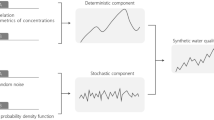
Abstract
This paper presents a methodology to assess the influence of the correlation-covariance structure of measurement errors in online monitoring over the propagation of uncertainties, applied to wet-weather environmental indicators in sustainable urban drainage systems (SUDSs). The effect of auto-correlated and heteroskedastic errors in measured time-series over the estimated probability density function (PDF) of different environmental indicators is analyzed for a wide variety of possible error structures in the data. For this purpose, multiple correlation-covariance structures are randomly generated from exploring the parametric space of a linear exponent autoregressive (LEAR) model, employing a Bayesian-based Markov Chain Monte Carlo sampling technique. Significant differences tests are proposed to identify the most correlated parameters of the correlation-covariance error model with statistics of the environmental indicator PDFs. The method is applied to total suspended solids (TSS) and chemical oxygen demand (COD) time-series recorded during 13 rainfall events at the inlet and outlet of a SUDS train (stormwater settling tank—horizontal constructed wetland). In this case, results showed that the total error in the estimation of the analyzed environmental indicators is mostly explained by standard uncertainties (flattening of the PDFs) rather than bias contributions (displacement of the PDFs). The correlation-covariance model parameters related to the temporal delimitation of hydrographs/pollutographs and the intensity of the autocorrelation showed to have the strongest influence in the propagation of measurement errors (flattening/displacement of the PDFs).






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used in this work have been collected and made available by the Pontificia Universidad Javeriana.
References
Ammann, L., Fenicia, F., & Reichert, P. (2019). A likelihood framework for deterministic hydrological models and the importance of non-stationary autocorrelation. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 23(4), 2147–2172. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-23-2147-2019
Andrés-Doménech, I., Hernández-Crespo, C., Martín, M., & Andrés-Valeri, V. C. (2018). Characterization of wash-off from urban impervious surfaces and SUDS design criteria for source control under semi-arid conditions. Science of the Total Environment, 612, 1320–1328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.011
Andrés-Valeri, V. C., Castro-Fresno, D., Sañudo-Fontaneda, L. A., & Rodriguez-Hernandez, J. (2014). Comparative analysis of the outflow water quality of two sustainable linear drainage systems. Water Science and Technology, 70(8), 1341–1347. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2014.382
Bertrand-Krajewski, J. L., & Bardin, J. P. (2002). Evaluation of uncertainties in urban hydrology: application to volumes and pollutant loads in a storage and settling tank. Water Science and Technology, 45(4–5), 437–444. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2002.0645
Bockhorn, B., Klint, K. E. S., Locatelli, L., Park, Y. J., Binning, P. J., Sudicky, E., & Bergen Jensen, M. (2017). Factors affecting the hydraulic performance of infiltration based SUDS in clay. Urban Water Journal, 14(2), 125–133. https://doi.org/10.1080/1573062X.2015.1076860
Carvajal, S. A., & Sánchez, C. A. (2018). Correlation effects in the uncertainty estimation of two-pressure humidity generators. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1065(12), 122018. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1065/12/122018
Commissie Voor Hydrologisch Onderzoek TNO. (1986). Desing Aspects of Hydrological Networks. Netherlands Organization for Applied Scientific Research TNO.
Dabrowski, J. J., Rahman, A., George, A., Arnold, S., & McCulloch, J. (2018). State space models for forecasting water quality variables: an application in aquaculture prawn farming. Proceedings of the ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, 177–185. https://doi.org/10.1145/3219819.3219841
Désenfant, M., & Priel, M. (2017). Reference and additional methods for measurement uncertainty evaluation. Measurement: Journal of the International Measurement Confederation, 95, 339–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2016.10.022
Ebrahimian, A., Wilson, B. N., & Gulliver, J. S. (2016). Improved methods to estimate the effective impervious area in urban catchments using rainfall-runoff data. Journal of Hydrology, 536, 109–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.02.023
EN 872. (2005). Water quality – determination of suspended solids – method by filtration through glass fibre filters. CEN – European Committee for Standardization.
