graphite, and activated carbon as anode materials for sodium-ion batteries. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 3(19), 10320–10326. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TA00727E
Lv, X., Huang, Y., Liu, Z., Tian, J., Wang, Y., Ma, Y., Liang, J., Fu, S., Wan, X., & Chen, Y. (2009). Photoconductivity of Bulk-Film-Based Graphene Sheets. Small, 5(14), 1682–1687. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.200900044
Mishra, S., & Sankararamakrishnan, N. (2018). Characterization, evaluation, and mechanistic insights on the adsorption of antimonite using functionalized carbon nanotubes. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(13), 12686–12701. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1347-1
Mishra, S., Dwivedi, J., Kumar, A., & Sankararamakrishnan, N. (2016). Removal of antimonite (Sb (III)) and antimonate (Sb (V)) using zerovalent iron decorated functionalized carbon nanotubes. RSC Advances, 6(98), 95865–95878. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA18965B
Mitrakas, M., Mantha, Z., Tzollas, N., Stylianou, S., Katsoyiannis, I., & Zouboulis, A. (2018). Removal of antimony species, Sb (III)/Sb (V), from water by using iron coagulants. Water, 10(10), 1328. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101328
Navarro, P., & Alguacil, F. J. (2002). Adsorption of antimony and arsenic from a copper electrorefining solution onto activated carbon. Hydrometallurgy, 66(1–3), 101–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-386X(02)00108-1
NazarzadehZare, E., Mudhoo, A., Ali Khan, M., Otero, M., Bundhoo, Z. M. A., Patel, M., Srivastava, A., Navarathna, C., Mlsna, T., Mohan, D., & Pittman, C. U., Jr. (2021). Smart adsorbents for aquatic environmental remediation. Small, 17(34), 2007840. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202007840
Nishad, P. A., & Bhaskarapillai, A. (2021). Antimony, a pollutant of emerging concern: A review on industrial sources and remediation technologies. Chemosphere, 277, 130252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130252
Nishad, P. A., Bhaskarapillai, A., & Velmurugan, S. (2014). Nano-titania-crosslinked chitosan composite as a superior sorbent for antimony (III) and (V). Carbohydrate Polymers, 108, 169–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.02.091
Nishad, P. A., Bhaskarapillai, A., Srinivasan, M. P., & Rangarajan, S. (2021). New insight into the role of crosslinkers and composition on selectivity and kinetics of antimony uptake by chitosan-titania composite beads. SN Applied Sciences, 3, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-021-04158-7
Nundy, S., Ghosh, A., Nath, R., Paul, A., Tahir, A. A., & Mallick, T. K. (2021). Reduced graphene oxide (rGO) aerogel: Efficient adsorbent for the elimination of antimony (III) and (V) from wastewater. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 420, 126554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126554
Obiakor, M. O., Tighe, M., Pereg, L., & Wilson, S. C. (2017). Bioaccumulation, trophodynamics and ecotoxicity of antimony in environmental freshwater food webs. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 47(22), 2208–2258. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2017.1419790
Okkenhaug, G., Gebhardt, K. A. G., Amstaetter, K., Bue, H. L., Herzel, H., Mariussen, E., & Mulder, J. (2016). Antimony (Sb) and lead (Pb) in contaminated shooting range soils: Sb and Pb mobility and immobilization by iron based sorbents, a field study. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 307, 336–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.01.005
Patel, M., Kumar, R., Kishor, K., Mlsna, T., Pittman, C. U., Jr., & Mohan, D. (2019). Pharmaceuticals of emerging concern in aquatic systems: Chemistry, occurrence, effects, and removal methods. Chemical Reviews, 119(6), 3510–3673. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00299
Patel, M., Kumar, R., Pittman, C. U., Jr., & Mohan, D. (2021). Ciprofloxacin and acetaminophen sorption onto banana peel biochars: environmental and process parameter influences. Environmental Research, 201, 111218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.111218
