Abstract
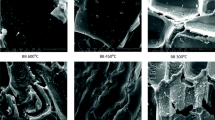
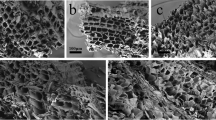
Biochar derived from waste pine needles was chemically modified using polyethyleneimine (PEI) to increase its adsorptive potential for withdrawal of anionic dye Congo red from aqueous solution. PEI impregnation on biochar was confirmed from scanning electron microscopy and energy-dispersive X-ray analysis, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and X-ray diffraction analysis. The surface area of biochar decreased after PEI treatment, but the amine groups increased on biochar surface. PEI-treated biochar displayed considerable increase in adsorption at acidic conditions. Adsorption isotherm was best explained by Langmuir model (R2 > 99) and the adsorption kinetics agrees well with pseudo-second-order model. The maximum adsorption capacity of PEI-treated biochar was observed to be 294.11 mg g−1 and 30.76 mg g−1 for pristine biochar displaying a 9.5-fold increase. The positive value of standard enthalpy of adsorption (∆H° = 14.96 KJmole−1) indicated the endothermic nature of adsorption, and positive value of entropy (∆S° = 74.43 Jmole−1 K−1) revealed the affinity of biochar towards dye molecules. Negative value of Gibb’s free energy ∆G° (− 7.2 KJmole−1) revealed that the process was spontaneous. Electrostatic interaction appeared to be the key mechanism governing the adsorption process. Thus, PEI-impregnated biochar represents novel low-cost sorbent that can effectively remove anionic dyes which are poorly removed by pristine biochar.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avcı, A., Inci, I., & Baylan, N. (2020). Adsorption of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride on multiwall carbon nanotube. Journal of Molecular Structure, 1206, 127711.
Benkhaya, S., M’rabet, S., & El Harfi, A. (2020). Classifications, properties, recent synthesis and applications of azo dyes. Heliyon, 6(1), e03271.
Choudhary, V., Patel, M., Pittman Jr, C. U., & Mohan, D. (2020). Batch and continuous fixed-bed lead removal using himalayan pine needle biochar: isotherm and kinetic studies. ACS Omega, 5(27), 16366–16378.
Du, J., Bao, J., Hassan, M. A., Irshad, S., & Talib, M. A. (2019). Multi-functional biochar novel surface chemistry for efficient capture of anionic Congo red dye: Behavior and mechanism. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 44(12), 10127–10139.
Dutta, S., Gupta, B., Srivastava, S. K., & Gupta, A. K. (2021). Recent advances on the removal of dyes from wastewater using various adsorbents: A critical review. Materials Advances, 2, 4497–4531.
Essandoh, M., Garcia, R. A., Palochik, V. L., Gayle, M. R., & Liang, C. (2021). Simultaneous adsorption of acidic and basic dyes onto magnetized polypeptidylated-Hb composites. Separation and Purification Technology, 255, 117701.
Gupta, V. K., Agarwal, S., Ahmad, R., Mirza, A., & Mittal, J. (2020). Sequestration of toxic congo red dye from aqueous solution using ecofriendly guar gum/activated carbon nanocomposite. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 158, 1310–1318.
Huang, X., Yu, F., Peng, Q., & Huang, Y. (2018). Superb adsorption capacity of biochar derived from leather shavings for Congo red. RSC Advances, 8(52), 29781–29788.
Iark, D., dos Reis Buzzo, A. J., Garcia, J. A. A., Côrrea, V. G., Helm, C. V., Corrêa, R. C. G., et al. (2019). Enzymatic degradation and detoxification of azo dye Congo red by a new laccase from Oudemansiella canarii. Bioresource Technology, 289, 121655.
Ighalo, J. O., & Adeniyi, A. G. (2020). A mini-review of the morphological properties of biosorbents derived from plant leaves. SN Applied Sciences, 2(3), 1–16.
Imam, A., Suman, S. K., Singh, R., Vempatapu, B. P., Ray, A., & Kanaujia, P. K. (2021). Application of laccase immobilized rice straw biochar for anthracene degradation. Environmental Pollution, 268, 115827.
Jung, K. W., Kim, K., Jeong, T. U., & Ahn, K. H. (2016). Influence of pyrolysis temperature on characteristics and phosphate adsorption capability of biochar derived from waste marine macroalgae (Undaria pinnatifida roots). Bioresource Technology, 200, 1024–1028.
Li, T., Tong, Z., Gao, B., Li, Y. C., Smyth, A., & Bayabil, H. K. (2020). Polyethyleneimine-modified biochar for enhanced phosphate adsorption. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(7), 7420–7429.
Lv, Z., Yang, S., Liu, Y., Zhou, J., Xing, L., & Chen, L. (2018). The novel PEI-modified biochars and their application for the efficient elimination of Cr (VI) from aqueous solutions. Water Science and Technology, 77(8), 2045–2056.
Ma, Y., Liu, W.-J., Zhang, N., Li, Y.-S., Jiang, H., & Sheng, G.-P. (2014). Polyethylenimine modified biochar adsorbent for hexavalent chromium removal from the aqueous solution. Bioresource Technology, 169, 403–408.
Murcia-Salvador, A., Pellicer, J. A., Fortea, M. I., Gómez-López, V. M., Rodríguez-López, M. I., Núñez-Delicado, E., & Gabaldón, J. A. (2019). Adsorption of Direct Blue 78 using chitosan and cyclodextrins as adsorbents. Polymers, 11(6), 1003.
