Abstract
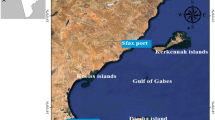
This study evaluated metal contamination in surface sediments and macroalgae of mangroves and port complexes on the Brazilian equatorial margin. Samples were collected between August 2020 and February 2021 at seven points in a mangrove swamp under the influence of port activity and at two points without port activity. Metal concentrations in the macroalgae and sediments were determined using inductively coupled plasma‒optical emission spectrometry. All macroalgal species bioaccumulated metals, as demonstrated by their bioaccumulation factors. The geochemical contamination indices indicated that the estuarine complex was influenced by port activity as moderately contaminated by Pb, Cr, Mn, and Fe and considerably contaminated by Zn and Cu. The enrichment factor confirmed significant mineral enrichment of Zn and Cu in this environment. The concentrations of the metals in the sediment followed the order Fe > Mn > Cr > Zn > Cu > Pb at most sampling points. Cladophoropsis membranacea recorded the highest bioaccumulation values for Pb (0.44), Rhizoclonium africanum for Zn (1.08), Cr (0.55), and Fe (0.30), and Bostrychia radicans for Mn (2.22). The bioaccumulation pattern of metals in the most abundant macroalgal species followed the order Bostrychia radicans (Mn > Zn > Cu > Cr > Pb > Fe) and Rhizoclonium africanum (Zn > Mn > Cr > Cu > Pb > Fe).








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available in the Figshare repository, https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.21221576.v1.
References
Akcali, I., & Kucuksezgin, F. (2011). A biomonitoring study: Heavy metals in macroalgae from eastern Aegean coastal areas. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 62(3), 637–645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2010.12.021
Amado Filho, G. M., Andrade, L. R., Karez, C. S., Farina, M., & Pfeiffer, W. C. (1999). Brown algal species as biomonitors of Zn and Cd at Sepetiba Bay, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Marine Environmental Research, 48(3), 213–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-1136(99)00042-2
Atkinson, C. A., Jolley, D. F., & Simpson, S. L. (2007). Effect of overlying water pH, dissolved oxygen, salinity and sediment disturbances on metal release and sequestration from metal contaminated marine sediments. Chemosphere, 69(9), 1428–1437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.04.068
Bakshi, M., Ghosh, S., Chakraborty, D., Hazra, S., & Chaudhuri, P. (2018). Assessment of potentially toxic metal (PTM) pollution in mangrove habitats using biochemical markers: A case study on Avicennia officinalis L. in and around Sundarban, India. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 133, 157–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.05.030
Baoli, W., & Congqiang, L. (2004). Factors controlling the distribution of trace metals in macroalgae. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 23(4), 366–372. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02871309
Baumann, H. A., Morrison, L., & Stengel, D. B. (2009). Metal accumulation and toxicity measured by PAM—chlorophyll fluorescence in seven species of marine macroalgae. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 72(4), 1063–1075. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2008.10.010
Billah, M. M., Kamal, A. H. M., Idris, M. H., & Ismail, J. (2017). Mangrove macroalgae as biomonitors of heavy metal contamination in a tropical estuary, Malaysia. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 228(9), 228–347. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3500-8
Borgesen, F. (1905). Contributions à la connaissance du genre Siphonocladus Schmitz. Oversight Over Det Kgl Danske Videnskabernes Selskabs Forhandlingar, 3, 259–291.
Brito, G. B., De Souza, T. L., Bressy, F. C., Moura, C. W. N., & Korn, M. G. A. (2012). Levels and spatial distribution of trace elements in macroalgal species from the Todos os Santos Bay, Bahia, Brazil. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 64(10), 2238–2244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2012.06.022
Buruaem, L. M., Hortellani, M. A., Sarkis, J. E., Costa-Lotufo, L. V., & Abessa, D. M. S. (2012). Contamination of port zone sediments by metals from Large Marine Ecosystems of Brazil. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 64(3), 479–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2012.01.017
Casado-Martínez, M. C., Buceta, J. L., Belzunce, M. J., & DelValls, T. A. (2006). Using sediment quality guidelines for dredged material management in commercial ports from Spain. Environment International, 32, 388–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2005.09.003
Cavalcanti, L. F., & Cutrim, M. V. J. (2018). Structure of microphytoplankton community and environmental variables in a macrotidal estuarine complex, São Marcos Bay, Maranhão - Brazil. Brazilian Journal of Oceanography, 66(3), 283–300. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1679-87592018021906603
CCME. (1999). Canadian sediment quality guidelines for the protection of aquatic life – copper. Canadian Environmental Quality Guidelines, Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment.