Peiris, C., Gunatilake, S. R., Mlsna, T. E., Mohan, D., & Vithanage, M. (2017). Biochar based removal of antibiotic sulfonamides and tetracyclines in aquatic environments: A critical review. Bioresource Technology, 246, 150–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.07.150
Qi, C., Liu, G., Chou, C. L., & Zheng, L. (2008). Environmental geochemistry of antimony in Chinese coals. Science of the Total Environment, 389(2–3), 225–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.09.007
Qi, Z., Joshi, T. P., Liu, R., Liu, H., & Qu, J. (2017). Synthesis of Ce (III)-doped Fe3O4 magnetic particles for efficient removal of antimony from aqueous solution. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 329, 193–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.01.007
Ren, S., Ai, Y., Zhang, X., Ruan, M., Hu, Z. N., Liu, L., Li, J., Wang, Y., Liang, J., Jia, H., & Liu, Y. (2019). Recycling Antimony (III) by magnetic carbon nanospheres: Turning waste to recoverable catalytic for synthesis of esters and triazoles. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 8(1), 469–477. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b05802
Rinklebe, J., Shaheen, S. M., El-Naggar, A., Wang, H., Du Laing, G., Alessi, D. S., & Ok, Y. S. (2020). Redox-induced mobilization of Ag, Sb, Sn, and Tl in the dissolved, colloidal and solid phase of a biochar-treated and un-treated mining soil. Environment International, 140, 105754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.105754
Saerens, A., Ghosh, M., Verdonck, J., & Godderis, L. (2019). Risk of cancer for workers exposed to antimony compounds: A systematic review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(22), 4474. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16224474
Salam, M. A., & Mohamed, R. M. (2013). Removal of antimony (III) by multi-walled carbon nanotubes from model solution and environmental samples. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 91(7), 1352–1360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2013.02.007
Saleh, T. A., Sarı, A., & Tuzen, M. (2017). Effective adsorption of antimony (III) from aqueous solutions by polyamide-graphene composite as a novel adsorbent. Chemical Engineering Journal, 307, 230–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.08.070
Schildroth, S., Osborne, G., Smith, A. R., Yip, C., Collins, C., Smith, M. T., & Zhang, L. (2021). Occupational exposure to antimony trioxide: A risk assessment. Occupational and Environmental Medicine, 78(6), 413–418. https://doi.org/10.1136/oemed-2020-106980
Shahid, M., Khalid, S., Dumat, C., Pierart, A., & Niazi, N. K. (2019). Biogeochemistry of antimony in soil-plant system: Ecotoxicology and human health. Applied Geochemistry, 106, 45–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2019.04.006
Shakerian, F., Dadfarnia, S., & Shabani, A. M. H. (2014). Synthesis and characterisation of nano-pore antimony imprinted polymer and its use in the extraction and determination of antimony in water and fruit juice samples. Food Chemistry, 145, 571–577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.08.110
Smichowski, P. (2008). Antimony in the environment as a global pollutant: A review on analytical methodologies for its determination in atmospheric aerosols. Talanta, 75(1), 2–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2007.11.005
Sridharan, S., Kumar, M., Saha, M., Kirkham, M.B., Singh, L., & Bolan, N.S. (2022). The polymers and their additives in particulate plastics: What makes them hazardous to the fauna?. Science of The Total Environment, 824, 153828. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153828
Sundar, S., & Chakravarty, J. (2010). Antimony toxicity. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 7(12), 4267–4277. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph7124267
Ungureanu, G., Santos, S., Boaventura, R., & Botelho, C. (2015). Arsenic and antimony in water and wastewater: Overview of removal techniques with special reference to latest advances in adsorption. Journal of Environmental Management, 151, 326–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2014.12.051
United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA, 1979) (1979). Water related fate of the 129 priority pollutants, vol. 1. Washington: USEPA.
US Department of Health and Human Services. (2007). Agency for toxic substances and disease registry: Atlanta. GA, USA (pp. 1-291).
