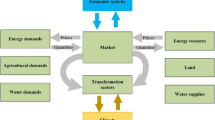
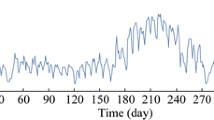
Abstract
Sustainable development and reducing greenhouse gas emissions require optimizing the structure of energy production as the main factor in the emission of pollutants in Iran’s electricity industry. Over the past years, environmental scientists have proposed carbon tax (CT) and carbon emission trading (CET) as policy tools to reduce pollutant emissions in developed and developing economies. Due to poor access to environmental data and the lack of effective pollution control laws and policies in Iran, efforts to realize the effectiveness of these policies in Iran have been inadequate. The present paper establishes a system dynamics model with feedback to fill these gaps in analyzing the effects of the CT and CET schemes. The following eight scenarios were considered and examined: a baseline scenario (BAU scenario), an emission tax scenario, an emission trading mechanism scenario, an energy supply scenario (to increase electricity generation), an emission tax scenario with investment in technology research and development (to increase energy efficiency), a tax scenario on emissions along with increasing energy supply, the scenario of emission trading mechanism with investment in technology research and development, and the scenario of emission trading mechanism with increasing energy supply. The results showed that while both CT and CET policy groups can be effective in reducing carbon emissions in thermal power plants, in the long run, using price tools to maintain energy security reduces the efficiency of policies greatly. Nevertheless, the effectiveness of CT policy in reducing emissions is higher. Also, despite the allocation of revenue from the application of scenarios to the development of renewable energy, the development of this sector cannot compensate for the reduction in the supply of thermal power plants following the implementation of these policies. As a result, other supportive policies are necessary for the further and faster development of the renewable sector and optimizing the energy structure with an emission reduction approach.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statements
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Abbaszadeh Karamjavan, S., & Abbaszadeh, N. (2020). Economic assessment of carbon tax policy: Applied computable general equilibrium model. Quarterly Journal of Energy Policy and Planning Research, 6(1), 1–31. Retrieved from http://epprjournal.ir/article-1-658-fa.html
Abrell, J., Betz, R., & Kosch, M. (2020). The European Emissions Trading System and the German and Polish Electricity Market. Influence of market structures and market regulation on the carbon market. German Environment Agency. Zurich University of Applied Sciences (ZHAW). Retrieved from http://www.umweltbundesamt.de/publikationen
Ahmadi, Y., Yamazaki, A., & Kabore, P. (2022). How do carbon taxes affect emissions? Plant-level evidence from manufacturing. Environmental and Resource Economics, 119, 1–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euroecorev.2019.08.001
Barkhordari, S., & Fattahi, M. (2017). Reform of energy prices, energy intensity and technology: A case study of Iran (ARDL approach). Energy Strategy Reviews, 18, 18–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esr.2017.09.004
Bayer, S., & Sterman, J. (2004). Business dynamics: Systems thinking and modeling for a complex world. Interfaces, 34(4), 324–327.