Chakraborty, S., Bhattacharya, T., Singh, G., & Maity, J. P. (2014). Benthic macroalgae as biological indicators of heavy metal pollution in the marine environments: A biomonitoring approach for pollution assessment. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 100, 61–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.12.003
Conti, M. E., & Cecchetti, G. A. (2003). Biomonitoring study: Trace metals in algae and mollusks from Tyrrhenian coastal areas. Environmental Research, 93(1), 99–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0013-9351(03)00012-4
Costa, E. S., Grilo, C. F., Wolff, G. A., Thompson, A., Figueira, R. C. L., & Neto, R. R. (2015). Evaluation of metals and hydrocarbons in sediments from a tropical tidal flat estuary of Southern Brazil. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 92(1–2), 259–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.11.028
CPRM. (2000). Programa Levantamentos Geológicos Básicos do Brasil - São Luís NE/SE, Folhas SA23-X e SA23-Z Estados do Maranhão e Piauí Brasília (in portuguese).
Dawes, C., Siar, K., & Marlett, D. (1999). Mangrove structure, litter and macroalgal productivity in a northern-most forest of Florida. Mangroves and Salt Marshes, 3, 259–267. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009976025000
De Paula Filho, F. J., Marins, R. V., Lacerda, L. D., Aguiar, J. E., & Peres, T. F. (2015). Background values for evaluation of heavy metal contamination in sediments in the Parnaíba River Delta estuary NE/Brazil. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 91(2), 424–428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.08.022
De Paula Filho, F. J., Marins, R. V., Santos, V. D., Pereira-Junior, R. F., Menezes, J. M. C., Gastão, F. G. C., Guzzi, A., & Teixeira, R. N. P. (2021). Assessment of heavy metals in sediments of the Parnaíba River Delta in the semiarid coast of Brazil. Environmental Earth Science, 80, 167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2020.100364
Diniz, C., Cortinhas, L., Nerino, G., Rodrigues, J., Sadeck, L., Adami, M., & Souza-Filho, P. W. M. (2019). Brazilian mangrove status: Three decades of satellite data analysis. Remote Sensing, 11(7), 2–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11070808
Fernandes, M. E. B., & Alves, E. F. S. (2011). Occurrence and distribution of macroalgae (Rhodophyta) associated with mangroves on the Ajuruteua Peninsula, Bragança, Pará, Brasil. UAKARI, 7(2), 35–42. https://doi.org/10.31420/UAKARI.V7I2.97
Ferreira, A. C., & Lacerda, L. D. (2016). Degradation and conservation of Brazilian mangroves, status and perspectives. Ocean & Coastal Management, 125, 38–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2016.03.011
Folk, R. L., & Ward, W. C. (1957). A study in the significance of grain-size parameters. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 27, 3–26. https://doi.org/10.1306/74D70646-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D
Gerringa, L. (1991). Mobility of Cu, Cd, Ni, Pb, Zn, Fe and Mn in marine sediment slurries under anaerobic conditions and at 20% air saturation. Netherlands Journal of Sea Research, 27(2), 145–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/0077-7579(91)90007-N
Ghosh, S., Bakshi, M., Mahanty, S., & Chaudhuri, P. (2021). Understanding potentially toxic metal (PTM) induced biotic response in two riparian mangrove species Sonneratia caseolaris and Avicennia officinalis along river Hooghly, India: Implications for sustainable sediment quality management. Marine Environmental Research, 172, 105486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2021.105486
Gledhill, M., Nimmo, M., Hill, S. J., & Brown, M. T. (1997). The toxicity of copper (II) species to marine algae, with particular reference to macroalgae. Journal of Phycology, 33(1), 2–11. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0022-3646.1997.00002.x
González-Gorbeña, E., Rosman, P. C. C., & Qassim, R. Y. (2015). Assessment of the tidal current energy resource in São Marcos Bay, Brazil. Journal of Ocean Engineering and Marine Energy, 1(4), 421–433. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40722-015-0031-5
Hakanson, L. (1980). An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: A sedimentological approach. Water Research, 14(8), 975–1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
Hall, M. J., & Brown, M. T. (2002). Copper and manganese influence the uptake of cadmium in marine macroalgae. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 68(1), 49–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-001-0218-4
Huang, Y., Zhang, D., Xu, Z., Yuan, S., Li, Y., & Wang, L. (2017). Effect of overlying water pH, dissolved oxygen and temperature on heavy metal release from river sediments under laboratory conditions. Archives of Environmental Protection, 43, 28–36. https://doi.org/10.1515/aep-2017-0014
Jahan, S., & Strezov, V. (2019). Assessment of trace elements pollution in the sea ports of New South Wales (NSW), Australia using oysters as bioindicators. Scientific Report, 9, 1416. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-38196-w
Jha, B., Reddy, C. R. K., Thakur, M. C., & Rao, U. M. (2009). Seaweeds of India: The diversity and distribution of seaweeds of the Gujarat coast. Dordrecht: Springer.
