Abstract
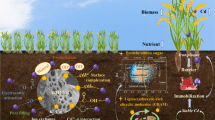
Rehabilitation of degraded lands due to mining and other activities requires rebuilding of the appropriate soil structure and microbial integrity. Organic wastes, in particular plant-based materials, play a vital role in restoration of degraded land when used as amendments for topsoil integrated with microbe-assisted phytoremediation. In this present study, a biotechnological approach using the combination of organic waste amendments, i.e., ETP (effluent treatment plant), sludge from sugarcane and paper industry, and the press mud respectively along with microbial and fungal inoculum isolated from the soil rhizosphere have been applied to study the influence on fertility and productivity of mine spoil from manganese and coal dumps. The organic amendments applied as 100-ton ha−1 and application of biofertilizers boosted the survival of plants such as Tectona grandis (Teak), Dalbergia sisso (North Indian rosewood), Phyllanthus emblica (Indian gooseberry), Gmelina arborea (Gamhar), and Acacia auriculiformis (Earpod wattle) from 80 to 100% with robust growth and development during the short span of 25 years. The physicochemical attributes of soil and the microbial count also increased significantly. The pH of mine soil dumps slightly shifted toward alkaline conditions (7.4 to 7.8) whereas bulk density, porosity, and the water holding capacity were greatly improved. Other than this, the nutrient status of mine dump soil and the plants such as available nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and the organic carbon content in soil were improvised to a greater extent simultaneously decreasing the available manganese concentration. The findings of the study assure a better land reclamation and restoration approach.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
References
Adekiya, A. O., Agbede, T. M., Aboyeji, C. M., Dunsin, O., & Ugbe, J. O. (2019). Green manures and NPK fertilizer effects on soil properties, growth, yield, mineral and vitamin C composition of okra (Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench). Journal of the Saudi Society of Agricultural Sciences, 18, 218–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssas.2017.05.005
Amoah-Antwi, C., Kwiatkowska-Malina, J., Thornton, S. F., Fenton, O., Malina, G. & Szara, E. (2020). Restoration of soil quality using biochar and brown coal waste: a review. Science of The Total Environment, 722, 137852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137852
Araújo, A. S. F. D., & Melo, W. J. D. (2010). Soil microbial biomass in organic farming system. Ciência Rural, 40(11), 2419–2426. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0103-84782010005000192
Arshi, A. (2017). Reclamation of coalmine overburden dump through environmental friendly method. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 24(2), 371–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2015.09.009
Awotwi, A., Anornu, G. K., Quaye‐Ballard, J. A., & Annor, T. (2018). Monitoring land use and land cover changes due to extensive gold mining, urban expansion, and agriculture in the Pra River Basin of Ghana, 1986–2025. Land Degradation & Development, 29(10), 3331–3343. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.3093
Black, C. A. (ed.). (1965). Methods of soil analysis. Madison, Wis.: American Society of Agronomy.
Brown, S., Mahoney, M., & Sprenger, M. (2014). A comparison of the efficacy and ecosystem impact of residual-based and topsoil-based amendments for restoring historic mine tailings in the Tri-State mining district. Science of the Total Environment, 485–486, 624–632.
Chatterjee, R., Gajjela, S., & Thirumdasu, R. K. (2017). Recycling of organic wastes for sustainable soil health and crop growth. International Journal of Waste Resources, 7(03), 296–302. https://doi.org/10.4172/2252-5211.1000296
Chen, Y., Camps-Arbestain, M., Shen, Q., Singh, B., & Cayuela, M. L. (2018). The long-term role of organic amendments in building soil nutrient fertility: A meta-analysis and review. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 111, 103–125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-017-9903-5
Choi, B., Lim, J. E., Sung, J. K., Jeon, W. T., Lee, S. S., Oh, S. E., et al. (2014). Effect of rapeseed green manure amendment on soil properties and rice productivity. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 45, 751–764.
