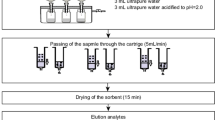
Abstract
This study presents the development of an analytical method for the simultaneous determination of multiclass illicit drugs (cocainoids, opiates, amphetamines, and cannabinoids) and psychoactive pharmaceuticals (anxiolytics, hypnotics, antipsychotics, antidepressants, and antiparkinsonian), in municipal wastewater. The analytical method was validated in terms of specificity, linearity, precision, and accuracy. The recoveries (%) for the majority of the analytes ranged between 70 and 120%, while the method showed good repeatability (2.4–29.2%). The limits of detection (LOD) of the method ranged between 0.8 and 9.4 ng L−1. The method was implemented on influent and effluent samples from Thessaloniki (N. Greece) wastewater treatment plant (WWTP), and it revealed the daily presence of benzoylecgonine (BEG) (84.0–202.2 ng L−1), methadone (12.3–17.5 ng L−1), 11-Nor-9-carboxy-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC-COOH) (80.3–171.9 ng L−1), morphine (144.2–264.3 ng L−1), and 6-monoacetylmorphine (6-MAM) (5.8–12.0 ng L−1) in the influent samples of WWTP. Clozapine (101.6–315.5 ng L−1), quetiapine (33.5–109.7 ng L−1), and fluoxetine (20.9–124.4 ng L−1) were pharmaceutical psychotics with the highest concentration in the influents. Back calculation estimated that the daily consumption of cocaine, heroin, cannabis, and methadone was 36–95, 86–164, 2300–5400, and 8–12 mg day−1 per 1000 inhabitants, respectively. The consumption was estimated between 7–16 and 15 mg day−1 per 1000 inhabitants for methyl diethanolamine (MDEA) and 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA), respectively.
Graphical Abstract


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Arsand, J. B., Hoff, R. B., Jank, L., Dallegrave, A., Galeazzi, C., Barreto, F., & Pizzolato, T. M. (2018). Wide-scope determination of pharmaceuticals and pesticides in water samples: Qualitative and confirmatory screening method using LC-qTOF-MS. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 229(12). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-4036-2
Asimakopoulos, A. G., Kannan, P., Higgins, S., & Kannan, K. (2017). Determination of 89 drugs and other micropollutants in unfiltered wastewater and freshwater by LC-MS/MS: An alternative sample preparation approach. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 409(26), 6205–6225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0561-x
Baker, D. R., Barron, L., & Kasprzyk-Hordern, B. (2014). Illicit and pharmaceutical drug consumption estimated via wastewater analysis. Part A: Chemical analysis and drug use estimates. Science of the Total Environment, 487(1), 629–641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.11.107
Baz-Lomba, J. A., Salvatore, S., Gracia-Lor, E., Bade, R., Castiglioni, S., Castrignanò, E., Causanilles, A., Hernandez, F., Kasprzyk-Hordern, B., Kinyua, J., McCall, A. K., van Nuijs, A., Ort, C., Plósz, B. G., Ramin, P., Reid, M., Rousis, N. I., Ryu, Y., de Voogt, P., & Thomas, K. (2016). Comparison of pharmaceutical, illicit drug, alcohol, nicotine and caffeine levels in wastewater with sale, seizure and consumption data for 8 European cities. BMC Public Health, 16(1), 1035.
Binelli, A., Pedriali, A., Riva, C., & Parolini, M. (2012). Illicit drugs as new environmental pollutants: Cyto-genotoxic effects of cocaine on the biological model Dreissena polymorpha. Chemosphere, 86(9), 906–911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.10.056
Borova, V. L., Maragou, N. C., Gago-Ferrero, P., Pistos, C., & Thomaidis, N. S. (2014). Highly sensitive determination of 68 psychoactive pharmaceuticals, illicit drugs, and related human metabolites in wastewater by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 406(17), 4273–4285. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-014-7819-3
Bringolf, R. B., Heltsley, R. M., Newton, T. J., Eads, C. B., Fraley, S. J., & Shea, D. (2010). Environmental occurrence and reproductive effects of the pharmaceutical fluoxetine in native freshwater mussels. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 29(6), 1311–1318.