Fardel, A., Peyneau, P. E., Béchet, B., Lakel, A., & Rodriguez, F. (2019). Analysis of swale factors implicated in pollutant removal efficiency using a swale database. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(2), 1287–1302. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3522-9
Fryd, O., Dam, T., & Jensen, M. B. (2012). A planning framework for sustainable urban drainage systems. Water Policy, 14(5), 865–886. https://doi.org/10.2166/wp.2012.025
Galarza-Molina, S. L. (2017). Decision-making tool for the operation of a stormwater harvesting system. Doctoral dissertation, Pontificia Universidad Javeriana, Bogotá, Colombia.
Galarza-Molina, S. L., Torres, A., Lara-Borrero, J., Méndez-Fajardo, S., Solarte, L., & González, L. (2015). Towards a constructed-wetland/reservoir- tank system for rainwater harvesting in an experimental catchment in Colombia. Ingenieria y Universidad, 19(2), 415–421. https://doi.org/10.11144/Javeriana.iyu19-2.tcws
Grenni, P., Barra Caracciolo, A., Mariani, L., Cardoni, M., Riccucci, C., Elhaes, H., & Ibrahim, M. A. (2019). Effectiveness of a new green technology for metal removal from contaminated water. Microchemical Journal, 147, 1010–1020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.04.026
Hailegeorgis, T. T., & Alfredsen, K. (2017). Analyses of extreme precipitation and runoff events including uncertainties and reliability in design and management of urban water infrastructure. Journal of Hydrology, 544, 290–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.11.037
Harmel, R. D., & Smith, P. K. (2007). Consideration of measurement uncertainty in the evaluation of goodness-of-fit in hydrologic and water quality modeling. Journal of Hydrology, 337, 326–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2007.01.043
Hartin, F., Minunno, F., Cameron, D., Ott, T., & Pichler, M. (2019). Package “BayesianTools.”
Hatt, B. E., Fletcher, T. D., & Deletic, A. (2009). Hydrologic and pollutant removal performance of stormwater biofiltration systems at the field scale. Journal of Hydrology, 365(3–4), 310–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2008.12.001
He, Z. (2018). A class of generalized dynamic correlation models. SSRN Electronic Journal, 1(20). https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3129418
Hoang, L., & Fenner, R. A. (2016). System interactions of stormwater management using sustainable urban drainage systems and green infrastructure. Urban Water Journal, 13(7), 739–758. https://doi.org/10.1080/1573062X.2015.1036083
Horner, I., Renard, B., Le Coz, J., Branger, F., McMillan, H. K., & Pierrefeu, G. (2018). Impact of stage measurement errors on streamflow uncertainty. Water Resources Research, 54(3), 1952–1976. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017WR022039
Jia, H., Xu, T., Liang, S., Zhao, P., & Xu, C. (2018). Bayesian framework of parameter sensitivity, uncertainty, and identifiability analysis in complex water quality models. Environmental Modelling and Software, 104, 13–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2018.03.001
Lepot, M., Aubin, J. B., & Clemens, F. H. L. R. (2017). Interpolation in time series: an introductive overview of existing methods, their performance criteria and uncertainty assessment. Water (Switzerland), 9(10). https://doi.org/10.3390/w9100796
Lepot, M., Torres, A., Hofer, T., Caradot, N., Gruber, G., Aubin, J. B., & Bertrand-Krajewski, J. L. (2016). Calibration of UV/Vis spectrophotometers: a review and comparison of different methods to estimate TSS and total and dissolved COD concentrations in sewers, WWTPs and rivers. Water Research, 101, 519–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.05.070
Leutnant, D., Muschalla, D., & Uhl, M. (2016). Stormwater pollutant process analysis with long-term online monitoring data at micro-scale sites. Water, 8(7), 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/W8070299
Luo, J., Chen, L., & Zhang, W. (2019). Covariance breakdowns and connectedness of crude oil futures markets with non-synchronous data. Applied Economics, 51(5), 422–443. https://doi.org/10.1080/00036846.2018.1489510
McMillan, H., Krueger, T., & Freer, J. (2012). Benchmarking observational uncertainties for hydrology: rainfall, river discharge and water quality. Hidrological Processes, 26, 4078–4111. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp
Merriman, L. S., Hathaway, J. M., Burchell, M. R., & Hunt, W. F. (2017). Adapting the relaxed tanks-in-series model for stormwaterwetland water quality performance. Water, 9, 691. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9090691
Métadier, M., & Bertrand-Krajewski, J. L. (2012). The use of long-term on-line turbidity measurements for the calculation of urban stormwater pollutant concentrations, loads, pollutographs and intra-event fluxes. Water Research, 46(20), 6836–6856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.12.030
Meyer, D., Dimitriadou, E., Hornik, K., Weingessel, A., Leisch, F., Chang, C.-C., & Lin, C.-C. (2019). Package “e1071.”