Bi, H., Xiao, H., & Sun, K. (2018). The impact of carbon market and carbon tax on green growth pathway in China: A dynamic CGE model approach. Emerging Markets Finance and Trade, 55(6), 1312–1325. https://doi.org/10.1080/1540496X.2018.1505609
Cabello, M., & Mardones, C. (2019). Effectiveness of local air pollution and GHG taxes: The case of Chilean industrial sources. Energy Economics, 83, 491–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2019.08.007
Central Bank of Iran. (2022). Economic indicators, number 107. Central Bank of Iran. Retrieved from https://www.cbi.ir/simplelist/23933.aspx
Chen, Y., Wang, M., Feng, C., Zhou, H., & Wang, K. (2020). Total factor energy efficiency in Chinese manufacturing industry under industry and regional heterogeneities. Resources, Conservation and Recycling. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2020.105255
Currie, D. J., Smith, C., & Jagals, P. (2018). The application of system dynamics modelling to environmental health decision-making and policy-A scoping review. BMC Public Health, 18(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-018-5318-8
Diaz-Rainey, I., & Tulloch, D. J. (2018). Carbon pricing and system linking: Lessons from the New Zealand Emissions Trading Scheme. Energy Economics, 73, 66–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2018.04.035
Dong, H., Dai, H., Geng, Y., Fujita, T., Liu, Z., Xie, Y., & Tang, L. (2017). Exploring impact of carbon tax on China’s CO2 reductions and provincial disparities. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 77, 596–603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.04.044
EIA. (2019). Country Analysis Executive Summary: Iran. Retrieved from https://www.eia.gov/international/content/
Ellerman, A. D., Marcantonini, C., & Zaklan, A. (2016). The European Union Emissions Trading System: Ten years and counting. Review of Environmental Economics and Policy, 10(1), 89–107. https://doi.org/10.1093/reep/rev014
EPA. (2003). Tools of the trade : A guide to designing and United States Environmental Protection Agency. Retrieved from http://www.epa.gov/airmarkets
Ervine, K. (2018). How Low Can It Go? Analyzing the political economy of carbon market design and low carbon prices. New Political Economy, 23(6), 690–710. https://doi.org/10.1080/13563467.2018.1384454
Esmaieli, M., & Ahmadian, M. (2018). The effect of research and development incentive on wind power investment, a system dynamics approach. Renewable Energy, 126, 765–773. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2018.04.009
Feng, T. T., Yang, Y. S., & Yang, Y. H. (2018). What will happen to the power supply structure and CO2 emissions reduction when TGC meets CET in the electricity market in China? Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 92, 121–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.04.079
Gallagher, K. S., Zhang, F., Orvis, R., Rissman, J., & Liu, Q. (2019). Assessing the Policy gaps for achieving China’s climate targets in the Paris Agreement. Nature Communications, 10(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09159-0
Ghazouani, A., Xia, W., Ben Jebli, M., & Shahzad, U. (2020). Exploring the role of carbon taxation policies on CO2 emissions: Contextual evidence from tax implementation and non-implementation European Countries. Sustainability, 12, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12208680
Godarzi, A. A., & Maleki, A. (2021). Optimal electricity supply system under Iranian framework limitations to meet its emission pledge under the Paris climate agreement. International Journal of Sustainable Energy Planning and Management, 30, 75–96. https://doi.org/10.5278/ijsepm.5896
Han, F., & Li, J. (2020). Assessing impacts and determinants of China’s environmental protection tax on improving air quality at provincial level based on Bayesian statistics. Journal of Environmental Management, 271, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111017
Hasani, M., & Hosseini, S. H. (2011a). Dynamic assessment of capacity investment in electricity market considering complementary capacity mechanisms. Energy, 36(1), 277–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2010.10.041
Hasani-Marzooni, M., & Hosseini, S. H. (2011b). Dynamic model for market-based capacity investment decision considering stochastic characteristic of wind power. Renewable Energy, 36(8), 2205–2219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2011.01.018
Hasani-Marzooni, M., & Hosseini, S. H. (2012a). Dynamic interactions of TGC and electricity markets to promote wind capacity investment. IEEE Systems Journal, 6(1), 46–57. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSYST.2011.2162891
Hasani-Marzooni, M., & Hosseini, S. H. (2012b). Trading strategies for wind capacity investment in a dynamic model of combined tradable green certificate and electricity markets. IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution, 6(4), 320–330. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-gtd.2011.0234
Hasani-Marzooni, M., & Hosseini, S. H. (2013). Dynamic analysis of various investment incentives and regional capacity assignment in Iranian electricity market. Energy Policy, 56, 271–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2012.12.059
He, P., Ning, J., Yu, Z., Xiong, H., Shen, H., & Jin, H. (2014). Can environmental tax policy really help to reduce pollutant emissions? An empirical study of a panel ARDL model based on OECD countries and China. Sustainability, 11(16), 1–32. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11164384
Hsu, C. W. (2012). Using a system dynamics model to assess the effects of capital subsidies and feed-in tariffs on solar PV installations. Applied Energy, 100, 205–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2012.02.039
Hsu, C. W., & Ho, S. P. (2016). Assessing feed-in tariffs on wind power installation and industry development in Taiwan. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 58, 548–557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.12.255
Hu, H., Dong, W., & Zhou, Q. (2021). A comparative study on the environmental and economic effects of a resource tax and carbon tax in China: Analysis based on the computable general equilibrium model. Energy Policy, 156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2021.112460
Hu, X., Sun, Y., Liu, J., Meng, J., Wang, X., & Yang, H.., Tao, S. (2019). The impact of environmental protection tax on sectoral and spatial distribution of air pollution emissions in China. Environmental Research Letters, 14(5), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/ab1965
IGMC. (2022). Retrieved from Iran Grid Management Company. https://www.igmc.ir/About-Us/Task-Mission
IPCC. (2015). Climate change 2014: mitigation of climate change (Vol. 3). Cambridge University Press.
