Abstract
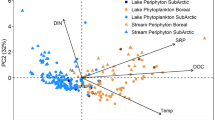
Nutrient input from internal and external sources could regulate the variability and abundance of algal and macrophytes in freshwater lakes. This study explores the response of algal and macrophyte growth in relation to internal and external nutrient loading. This study was conducted over a 12-month period in a eutrophic shallow urban lake known as Slim River Lake, which located in Perak state, Malaysia. The internal nutrient loading was calculated during five identified dry periods. Meanwhile, external nutrient loading was measured from stormwater runoff after storm events. Algal biomass was measured twice a month, while total macrophyte abundance was measured once in a month. In this lake, internal nutrient loading could contribute up to 7538.33 kg total phosphorus and 42.23 kg total nitrogen during dry periods. Meanwhile, external nutrient loading quantified from the stormwater runoff contributed up to 401,500 kg total phosphorus and 4611.67 kg total nitrogen. The highest monthly mean for algal biomass and total macrophyte abundance was recorded as 60,343.75 cells/mL and 821.50, respectively. Based on the Pearson correlation analysis, algal biomass was significantly correlated with the internal total phosphorus loading (r = 0.54, p < 0.05). In addition, algal biomass also shows an inverse relationship with the external total phosphorus loading (r = − 0.44, p < 0.05). In contrast, total macrophyte abundance was significantly correlated with the external total phosphorus loading (r = 0.50, p < 0.05) and external total nitrogen loading (r = 0.44, p < 0.05). These results suggest that variation of nutrient sources triggers a different response by algal and macrophytes in the study lake. In implications, these findings show that a combination approach in reducing nutrients from sediment and anthropogenic sources is required for potential lake restoration.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Data are available from the authors upon reasonable request.
References
Aeriyanie, A. R., Sinang, S. C., Nayan, N., & Poh, K. B. (2021). Role of internal and external nutrients loading in regulating in-lake nutrient concentrations in a eutrophic shallow lake. Environment Asia, 14(1), 63–68. https://doi.org/10.14456/ea.2021.7
Aeriyanie, A. R., Sinang, S. C., Nayan, N., & Song, H. (2020). Comparison of water level and eutrophication indicators during the wet and dry period in a eutrophic urban lake. Acta Ecologica Sinica. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chnaes.2020.03.003
Alahuhta, J. (2014). Geographic patterns of lake macrophyte communities and species richness at regional scale. Journal of Vegetation Science, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1111/jvs.12261
APHA. (2005). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater (21st ed.). American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation. Wash ington, DC.
Ayoade, A. A., & Aderogba, A. (2020). Spatial and temporal distribution of plankton in a tropical reservoir, southwestern nigeria. Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Biology and Fisheries, 24(5), 161–181. https://doi.org/10.21608/ejabf.2020.104724
Bakker, E. S., & Hilt, S. (2016). Impact of water-level fluctuations on cyanobacterial blooms: Options for management. Aquatic Ecology, 50(3), 485–498. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10452-015-9556-x
Bensafia, N., Djabourabi, A., Touati, H., Rachedi, M., & Belhaoues, S. (2020). Evolution of physicochemical parameters and trophic state of three Park National of El-Kala water bodies (North-east Algeria). Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Biology & Fisheries, 24(2), 249–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2007.11.012
Cai, L., Zhu, G., Zhu, M., Xu, H., & Qin, B. (2012). Effects of temperature and nutrients on phytoplankton biomass during bloom seasons in Taihu Lake. Water Science and Engineering, 5(4), 361–374. https://doi.org/10.3882/j.issn.1674-2370.2012.04.001
Champion, P., & Reeves, P. (2004). Macrophyte identification guides, https://www.niwa.co.nz/freshwater-and-estuaries/managementtools/identificationguides-and-fact-sheets/macrophyte-plant-id-guides
Cheruvelil, K. S., & Soranno, P. A. (2008). Relationships between lake macrophyte cover and lake and landscape features. Aquatic Botany, 88(3), 219–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquabot.2007.10.005
Dalu, T., Clegg, B., & Nhiwatiwa, T. (2012). Aquatic macrophytes in a tropical african reservoir: Diversity, communities and the impact of reservoir-level fluctuations. Transactions of the Royal Society of South Africa, 67(3), 117–125. https://doi.org/10.1080/0035919X.2012.712554
Dar, N. A., Pandit, A. K., & Ganai, B. A. (2015). Factors affecting the distribution patterns of aquatic macrophytes. Limnological Review, 14(2), 75–81. https://doi.org/10.2478/limre-2014-0008
Dubey, D., & Dutta, V. (2020). Nutrient enrichment in lake ecosystem and its effects on algae and macrophytes. In V. Shukla, & N. Kumar (Eds.), Environmental concerns and sustainable development (pp. 81–126). Singapore: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-6358-0_5
Engloner, A. I., Szalma, E., Sipos, K., & Dinka, M. (2013). Occurence and habitat preference of aquatic macrophytes in a large river channel. Community Ecology, 14, 243–248.
