Abstract
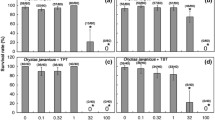
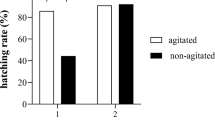
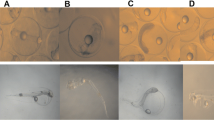
To determine whether the marine medaka Oryzias melastigma is a suitable model organism for in vivo acute toxicity bioassay in seawater, we first determined whether there were differences in the concentrations of chemicals that were toxic to marine medaka (O. melastigma) and freshwater medaka (O. latipes). We performed in vivo acute toxicity bioassay with 3-chloroaniline, triclosan, 3,4-dichloroaniline, fenitrothion, and pyriproxyfen on larvae of both species. Although the concentrations of 3-chloroaniline and fenitrothion that were lethal to the larvae were identical for both species, the toxic concentrations of triclosan, 3,4-dichloroaniline, and pyriproxyfen were lower for O. melastigma than for O. latipes. We then used an in vivo acute toxicity bioassay to monitor the quality of coastal seawater in Akita, Japan. No lethal effects were observed in the harbor and canal in 2019. O. melastigma could be used to monitor the quality of seawater with salinities in the range 2–25. Our findings suggest that O. melastigma can be used as the test fish for in vivo acute toxicity bioassay intended for water quality monitoring.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The authors confirm that all data underlying the findings are fully available without restriction.
References
Añasco, N. C., Koyama, J., & Uno, S. (2010). Pesticide residues in coastal waters affected by rice paddy effluents temporarily stored in a wastewater reservoir in southern Japan. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 58(2), 352–360. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-009-9364-1
Bayen, S., Zhang, H., Desai, M. M., Ooi, S. K., & Kelly, B. C. (2013). Occurrence and distribution of pharmaceutically active and endocrine disrupting compounds in Singapore’s marine environment: Influence of hydrodynamics and physical-chemical properties. Environmental Pollution, 182, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.06.028
Belenguer, V., Martinez-Capel, F., Masiá, A., & Picó, Y. (2014). Patterns of presence and concentration of pesticides in fish and waters of the Júcar river (Eastern Spain). Journal of Hazardous Materials, 265, 271–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.11.016
Bester, K. (2005). Fate of triclosan and triclosan-methyl in sewage treatment plants and surface waters. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 49(1), 9–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-004-0155-4
Bosker, T., Santoro, G., & Melvin, S. D. (2017). Salinity and sensitivity to endocrine disrupting chemicals: A comparison of reproductive endpoints in small-bodied fish exposed under different salinities. Chemosphere, 183, 186–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.05.063
Campos, da Rocha, F.O., Martinez, S.T., Campos, V.P., da Rocha, G.O., de Andrade, J.B. (2021). Microplastic pollution in Southern Atlantic marine waters: Review of current trends, sources, and perspectives. Science of the Total Environment, 782, 146541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146541
Chen, T. H., Chen, Y. L., Chen, C. Y., Liu, P. J., Cheng, J. O., & Ko, F. C. (2015). Assessment of ichthyotoxicity and anthropogenic contamination in the surface waters of Kenting National Park. Taiwan. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187(5), 265. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4511-9
Cristiano, W., Lacchetti, I., Di Domenico, K., Corti, M., Mancini, L., & Carere, M. (2020). Application of effect-based methods (EBMs) in a river basin: A preliminary study in Central Italy. Annali Dell’istituto Superiore Di Sanità, 56(1), 114–121. https://doi.org/10.4415/ANN_20_01_16
Dong, X., Zhang, L., Chen, M., Yang, Z., Zuo, Z., & Wang, C. (2018). Exposure to difenoconazole inhibits reproductive ability in male marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma). Journal of Environmental Sciences, 63, 126–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2017.05.030
Escher, B. I., Aїt-Aїssa, S., Behnisch, P. A., Brack, W., Brion, F., Brouwer, A., Buchinger, S., Crawford, S. E., Du Pasquier, D., Hamers, T., Hettwer, K., Hilscherová, K., Hollert, H., Kase, R., Kienle, C., Tindall, A. J., Tuerk, J., van der Oost, R., Vermeirssen, E., & Neale, P. A. (2018). Effect-based trigger values for in vitro and in vivo bioassays performed on surface water extracts supporting the environmental quality standards (EQS) of the European Water Framework Directive. Science of the Total Environment, 628–629, 748–765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.340
Fauziah, S. H., Rizman-Idid, M., Cheah, W., Loh, K. H., Sharma, S. M. R. N., Bordt, M., Praphotjanaporn, T., Samah, A. A., Sabaruddin, J. S. B., & George, M. (2021). Marine debris in Malaysia: A review on the pollution intensity and mitigating measures. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 167, 112258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112258
Fox, J., Bouchet-Valat, M. (2018). Rcmdr: R Commander. R package version 2.5–1.