Vithanage, M., Rajapaksha, A. U., Ahmad, M., Uchimiya, M., Dou, X., Alessi, D. S., & Ok, Y. S. (2015). Mechanisms of antimony adsorption onto soybean stover-derived biochar in aqueous solutions. Journal of Environmental Management, 151, 443–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2014.11.005
Wan, S., Qiu, L., Li, Y., Sun, J., Gao, B., He, F., & Wan, W. (2020). Accelerated antimony and copper removal by manganese oxide embedded in biochar with enlarged pore structure. Chemical Engineering Journal, 402, 126021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.126021
Wang, Y., Li, L., Li, X., Li, G., Li, Z., & Li, H. (2012). Adsorption of Sb(III) and Sb(V) on modified activated carbon. Chemical Engineering Journal, 189–190, 300–307.
Wang, L., Wang, J. M., Zhang, R., Liu, X. G., Song, G. X., Chen, X. F., Wang, Y., & Kong, J. L. (2016). Highly efficient As (V)/Sb (V) removal by magnetic sludge composite: Synthesis, characterization, equilibrium, and mechanism studies. Rsc Advances, 6(49), 42876–42884. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA06208C
Wang, J., Chen, Y., Zhang, Z., Ai, Y., Liu, L., Qi, L., Zhou, J., Hu, Z., Jiang, R., Bao, H., & Ren, S. (2018a). Microwell confined iron oxide nanoparticles in honeycomblike carbon spheres for the adsorption of Sb (III) and sequential utilization as a catalyst. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 6(10), 12925–12934. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b02300
Wang, L., Wang, J., Wang, Z., He, C., Lyu, W., Yan, W., & Yang, L. (2018b). Enhanced antimonate (Sb (V)) removal from aqueous solution by La-doped magnetic biochars. Chemical Engineering Journal, 354, 623–632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.08.074
Wani, I., Kushvaha, V., Garg, A., Kumar, R., Naik, S., & Sharma, P. (2022). Review on effect of biochar on soil strength: towards exploring usage of biochar in geo-engineering infrastructure. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery, 1–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-02795-5
Wei, C., Ge, Z., Chu, W., & Feng, R. (2015). Speciation of antimony and arsenic in the soils and plants in an old antimony mine. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 109, 31–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2014.08.002
Xu, X., Zhang, Z., Dong, J., Yi, D., Niu, J., Wu, M., Lin, L., Yin, R., Li, M., Zhou, J., & Wang, S. (2017). Ultrafast epitaxial growth of metre-sized single-crystal graphene on industrial Cu foil. Science Bulletin, 62(15), 1074–1080. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2017.07.005
Xue, W., Zhao, Y., Yu, H., & Sun, H. (2019). Adsorption of antimony onto Fe-Mn binary oxide: Effects of dissolved ions, humic acid, and temperature. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(25), 25599–25613.
Yang, X., Shi, Z., Yuan, M., & Liu, L. (2015). Adsorption of trivalent antimony from aqueous solution using graphene oxide: Kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 60(3), 806–813. https://doi.org/10.1021/je5009262
Yang, X., Wan, Y., Zheng, Y., He, F., Yu, Z., Huang, J., Wang, H., Ok, Y. S., Jiang, Y., & Gao, B. (2019a). Surface functional groups of carbon-based adsorbents and their roles in the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions: A critical review. Chemical Engineering Journal, 366, 608–621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.02.119
Yang, Y., Yang, X., Liang, L., Gao, Y., Cheng, H., Li, X., Zou, M., Ma, R., Yuan, Q., & Duan, X. (2019b). Large-area graphene-nanomesh/carbon-nanotube hybrid membranes for ionic and molecular nanofiltration. Science, 364(6445), 1057–1062. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aau5321
Yang, X., Zhou, T., Deng, R., Zhu, Z., Saleem, A., & Zhang, Y. (2021). Removal of Sb (III) by 3D-reduced graphene oxide/sodium alginate double-network composites from an aqueous batch and fixed-bed system. Scientific Reports, 11(1), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-01788-0
Yu, T., Zeng, C., Ye, M., & Shao, Y. (2013). The adsorption of Sb (III) in aqueous solution by Fe2O3-modified carbon nanotubes. Water Science and Technology, 68(3), 658–664. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2013.290
Yu, T. C., Wang, X. H., & Li, C. (2014). Removal of antimony by FeCl 3-modified granular-activated carbon in aqueous solution. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 140(9), A4014001. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)EE.1943-7870.0000736
Yu, H., Zhao, Y., & Sun, H. (2019). Adsorption of antimony(V) onto modified zeolite: Effects of pH, temperature, and coexisting ions. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(25), 25615–25625.
