Abstract
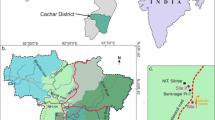
Wastewater Treatment Pond (WTP) is an effective remediation technology for economically developing nations. Although it's excessive organic and nutrient loads with higher water logging time triggers mixed and unprofitable microalgal mats. This may serve as a seeding source for Cyanobacterial bloom in receiving waterbodies. Since, to maintain the growth of desirable algal species in WTPs, understanding towards environmental regulation and algal mat composition is important, especially for tropical countries, like India. In this study, biological treatment pond (BTP) and outlet pond (OP), of a tannery effluent treatment plant in eastern coast of India, were chosen for surveying the algal community composition concerning ecological parameters. Nearly, both the ponds were polluted, but the diversity was lower in BTP due to its elevated nutrient content (Ammonia 173 mg L−1) and higher persistent organic matters (COD 301.7 mg L−1) than OP. Using canonical correspondence analysis, seasonal variations showed higher species abundance during early summer compared to other seasons. A total of 37 taxa forming thick algal mats were recorded. The matrix of mats was mainly composed of Cyanobacterial members such as Phormidium, Leptolyngbya, Spirulina, and Pseudanabaena, followed by diatoms, especially Amphora and Nitzschia. Diatoms commonly occurred as embedded component in the entangled matrix of blue-green algal filaments. Hierarchical cluster analysis was employed to group all these taxa based on their seasonal appearance and abundance. This year-long intensive study revealing seasonal algal mat composition patterns in these WTPs will ultimately safeguard the livelihood and security of adjoining localities through proper site-specific pollution control.










Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
All the data are enclosed within the manuscript. There is no associated data.
References
Ács, É., Szabó, K., Tóth, B., & Kiss, K. T. (2004). Investigation of benthic algal communities, especially diatoms of some Hungarian streams in connection with reference conditions of the water framework directives. Acta Botanica Hungarica, 46, 255–278. https://akjournals.com/view/journals/034/46/3-4/article-p255.xml
Akiyama, M. (1977). Illustrations of the Japanese fresh-water algae. Uchidarokakuho Publishing Company Limited
Ammel, R. (2018). Understanding biochemical oxygen demand. EBH. https://ebhengineering.com/2018/02/07/understanding-biochemical-oxygen-demand-bod/
Anene, A. (2003). Techniques in hydrobiology. In E. Onyeike & J. O. Osuji (Eds.), Research techniques in biological and chemical sciences (pp. 174–189). Springfield Publishers Ltd.
APHA. (1998). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater (Ed. 20). Washington DC, USA
APHA. (2005). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. Port City Press.
Atici, T. (2018). Use of cluster analyze and similarity of algae in Eastern Black Sea Region Glacier Lakes (Turkey), key area: Artabel Lakes Natural Park. Gazi University Journal of Science, 31(1), 25–40.
Atici, T., & Tokatli, C. (2018). Use of biological diatom index (BDI) to evaluate the surface water quality: a case study in a freshwater ecosystem from Central Anatolia Region of Turkey. New Technologies in Water Sector, 1, 25–26.
Atici, T., Tafli, T., & Solak, C. (2018). Determination of epipelic, epiphytic and epilitic indicator algae; Sarısu Creek (Antalya) sampling area. Biological Diversity and Conservation, 11(3), 174–179.
Atici, T. Tokatli, C., & Çiçek, A. (2018). Dıatoms of Seydısuyu Stream Basın (Turkey) and assessment of water qualıty by statıstıcal and bıologıcal approaches. Sigma: Journal of Engineering & Natural Sciences/Mühendislik ve Fen Bilimleri Dergisi, 36(1), 271–288.
Badr, S., El-Deeb, M., Ghazy, M., & Moghazy, R. (2010). Toxicity assessment of Cyanobacteria in a wastewater treatment plant Egypt. Journal of Applied Sciences Research, 6, 1511–1516.
Banerjee, S., & Pal, R. (2017). Morphotaxonomic study of blue green algae from pristine areas of West Bengal with special reference to SEM studies of different morphotypes and four new reports. Phytomorphology, 67, 67–83.
Bartram, J., & Chorus, I. (1999). Toxic Cyanobacteria in water: a guide to their public health consequences, monitoring and management. CRC Press.