Iran Data Portal. (2008). Energy Balance Sheets. Retrieved from https://irandataportal.syr.edu/energy-environment
Iranian Ministry of Energy. (2011). Annual Energy Balance Sheet. Iranian Ministry of Energy.
King, M., Tarbush, B., & Teytelboym, A. (2019). Targeted carbon tax reforms. European Economic Review, 119, 526–547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euroecorev.2019.08.001
Lee, C., Lin, S., & Lewis, C. (2008). Analysis of the impacts of combining carbon taxation and emission trading on different industry sectors. Energy Policy, 36(2), 722–729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2007.10.025
Li, G., & Masui, T. (2018). Assessing the impacts of China’s environmental tax using a dynamic computable general equilibrium model. Journal of Cleaner Production, 208, 316–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.016
Li, P., Lin, Z., Du, H., Feng, T., & Zuo, J. (2021). Do environmental taxes reduce air pollution? Evidence from fossil-fuel power plants in China. Journal of Environmental Management, 295, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113112
Li, W., & Jia, Z. (2017). Carbon tax, emission trading, or the mixed policy: Which is the most effective strategy for climate change mitigation in China? Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies for Global Change, 22(6), 973–992. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11027-016-9710-3
Li, Y., Yang, P., & Wang, H. (2018). Collecting coal fired power environmental tax to promote wind power development and environmental improvement. Acta Scientifica Malaysia, 2(1), 5–8. https://doi.org/10.26480/asm.01.2018.05.08
Lin, B., & Jia, Z. (2018). The energy, environmental and economic impacts of carbon tax rate and taxation industry: A CGE based study in China. Energy, 159, 558–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.06.167
Liu, W., & Liu, T. (2022). Exploring the impact and path of environmental protection tax on different air pollutant emissions. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(8), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19084767
Liu, X. N., Wang, B., Du, M. Z., & Zhang, N. (2018). Potential economic gains and emissions reduction on carbon emissions trading for China’s large-scale thermal power plants. Journal of Cleaner Production, 204, 247–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.131
Mardani, H. (2018). A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the Ph.D. degree. Sharif University of Technology, Management and Economics. Tehran: Sharif University of Technology.
Mardones, C. (2020). Analysis on complementarity between a CO2 tax and an emissions trading system to reduce industrial emissions in Chile. Energy & Environment, 1–14.
