Abstract
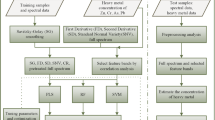
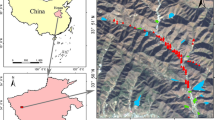
Given the limitation of conventional soil pollution monitoring through mapping which is a costly, time-consuming work, the study aims to establish an image recognition model to identify the source of pollution automatically. The study choses a contaminated land and then use a non-destructive instrument that can quickly and effectively measure the content of heavy metals. A two concentration prediction models of Ni, Cu, Zn, Cr, Pb, As, Cd, and Hg using hyperspectral imaging were developed, Decision Tree and Back Propagation Neural Network, in combination of particle swarm optimization employed for optimization algorithm. As a result, random forest is more accurate than the forecast result of back propagation neural network. This study has established an excellent Cu and Cr model, which can accurately capture the pollution source. In addition, through aerial photographs, we also found that there were also high pollution reactions on the banks of the river. The developed model is beneficial for high pollution areas which can be quickly found, thereby following investigation and remediation work can be carried out with less time and cost consuming comparing with the conventional soil monitoring.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files]. The raw data is available on request from the authors.
References
Albanese, S., De Vivo, B., Lima, A., & Cicchella, D. (2007). Geochemical background and baseline values of toxic elements in stream sediments of Campania region (Italy). Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 93(1), 21–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2006.07.006
Antoniadis, V., Shaheen, S., Levizou, E., Shahid, M., Niazi, N., Vithanage, M., et al. (2019). A critical prospective analysis of the potential toxicity of trace element regulation limits in soils worldwide: Are they protective concerning health risk assessment? - A review. Environment International, 127, 819–847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.03.039
Bell, R., & Russell, C. (2002). Environmental policy for developing countries. Issues in Science and Technology, 18(3), 63–70. Retrieved May 28, 2021, from http://www.jstor.org/stable/43314167. Accessed 15 January 2021.
Briffa, J., Sinagra, E., & Blundell, R. (2020). Heavy metal pollution in the environment and their toxicological effects on humans. Heliyon, 6(9), e04691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04691
Buaisha, M., Balku, S., & Özalp-Yaman, S. (2020). Heavy metal removal investigation in conventional activated sludge systems. Civil Engineering Journal, 6(3), 470–477.
Bundschuh, J., Litter, M., Parvez, F., Román-Ross, G., Nicolli, H., Jean, J., et al. (2012). One century of arsenic exposure in Latin America: A review of history and occurrence from 14 countries. Science of the Total Environment, 429, 2–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.06.024
Chowdhury, S., Mazumder, M., Al-Attas, O., & Husain, T. (2016). Heavy metals in drinking water: Occurrences, implications, and future needs in developing countries. Science of the Total Environment, 569–570, 476–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.06.166
Díez, M., Simón, M., Martín, F., Dorronsoro, C., García, I., & Van Gestel, C. (2009). Ambient trace element background concentrations in soils and their use in risk assessment. Science of the Total Environment, 407(16), 4622–4632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.05.012
Hafez, Y., & Awad, E. (2016). Finite element modeling of radon distribution in natural soils of different geophysical regions. Cogent Physics, 3(1). https://doi.org/10.1080/23311940.2016.1254859
Hu, P., Huang, J., Ouyang, Y., Wu, L., Song, J., Wang, S., et al. (2013). Water management affects arsenic and cadmium accumulation in different rice cultivars. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 35(6), 767–778. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-013-9533-z
Jia, X., Cao, Y., O’Connor, D., Zhu, J., Tsang, D. C., Zou, B., & Hou, D. (2021). Mapping soil pollution by using drone image recognition and machine learning at an arsenic-contaminated agricultural field. Environmental Pollution, 270, 116281.
Kennedy, J., & Eberhart, R. (1995). Particle swarm optimization. Proceedings Of ICNN'95 - International Conference On Neural Networks. https://doi.org/10.1109/icnn.1995.488968
Lai, H., Hseu, Z., Chen, T., Chen, B., Guo, H., & Chen, Z. (2010). Health risk-based assessment and management of heavy metals-contaminated soil sites in Taiwan. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 7(10), 3595–3614. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph7103596
Lal, R. (2000). Soil management in the developing countries. Soil Science, 165(1), 57–72. https://doi.org/10.1097/00010694-200001000-00008
Lan, Y., Huang, Z., Deng, X., Zhu, Z., Huang, H., Zheng, Z., ... & Tong, Z. (2020). Comparison of machine learning methods for citrus greening detection on UAV multispectral images. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 171, 105234.
Lin, Y., Teng, T., & Chang, T. (2002). Multivariate analysis of soil heavy metal pollution and landscape pattern in Changhua county in Taiwan. Landscape and Urban Planning, 62(1), 19–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0169-2046(02)00094-4
Myint, H. (1973). The economic of the developing countries. Hutchinson University library.
Qin, G., Niu, Z., Yu, J., Li, Z., Ma, J., & Xiang, P. (2021). Soil heavy metal pollution and food safety in China: Effects, sources and removing technology. Chemosphere, 267, 129205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129205
Qun’ou, J., Lidan, X., Siyang, S., Meilin, W., & Huijie, X. (2021). Retrieval model for total nitrogen concentration based on UAV hyper spectral remote sensing data and machine learning algorithms–A case study in the Miyun Reservoir, China. Ecological Indicators, 124, 107356.
Rajaganapa, V., Xavier, F., Sreekumar, D., & Mandal, P. (2011). Heavy metal contamination in soil, water and fodder and their presence in livestock and products : A review. Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 4(3), 234–249. https://doi.org/10.3923/jest.2011.234.249
Rodríguez Eugenio, N., McLaughlin, M., & Pennock, D. (2018). Soil pollution. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
Sutherland, R. A. (2000). Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu, Hawaii. Environmental Geology, 39(6), 611–627.
Zwolak, A., Sarzyńska, M., Szpyrka, E., & Stawarczyk, K. (2019). Sources of soil pollution by heavy metals and their accumulation in vegetables: A review. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 230(7). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4221-y
Funding
The authors received financial support from the Environmental Protection Administration in Taiwan under Contract No. 109C003942.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendices
Appendix 1. Random forest-based prediction for Ni

Appendix 2. Random forest-based prediction for Cu

Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H.W., Chen, CY., Nguyen, K.L.P. et al. Hyperspectral sensing of heavy metals in soil by integrating AI and UAV technology. Environ Monit Assess 194, 518 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10125-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10125-5