Abstract
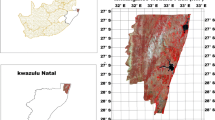
This study takes place in Erzurum city of Eastern Anatolia Region of Turkey Erzurum Plain Wetland, one of the wetlands of international importance that has biodiversity and countless benefits to its environment. Studies to offer opportunities to monitor long-term changes in the area by using advanced technology economically and effectively are expected to guide decision makers. In the present study, the changes in surface area of Erzurum Plain Wetland were investigated between 1998 and 2017 by using remote sensing techniques. As a result of the change analysis conducted using Landsat 5 TM, Landsat 7 ETM, and Landsat 8 OLI satellite data, it has been determined there is an expansion in deep and shallow water areas of the wetland. According to the results of the study, deep water areas expanded by 118.64% in 28 years. During this period, the total of deep water and shallow water reed areas increased by 9.08%. In the period of 1989–2017, the total area of the Erzurum Plain Wetland consisting of deep water, shallow water/reeds, and wet meadow/soil parts grew by 26.88%. In the study, the effects of change and human activities on this surface area change were also examined and it was found as a result of the evaluation that more than climatic factors, change of hydrological structure caused by increase in underground water reserves may be effective on the expansion.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Some or all data, models, or code that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Aazami, M., & Shanazi, K. (2020). Tourism wetlands and rural sustainable livelihood: The case from Iran. Journal of Outdoor Recreation and Tourism, 30, 100284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jort.2020.1002844
Abburu, S., & Golla, S. B. (2015). Satellite image classification methods and techniques: A review. International Journal of Computer Applications, 119(8), 20–25. https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.695.1415&rep=rep1&type=pdf
Aher, S., Shinde, S. D., Jarag, A. P., Babu, M., & Gawali, P. B. (2014). Identification of lineaments in the Pravara Basin from ASTER-DEM data and satellite images for their geotectonic implication. International Research Journal of Earth Sciences, 2(7), 1–10.
Bridgewater, P., & Kim, R. E. (2021). The Ramsar convention on wetlands at 50. Nature Ecology & Evolution. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41559-021-01392-5
Cai, Y., Zhang, H., Pan, W., et al. (2012). Urban expansion and its influencing factors in Natural Wetland Distribution Area in Fuzhou City. China. Chin. Geogr. Sci., 22, 568–577. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-012-0564-7
Cho, E., Choi, M., & Wagner, W. (2015). An assessment of remotely sensed surface and root zone soil moisture through active and passive sensors in northeast Asia. Remote Sensing of Environment, 60, 166–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2015.01.013
Dwyer, J. L., Roy, D. P., Sauer, B., Jenkerson, C. B., Zhang, H. K., & Lymburner, L. (2018). Analysis ready data: Enabling analysis of the Landsat archive. Remote Sensing, 10(9), 1363. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10091363
De Jong, S. M., Meer, F. D., & Clevers, J. G. (2004). Basics of remote sensing. In: Jong S.M.D., Meer F.D.V. (eds) Remote sensing image analysis: Including the spatial domain. remote sensing and digital image processing, 5
Duarte, D. C., De, O., Zanetti, J., Gripp J. J., & Medeiros, N. D. G. (2018). Comparison of supervised classification methods of maximum likelihood, minimum distance, parallelepiped and neural network in images of unmanned air vehicle (UAV) in Viçosa - MG. Revista Brasileira de Cartografia, 70(2), 437–452. https://doi.org/10.14393/rbcv70n2-45377
Elfadaly, A., Lasaponara, R., Murgante, B., & Qelichi, M.M. (2017). Cultural heritage management using analysis of satellite images and advanced GIS techniques at East Luxor, Egypt and Kangavar, Iran (A Comparison Case Study). In: Gervasi O. et al. (eds) Computational Science and Its Applications – ICCSA 2017. ICCSA 2017. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 10407. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-62401-3_12
El Rahman, S. A. (2015). Hyperspectral imaging classification using ISODATA algorithm: Big data challenge. Fifth International Conference on e-Learning, 2015, 247–250. https://doi.org/10.1109/ECONF.2015.39
Foody, G. M. (2020). Explaining the unsuitability of the kappa coefficient in the assessment and comparison of the accuracy of thematic maps obtained by image classification. Remote Sensing of Environment, 239, 111630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2019.111630
Gelagay, H. S., & Minale, A. S. (2016). Soil loss estimation using GIS and Remote sensing techniques: A case of Koga watershed, Northwestern Ethiopia. International Soil and Water Conservation Research, 4(2), 126–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswcr.2016.01.002