Engloner, A. I. (2012). Alternative ways to use and evaluate Kohler’s ordinal scale to assess aquatic macrophyte abundance. Ecological Indicators, 20, 238–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2012.02.023
Frumin, G. T., & Gildeeva, I. M. (2014). Eutrophication of water bodies—A global environmental problem. Russian Journal of General Chemistry, 84(13), 2483–2488. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1070363214130015
Hilt, S., Alirangues Nuñez, M. M., Bakker, E. S., Blindow, I., Davidson, T. A., Gillefalk, M., … Sayer, C. D. (2018). Response of submerged macrophyte communities to external and internal restoration measures in north temperate shallow lakes. Frontiers in Plant Science, 9(February). https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00194
Horppila, J. (2019). Sediment nutrients, ecological status and restoration of lakes. Water Research, 160, 206–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.05.074
Hu, S., Wang, T., Xu, S., Ma, L., & Sun, X. (2019). Seasonal release potential of sediments in reservoirs and its impact on water quality assessment. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16183303
Huang, T., Li, X., Rijnaarts, H., Grotenhuis, T., Ma, W., Sun, X., & Xu, J. (2014). Effects of storm runoff on the thermal regime and water quality of a deep, stratified reservoir in a temperate monsoon zone, in Northwest China. Science of the Total Environment, 485–486(1), 820–827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.01.008
Huang, Y. F., Ang, S. Y., Lee, K. M., & Lee, T. S. (2015). Quality of water resources in Malaysia. In T. S. Lee (Ed.), Research and practices in water quality. Intech. https://doi.org/10.5772/58969
Huisman, J., Codd, G. A., Paerl, H. W., Ibelings, B. W., Verspagen, J. M. H., & Visser, P. M. (2018). Cyanobacterial blooms. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 16(August). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-018-0040-1
Janke, B. D., Finlay, J. C., & Hobbie, S. E. (2017). Trees and streets as drivers of urban stormwater nutrient pollution. Environmental Science and Technology. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b02225
Jeppesen, E., Søndergaard, M., Jensen, J. P., Havens, K. E., Anneville, O., Carvalho, L., … Winder, M. (2005). Lake responses to reduced nutrient loading–An analysis of contemporary long-term data from 35 case studies. Freshwater Biology, 50(10), 1747–1771. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2005.01415.x
Johnson, J. (2010). Estimation of internal phosphorus loading for Cedar Island Lake. Freshwater Scientific Services.