Kang, M., Tian, Y., Peng, S., & Wang, M. (2019). Effect of dissolved oxygen and nutrient levels on heavy metal contents and fractions in river surface sediments. Science Total Environmental, 648, 861–870. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.201
Karbassi, A. R., & Heidari, M. (2015). An investigation on role of salinity, pH and DO on heavy metals elimination throughout estuarial mixture. Global Journal of Environmental Science and Management, 1(1), 41–46. https://doi.org/10.7508/gjesm.2015.01.004
Karbassi, A. R., Fakhraee, M., Heidari, M., Vaezi, A. R., & Samani, A. V. (2015). Dissolved and particulate trace metal geochemistry during mixing of Karganrud River with Caspian Sea water. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 8(4), 2143–2151. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1267-4
Karez, C. S., Magalhaes, V. F., Pfeiffer, W. C., & Amado Filho, G. M. (1994). Trace metal accumulation by algae in Sepetiba Bay. Brazil. Environmental Pollution, 83(3), 351–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/0269-7491(94)90157-0
Kutzing, F. T. (1845). Phycologia germanica, d. i. Deutschlands Algen in bündigen Beschreibungen. Nebst einer Anleitung zum Untersuchen und Bestimmen dieser Gewächse für Anfänger. pp. [i]-x, [1]-340 ['240']. Nordhausen: zu finden bei Wilh. Köhne.
Kutzing, F. T. (1853). Tabulae phycologicae; oder, Abbildungen der Tange. Vol. III pp. 1-28, 100 pls. Nordhausen: Gedruckt auf kosten des Verfassers (in commission bei W. Köhne).
Lacerda, L. D., Ribeiro, J., & Gueiros, B. B. (1999). Manganese dynamics in a mangrove mud flat tidal creek in SE Brazil. Mangroves and Salt Marshes, 3(2), 105–115.
Lacerda, L. D., Teixeira, V. L., & Guimarães, J. R. D. (1985). Seasonal variation of heavy metals in seaweeds from Conceição de Jacareí (RJ), Brazil. Botanica Marina, 28(8), 339–343. https://doi.org/10.1515/botm.1985.28.8.339
Li, H., Shi, A., Li, M., & Zhang, X. (2013). Effect of pH, temperature, dissolved oxygen, and flow rate of overlying water on heavy metals release from storm sewer sediments. Journal of Chemistry, 2013, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/434012
Linnaeus, C. von, Salvius, L. (1753) Caroli Linnaei ... Species plantarum: exhibentes plantas rite cognitas, ad genera relatas, cum differentiis specificis, nominibus trivialibus, synonymis selectis, locis natalibus, secundum systema sexuale digestas... Holmiae, Impensis Laurentii Salvii. pp. 572. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.669
Liu, J. J., Diao, Z. H., Xu, X. R., & Xie, Q. (2019). Effects of dissolved oxygen, salinity, nitrogen and phosphorus on the release of heavy metals from coastal sediments. Science of the Total Environment, 666, 894–901. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.288
Lombardi, A. T., & Vieira, A. A. H. (1998). Copper and lead complexation by high molecular weight compounds produced by Synura sp (Chrysophyceae). Phycologia, 37, 34–39. https://doi.org/10.2216/i0031-8884-37-1-34.1
Long, E. R., Macdonald, D. D., Smith, S. L., & Calder, F. D. (1995). Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments. Environmental Management, 19(1), 81–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02472006
Luoma, S. N. (1983). Bioavailability of trace metals to aquatic organisms − a review. The Science of the Total Environment, 28, 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0048-9697(83)80004-7
Luoma, S. N., Bryan, G. W., & Langstone, W. T. (1982). Scavenging heavy metals from particles by brown seaweed. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 13(11), 394–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/0025-326X(82)90116-3
MacDonald, D. D. (1994). Approach to the assessment of sediment quality in Florida coastal waters. vol. 1 - development and evaluation of sediment quality assessment guidelines. Florida Department of Environmental Protection Office of Water Policy.