Ghani, S. A., & Hanafi, A. H. (2016). QuEChERS method combined with GC-MS for pesticide residues determination in water. Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 71(5), 508–512.
Horie, Y., Yamagishi, T., Takahasgi, H., Shintaku, Y., Iguchi, T., & Tatarazako, N. (2017). Assessment of the lethal and sublethal effects of 20 environmental chemicals in zebrafish embryos and larvae by using OECD TG 212. Journal of Applied Toxicology, 37, 1245–1253.
Horie, Y., Kanazawa, N., Yamagishi, T., Yonekura, K., & Tatarazako, N. (2018). Ecotoxicological test assay using OECD TG 212 in marine Java medaka (Oryzias javanicus) and freshwater Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes). Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 101, 344–348.
Horie, Y., Kanazawa, N., Suzuki, A., Yonekura, K., & Chiba, T. (2019). Influences of salinity and organic compounds on embryo development in three medaka oryzias congeners with habitats ranging from freshwater to marine. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 103(3), 411–415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-019-02649-3
Huang, Q., Liu, Y., Chen, Y., Fang, C., Chi, Y., Zhu, H., Lin, Y., Ye, G., & Dong, S. (2018). New insights into the metabolism and toxicity of bisphenol A on marine fish under long-term exposure. Environmental Pollution, 242(Pt A), 914–921. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.07.048
Inoue, K., & Takei, Y. (2002). Diverse adaptability in Oryzias species to high environmental salinity. Zoological Science, 19(7), 727–734.
Issac, M. N., & Kandasubramanian, B. (2021). Effect of microplastics in water and aquatic systems. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2, 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13184-2
Kaonga, C. C., Takeda, K., & Sakugawa, H. (2015). Diuron, Irgarol 1051 and Fenitrothion contamination for a river passing through an agricultural and urban area in Higashi Hiroshima City, Japan. Science of the Total Environment, 518–519, 450–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.03.022
Kuster, M., & López de, Alda, M.J., Barata, C., Raldúa, D., Barceló, D. (2008). Analysis of 17 polar to semi-polar pesticides in the Ebro river delta during the main growing season of rice by automated on-line solid-phase extraction-liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta, 75(2), 390–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2007.11.027
Lee, P. Y., Lin, C. Y., & Chen, T. H. (2014). Environmentally relevant exposure of 17α-ethinylestradiol impairs spawning and reproductive behavior in the brackish medaka Oryzias melastigma. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 85, 338–343.
Leris, I., Kalogianni, E., Tsangaris, C., Smeti, E., Laschou, S., Anastasopoulou, E., Vardakas, L., Kapakos, Y., & Skoulikidis, N. T. (2019). Acute and sub-chronic toxicity bioassays of olive mill wastewater on the Eastern mosquitofish Gambusia holbrooki. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 175, 48–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.03.025
Maier, D., Blaha, L., Giesy, J. P., Henneberg, A., Köhler, H. R., Kuch, B., Osterauer, R., Peschke, K., Richter, D., Scheurer, M., & Triebskorn, R. (2015). Biological plausibility as a tool to associate analytical data for micropollutants and effect potentials in wastewater, surface water, and sediments with effects in fishes. Water Research, 72, 127–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.08.050
Nishi, I., Kawakami, T., & Onodera, S. (2008). Monitoring of triclosan in the surface water of the Tone Canal, Japan. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 80(2), 163–166. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-007-9338-9
OECD. (2013). Guidelines for the testing of chemicals, test no. 210: Fish, early-life stage toxicity test. OECD Publishing.
Seki, M., Yokota, H., Matsubara, H., Tsuruda, Y., Maeda, M., Tadokoro, H., & Kobayashi, K. (2002). Effect of ethinylestradiol on the reproduction and induction of vitellogenin and testis-ova in medaka (Oryzias latipes). Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 21(8), 1692–1698.
Takehana, Y., Naruse, K., & Sakaizumi, M. (2005). Molecular phylogeny of the medaka fishes genus Oryzias (Beloniformes: Adrianichthyidae) based on nuclear and mitochondrial DNA sequences. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 36(2), 417–428.