Behera, M. D., Patidar, N., Chitale, V. S., Behera, N., Gupta, D., Matin, S., Tare, V., Panda, S. N. & Sen, D. J. (2014). Increase in agricultural patch contiguity over the past three decades in Ganga River Basin, India. Current Science, 502–511. https://www.jstor.org/stable/24103504
Benemann, J. R. (2008). Opportunities and challenges in algae biofuels production. Algae World, p. 15. Singapore.
Bere, T., & Tundisi, J. G. (2011). Diatom-based water quality assessment in streams influenced by urban pollution: effects of natural and two selected artificial substrates, São Carlos-SP, Brazil. Brazilian Journal of Aquatic Sciences and Technology, 15, 54–63.
Bose, R., Bar, R., & Pal, R. (2017). Floristic assortment of planktonic and epipsammic diatoms from Eastern India with new reports. Journal of Algal Biomass Utilization, 51–68.
Bosnic, M., Buljan, J., & Daniels, R.P. (2000). Pollutants in tannery effluents. UNIDO.
Chowdhury, M., Mostafa, M. G., Biswas, T. K., Mandal, A., & Saha, A. K. (2015). Characterization of the effluents from leather processing industries. Environmental Processing, 2, 173–187. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-015-0065-7
Craggs, R., Park, J., Heubeck, S., & Sutherland, D. (2014). High rate algal pond systems for low-energy wastewater treatment, nutrient recovery and energy production. New Zealand Journal of Botany, 52(1), 60–73. https://doi.org/10.1080/0028825X.2013.861855
Dawn, A., & Basu, R. (2016). A profile of industrial pollution in Kolkata Municipal Corporation Area: The case of Tanneries Kolkata West Bengal. Transactions, 38(1), 79–88.
Derakhshandeh, M., Atici, T., & Un, U. T. (2020). Evaluation of wild-type microalgae species biomass as carbon dioxide sink and renewable energy resource. Waste and Biomass Valorization, 12, 105–121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-020-00969-8
Dey, S., Botta, S., Kallam, R., Angadala, R., & Andugala, J. (2021). Seasonal variation in water quality parameters of Gudlavalleru Engineering College pond. Current Research in Green and Sustainable Chemistry, 4, 100058. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crgsc.2021.100058
Dineshkumar, R., & Sen, R. (2020). A sustainable perspective of microalgal biorefinery for co-production and recovery of high-value carotenoid and biofuel with CO2 valorization. Biofuels, Bioproducts and Biorefining, 14(4), 879–897. https://doi.org/10.1002/bbb.2107
Douterelo, I., Perona, E., & Mateo, P. (2004). Use of Cyanobacteria to assess water quality in running waters. Environmental Pollution, 127, 377–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2003.08.016
Duong, T. T., Feurtet-Mazel, A., Coste, M., Dang, D. K., & Boudou, A. (2007). Dynamics of diatom colonization process in some rivers influenced by urban pollution (Hanoi, Vietnam). Ecological Indicators, 7(4), 839–851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2006.10.003
Durai, G., & Rajasimman, M. (2011). Biological treatment of tannery wastewater - A review. Journal of Environmental Science and Technology., 4, 3910–3923. https://doi.org/10.3923/jest.2011.1.17
Esteves, S. M., Almeida, S. F., Gonçalves, S., Rimet, F., Bouchez, A., & Figueira, E. (2018). Sensitive vs. tolerant Nitzschia palea (Kützing) W. Smith strains to atrazine: a biochemical perspective. Ecotoxicology, 27(7), 860–870. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-018-1953-1
Garcia-pichel, F., Nubel, U., Muyzer,G., & Kuhl, M. (1999). Cyanobacterial community diversity and its quantification. In Bell, C. R., Brylinsky, M. & Johnson G. P. Microbial Biosystems: New Frontiers, Proceedings of 8th International Symposium on Microbial Ecology. Halifax, Canada: Atlantic Canada Society for Microbial Ecology.
Graneli, E., Weberg, M., & Salomon, P. S. (2008). Harmful algal blooms of allelopathic microalgal species: The role of eutrophication. Harmful Algae, 8(1), 94–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2008.08.011
Hamilton, Tr. L., Klatt, J. M., de Beer, D., & Macalady, J. L. (2018). Cyanobacterial photosynthesis under sulfidic conditions: insights from the isolate Leptolyngbya sp. strain hensonii. The ISME Journal, 12, 568–584.