Zand, A. D., & Heir, A. V. (2020). Phytoremediation: Data on effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on phytoremediation of antimony polluted soil. Data in Brief, 31, 105959. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2020.105959
Zare, E. N., Mudhoo, A., Khan, M. A., Otero, M., Bundhoo, Z. M. A., Navarathna, C., Patel, M., Srivastava, A., Pittman, C. U., Jr., Mlsna, T., & Mohan, D. (2021). Water decontamination using bio-based, chemically functionalized, doped, and ionic liquid-enhanced adsorbents. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 19(4), 3075–3114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-021-01207-w
Zhang, J., Deng, R., Ren, B., Yaseen, M., & Hursthouse, A. (2020). Enhancing the removal of Sb (III) from water: A Fe3O4@ HCO composite adsorbent caged in sodium alginate microbeads. Processes, 8(1), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8010044
Zhang, X. Y., Tang, L. S., Zhang, G., & Wu, H. D. (2009). Heavy metal contamination in a typical mining town of a minority and mountain area, South China. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 82, 31–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-008-9569-4
Zhang, X., Wang, Y., Ju, N., Ai, Y., Liu, Y., Liang, J., Hu, Z. N., Guo, R., Xu, W., Zhang, W., & Qi, Y. (2021a). Ultimate resourcization of waste: Crab shell-derived biochar for antimony removal and sequential utilization as an anode for a Li-ion battery. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 9(26), 8813–8823. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.1c01851
Zhang, X., Xie, N., Guo, Y., Niu, D., Sun, H. B., & Yang, Y. (2021). Insights into adsorptive removal of antimony contaminants: Functional materials, evaluation and prospective. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 418, 126345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126345
Zhao, X., Dou, X., Mohan, D., Pittman, C. U., Jr., Ok, Y. S., & Jin, X. (2014). Antimonate and antimonite adsorption by a polyvinyl alcohol-stabilized granular adsorbent containing nanoscale zero-valent iron. Chemical Engineering Journal, 247, 250–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.02.096
Zhu, G., Lin, J., Yuan, Q., Wang, X., Zhao, Z., Hursthouse, A. S., & Li, Q. (2021). A biochar supported magnetic metal organic framework for the removal of trivalent antimony. Chemosphere, 282, 131068. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131068
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Kumar Abhishek, Ph.D: Conceptualization, writing-original draft, editing, validation, and visualization; Neha Parashar, Ph.D: Writing-original draft, editing, validation, and visualization; Manvendra Patel, Ph.D: Writing-original draft, validation, and editing; Subrata Hait, Ph.D: Writing-original draft, editing and validation; Anamika Srivastava, Ph.D: Writing-original draft, validation, and editing; Pooja Ghosh, Ph.D: Writing-original draft, validation, and editing; Prabhakar Sharma, Ph.D: Writing-original draft, validation, and editing; Ashok Pandey, Ph.D: Writing-original draft, validation, and editing; Manish Kumar, Ph.D: Conceptualization, writing-original draft, editing, validation, and supervision
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics
All authors have read, understood, and have complied as applicable with the statement on "Ethical responsibilities of Authors”.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Abhishek, K., Parashar, N., Patel, M. et al. Recent advancements in antimony (Sb) removal from water and wastewater by carbon-based materials: a systematic review. Environ Monit Assess 195, 758 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11322-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11322-6