Negi, G. C. S. (2019). Forest fire in Uttarakhand: Causes, consequences and remedial measures. International Journal of Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 45(1), 31–37.
Pandey, D., Daverey, A., Dutta, K., Yata, V. K., & Arunachalam, K. (2021). Valorization of waste pine needle biomass into biosorbents for the removal of methylene blue dye from water: Kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamics study. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 102200.
Sahoo, J. K., Paikra, S. K., Mishra, M., & Sahoo, H. (2019). Amine functionalized magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, antibacterial activity and rapid removal of Congo red dye. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 282, 428–440.
Sharma, A., Siddiqui, Z. M., Dhar, S., Mehta, P., & Pathania, D. (2019). Adsorptive removal of congo red dye (CR) from aqueous solution by Cornulaca monacantha stem and biomass-based activated carbon: Isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamics. Separation Science and Technology, 54(6), 916–929.
Singh, G., Giri, A., & Paul, S. (2017). Pinus roxburghii Sarg.(Chir Pine): a valuable forest resource of Uttarakhand. Indian Forester, 143(7), 700–709.
Sun, L., Chen, D., Wan, S., & Yu, Z. (2015). Performance, kinetics, and equilibrium of methylene blue adsorption on biochar derived from eucalyptus saw dust modified with citric, tartaric, and acetic acids. Bioresource Technology, 198, 300–308.
Tian, C., Feng, C., Wei, M., & Wu, Y. (2018). Enhanced adsorption of anionic toxic contaminant Congo Red by activated carbon with electropositive amine modification. Chemosphere, 208, 476–483.
Tran, H. N., You, S.-J., & Chao, H.-P. (2016). Thermodynamic parameters of cadmium adsorption onto orange peel calculated from various methods: A comparison study. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 4(3), 2671–2682.
Wang, L., Yan, W., He, C., Wen, H., Cai, Z., Wang, Z., et al. (2018). Microwave-assisted preparation of nitrogen-doped biochars by ammonium acetate activation for adsorption of acid red 18. Applied Surface Science, 433, 222–231.
Wang, X., Feng, J., Cai, Y., Fang, M., Kong, M., Alsaedi, A., et al. (2020). Porous biochar modified with polyethyleneimine (PEI) for effective enrichment of U (VI) in aqueous solution. Science of the Total Environment, 708, 134575.
Wekoye, J. N., Wanyonyi, W. C., Wangila, P. T., & Tonui, M. K. (2020). Kinetic and equilibrium studies of Congo red dye adsorption on cabbage waste powder. Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology, 2, 24–31.
Wong, S., Tumari, H. H., Ngadi, N., Mohamed, N. B., Hassan, O., Mat, R., & Amin, N. A. S. (2019). Adsorption of anionic dyes on spent tea leaves modified with polyethyleneimine (PEI-STL). Journal of Cleaner Production, 206, 394–406.
Wu, J., Yang, J., Feng, P., Huang, G., Xu, C., & Lin, B. (2020). High-efficiency removal of dyes from wastewater by fully recycling litchi peel biochar. Chemosphere, 246, 125734.
Wu, Z., Wang, X., Yao, J., Zhan, S., Li, H., Zhang, J., & Qiu, Z. (2021). Synthesis of polyethyleneimine modified CoFe2O4-loaded porous biochar for selective adsorption properties towards dyes and exploration of interaction mechanisms. Separation and Purification Technology, 277, 119474.
Yagub, M. T., Sen, T. K., Afroze, S., & Ang, H. M. (2014). Dye and its removal from aqueous solution by adsorption: A review. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 209, 172–184.
Yang, G., Wu, L., Xian, Q., Shen, F., Wu, J., & Zhang, Y. (2016). Removal of congo red and methylene blue from aqueous solutions by vermicompost-derived biochars. PLoS ONE, 11(5), e0154562.
Yek, P. N. Y., Peng, W., Wong, C. C., Liew, R. K., Ho, Y. L., Mahari, W. A. W., et al. (2020). Engineered biochar via microwave CO2 and steam pyrolysis to treat carcinogenic Congo red dye. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 395, 122636.
Younas, F., Mustafa, A., Farooqi, Z. U. R., Wang, X., Younas, S., Mohy-Ud-Din, W., et al. (2021). Current and emerging adsorbent technologies for wastewater treatment: Trends, limitations, and environmental implications. Water, 13(2), 215.
Yu, K. L., Lee, X. J., Ong, H. C., Chen, W.-H., Chang, J.-S., Lin, C.-S., et al. (2021). Adsorptive removal of cationic methylene blue and anionic Congo red dyes using wet-torrefied microalgal biochar: Equilibrium, kinetic and mechanism modeling. Environmental Pollution, 272, 115986.
Zhao, D., Gao, X., Wu, C., Xie, R., Feng, S., & Chen, C. (2016). Facile preparation of amino functionalized graphene oxide decorated with Fe3O4 nanoparticles for the adsorption of Cr (VI). Applied Surface Science, 384, 1–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pandey, D., Daverey, A., Dutta, K. et al. Enhanced adsorption of Congo red dye onto polyethyleneimine-impregnated biochar derived from pine needles. Environ Monit Assess 194, 880 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10563-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10563-1