Guo, M., Li, J., Sheng, C., Xu, J., & Wu, L. (2017). A review of wetland remote sensing. Sensors (Basel), 17(4), 1–36. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17040777
Homolova, L., Malenovsky, Z., Clevers, J., Garcia-Santos, G., & Schaepmana, M. E. (2013). Review of optical-based remote sensing for plant trait mapping. Ecological Complexity, 15, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecocom.2013.06.003
Jacintha, T. G. A., Rajasree, S. R. R., Kumar, J. D., & Sriganesh, J. (2019). Assessment of wetland change dynamics of Chennai coast, Tamil Nadu, India, using satellite remote sensing. Indian Journal of Geo Marine Sciences, 48(8), 1258–1266
Lemenkova, P. (2013). Monitoring changes in agricultural landscapes of Central Europe, Hungary: Application of ILWIS GIS for image processing. European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers. https://doi.org/10.3997/2214-4609.20142479
Liau, K., Xu, S., Wu, J., & Zhu, Q. (2013). Spatial estimation of surface soil texture using remote sensing data. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 59(4), 488–500. https://doi.org/10.1080/00380768.2013.802643
Moreno-Mateos, D., Power, M. E., Comin, F. A., & Yockteng, R. (2012). Structural and functional loss in restored wetland ecosystems. Plos Biology, 10(1), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1001247
Niu, Z., Zhang, H., Wang, X., et al. (2012). Mapping wetland changes in China between 1978 and 2008. Chinese Science Bulletin, 57, 2813–2823. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-012-5093-3
Pan, P., Xi, X., & Wang, C. (2019). A MATLAB-based digital elevation model (DEM) data processing toolbox (MDEM). Environmental Modelling & Software, 122, 104566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2019.104566
Redy, G. P. O. (2018). Satellite remote sensing sensors: Principles and applications, geospatial technologies in land resources mapping. Monitoring and Management, 21, 21–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-78711-4_2
Wang, J., Qi, J., Zhang D. & Fu, Z. (2018). Sensitivity analysis about FLAASH model parameters. 2018 Fifth International Workshop on Earth Observation and Remote Sensing Applications (EORSA), Xi'an, 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/EORSA.2018.8598564
Wu, H., Zeng, G., Liang, J., Chen, J., Xu, J., Dai, J., Sang, L., Li, X., & Ye, S. (2017). Responses of landscape pattern of China’s two largest freshwater lakes to early dry season after the impoundment of Three-Gorges Dam. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 56, 36–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2016.11.006
Wu, H., Chen, J., Zeng, G., Xu, J., Sang, L., Liu, Q., Dai, J., Xiong, W., Yuan, Z., Wang, Y., & Ye, S. (2019a). Effects of Early dry season on habitat suitability for migratory birds in China’s two largest freshwater lake wetlands after the impoundment of Three Gorges Dam. Journal Of Envıronmental Informatıcs, 36(2), 82–92
Wu, H., Chen, J., Xu, J., Zeng, G., Sang, L., Liu, Q., Yin, Z., Dai, J., Yin, D., Liang, J., & Ye, S. (2019b). Effects of dam construction on biodiversity: A review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 221, 480–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.03.001
Wu, H., Hu, X., Sun, S., Dai, J., Ye, S., Du, C., Chen, H., Yu, G., Zhou, L., & Chen, J. (2020). Effect of increasing of water level during the middle of dry season on landscape pattern of the two largest freshwater lakes of China. Ecological Indicators, 113, 106283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106283
Wu, H., Dai, J., Sun, S., Du, C., Long, Y., Chen, H., Yu, G., Ye, S., & Chen, J. (2021). Responses of habitat suitability for migratory birds to increased water level during middle of dry season in the two largest freshwater lake wetlands of China. Ecological Indicators, 121, 107065. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.107065
Yan, W., Shaker, A., Habib, A., & Kersting, A. P. (2012). Improving classification accuracy of airborne LiDAR intensity data by geometric calibration and radiometric correction. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 67, 35–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2011.10.005
Yıldız, N. D., Yılmaz, S., & Demir, M. (2010). Determination of the Change in Wetland Boundary with GIS-UA; Erzurum Example (in Turkish). Annual Journal of Rural Environment, 23–33
Young, N. E., Anderson, R. S., Chignell, S. M., Vorster, A. G., Lawrence, R., & Evangelista, P. H. (2017). A survival guide to landsatpreprocessing. Concepts & Synthesis, 98, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecy.1730
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
İrdemez, Ş., Eymirli, E.B. Determination of spatiotemporal changes in Erzurum plain wetland system using remote sensing techniques. Environ Monit Assess 193, 265 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09041-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09041-x