Macdonald, D. D., Carr, R. S., Calder, F. D., et al. (1996). Development and evaluation of sediment quality guidelines for Florida coastal waters. Ecotoxicology, 5, 253–278. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00118995
Macedo, S. J., Calado, S. C. S., Koening, M. L., Silva, V. L., & Neumann-Leitão, S. (2009). Concentrations of heavy metals in macroalgae in the tropical western Atlantic. Water Resource Management V, 125, 209–218. https://doi.org/10.2495/WRM090191
Mamboya, F. A., Pratap, H. B., Mtolera, M., & Bjork, M. (1999). The effect of copper on the daily growth rate and photosynthetic efficiency of the brown macroalga Padina boergensenii. In: Richmond MD, Francis J (Eds.) Proceedings of the Conference on Advances on Marine Sciences in Tanzania, pp. 185–192.
Ministério dos Transportes, Portos e Aviação Civil - MTPA. (2018). Plano Mestre Complexo Portuário do Itaqui. (in portuguese).
Montagne, C. (1842). Bostrychia. Dictionnaire Universel d'Histoire Naturelle [Orbigny], 2, 660–661.
Muller, G. (1979). Schwermetalle in den sediment des Rheins: Veranderungem Seit 1971. Umschau, 79, 778–783.
Neumann, B., Vafeidis, A. T., Zimmermann, J., & Nicholls, R. J. (2015). Future coastal population growth and exposure to sea-level rise and coastal flooding - a global assessment. PLoS ONE, 10(3), e0118571.
Nittrouer, C. A., Brunskill, G. L., & Figueiredo, A. G. (1995). Importance of tropical coastal environments. Geo-Marine Letters, 15, 121–126. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01204452
Nowrouzi, M., & Pourkhabbaz, A. (2014). Application of geoaccumulation index and enrichment factor for assessing metal contamination in the sediments of Hara Biosphere Reserve, Iran. Chemical Speciation & Bioavailability, 26, 99–105. https://doi.org/10.3184/095422914X13951584546986
Oliveira-Filho, E. C. (1984). Brazilian mangal vegetation with special emphasis on the seaweeds. In: Por FD, Dor I (Eds.). Hydrobiology of the Mangal. Dr W Junk Publishers, Boston.
Online document Climate-Data. (2021, January 20). São Luís Clima. https://pt.climate-data.org/america-do-sul/brasil/maranhao/sao-luis-1671/
Ozkan, E. Y. (2012). A new assessment of heavy metal contaminations in an Eutrophicated Bay (Inner Izmir Bay, Turkey). Turkish Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 12, 135–147. https://doi.org/10.4194/1303-2712-v12_1_16
Parke, M., & Dixon, P. S. (1976). Check-list of British marine algae - third revision. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 56, 527–594. https://doi.org/10.1017/S002531540002066X
Pejrup, M. 1988. The triangular diagram used for classification of estuarine sediments: a new approach. In: Boer, P.L., van Gelder, A., & Nio, S.D. (Ed.). Tide-influenced sedimentary environments and facies. D. Reidel, Dordrecht. p. 289–300.