Harris, T. D., Smith, V. H., Graham, J. L., Van de Waal, D. B., Tedesco, L. P., & Clercin, N. (2016). Combined effects of nitrogen to phosphorus and nitrate to ammonia ratios on Cyanobacterial metabolite concentrations in eutrophic Midwestern USA reservoirs. Inland Waters, 6(2), 199–210. https://doi.org/10.5268/IW-6.2.938
Hauer, F. R., & Lamberti, G. (2017). Methods in stream ecology. In Ecosystem Structure (Vol. 1). Academic Press
Heath, M. W., Wood, S. A., Brasell, K. A., Young, R. G., & Ryan, K. G. (2015). Development of habitat suitability criteria and in-stream habitat assessment for the benthic Cyanobacteria Phormidium. River Research and Applications, 1, 98–108. https://doi.org/10.1002/rra.2722
Heath, M., Wood, S. A., Young, R. G., & Ryan, K. G. (2016). The role of nitrogen and phosphorus in regulating Phormidium sp. (Cyanobacteria) growth and anatoxin production. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 92(3), fiw021. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsec/fiw021
Heisler, J., Glibert, P. M., Burkholder, J. M., Anderson, D. M., Cochlan, W., Dennison, W. C., Dortch, Q., Gobler, C. J., Heil, C. A., Humphries, E., Lewitus, A., Magnien, R., Marshall, H. G., Sellner, K., Stockwell, D. A., Stoecker, D. K., & Suddleson, M. (2008). Eutrophication and harmful algal blooms: A scientific consensus. Harmful Algae, 8, 3–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2008.08.006
Iloms, E., Ololade, O. O., Ogola, H. J., & Selvarajan, R. (2020). Investigating industrial effluent impact on municipal wastewater treatment plant in Vaal, South Africa. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(3), 1096. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17031096
Jamie, L. M., & Laurie, L. R. (2008). Adaptation of Cyanobacteria to the sulfide-rich microenvironment of black band disease of coral. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 67(2), 242–251. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.15746941.2008.00619.x
Jauffrais, T., Agogué, H., Gemin, M. P., Beaugeard, L., & Martin-Jézéquel, V. (2017). Effect of bacteria on growth and biochemical composition of two benthic diatoms Halamphora coffeaeformis and Entomoneis paludosa. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 495, 65–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jembe.2017.06.004
Jeyanthi, S., Santhanam, P., & Devi, A. S. (2018). Halophilic benthic diatom Amphora coffeaeformis—A potent biomarker for lipid and biomedical application. Indian Journal of Experimental Biology, 56, 698–701.
Jitha, G., & Gopal, M. (2017). Column type photobioreactor for waste water treatment in petrochemical industries. Journal of Technological Advancement and Scientific Research, 3(2), 23–26. https://doi.org/10.14260/jtasr/2017/07
Karthick, B., Hamilton, P. B., & Kociolek, J. P. (2013). An Illustrated Guide to Common Diatoms of Peninsular India. Gubbi: Gubbi Labs.
Kim, B. H. (1999). Ecology of a Cyanobacterial mat community in a Korean thermal wastewater stream. Aquatic Ecology, 33(4), 331–338. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009986606414
Kim, H., Jo, B. Y., Kim, H. S., Kim, H., Jo, B. Y., & Kim, H. S. (2017). Effect of different concentrations and ratios of ammonium, nitrate, and phosphate on growth of the blue-green alga (cyanobacterium) Microcystis aeruginosa isolated from the Nakdong River Korea. Algae, 32(4), 275–284. https://doi.org/10.4490/algae.2017.32.10.23
Klemenčić, K. A., & Toman, M. J. (2010). Influence of environmental variables on benthic algal associations from selected extreme environments in Slovenia in relation to the species identification. Periodicum Biologorum, 112(2), 179–191.
Kolayli, S., & Sahin, B. (2009). Species composition and diversity of epipelic algae in Balikli Dam Reservoir, Turkey. Journal of Environmental Biology, 30, 939–944.