Corrêa, R. S., Balduíno, A. P. D. C., Teza, C. T. V., & Baptista, G. M. D. M. (2018). Vegetation cover development resulting from different restoration approaches of exploited mines. Floresta e Ambiente, 25(4). https://doi.org/10.1590/2179-8087.111617
de Oliveira, A. G., Barros, A. D., Lucena, L. C. D. F. L., Lucena, A. E. D. F. L., & Patricio, J. D. (2020). Evaluation of calcined textile sludge as a stabilizing material for highway soil. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering (english Edition). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtte.2019.02.004\
Defoe, P. P., Hettiarachchi, G. M., Benedict, C., & Martin, S. (2014). Safety of gardening on leadand arsenic-contaminated urban brownfields. Journal of Environmental Quality, 43, 2064–2078.
Diacono, M., & Montemurro, F. (2010). Long-term effects of organic amendments on soil fertility. A review. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 30, 401–422. https://doi.org/10.1051/agro/2009040
Dotaniya, M. L., Datta, S. C., & Biswas, D. R. (2016). Use of sugarcane industrial by-products for improving sugarcane productivity and soil health. International Journal of Recycling of Organic Waste in Agriculture 5, 185–194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40093-016-0132-8
FAO. (1978). Establishment techniques for forest plantations. Link: http://www.fao.org/3/an766e/an766e00.pdf (Accessed on 21st July 2020)
Festin, E. S., Tigabu, M., & Chileshe, M. N. (2019). Progresses in restoration of post-mining landscape in Africa. Journal of Forest Research, 30, 381–396. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-018-0621x
Gopalakrishnan, S., Sathya, A., & Vijayabharathi, R. (2015). Plant growth promoting rhizobia: Challenges and opportunities. Biotech, 5, 355–377. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-014-0241-x
Gupta, M., & Kumar, A. (2000). Yunus, M. Effect of fly-ash on metal composition and physiological responses in Leucaena Leucocephala (Lamk.) de. Wit. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 61, 399–406.
Haigh, M., Reed, H., Flege, A., D'Aucourt, M., Plamping, K., Cullis, M., & Powell, S. (2015). Effect of planting method on the growth of alnus glutinosa and Quercus petraea in compacted opencast coal-mine spoils, South Wales. Land Degradation & Development, 26(3), 227–236. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.2201
Horta, C., Roboredo, M., Carneiro, J. P., Duarte, A. C., Torrent, J., & Sharpley, A. (2018). Organic amendments as a source of phosphorus: Agronomic and environmental impact of different animal manures applied to an acid soil. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science, 64, 257–271. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2017.1346372
Hossain, M. Z., Von Fragstein, P., Von Niemsdorff, P., & Heß, J. (2017). Effect of different organic wastes on soil propertie s and plant growth and yield: A review. Scientia Agriculturae Bohemica, 48(4), 224–237. https://doi.org/10.1515/sab-2017-0030
IS 3025. (1988). Methods of sampling and test (physical and chemical) for water and waste water (IS 3025 (part 11)). Link: http://www.iitk.ac.in/ce/test/IS-codes/is.3025.11.1983.pdf (Accessed on 21st July 2020).
ISWA. (2020). Global assessment of municipal organic waste production and recycling. International Solid Waste Association (ISWA) (2020). Link: https://www.iswa.org/uploads/media/Report_1_Global_Assessment_of_Municipal_Organic_Waste_Compressed_v2.pdf (Accessed on 21st July, 2020).
Jackson, M. L. (1958). Soil chemical analysis. Englewood Cliffs, N.J.: Prentice-Hall.
Jones, B. E. H., Haynes, R. J., & Phillips, I. R. (2011). Influence of organic waste and residue mud additions on chemical, physical and microbial properties of bauxite residue sand. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 18, 199–211.
Jones, B. E. H., Haynes, R. J., & Phillips, I. R. (2012). Addition of an organic amendment and/or residue mud to bauxite residue sand in order to improve its properties as a growth medium. Journal of Environmental Management, 95, 29–38.