Phillips, A., Lambert, G., Granger, J. E., & Steinke, T. D. (1994). Horizontal zonation of epiphytic algae associated with Avicennia marina (Forsk) Vierh pneumatophores at beach woods mangroves nature reserve, Durban, South Africa. Botanica Marina, 37, 567–576. https://doi.org/10.1515/botm.1994.37.6.567
Phillips, A., Lambert, G., Granger, J. E., & Steinke, T. D. (1996). Vertical zonation of epiphytic algae associated with Avicennia marina (Forssk) Vierh pneumatophore at Beachwood Mangrove Nature Reserve, Durban, South Africa. Botanica Marina, 39, 167–175. https://doi.org/10.1515/botm.1996.39.1-6.167
Pinto, E., Sigaud-Kutner, T. C. S., Leitão, M. A. S., Okamoto, O. K., Morse, D., & Colepicolo, P. (2003). Heavy metal-induced oxidative stress in algae. Journal of Phycology, 39, 1008–1018. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0022-3646.2003.02-193.x
Rebelo-Mochel, F. (1997). Mangroves on São Luís Island, Maranhão, Brazil. In B. Kjerfve, L. D. Lacerda, & E. H. S. Diop (Eds.), Mangrove ecosystem studies in Latin America and Africa (pp. 145–154). UNESCO.
Reimann, C., & De Caritat, P. (2000). Intrinsic flaws of element enrichment factors (EFs) in environmental geochemistry. Environmental Science & Technology, 34, 5084–5091. https://doi.org/10.1021/ES001339O
Reis, P. A., Gonçalves, J., Abreu, H., Pereira, R., Benoit, M., O’Mahony, F., Connellan, I., Maguire, J., & Ozório, R. (2016). Seaweed Alaria esculenta as a biomonitor species of metal contamination in Aughinish Bay (Ireland). Ecological Indicators, 69, 19–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.03.041
Samani, A. R. V., Karbassi, A. R., Fakhraee, M., Heidari, M., Vaezi, A. R., & Valikhani, Z. (2014). Effect of dissolved organic carbon and salinity on flocculation process of heavy metals during mixing of the Navrud River water with Caspian Seawater. Desalination Water Treatment, 55(4), 926–934. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.920730
Santos, T. T. L., Marins, R. V., & Da Silva Dias, F. J. (2019). Carbon influence on metal distribution in sediment of Amazonian macrotidal estuaries of northeastern Brazil. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191(9), 552. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7626-6
Sari, E., Unlu, S., Apak, R., Balci, N., & Koldemir, B. (2014). Distribution and contamination of heavy metals in the surface sediments of Ambarli Port Area (Istanbul, Turkey). Ekoloji, 23, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.5053/ekoloji.2014.901
Schintu, M., Marras, B., Durante, L., Meloni, P., & Contu, A. (2010). Macroalgae and DGT as indicators of available trace metals in marine coastal waters near a lead–zinc smelter. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 167, 653–661.
Schuhmacher, M., Domingo, J. L., Llobet, J. M., & Corbella, J. (1995). Variations of heavy metals in water, sediments, and biota from the delta of Ebro River, Spain. Journal of Environmental Science and Health. Part a, Toxic/hazardous Substances & Environmental Engineering, 30(6), 1361–1372. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529509376269
Serejo, J. H. F., Santos, T. T. L., & Lima, H. P. (2020). Fortnightly variability of total suspended solids and bottom sediments in a macrotidal estuarine complex on the Brazilian northern coast. Journal of Sedimentary Environments, 5, 101–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43217-020-00005-8
Shafie, N. A., Aris, A. Z., Zakaria, M. P., Haris, H., Lim, W. Y., & Isa, N. M. (2013). Application of geoaccumulation index and enrichment factors on the assessment of heavy metal pollution in the sediments. Journal of Environmental Science and Health. Part a, Toxic/hazardous Substances & Environmental Engineering, 48(2), 182–190. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2012.717810
Stearn, W. T. (1958). Botanical Exploration to the time of Linnaeus. Proceedings Linnean Society London, 169(3), 173–196. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8312.1958.tb01472.x
Sutherland, R. A. (2000). Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu, Hawaii. Environmental Geology, 39, 611–637. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002540050473
Taylor, A. M., Edge, K. J., Ubrihien, R. P., & Maher, W. A. (2017). The freshwater bivalve Corbicula australis as a sentinel species for metal toxicity assessment: An in situ case study integrating chemical and biomarker analyses. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 36(3), 709–719. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.3582
Trifan, A., et al. (2015). Heavy metal content in macroalgae from the Roumanian Black Sea. Revue Roumaine De Chimie, 60(9), 915–920.
