Abstract
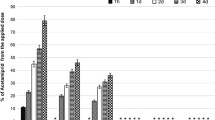
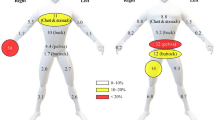
This study measured pesticide levels on children’s hands, home indoor surfaces, and drinking water among Thai conventional and organic farm families in three provinces. Farm families in Nakhonsawan and Phitsanulok provinces were the conventional farmers and those in Yasothon province were the organic farmers. Samples were collected in the dry and wet seasons over 2 years (2017 and 2018). All samples were analyzed for organophosphates (OPs), carbamate, pyrethroid, triazines, glyphosate, and aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA). On children’s hands, the highest concentrations for the 2 palmar surfaces were found for cypermethrin (7.46 μg) and fipronil (2.88 μg). On home surfaces of approximately 1000 cm2, the highest concentrations were found for cypermethrin (27.94 μg) and fipronil 49.76 μg)/1000 cm2. For the conventional farmers, the most common pesticides on children’s hand wipes were cypermethrin and fipronil, which are used as in-home pesticides as well as agricultural pesticides. However, home surface wipes showed other pesticides associated with agriculture were presented in the home during the seasons when they were used, suggesting spray drift or carry home sources for these pesticides. During the wet season, pesticides were found in the drinking water of all provinces. Most common were fenitrothion, profenofos, fenthion, atrazine, and AMPA. Profenofos was found at levels above the health guidelines. During 2017, there was extensive flooding in Thailand which may have contributed to the drinking water contamination, even though most farmers report using tap water or bottled drinking water. Future work is needed to assess the risk of all sources of pesticide exposures in children and to repeat the drinking water pesticide contamination analysis.

Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The original datasets are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abass, K., Reponen, P., Jalonen, J., & Pelkonen, O. (2007). In vitro metabolism and interaction of profenofos by human, mouse and rat liver preparations. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 87(3), 238–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2006.08.002
Bradman, A., Whitaker, D., Quirós, L., Castorina, R., Henn, B. C., Nishioka, M., Morgan, J., Barr, D. B., Harnly, M., Brisbin, J. A., Sheldon, L.S., McKone, T. E., & Eskenazi, B. (2007). Pesticides and their metabolites in the homes and urine of farmworker children living in the Salinas Valley, CA. Journal of exposure science & environmental epidemiology, 17(4), 331–349. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jes.7500507
Butte, W., & Heinzow, B. (2002). Pollutants in house dust as indicators of indoor contamination. Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 175, 1–46.
Chau, N. D. G., Son, L. L., & Hop, N. V. (2020). Dissipation of the pesticides fipronil, cypermethrin, and tebuconazole in vegetables: A case study in Thua Thien-Hue province, Central Vietnam. Journal of Pesticide Science, 45(4), 245–252. https://doi.org/10.1584/jpestics.D20-044
Chouichom, S., & Yamao, M. (2010). Comparing opinions and attitudes of organic and non-organic farmers towards organic rice farming system in north-eastern Thailand. Journal of Organic Systems, 5(1), 25–35.
Dereumeaux, C., Fillol, C., Quenel, P., & Denys, S. (2020). Pesticide exposures for residents living close to agricultural lands: A review. Environment International, 134, 105210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.105210
Eskenazi, B., Marks, A. R., Bradman, A., Harley, K., Barr, D. B., Johnson, C., Morga, N., & Jewell, N. P. (2007). Organophosphate pesticide exposure and neurodevelopment in young Mexican-American children. Environmental Health Perspectives, 115(5), 792–798. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.9828
Flower, K. B., Hoppin, J. A., Lynch, C. F., Blair, A., Knott, C., Shore, D. L., & Sandler, D. P. (2004). Cancer risk and parental pesticide application in children of agricultural health study participants. Environmental Health Perspectives, 112, 631–635. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.6586
Freeman, N. C., Hore, P., Black, K., Jimenez, M., Sheldon, L., Tulve, N., & Lioy, P. J. (2005). Contributions of children’s activities to pesticide hand loadings following residential pesticide application. Journal of exposure science & environmental epidemiology, 15(1), 81–88. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jea.7500348
Government of Canada. (2015). Organic production systems. General principles and management standards. CAN/CGSB-32.310–2015 Supersedes CAN/CGSB-32.310–2006. Canadian General Standards Board. Retrieve July 28, 2021 from https://www.tpsgc-pwgsc.gc.ca/ongc-cgsb/programme-program/normes-standards/internet/bio-org/pgng-gpms-eng.html
Gotoh, M., Sakata, M., Endo, T., Hayashi, H., Seno, H., & Suzuki, O. (2001). Profenofos metabolites in human poisoning. Forensic Science International, 116, 221–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0379-0738(00)00377-7
Greish, S., Ismail, S. M., Mosleh, Y., Loutfy, N., Dessouki, A. A., & Ahmed, M. T. (2011). Human risk assessment of profenofos: A case study in Ismailia. Egypt. Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds, 31, 28–47. https://doi.org/10.1080/10406638.2011.545727
Gunier, R. B., Ward, M. H., Airola, M., Bell, E. M., Colt, J., Nishioka, M., Buffler, P. A., Reynolds, P., Rull, R. P., Hertz, A., Metayer, C., & Nuckols, J. R. (2011). Determinants of agricultural pesticide concentrations in carpet dust. Environmental Health Perspectives, 119(7), 970–976. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1002532
Hamilton, D. J., Ambrus, A., Dieterle, R. M., Felsot, A. S., Harris, C. A., Holland, P. T., Katayama, A., Kurihara, N., Linders, J., Unsworth, J., & Wong, S. S. (2003). Regulatory limits for pesticides residues in water. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 75(8), 1123–1155. https://doi.org/10.1351/pac200375081123
Harnly, M., Bradman, A., Nishioka, M., McKone, T., Smith, D., McLaughlin, R., Baird-Kavannah, G., Castorina, R., & Eskenazi, B. (2009). Pesticides in dust from homes in an agricultural area. Science of the Total Environment, 43, 8767–8774. https://doi.org/10.1021/es9020958.