Kowalczewska-Madura, K., Kozak, A., Dera, M., & Goldyn, R. (2019a). Internal loading of phosphorus from bottom sediments of two meso-eutrophic lakes. International Journal of Environmental Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-019-00167-y
Kowalczewska-Madura, K., Kozak, A., Martyna, D., & Goldyn, R. (2019b). Internal loading of phosphorus from bottom sediments of two meso‑eutrophic lakes. International Journal of Environmental Research, (Petterson 1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-019-00167-y
Kuiper, J. J., Verhofstad, M. J. J. M., Louwers, E. L. M., Bakker, E. S., Brederveld, R. J., Gerven, L. P. A. Van, … Mooij, W. M. (2017). Mowing submerged macrophytes in shallow lakes with alternative stable states: Battling the good guys ? Environmental Management, 59, 619–634. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-016-0811-2
Lee, H. W., Lee, Y. S., Kim, J., Lim, K. J., & Choi, J. H. (2019). Contribution of internal nutrients loading on the water quality of a reservoir. Water.
Lewis, A. S. L., Kim, B. S., Edwards, H. L., Wander, H. L., Garfield, C. M., Murphy, H. E., … Bruesewitz, D. A. (2020). Prevalence of phytoplankton limitation by both nitrogen and phosphorus related to nutrient stoichiometry, land use, and primary producer biomass across the northeastern United States northeastern United States. Inland Waters, 10(1), 42–50. https://doi.org/10.1080/20442041.2019.1664233
Lougheed, V. L., Crosbie, B., & Chow-fraser, P. (2001). Primary determinants of macrophyte community structure in 62 marshes across the Great Lakes basin: Latitude, land use, and water quality effects. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 58, 1603–1612. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjfas-58-8-1603
Malik, D. S., & Joshi, N. (2013). Distribution pattern of aquatic macrophytes and their biomass in relation to some nutrients in Asan wetland, India. International Journal for Environmental Rehabilitation and Cinservation, 4(1), 1–16.
McCarthy, J. (2008). Chapter 8 Pollutant loading calculations. In New Hampshire stormwater manual: Volume 1: Stormwater and antidegradation. New Hampshire Department of Environmental Services.
NAHRIM. (2015). National Lake Water Quality Criteria and Standards. National Hydraulic Research Institute of Malaysia (NAHRIM), 1–25.
Narasimha Ramulu, K., & Benarjee, G. (2016). Diversity and distribution of macrophytes in Nagaram tank of Warangal district, Telangana state. International Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Studies, 4(1), 270–275.
Ni, Z., Wang, S., & Wang, Y. (2016). Characteristics of bioavailable organic phosphorus in sediment and its contribution to lake eutrophication in China. Environmental Pollution, 219, 537–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.05.087
Nikolai, S. J., & Dzialowski, A. R. (2014). Effects of internal phosphorus loading on nutrient limitation in a eutrophic reservoir. Limnologica, 49, 33–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.limno.2014.08.005
Nürnberg, G. K., Molot, L. A., Connor, E. O., Jarjanazi, H., Winter, J., & Young, J. (2013). Evidence for internal phosphorus loading, hypoxia and effects on phytoplankton in partially polymictic Lake Simcoe, Ontario. Journal of Great Lakes Research, 39(2), 259–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jglr.2013.03.016
Orihel, D. M., Hadas, O., Pinkas, R., Viner-mozzini, Y., & Sukenik, A. (2013). Internal nutrient loading may increase microcystin concentrations in freshwater lakes by promoting growth of Microcystis populations. Annales de Limnologie, 49, 225–235. https://doi.org/10.1051/limn/2013052