Komárek, J., & Anagnostidis, K. (1998). Cyanoprokaryota 1. Teil Chroococcales. Süsswasserflora von Mitteleuropa, Bd. 19/1. Jena: Gustav Fisher Verlag.
Komárek, J., & Anagnostidis, K. (2005). Cyanoprokaryota 2. Teil Oscillatoriales. Süsswasserflora von Mitteleuropa, Bd. 19/2. Jena: Gustav Fisher Verlag.
Komárek, J., Ventura, S., Turicchia, S., Komárková, J., Mascalchi, C., & Soldati, E. (2005). Cyanobacterial diversity in alkaline marshes of northern Belize (Central America). Algological Studies, 117, 265–278. https://doi.org/10.1127/1864-1318/2005/0117-0265
Kozak, A., Budzyńska, A., Dondajewska-Pielka, R., Kowalczewska-Madura, K., & Gołdyn, R. (2020). Functional groups of phytoplankton and their relationship with environmental factors in the restored Uzarzewskie Lake. Water, 12(2), 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020313
Kutlu, B., Aydın, R., Danabas, D., & Serdar, O. (2020). Temporal and seasonal variations in phytoplankton community structure in Uzuncayir Dam Lake (Tunceli, Turkey). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 192(2), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-8046-3
Li, X., Wang, Y. N., Li, J., & Shi, B. (2016). Effect of sodium chloride on structure of collagen fiber network in pickling and tanning. Journal of the American Leather Chemists Association, 111(6), 230–237.
Liao, C. C., Liu, S. L., & Wang, W. L. (2006). Effects of temperature and pH on growth and photosynthesis of the thermophilic cyanobacterium Synechococcus lividus as measured by pulse-amplitude modulated fluorometry. Phycological Research, 54(4), 260–268. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1835.2006.00432.x
Likhoshway, E. V., Sorokovikova, E. G., Bel’kova, N. L. , et al. (2006). Silicon mineralization in the culture of Cyanobacteria from hot springs. Doklady Biological Sciences, 407(1), 201–205. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0012496606020256
Lin, Y. P., Wang, C. L., Chang, C. R., & Yu, H. H. (2011). Estimation of nested spatial patterns and seasonal variation in the longitudinal distribution of Sicyopterus japonicus in the Datuan Stream, Taiwan by using geostatistical methods. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 178(1), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1666-2
Mara, D. D. (2006). Natural wastewater treatment. In Manual of Best Practice. University of Leeds.
Martin-Jézéquel, V., Hildebrand, M., & Brzezinski, M. A. (2000). Silicon metabolism in diatoms: Implications for growth. Journal of Phycology, 36(5), 821–840. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1529-8817.2000.00019.x
Mateo, P., Leganés, F., Perona, E., Loza, V., & Fernández-Piñas, F. (2015). Cyanobacteria as bioindicators and bioreporters of environmental analysis in aquatic ecosystems. Biodiversity and Conservation, 24(4), 909–948. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10531-015-0903-y
Meijer, N. (2017). The relationship between enhanced Phormidium growth and fine sediment deposition in New Zealand Rivers: An experiment executed in collaboration with the Cawthron Institute in Nelson, New Zealand. Norway: Master's thesis, University College of Southeast.
Milferstedt, K., Kuo-Dahab, W. C., Butler, C. S., et al. (2017). The importance of filamentous Cyanobacteria in the development of oxygenic photogranules. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-16614-9
Miloslav, K., & Aloisie, P. (2003). Litoral diatoms as indicators for the eutrophication of shallow lakes. Hydrobiology, 506–509(1–3), 519–524.
Muga, H. E., & Mihelcic, J. R. (2008). Sustainability of wastewater treatment technologies. Journal of Environmental Management, 88, 437–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2007.03.008
Muruganantham, P., Gopalakrishnan, T., Chandrasekaran, R., & Jeyachandran, S. (2012). Seasonal variations and diversity of planktonic diatoms of Kodikkarai and Velanganni, Southeast Coast of India. Journal of Oceanography and Marine Environmental System, 2(1), 1–10.
Nashaat, M. R., Merhoon, K. A., Salman, S. K., Abbas, E. K., & Ali, E. H. (2019). Impact of Al-Rasheed power plant effluents on phytoplankton-biodiversity in Tigris river, Southern Bagdad. Journal of Physics, 1234, 012064.