Tamura, I., Yasuda, Y., Kagota, K. I., Yoneda, S., Nakada, N., Kumar, V., Kameda, Y., Kimura, K., Tatarazako, N., & Yamamoto, H. (2017). Contribution of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) to whole toxicity of water samples collected in effluent-dominated urban streams. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 144, 338–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.06.032
Thuy, H. T., le Nga, P., & Loan, T. T. (2011). Antibiotic contaminants in coastal wetlands from Vietnamese shrimp farming. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 18(6), 835–841. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-011-0475-7
Tsuji, S., Tonogai, Y., Ito, Y., Kanoh, S. (1986). The influence of rearing temperature on the toxicity of various environmental pollutants for killfish (Orizas latipes). EISEI KAGAKU, 32(1):46–53. (Japanese)
Vajda, A. M., Kumar, A., Woods, M., Williams, M., Doan, H., Tolsher, P., Kookana, R. S., & Barber, L. B. (2015). Integrated assessment of wastewater treatment plant effluent estrogenicity in the upper Murray River, Australia, using the native Murray rainbowfish (Melanotaenia fluviatilis). Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 34(5), 1078–1087. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.2895
Wang, Z., Yeung, K. W. Y., Zhou, G. J., Yung, M. M. N., Schlekat, C. E., Garman, E. R., Gissi, F., Stauber, J. L., Middleton, E. T., Lin Wang, Y. Y., & Leung, K. M. Y. (2020a). Acute and chronic toxicity of nickel on freshwater and marine tropical aquatic organisms. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 206, 111373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111373
Wang, R. F., Zhu, L. M., Zhang, J., An, X. P., Yang, Y. P., Song, M., & Zhang, L. (2020b). Developmental toxicity of copper in marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma) embryos and larvae. Chemosphere, 247, 125923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.125923
Wang, J., Zheng, M., Lu, L., Li, X., Zhang, Z., & Ru, S. (2021). Adaptation of life-history traits and trade-offs in marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma) after whole life-cycle exposure to polystyrene microplastics. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 414, 125537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125537
Wilson, E. W., Castro, V., Chaves, R., Espinosa, M., Rodil, R., Quintana, J. B., Vieira, M. N., & Santos, M. M. (2021). Using zebrafish embryo bioassays combined with high-resolution mass spectrometry screening to assess ecotoxicological water bodies quality status: A case study in Panama rivers. Chemosphere, 272, 129823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129823
Wittlerová, M., Jírová, G., Vlková, A., Kejlová, K., Malý, M., Heinonen, T., Wittlingerová, Z., Zimová, M. (2020). Sensitivity of zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos to hospital effluent compared to Daphnia magna and Aliivibrio fischeri. Physiological Research, 31(69), S681-S691.
Yamagishi, T., Fuchida, S., Katsumata, M., Horie, Y., Mori, F., Kitayama, A., Kawachi, M., Koshikawa, H., Nozaki, T., Kumagai, H., Ishibashi, J.I., Tatarazako, N. (2018). Evaluation of the toxicity of leaches from hydrothermal sulfide deposits by means of a delayed fluorescence-based bioassay with the marine cyanobacterium Cyanobium sp. NIES-981. Ecotoxicology, 27(10), 1303–1309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-018-1989-2
Yi, X., Bao, V. W. W., & Leung, K. M. Y. (2017). Binary mixture toxicities of triphenyltin with tributyltin or copper to five marine organisms: Implications on environmental risk assessment. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 124(2), 839–846. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.02.031
Yue, Z., Tian, E., Chen, Y., Luo, L., Yang, L., He, L., Li, L., & Wang, J. (2021). The adverse effects of acrylamide exposure on the early development of marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma) and its mechanisms. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 163, 111875. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111875
Zhao, J. L., Ying, G. G., Liu, Y. S., Chen, F., Yang, J. F., & Wang, L. (2010). Occurrence and risks of triclosan and triclocarban in the Pearl River system, South China: From source to the receiving environment. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 179(1–3), 215–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.02.082
Zhang, L., Li, Q., Chen, L., Zhang, A., He, J., Wen, Z., & Wu, L. (2015). Toxicity of surface water from Huangpu River to luminous bacteria (Vibrio qinghaiensis SP. Q67) and zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 112, 137–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.10.037
Zheng, D., Yin, G., Liu, M., Chen, C., Jiang, Y., Hou, L., & Zheng, Y. (2021). A systematic review of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in estuarine and coastal environments. Science of the Total Environment, 777, 146009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146009
Zheng, Y., Li, Y., Yue, Z., Samreen, Li., & Z., Li, X., Wang, J. (2020). Teratogenic effects of environmentally relevant concentrations of phenanthrene on the early development of marine medaka (Oryzia melastigma). Chemosphere, 254, 126900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126900
Funding
This study was supported partly by the Salt Science Research Foundation, Japan (grant nos. 1915 and 2021) and a grant from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan (Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research [B] grant no. 19H04294) to Y.H.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yoshifumi Horie, all experiment except sampling for in vivo acute bioassays; Chiho Takahashi, sampling for in vivo acute bioassays. All authors listed on the current study contributed to the experimental design or data analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The fish which was used in the present study were handled according to guidelines of Akita Prefectural University.
Consent to participate
This research did not involve human subjects, so clinical trial registration is not applicable.
Consent for publication
The authors certify that this manuscript is our original unpublished work, has not been published elsewhere, and is not under consideration by another journal. All authors have approved the manuscript and agree with its submission.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horie, Y., Takahashi, C. Development of an in vivo acute bioassay using the marine medaka Oryzias melastigma. Environ Monit Assess 193, 725 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09527-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09527-8