Paerl, H. W., & Otten, T. G. (2013). Harmful cyanobacterial blooms: Causes, consequences, and controls. Microbial Ecology, 65(4), 995–1010. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-012-0159-y
Paerl, H. W., Xu, H., Hall, N. S., Rossignol, K. L., Joyner, A. R., Zhu, G., & Qin, B. (2015). Nutrient limitation dynamics examined on a multi-annual scale in Lake Taihu, China: Implications for controlling eutrophication and harmful algal blooms. Journal of Freshwater Ecology, 30(1), 5–24. https://doi.org/10.1080/02705060.2014.994047
Radbourne, A. D., Elliott, J. A., Maberly, S. C., Ryves, D. B., & Anderson, N. J. (2019a). The impacts of changing nutrient load and climate on a deep, eutrophic, monomictic lake. Freshwater Biology, 64(6), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1111/fwb.13293
Radbourne, A. D., Elliott, J. A., Maberly, S. C., Ryves, D. B., & Anderson, N. J. (2019b). The impacts of changing nutrient load and climate on a deep, eutrophic, monomictic lake. Freshwater Biology, 64(6), 1169–1182. https://doi.org/10.1111/fwb.13293
Randall, M. C., Carling, G. T., Dastrup, D. B., Miller, T., Nelson, S. T., Rey, K. A., … Aanderud, Z. T. (2019). Sediment potentially controls in-lake phosphorus cycling and harmful cyanobacteria in shallow, eutrophic Utah Lake. PLoS ONE, 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0212238
Reichwaldt, E. S., & Ghadouani, A. (2012). Effects of rainfall patterns on toxic cyanobacterial blooms in a changing climate: Between simplistic scenarios and complex dynamics. Water Research, 46(5), 1372–1393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.11.052
Reichwaldt, E. S., Stone, D., Barrington, D. J., Sinang, S. C., & Ghadouani, A. (2016). Development of toxicological risk assessment models for acute and chronic exposure to pollutants. Toxins, 8(9), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8090251
Richardson, J., Feuchtmayr, H., Miller, C., Hunter, P. D., Maberly, S. C., & Carvalho, L. (2019). Response of cyanobacteria and phytoplankton abundance to warming, extreme rainfall events and nutrient enrichment. Global, 3365–3380. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.14701
Rosset, V., Lehmann, A., & Oertli, B. (2010). Warmer and richer ? Predicting the impact of climate warming on species richness in small temperate waterbodies. Global Change Biology, 16, 2376–2387. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2010.02206.x
Schneider, S. C., Cara, M., Eriksen, T. E., Budzakoska Goreska, B., Imeri, A., Kupe, L., … Veljanoska Sarafiloska, E. (2014). Eutrophication impacts littoral biota in Lake Ohrid while water phosphorus concentrations are low. Limnologica, 44, 90–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.limno.2013.09.002
Sharip, Z, Schooler, S. S., & Hipsey, M. R. (2012). Eutrophication, agriculture and water level control shift aquatic plant communities from floating-leaved to submerged macrophytes in Lake Chini, Malaysia. Biological Invasions, (February). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-011-0137-1
Sharip, Z., Zaki, A. T. A., Shapai, M. A. H. M., Suratman, S., & Shaaban, A. J. (2014). Lakes of Malaysia: Water quality, eutrophication and management. Lakes and Reservoirs: Research and Management, 19(2), 130–141. https://doi.org/10.1111/lre.12059
Silva, T. F. G., Vincon-Leite, B., Lemaire, B. J., Petrucci, G., Giani, A., Figueredo, C. C., & de O. Nascimento, N. (2019). Impact of urban stormwater runoff on cyanobacteria dynamics in a tropical urban lake. Water.