Joshi, R., & Ahmed, S. (2016). Status and challenges of municipal solid waste management in India: A review. Cogent Environmental Science, 2(1), 1139434. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311843.2016.1139434
Juwarkar, A., Yadav, S., & Thawale, P. (2010). Biotechnological approach for ecosystem restoration of mine spoil dump in India. International Journal of Environment and Pollution, 43, 251–263. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJEP.2010.035928
Juwarkar, A. A., Yadav, S. K., Kumar, P., & Singh, S. K. (2008). Effect of biosludge and biofertilizer amendment on growth of Jatropha curcas in heavy metal contaminated soils. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 145(1), 7–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-0012-9
Juwarkar, A. A., Yadav, S. K., Thawale, P. R., Kumar, P., Singh, S. K., & Chakrabarti, T. (2009). Developmental strategies for sustainable ecosystem on mine spoil dumps: a case of study. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 157(1), 471–481. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0549-2
Juwarkar, A. S., Juwarkar, A., Pande, V. S., & Bal, I. S. (1992). Restoration of manganese mine spoil productivity through pressmud utilization. Environmental Issue and Management of Waste Energy and Production, 827–830.
Klammsteiner, T., Turan, V., Juárez, M. F. D., Oberegger, S., & Insam, H. (2020). Suitability of black soldier fly frass as soil amendment and implication for organic waste hygienization. Agronomy, 10(10), 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10101578
Kumar, G. P., Yadav, S. K., Thawale, P. R., Singh, S. K., & Juwarkar, A. A. (2008). Growth of Jatropha curcas on heavy metal contaminated soil amended with industrial wastes and Azotobacter–A greenhouse study. Bioresource Technology, 99(6), 2078–2082. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.03.032
Lal, R. (2008). Soils and sustainable agriculture. A review. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 28, 57–64. https://doi.org/10.1051/agro:2007025
Lee, S. S., Lim, J. E., Abd El-Azeem, S. A. M., Choi, B., Moon, D. H., & Ok, Y. S. (2013). Heavy metal immobilization in soil near abandoned mines using eggshell waste and rapeseed residue. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 20, 1719–1726.
Li, L. L. (2018). Towards a protocol on fair compensation in cases of legitimate land tenure changes: Input document for a participatory process. Journal of Chinese Governance, 3(1), 124–127
Lindsay, W. L., & Norvell, W. A. (1978). Development of a DTPA soil test for zinc, iron, manganese, and copper. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 42, 421–428.
Mingorance, M. D., Oliva, S. R., Valdes, B., Gata, F. J. P., Leidi, E. O., Guzman, I., & Pena, A. (2014). Stabilized municipal sewage sludge addition to improve properties of an acid mine soil for plant growth. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 14, 703–712.
Mora, A. P. D., Burgos, P., Madejon, E., Cabrera, F., Jaeckel, P., & Schloter, M. (2006). Microbial community structure and function in a soil contaminated by heavy metals: Effects of plant growth and different amendments. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 38, 327–341.
Muniz, S., Lacarta, J., Pata, M. P., Jimenez, J. J., & Navarro, E. (2014). Analysis of the diversity of substrate utilisation of soil bacteria exposed to Cd and earthworm activity using generalised additive models. PLoS ONE, 9(1), e85057. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0085057
Ok, Y. S., Usman, A. R. A., Lee, S. S., Abd El-Azeem, S. A. M., Choi, B., Hashimoto, Y., & Yang, J. E. (2011). Effects of rapeseed residue on lead and cadmium availability and uptake by rice plants in heavy metal contaminated paddy soil. Chemosphere, 85, 677–682.
Onagwu, B. O. (2019). Organic amendments applied to a degraded soil: short term effects on soil quality indicators. African Journal of Agricultural Research, 14(4), 218–225. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJAR2018.13457
Padmavathiamma, P. K., Li, L. Y., & Kumari, U. R. (2008). An experimental study of vermi-biowaste composting for agricultural soil improvement. Bio Resource Technology, 99, 1672–1681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.04.028
Paustian, K., Larson, E., Kent, J., Marx, E., & Swan, A. (2020). Soil C sequestration as a biological negative emission strategy. The Role of Negative Emission Technologies in Addressing Our Climate Goals. https://doi.org/10.3389/fclim.2019.00008
Rastogi, M., Nandal, M., & Khosla, B. (2020). Microbes as vital additives for solid waste composting. Heliyon, 6(2), e03343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03343
Ren, F., Sun, N., Xu, M., Zhang, X., Wu, L., & Xu, M. (2019). Changes in soil microbial biomass with manure application in cropping systems: A meta-analysis. Soil and Tillage Research, 194, 104291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2019.06.008
Rodriguez-Vila, A., Covelo, E. F., Forjan, R., & Asensio, V. (2014). Phytoremediating a copper mine soil with Brassica juncea L., compost and biochar. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21, 11293–11304.