Masoomi, M., Panahi, M., & Samadi, R. (2020). Scenarios evaluation on the greenhouse gases emission reduction potential in Iran’s thermal power plants based on the LEAP model. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 192(4), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-8196-3
Ministry Of Energy. (2022). Retrieved from https://moe.gov.ir/
Mousavian, H. M., Shakouri, G. H., Mashayekhi, A. N., & Kazemi, A. (2020). Does the short-term boost of renewable energies guarantee their stable long-term growth? Assessment of the dynamics of feed-in tariff policy. Renewable Energy, 159, 1252–1268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2020.06.068
Movahednasab, A. R. (2017). A system dynamics analysis of the long run investment in market-based electric generation expansion with renewable resources. International Transactions on Electrical Energy Systems, 27(8), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1002/etep.2338
Murray, B., & Rivers, N. (2015). British Columbia’s revenue-neutral carbon tax: A review of the latest “grand experiment” in environmental policy. Energy Policy, 86, 674–683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2015.08.011
Niroo Research Institute. (2015a). the roadmap for increasing the efficiency of the country’s thermal power plants. Tehran. Retrieved from https://www.nri.ac.ir/Tech-Plan
Niroo Research Institute. (2015b). the strategic document and roadmap for the development of pollutant management technology (air, water, and soil) in the Iran electricity industry. Retrieved from Niroo Research Institute. https://international.nri.ac.ir/
Olsina, F. (2005). Long-term dynamics of liberalized electricity markets. National Doctoral dissertation, University of San Juan. Department of Engineering.
Olsina, F., Garcés, F., & Haubrich, H. J. (2006). Modeling long-term dynamics of electricity markets. Energy Policy, 34(12), 1411–1433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2004.11.003
Pakrooh, P., Nematian, J., Pishbahar, E., & Hayati, B. (2021). Reforming energy prices to achieve sustainable energy consumption in the agriculture sector of Iran’s provinces: Using game approach. Journal of Cleaner Production, 293, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126146
Pan, X., Li, M., Xu, H., Guo, S., Guo, R., & Lee, C. T. (2021). Simulation on the effectiveness of carbon emission trading policy: A system dynamics approach. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 72, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/01605682.2020.1740623
Pathak, L., & Shah, K. (2019). Renewable energy resources, policies and gaps in BRICS countries and the global impact. Front. Energy, 13(3), 506–521. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11708-018-0601-z
Pretis, F. (2022). Does a carbon tax reduce CO2 emissions? Evidence from British Columbia. Environmental and Resource Economics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10640-022-00679-w
Rafieisakhaei, M., & Barazandeh, B. (2017). The efficacy of market-based emission control systems: A system dynamics approach. In S. P. E. Health (Ed.), Safety, Security, Environment, & Social Responsibility Conference-North America (pp. 1–16). Society of Petroleum Engineers.
Rezaee, H. (2012). Modeling and policy simulation of long run of restructured electricity market of Iran: Hybrid system dynamics and optimization approachs. Doctoral dissertation, Imam Sadiq (a.s) University, Islamic Studies And Economics Science, Tehran.
Rios-Festner, D., Blanco, G., & Olsina, F. (2020). Long-term assessment of power capacity incentives by modeling generation investment dynamics under irreversibility and uncertainty. Energy Policy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2019.111185
Runst, P., & Höhle, D. (2022). The German eco tax and its impact on CO2 emissions. Energy Policy, 160, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2021.112655
Sarrakh, R., Renukappa, S., Suresh, S., & Mushatat, S. (2020). Impact of subsidy reform on the kingdom of Saudi Arabia’s economy and carbon emissions. Energy Strategy Reviews, 28, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esr.2020.100465
SATBA. (2020). Tehran: Renewable Energy and Energy Efficiency Organization (SATBA). Retrieved from https://www.satba.gov.ir/en/home
Saysel, A. K., & Hekimoğlu, M. (2013). Exploring the options for carbon dioxide mitigation in Turkish electric power industry: System dynamics approach. Energy Policy, 60, 675–686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2013.04.053
Shahzad, U., Radulescu, M., Rahim, S. I., Yousaf, Z., & Ionescu, S. A. (2021). Do environment-related policy instruments and technologies facilitate renewable energy generation? Exploring the contextual evidence from developed economies. Energies, 14(690), 1–25. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14030690
Shapiro, J. S., & Walker, R. (2018). Why is pollution from US manufacturing declining? The roles of environmental regulation, productivity, and trade. American Economic Review, 108(12), 3814–3854. https://doi.org/10.1257/aer.20151272
TAVANIR Co. (2010). The detailed annual data of Iran electric power industry: Generation section in 2009–2010.