Peng, Z., & Stovin, V. (2017). Independent validation of the SWMM green roof module. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering, 22(9), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0001558
R Core Team. (2019). R: a language and environment for statistical computing. In R Foundation for Statistical Computing (pp. 1159–1161). https://www.r-project.org
Ripley, B., Venables, B., Bates, D. M., Hornik, K., Gebhardt, A., & Firth, D. (2020). Package “MASS.”
Rizzo, A., Bresciani, R., Martinuzzi, N., & Masi, F. (2020). Online monitoring of a long-term full-scale constructed wetland for the treatment of winery wastewater in Italy. Applied Sciences (Switzerland), 10(2), 555. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10020555
Sadeghi-Tabas, S., Samadi, S. Z., & Zahabiyoun, B. (2017). Application of Bayesian algorithm in continuous streamflow modeling of a mountain watershed. European Water, 57, 101–108
Sandoval, S., & Bertrand-Krajewski, J.-L. (2016). Influence of sampling intake position on suspended solid measurements in sewers: two probability/time-series-based approaches. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 188(6), 347. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5335-y
Sandoval, S., Bertrand-Krajewski, J. L., Caradot, N., Hofer, T., & Gruber, G. (2018). Performance and uncertainties of TSS stormwater sampling strategies from online time series. Water Science and Technology, 78(6), 1407–1416. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2018.415
Sega, M., Pennecchi, F., Rinaldi, S., & Rolle, F. (2016). Uncertainty evaluation for the quantification of low masses of benzo [a] pyrene: comparison between the law of propagation of uncertainty and the Monte Carlo method. Analytica Chimica Acta, 920, 10–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2016.03.032
Sharior, S., McDonald, W., & Parolari, A. J. (2019). Improved reliability of stormwater detention basin performance through water quality data-informed real-time control. Journal of Hydrology, 573(March), 422–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.03.012
Simpson, S. L., Edwards, L. J., Muller, K. E., Sen, P. K., & Styner, M. A. (2010). A linear exponent AR(1) family of correlation structures. Statistics in Medicine, 29(17), 1825–1838. https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.3928
Sun, S., Leonhardt, G., Sandoval, S., Bertrand-Krajewski, J. L., & Rauch, W. (2017). A Bayesian method for missing rainfall estimation using a conceptual rainfall–runoff model. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 62(15), 2456–2468. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2017.1390317
Taboga, M. (2012). Lectures on probability theory and mathematical statistics (2nd ed.). CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform.
Torres-Matallana, J. A., Leopold, U., & Heuvelink, G. B. M. (2016). Uncertainty propagation in urban water quality modelling. Proceedings of Spatial Accuracy, 313–321.
Tukey, J. W. (1977). Exploratory data analysis (Vol. 2).
Wang, M., Sweetapple, C., Fu, G., Farmani, R., & Butler, D. (2017). A framework to support decision making in the selection of sustainable drainage system design alternatives. Journal of Environmental Management, 201, 145–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.06.034
Acknowledgements
Authors are also grateful to Nelson Obregón Neira, Pierre-Antoine Versini and an anonymous reviewer for their valuable comments that led to significantly improve the quality of this manuscript.
Funding
This work was jointly supported by MINCIENCIAS (Colombian Institute for the Development of Science and Technology) and Pontificia Universidad Javeriana, Bogotá, Colombia, with resources from “Fondo Nacional de Financiamiento para la Ciencia, la Tecnología y la Innovación Francisco José de Caldas” (call 811-2018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peña-Heredia, F., Sandoval, S., Escobar-Vargas, J.A. et al. The influence of the correlation-covariance structure of measurement errors over uncertainties propagation in online monitoring: application to environmental indicators in SUDS. Environ Monit Assess 193, 345 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09097-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09097-9