Ruangpan, L., & Tendencia, E. A. (2004). Laboratory manual of standardized methods for antimicrobial sensitivity tests for bacteria isolated from aquatic animals and environment. Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center. Link: https://repository.seafdec.org.ph/bitstream/handle/10862/1616/Chapter1-Bacterial-Isolation-Identification-and-Storage.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (Accessed on 21st July 2020)
Sahu, H. B., & Dash, S. (2011). Land degradation due to mining in India and its mitigation measures. Second International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology, February 26-28, 2011, Singapore. URL: http://hdl.handle.net/2080/141
Sanders, E. R. (2012). Aseptic laboratory techniques: Plating methods. JoVE (journal of Visualized Experiments), 63, e3064. https://doi.org/10.3791/3064
Santibanez, C., Fuente, L. M. D. L., Bustamante, E., Silva, S., Leon-Lobos, P., & Ginocchio, R. (2012). Potential use of organic-and hard-rock mine wastes on aided phytostabilization of large-scale mine tailings under semiarid Mediterranean climatic conditions: Short-term field study. Applied and Environmental Soil Science, 2012, 1–15.
Singh, A., & Kumari, K. (2019). An inclusive approach for organic waste treatment and valorisation using Black Soldier Fly larvae: A review. Journal of Environmental Management, 251, 109569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109569
Singh, A., Srikanth, B. H., & Kumari, K. (2021). Determining the Black Soldier fly larvae performance for plant based food waste reduction and the effect on Biomass yield. Waste Management, 130, 147–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2021.05.028
Sönmez, O. S. M. A. N., Turan, V., & Kaya, C. (2016). The effects of sulfur, cattle, and poultry manure addition on soil phosphorus. Turkish Journal of Agriculture and Forestry, 40(4), 536–541.
Srivastava, R., & Singh, A. (2017). Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) for sustainable agriculture. Article International Journal of Agricultural Science and Research (IJASR), 7(4), 505–510.
Taheri, W. I., & Bever, J. D. (2011). Adaptation of Liquidambar styraciflua to coal tailings is mediated by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Applied Soil Ecology, 48(2), 251–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2011.03.012
Turan, V. (2021). Calcite in combination with olive pulp biochar reduces Ni mobility in soil and its distribution in chili plant. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2021.1929826
Turan, V., Schröder, P., Bilen, S., Insam, H., & Juárez, M. F. D. (2019). Co-inoculation effect of Rhizobium and Achillea millefolium L. oil extracts on growth of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) and soil microbial-chemical properties. Scientific Reports, 9(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-51587-x
Tripathi, R. D., Vajpayee, P., Singh, N., Rai, U. N., Kumar, A., Ali, M. B., Kumar, B., & Yunus, M. (2004). Efficacy of various amendments for amelioration of fly-ash toxicity: Growth performance and metal composition of Cassia siamea Lamk. Chemosphere, 54, 1581–1588.
Uzarowicz, L., & Skiba, S. (2011). Technogenic soils developed on mine spoils containing iron sulphides: Mineral transformations as an indicator of pedogenesis. Geoderma, 163, 95–108.
Wijesekara, H., Bolan, N. S., Vithanage M., Xu Y., Mandal S., Brown S. L., & Kirkham, M. B. (2016). Utilization of biowaste for mine spoil rehabilitation. In Advances in agronomy, vol. 138. Academic Press, pp. 97–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.agron.2016.03.001
Xiao, W., Zhang, W., Ye, Y., Lv, X., & Yang, W. (2020). Is underground coal mining causing land degradation and significantly damaging ecosystems in semi‐arid areas? A study from an Ecological Capital perspective. Land Degradation & Development, 31(15), 1969–1989. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.3570
Zornoza, R., Faz, A., Carmona, D., Martinez-Martinez, S., & Acosta, J. (2012). Plant cover and soil biochemical properties in a mine tailing pond five years after application of marble wastes and organic amendments. Pedosphere, 22, 22–32.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raghunathan, K., Marathe, D., Singh, A. et al. Organic waste amendments for restoration of physicochemical and biological productivity of mine spoil dump for sustainable development. Environ Monit Assess 193, 599 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09379-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09379-2