TAVANIR Co. (2020). Iran electric power industry. Tavanir Expert Holding Company.
Villoria-Sáez, P., Tam, V. W., del Río Merino, M., Arrebola, C. V., & Wang, X. (2016). Effectiveness of greenhouse-gas emission trading schemes implementation: A review on legislations. Journal of Cleaner Production, 127, 49–58.
Vogstad, K. O. (2005). A system dynamics analysis of the Nordic electricity market: the transition from fossil fuelled toward a renewable supply within a liberalized electricity market. Doctoral dissertation, Norwegian University of Science and Technology Department of Electrical Power Engineering.
WB. (2017). State and Trends of Carbon Pricing 2017. World Bank.
Xie, L., Zhou, Z., & Hui, S. (2022). Does environmental regulation improve the structure of power generation technology? Evidence from China’s pilot policy on the carbon emissions trading market (CETM). Technological Forecasting and Social Change. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2021.121428
Yang, H., Li, X., Ma, L., & Li, Z. (2021). Using system dynamics to analyse key factors influencing China’s energy-related CO2 emissions and emission reduction scenarios. Journal of Cleaner Production, 320, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128811
Ye, F., Xiong, X., Li, L., & Li, Y. (2021). Measuring the effectiveness of the Chinese Certified Emission Reduction scheme in mitigating CO2 emissions: A system dynamics approach. Journal of Cleaner Production, 294, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125355
Yousefi, G. R., Kaviri, S. M., Latify, M. A., & Rahmati, I. (2017). Electricity industry restructuring in Iran. Energy Policy, 108, 212–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2017.05.018
Yu, X., Wu, Z., Wang, Q., Sang, X., & Zhou, D. (2020). Exploring the investment strategy of power enterprises under the nationwide carbon emissions trading mechanism: A scenario-based system dynamics approach. Energy Policy, 140, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2020.111409
Zakeri, A., Dehghanian, F., Fahimnia, B., & Sarkis, J. (2015). Carbon pricing versus emissions trading: A supply chain planning perspective. International Journal of Production Economics, 164, 197–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2014.11.012
Zhang, J., Sun, X., Li, H., & Philbin, S. P. (2021). Investigating the role of emissions trading policy to reduce emissions and improve the efficiency of industrial green innovation. Journal of Management Science and Engineering, 6(4), 377–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmse.2021.09.006
Zhang, L., Li, Y., & Jia, Z. (2018). Impact of carbon allowance allocation on power industry in China’s carbon trading market: Computable general equilibrium based analysis. Applied Energy, 229, 814–827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.08.055
Zhang, Y., Qi, L., Lin, X., Pan, H., & Sharp, B. (2022). Synergistic effect of carbon ETS and carbon tax under China’s peak emission target: A dynamic CGE analysis. Science of the Total Environment, 825, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154076
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
1-Shirin Azizi: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Validation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Resources, Data curation, Writing – the original draft, Writing – review & editing. 2-Reza Radfar: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Validation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Resources, Data curation, Writing – the original draft, Writing – review & editing. 3-Hanieh Nikoomaram: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Validation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Resources, Data curation, Writing – the original draft, Writing – review & editing. 4- Ali Rajabzadeh Ghatari: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Validation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Resources, Data curation, Writing – the original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
There is no contradiction between the article and the order of the article names.
Disclaimers
This article has been stabilized by the group and has no bearing on its responsibility in any institution or body.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Azizi, S., Radfar, R., Nikoomaram, H. et al. Dynamic modeling to analyze the impacts of carbon reduction policies, Iran’s electricity industry. Environ Monit Assess 195, 350 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10897-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10897-w