Turekian, K. K., & Wedepohl, K. H. (1961). Distribution of the elements in some major units of the earth’s crust. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 72, 175–192. https://doi.org/10.1130/0016-7606(1961)72[175:DOTEIS]2.0.CO;2
Udechukwu, B. E., Ismail, A., Zulkifli, S. Z., & Omar, H. (2014). Distribution, mobility, and pollution assessment of Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn, and Fe in intertidal surface sediments of Sg Puloh mangrove estuary, Malaysia. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 22(6), 4242–4255. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3663-4
Valentin, Y. Y., Dalto, A. G., & Gestinari, L. D. S. (2010). Benthic macroalgae diversity in Admiralty Bay (King George Island, South Shetland Islands, Antarctic Peninsula). Annual Activity Report of National Institute of Science and Technology Antarctic Environmental Research (INCT-APA), Cubo, São Carlos, 62–64. https://doi.org/10.4322/apa.2014.013
Varol, M. (2011). Assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Tigris River (Turkey) using pollution indices and multivariate statistical techniques. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 195, 355–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.08.051
Veglio, F., & Beolchini, F. (1997). Removal of metals by biosorption: A review. Hidrometal, 44, 301–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-386X(96)00059-X
Wentworth, C. K. A. (1922). Scale of grade and class terms for clastic sediments. The Journal of Geology, 30, 377–392. https://doi.org/10.1086/622910
Williams, J. A., & Antoine, J. (2020). Evaluation of the elemental pollution status of Jamaican surface sediments using enrichment factor, geoaccumulation index, ecological risk and potential ecological risk index. Marine Pollution Bulletin. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111288
Yahya, A. N., Mohamed, S. K., & Mohamed, A. G. (2018). Environmental pollution by heavy metals in the aquatic ecosystems of Egypt. Open Access Journal of Toxicology, 3(1), 001–009. https://doi.org/10.19080/OAJT.2018.03.555603
Yap, C. K., & Al-Mutairi, K. A. (2023). The ecological-health risks of potentially toxic metals in the surface sediments and leaves of salt-secreting Avicennia officinalis as potential phytoremediators: A field-based biomonitoring study from Klang Mangrove Area. Biology, 12(1), 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12010043
Yokoya, N. S., Plastino, E. M., Braga, M. R. A., Fujii, M. T., Cordeiro-Marino, M., Eston, V. R., & Harari, J. (1999). Temporal and spatial variations in the structure of macroalgal communities associated with mangrove trees of Ilha do Cardoso, São Paulo state, Brazil. Brazilian Journal of Botany, 22(2), 195–204. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-84041999000200010
Zhang, J., & Liu, C. L. (2002). Riverine composition and estuarine geochemistry of particulate metals in China - weathering features, anthropogenic impact and chemical fluxes. Estuarine Coastal Shelf ScieNce, 54, 1051–1070. https://doi.org/10.1006/ecss.2001.0879
Zhao, P., Sanganyado, E., Wang, T., Sun, Z., Jiang, Z., Zeng, M., Huang, Z., Li, Y., Li, P., Bi, R., & Liu, W. (2022). Accumulation of nutrients and potentially toxic elements in plants and fishes in restored mangrove ecosystems in South China. Science of the Total Environment, 838(Part 1), 155964. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155964
Zhao, S., Shi, X., Li, C., Zhang, H., & Wu, Y. (2013). Seasonal variation of heavy metals in sediment of Lake Ulansuhai, China. Chemistry and Ecology, 30(1), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1080/02757540.2013.841894
Zhiyuan, W., Wang, D., Zhou, H., & Qi, Z. (2011). Assessment of soil heavy metal pollution with principal component analysis and Geoaccumulation Index. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 10, 1946–1952. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2011.09.305
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Postgraduate Program in Oceanography (PPGOceano-UFMA) as well as the Laboratory of Phytoplankton of the Federal University of Maranhão (UFMA) and the Laboratory of Environmental Science (UENF) for technical and structural support.
Funding
This research was supported by a grant from the Foundation for Research and Scientific and Technological Development of Maranhão—Brazil (FAPEMA) through the concession of a Master’s scholarship (BM-00061/20) to the first author.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by James J.M. Corrêa, Marco V.J. Cutrim, and Quedyane Silva da Cruz. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Marco V.J. Cutrim, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Corrêa, J.J.M., Cutrim, M.V.J. & da Cruz, Q.S. Evaluation of metal contamination in surface sediments and macroalgae in mangrove and port complex ecosystems on the Brazilian equatorial margin. Environ Monit Assess 195, 432 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11024-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11024-z