Nayak, S., & Prasanna, R. (2007). Soil pH and its role in Cyanobacterial abundance and diversity in rice field soils. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research, 5(2), 103–113.
Oliveira, A. S., Bocio, A., Trevilato, T. M., Takayanagui, A. M., Domingo, J. L., & Segura-Munoz, S. I. (2007). Heavymetals in untreated/treated urban effluent and sludge from a biological wastewater treatment plant. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 14, 483–489. https://doi.org/10.1065/espr2006.10.355
Özer, T., Erkaya, İA., Koçer, M. A. T., Udoh, A. U., & Duygu, D. Y. (2019). Spatial and temporal variations in composition of algae assemblages with environmental variables in an urban stream (Ankara, Turkey). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191(6), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7527-8
Naselli-Flores, J. P. L. (2020). Phytoplankton in extreme environments: importance and consequences of habitat permanency. Hydrobiologia, 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-020-04353-4
Parikh, A., Shah, V., & Madamwar, D. (2006). Cyanobacterial flora from polluted industrial effluents. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 116(1–3), 91–102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-7229-x
Park, J. B. K., Craggs, R. J., & Shilton, A. N. (2011). Wastewater treatment high rate algal ponds for biofuel production. Bioresource Technology, 102, 35–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.06.158
Pinar, G., Duque, E., Haidour, A., et al. (1997). Removal of high concentrations of nitrate from industrial wastewaters by bacteria. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 63(5), 2071–2073.
Pradhan, A., Bhaumick, P., Das, S., Mishra, M., Khanam, S., Hoque, B. A., Mukherjee, I., Thakur, A. R., & Chaudhuri, S. R. (2008). Phytoplankton biodiversity as indicator of water quality for fish cultivation. Journal of Environmental Science, 4, 406–411.
Prasad, M. V., & Panigrahy, R. C. (2009). Phytoplankton community structure and its variability during southwest to northeast monsoon transition in the coastal waters of Kalpakkam, east coast of India. International Journal of Oceans and Oceanography, 3(1), 43–74.
Preisner, M., Neverova-Dziopak, E., & Kowalewski, Z. (2020). Mitigation of eutrophication caused by wastewater discharge: A simulation-based approach. Ambio, 50, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13280-020-01346-4
Prescott, G. W. (1982). Algae of the Western Great Lakes Area. Otto Koeltz Science Publishers.
Rawat, I., Kumar, R. R., Mutanda, T., & Bux, F. (2011). Dual role of microalgae: Phycoremediation of domestic wastewater and biomass production for sustainable biofuels production. Applied Energy, 88(10), 3411–3424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2010.11.025
Ríos, A., Ascaso, C., Wierzchos, J., Fernández-Valiente, E., & Quesada, A. (2004). Microstructural characterization of Cyanobacterial mats from the McMurdo Ice Shelf Antarctica. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 70(1), 569–580. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.70.1.569-580.2004
Romanis, C. S., Pearson, L. A., & Neilan, B. A. (2020). Cyanobacterial blooms in wastewater treatment facilities: Significance and emerging monitoring strategies. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 180, 106123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2020.106123
Round, F. E., Crawford, R. M., & Mann, D. G. (1990). The diatoms. Biology and morphology of the genera. Cambridge University Press.
Sahasranaman, A., & Emmanuel, K. V. (2001). Common Effluent Treatment Plant, Kolkata Leather Complex, Kolkata, India: UNIDO.
Saxena, A., Prakash, K., Phogat, S., Singh, P. K., & Tiwari, Archana. (2020). Inductively coupled plasma nanosilica based growth method for enhanced biomass production in marine diatom algae. Bioresource Technology, 314, 123747.
Senthil, P., Jeyachandran, S., Manoharan, C., & Vijayakumar, S. (2012). Microbial diversity in rubber industry effluent. International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences, 2(1), 123–131.