Sinang, S. C., Daud, N., Kamaruddin, N., & Poh, K. B. (2019). Potential growth inhibition of freshwater algae by herbaceous plant extracts. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(3), 229–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chnaes.2018.12.005
Sinang, S. C., Poh, K. B., Shamsudin, S., & Sinden, A. (2015). Preliminary assessment of cyanobacteria diversity and toxic potential in Ten Freshwater Lakes in Selangor, Malaysia. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 95(4), 542–547. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-015-1620-7
Smith, V., Wood, S., McBride, C., Atalah, J., & Hamilton, D. (2016). Phosphorus and nitrogen loading restraints are essential for successful eutrophication control of Lake Rotorua, New Zealand. Inland Waters, 6(2), 273–283. https://doi.org/10.5268/IW-6.2.998
Steinman, A. D., Isely, E. S., & Thompson, K. (2015). Stormwater runoff to an impaired lake: Impacts and solutions. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4776-z
Tamire, G., & Mengistou, S. (2012). Macrophyte species composition, distribution and diversity in relation to some physicochemical factors in the littoral zone of Lake Ziway Ethiopia. African Journal of Ecology, 1–12 https://doi.org/10.1111/aje.12007
Tammeorg, O., Horppila, J., Tammeorg, P., Haldna, M., & Niemistö, J. (2016). Internal phosphorus loading across a cascade of three eutrophic basins: A synthesis of short- and long-term studies. Science of the Total Environment, 12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.07.224
Thornton, J. A., Harding, W. R., Dent, M., Hart, R. C., Lin, H., Rast, C. L., … Slawski, T. M. (2013). Eutrophication as a “wicked” problem. Lakes and Reservoirs: Research and Management, 18(4), 298–316. https://doi.org/10.1111/lre.12044
Verbeek, L., Gall, A., Hillebrand, H., & Striebel, M. (2018). Warming and oligotrophication cause shifts in freshwater phytoplankton communities. Global Change Biology, 24(10), 4532–4543. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.14337
Vondracek, B., Koch, J. D., & Beck, M. W. (2014). A comparison of survey methods to evaluate macrophyte index of biotic integrity performance in Minnesota lakes. Ecological Indicators, 36, 178–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2013.07.002
Wong, C. L., Venneker, R., Uhlenbrook, S., Jamil, A. B. M., & Zhou, Y. (2009). Variability of rainfall in Peninsular Malaysia. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 6, 5471–5503. https://doi.org/10.5194/hessd-6-5471-2009
Wong, C. L., Yusop, Z., & Ismail, T. (2018). Trend of daily rainfall and temperature in Peninsular Malaysia based on gridded data set. International Journal of GEOMATE, 14(44), 65–72. https://doi.org/10.21660/2018.44.3707
Wu, Z., Liu, Y., Liang, Z., Wu, S., & Guo, H. (2017). Internal cycling, not external loading, decides the nutrient limitation in eutrophic lake: A dynamic model with temporal Bayesian hierarchical inference. Water Research, 116, 231–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.03.039
Yang, Y., & Lusk, M. G. (2018). Nutrients in urban stormwater runoff: Current state of the science and potential mitigation options. Current Pollution Reports, 4, 112–127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40726-018-0087-7
Yousry, M. M. (2017). Total and bio-available phosphorus in sediments and its contribution to Lake Nasser eutrophication, Egypt. Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Biology & Fisheries, 21(3), 29–44.
Zhang, H., Boegman, L., Scavia, D., & Culver, D. A. (2016). Spatial distributions of external and internal phosphorus loads in Lake Erie and their impacts on phytoplankton and water quality. Journal of Great Lakes Research, 42(6), 1212–1227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jglr.2016.09.005
Zhang, S., Wang, W., & Chang, J. (2019a). The contribution of cyanobacteria bloom decline to phosphorus in water column of Dianchi Lake, China. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 28(5), 3513–3520. https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/94217
Zhang, Y., Ma, R., Liang, Q., Guan, B., & Loiselle, S. (2019b). Secondary impacts of eutrophication control activities in shallow lakes: Lessons from aquatic macrophyte dynamics in Lake Taihu from 2000 to 2015. Freshwater Science, 38. https://doi.org/10.1086/706197
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank everyone who was directly or indirectly involved in this research.
Funding
This research was funded by the Malaysia Ministry of Higher Education under Fundamental Research Grant Scheme 2017–0078-101–02 (FRGS/1/2017/STG03/UPSI/02/01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
A Rahman, A.R.A., Sinang, S.C. & Nayan, N. Response of algal biomass and macrophyte communities to internal or external nutrient loading. Environ Monit Assess 194, 491 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10116-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10116-6