Haron, S. H., Ismail, B. S., & Latif, M. T. (2012). Composition of insecticidal residues in total suspended particulate and rain water at an agricultural area in Kedah, Malaysia. Research Journal of Environmental Sciences, 6(5), 169–185. https://doi.org/10.3923/rjes.2012.169.185
Hernandez, A. F., & Menendez, P. (2016). Linking pesticide exposure with pediatric leukemia: potential underlying mechanisms. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(4), 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040461
Hornung, R. W., & Reed, L. D. (1990). Estimation of average concentration in the presence of nondetectable values. Applied Occupational and Environmental Hygiene, 5(1), 46–51. https://doi.org/10.1080/1047322X.1990.10389587
Ikehata, K., & El-Din, M. G. (2005). Aqueous pesticide degradation by ozonation and ozone-based advanced oxidation processes: A review (part II). The Journal of the International Ozone Association, 27(3), 173–202. https://doi.org/10.1080/01919510590945732
Kongtip, P., Techasaensiri, B., Nankongnab, N., Adams, J., Phamonphon, A., Surach, A., Sangprasert, S., Thongsuksai, A., Srikumpol, P., & Woskie, S. (2017). The impact of prenatal organophosphate pesticide exposures on Thai infant neurodevelopment. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 14, 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14060570
Kumar, R., & Singh, B. (2013). Persistence and metabolism of fipronil in rice (Oryza sativa Linnaeus) field. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 90(4), 482–488. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-012-0926-y
Laohaudomchok, W., Nangkongnab, N., Siriruttanapruk, S., Klaimala, P., Lianchamroon, W., Ousap, P., Jatiket, M., Kajitvichyanukul, P., Kitana, N., Siriwong, W., Hemachudha, T., Satayavivad, J., Robson, M., Jaaks, L., Barr, D. B., Kongtip, P., & Woskie, S. (2021). Pesticide use in Thailand: Current situation, health risks, and gaps in research and policy. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: An International Journal, 27(5), 1147–1169. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2020.1808777
Le Bot, B., Colliaux, K., Pelle, D., Brines, C., Seux, R., & Clément, M. (2002). Optimization and performance evaluation of the analysis of glyphosate and AMPA in water by HPLC with fluorescence detection. Chromatographia, 56, 161–164.
Lewis, R. G., Fortmann, R. C., & Camann, D. E. (1994). Evaluation of methods for monitoring the potential exposure of small children to pesticides in the residential environment. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 26, 37–46.
Li, Z., & Jennings, A. (2018). Global variations in pesticide regulations and health risk assessment of maximum concentration levels in drinking water. Journal of Environmental Management, 212, 384–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.12.083
Lu, C., Fenske, R.A., Simcox, N.J., & Kalman, D. (2000). Pesticide exposure of children in an agricultural community: Evidence of household proximity to farmland and take home exposure pathways. Environmental Research Section A, 84, 290–302. https://doi.org/10.1006/enrs.2000.4076
Maele-Fabrya, G. V., Gamet-Payrastreb, G., & Lison, D. (2017). Residential exposure to pesticides as risk factor for childhood and young adult brain tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environment International, 106, 69–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2017.05.018
Mandal, K., & Singh, B. (2014). Persistence and metabolism of fipronil in sugarcane leaves and juice. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 92(2), 220–224. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-013-1176-3
McCauley, L. A., Lasarev, M. R., Higgins, G., Rothlein, J., Muniz, J., Ebbert, C., & Phillips, J. (2001). Work characteristics and pesticide exposures among migrant agricultural families: A community-based research approach. Environmental Health Perspectives, 109, 533–538. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.01109533
Naksen, W., Prapamontol, T., Mangklabruks, A., Chantara, S., Thavornyutikarn, P., Srinual, N., Panuwet, P., Ryan, P. B., Riederer, A. M., & Barr, D. B. (2015). Associations of maternal organophosphate pesticide exposure and PON1 activity with birth outcomes in SAWASDEE birth cohort, Thailand. Environmental Research, 142, 288–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2015.06.035
National npic pesticide information center. (2009). Fipronil. Retrieved July 28, 2021, from http://npic.orst.edu/factsheets/fipronil.html
Norkaew, S., Taneepanichskul, N., Siriwong, W., Siripattanakul, S., & Robson, M. (2012). Household pesticide use in agricultural community, Northeastern Thailand. Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, 3(10), 631–637.