Shanthala, M., Hosmani, S. P., & Hosetti, B. B. (2009). Diversity of phytoplanktons in a waste stabilization pond at Shimoga Town, Karnataka State, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 151, 437–443. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0287-5
Silva-Bedoya, L. M., Sánchez-Pinzón, M. S., Cadavid-Restrepo, G. E., & Moreno-Herrera, C. X. (2016). Bacterial community analysis of an industrial wastewater treatment plant in Colombia with screening for lipid-degrading microorganisms. Microbiological Research, 192, 313–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2016.08.006
Summerfield, T. C., & Sherman, L. A. (2008). Global transcriptional response of the alkali-tolerant cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803 to a pH 10 environment. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 74(17), 5276–5284. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00883-08
Sutherland, D. L., Turnbull, M. H., & Craggs, R. J. (2017). Environmental drivers that influence microalgal species in fullscale wastewater treatment high rate algal ponds. Water Research, 124, 504–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.08.012
Taylor, J. C., Harding, W. R., & Archibald, C. G. M. (2007). An illustrated guide to some common diatom species from South Africa. Pretoria: Water Research Commission.
Tekerlekopoulou, A. G., Akratos, C. S., & Vayenas, D. V. (2017). Integrated biological treatment of olive mill waste combining aerobic biological treatment, constructed wetlands, and composting. In Olive Mill Waste (pp. 139–159). Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-805314-0.00007-8
Telesh, I. V. (2004). Plankton of the Baltic estuarine ecosystems with emphasis on Neva Estuary: A review of present knowledge and research perspectives. Marine Pollution Bull, 49, 206–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2004.02.009
Tong, Y., Wang, M., Peñuelas, J., Liu, X., Paerl, H. W., Elser, J. J., Sardansb, J., Couture, R. M., Larssen, T., Hu, H., Dong, X., He, W., Zhang, W., Wang, X., Zhang, Y., Liu, Y., Zeng, S., Kong, X., Janssen, A. B. G., & Lin, Y. (2020). Improvement in municipal wastewater treatment alters lake nitrogen to phosphorus ratios in populated regions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 117(21), 11566–11572. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1920759117
Vasconcelos, V. M., & Pereira, E. (2001). Cyanobacteria diversity and toxicity in a wastewater treatment plant (Portugal). Water Research, 35(5), 1354–1357. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00512-1
Verma, T., Ramteke, P. W., & Grag, S. K. (2008). Quality assessment of treated tannery wastewater with special emphasis on pathogenic E. coli detection through serotyping. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 145, 243–249. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-0033-4
Wang, X., Wen, X., Xia, Y., Hu, M., Zhao, F., & Ding, K. (2012). Ammonia oxidizing bacteria community dynamics in a pilot-scale wastewater treatment plant. PLoS ONE, 7(4), e36272. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0036272
Wentzel, M. C., Ekama, G. A., & Loewenthal, R. E. (2003). Fundamentals of biological behaviour and wastewater strength tests. In (Ed. 1) The Handbook of Water and Wastewater Microbiology (pp. 145–173). London: Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-470100-7.X5000-6
Yan, M., Chen, S., Huang, T., Li, B., Li, N., Liu, K., Zong, R., Miao, Y., & Huang, X. (2020). Community compositions of phytoplankton and eukaryotes during the mixing periods of a drinking water reservoir: Dynamics and interactions. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(4), 1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17041128
Yang, X., Wu, X., Hao, H., & He, Z. (2008). Mechanisms and assessment of water eutrophication. Journal of Zhejiang University Science B, 9(3), 197–209. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B0710626
Yuan, T. Q. & Sun, R. C. (2010). Modification of straw for activated carbon preparation and application for the removal of dyes from aqueous solutions. In Sun, R. C. (Ed. 1) Cereal Straw as a Resource for Sustainable Biomaterials and Biofuels (pp. 239–252). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-53234-3.00009-2
Acknowledgements
Iman Dey would like to thank Centre for Research in Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, University of Calcutta; Centre for Advanced Study, Phase VII, Department of Botany, University of Calcutta; and Department of Science and Technology-Fund for Improvement of S & T Infrastructure in Higher Educational System program, for providing infrastructural facilities to conduct the research work.
Funding
Iman Dey was financially supported by the University Grants Commission (UGC-Ref. No.: 723/(CSIR-UGC NET JUNE 2017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RP gave the concept of investigation, ID has done all the experimental works and wrote the full manuscript, and SB and RB critically analyzed the manuscript. Finally, RP edited the whole manuscript.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dey, I., Banerjee, S., Bose, R. et al. Spatiotemporal variations in the composition of algal mats in wastewater treatment ponds of tannery industry. Environ Monit Assess 193, 359 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09144-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09144-5