Quirós-Alcalá, L., Bradman, A., Nishioka, M., Harnly, M. E., Hubbard, A., McKone, T. E., Ferber, J., & Eskenazi, B. (2011). Pesticides in house dust from urban and farmworker households in California: An observational measurement study. Environmental Health, 10, 19.
Roberts, J. R., & Karr, C. J. (2012). Council on Environmental health. Pesticide exposure in children. Pediatrics. 130(6), e1765–e1788. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2012-2758
Roberts, J. W., Wallace, L. A., Camann, D. E., Dickey, P., Gilbert, S. G., Lewis, R. G., & Takaro T. K. (2009). Monitoring and reducing exposure of infants to pollutants in house dust. Reviews of environmental contamination and toxicology, 201, 1–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-0032-6_1
Rohitrattana, J., Siriwong, W., Robson, M., Panuwet, P., Barr, D. B., & Fiedler, N. (2014). Pyrethroid insecticide exposure in school-aged children living in rice and aquacultural farming regions of Thailand. Risk Management and Healthcare Policy, 7, 211–217. https://doi.org/10.2147/RMHP.S67208
Simcox, N. J., Fenske, R. A., Wolz, S. A., Lee, I. C., & Kalman, D. A. (1995). Pesticides in household dust and soil: Exposure pathways for children of agricultural families. Environmental Health Perspectives, 103(12), 1126–1134. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.951031126
Singh, J. K., Roy, A. K., & Pankaj, P. P. (2006). Ameliorative effect of curcumin on profenofos induced oxidative damage of renal tissue in mice. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research, 7(8), 3550–3556.
Siriwat, S., Ong-artborirak, P., Nganchamung, T., Robson, M. G., & Siriwong, W. (2019). Health risk assessment of residential exposure to cypermethrin among young children in agricultural communities in northeastern Thailand. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: An International Journal, 25(3), 614–623. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2018.1539635
Stout, D. M., Bradham, K. D., Egeghy, P. P., Jones, P. A., Croghan, C. W., Ashley, P. A., Pinzer, E., Friedman, W., Brinkman, M. C., Nishioka, M. G., & Cox, D. C. (2009). American Healthy Homes Survey: A national study of residential. pesticides measured from floor wipes. Environmental Science & Technology, 43, 4294–4300. https://doi.org/10.1021/es8030243
Whitmore, R. W., Immerman, F. W., Gamann, D. E., Bond, A. E., Lewis, R. G., & Schaum, J. L. (1994). Non-occupational exposures to pesticides for residents of two U.S. cities. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 26(1), 47–59. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00212793
WHO. (2017). Guidelines for drinking-water quality: fourth edition incorporating the first addendum. Geneva: World Health Organization. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
Win, H. E. (2017). Organic agriculture in Thailand. Retriveved July 28, 2021, from http://ap.fftc.agnet.org/ap_db.php?id=734
Woskie, S., Kongtip, P., Thanasanpaiboon, W., Kiatdamrong, N., Charoonrungsirikul, N., Nankongnab, N., Surach, A., & Phamonphon, A. (2017). A pilot study of maternal exposure to organophosphate pesticides and newborn neurodevelopment in Thailand. International Journal of Occupational and Environmental Health, 23(3), 193–201. https://doi.org/10.1080/10773525.2018.1450324
Younes, M., & Galal-Gorchev, H. (2000). Pesticides in drinking water -A case study. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 38, S87–S90.
Funding
This research was supported by the NIH Fogarty International Center, National Institutes of Environmental Health Sciences, and the NIH under Award Number U01 TW010091 and U2RTW010088.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Pakasinee Klaimala (acquisition of data, analysis, and interpretation of samples), Paphatsara Khunlert (collection and analysis of samples), Prakit Chuntib (collection and analysis of samples), Ritthirong Pundee (collection of data, interpretation of data), Nichcha Kallayanatham (management of the project, data collection), Noppanun Nankongnab (design of the study, interpretation of data), Pornpimol Kongtip (conceptual and design, writing the first draft), Susan Woskie (conceptual and design, revising the final draft). All authors helped revising the draft and approved the final version before submitted to the journal.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Approval was obtained from the ethics review committee for human research faculty of Public Health, Mahidol University (MUPH 2015–146). The procedures used in this study adhere to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klaimala, P., Khunlert, P., Chuntib, P. et al. Pesticide residues on children’s hands, home indoor surfaces, and drinking water among conventional and organic farmers in Thailand. Environ Monit Assess 194, 427 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10051-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10051-6