Carraro, E., Bonetta, S., & Bonetta, S. (2018). Hospital wastewater: Existing regulations and current trends in management. In Handbook of Environmental Chemistry (Vol. 60, pp. 1–16). https://doi.org/10.1007/698_2017_10
Castiglioni, S., Borsotti, A., Riva, F., & Zuccato, E. (2016). Illicit drug consumption estimated by wastewater analysis in different districts of Milan: A case study. Drug and Alcohol Review, 35(2), 128–132. https://doi.org/10.1111/dar.12233
Castiglioni, S., Zuccato, E., Crisci, E., Chiabrando, C., Fanelli, R., & Bagnati, R. (2006). Identification and measurement of illicit drugs and their metabolites in urban wastewater by liquid chromatography−tandem mass spectrometry. Analytical Chemistry, 78(24), 8421–8429. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac061095b
Castiglioni, S., Zuccato, E., & Fanelli, R. (2011). Illicit drugs in the environment: Occurrence, analysis, and fate using mass spectrometry. In Illicit drugs in the environment: Occurrence, analysis, and fate using mass spectrometry. WILEY. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118000816
Choi, P. M., Tscharke, B. J., Donner, E., O’Brien, J. W., Grant, S. C., Kaserzon, S. L., Mackie, R., O’Malley, E., Crosbie, N. D., Thomas, K. V., & Mueller, J. F. (2018). Wastewater-based epidemiology biomarkers: Past, present and future. TrAC - Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 105, 453–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2018.06.004
Daughton, C. G., & Ruhoy, I. S. (2009). Environmental footprint of pharmaceuticals: The significance of factors beyond direct excretion to sewers. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 28(12), 2495–2521. https://doi.org/10.1897/08-382.1
EC. (2017). DIRECTIVE 2017/1572 of 15 September 2017 supplementing Directive 2001/83/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards the principles and guidelines of good manufacturing practice for medicinal products for human use. In E. U. Commission (Ed.), 2017/1572.
Fong, P. P. (2013). Antidepressants cause foot detachment from substrate in five species of marine snail. Marine Environmental Research, 84, 24–30.
Foppe, K. S., & Subedi, B. (2018). Analysis of illicit drugs in wastewater using high-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-ESI-MS/MS). In Methods in Molecular Biology (Vol. 1810, pp. 183–191). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-8579-1_16
Gaw, S., Thomas, K. V., & Hutchinson, T. H. (2014). Sources, impacts and trends of pharmaceuticals in the marine and coastal environment. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 369(1656), 20130572. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2013.0572
González-Mariño, I., Baz-Lomba, J. A., Alygizakis, N. A., Andrés-Costa, M. J., Bade, R., Bannwarth, A., Been, F., Benaglia, L., Berset, J.-D., Bijlsma, L., Bodík, I., Brenner, A., Brock, A. L., Burgard, D. A., Castrignanò, E., Celma, A., Christophoridis, C. E., Covaci, A., Emke, E., Ort, C. (2020). Spatio-temporal assessment of illicit drug use at large scale: Evidence from 7 years of international wastewater monitoring. Addiction, 115(1). https://doi.org/10.1111/add.14767
González-Mariño, I., Castro, V., Montes, R., Rodil, R., Lores, A., Cela, R., & Quintana, J. B. (2018). Multi-residue determination of psychoactive pharmaceuticals, illicit drugs and related metabolites in wastewater by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A, 1569, 91–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.07.045
González-Mariño, I., Quintana, J. B., Rodríguez, I., González-Díez, M., & Cela, R. (2012). Screening and selective quantification of illicit drugs in wastewater by mixed-mode solid-phase extraction and quadrupole-time-of-flight liquid chromatography−mass spectrometry. Analytical Chemistry, 84, 1708–1717.
Gracia-Lor, E., Castiglioni, S., Bade, R., Been, F., Castrignanò, E., Covaci, A., González-Mariño, I., Hapeshi, E., Kasprzyk-Hordern, B., Kinyua, J., Lai, F. Y., Letzel, T., Lopardo, L., Meyer, M. R., O’Brien, J., Ramin, P., Rousis, N. I., Rydevik, A., Ryu, Y., & Bijlsma, L. (2017). Measuring biomarkers in wastewater as a new source of epidemiological information: Current state and future perspectives. Environment International, 99, 131–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2016.12.016
Gracia-Lor, E., & Sancho, J. V. (2010). Simultaneous determination of acidic, neutral and basic pharmaceuticals in urban wastewater by ultra high-pressure liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A, 1217, 622–632.
Hapeshi, E., Gros, M., Lopez-Serna, R., Boleda, M. R., Ventura, F., Petrovic, M., Barceló, D., & Fatta-Kassinos, D. (2015). Licit and illicit drugs in urban wastewater in Cyprus. Clean - Soil, Air, Water, 43(9), 1272–1278. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201400483
Huerta-Fontela, M., Galceran, M. T., & Ventura, F. (2007). Ultraperformance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis of stimulatory drugs of abuse in wastewater and surface waters. Analytical Chemistry, 79, 3821–3829.
Hummel, D., Loffler, D., Fink, G., & Ternes, T. (2006). Simultaneous determination of psychoactive drugs and their metabolites in aqueous matrices by liquid chromatography massspectrometry. Environmental Science and Technology, 40, 7321–7328.
Ibáñez, M., Borova, V., Boix, C., Aalizadeh, R., Bade, R., Thomaidis, N. S., & Hernández, F. (2017). UHPLC-QTOF MS screening of pharmaceuticals and their metabolites in treated wastewater samples from Athens. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 323, 26–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.03.078
Kasprzyk-Hordern, B. (2011). Multi-residue analysis of drugs of abuse in wastewater and surface water by solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography–positive electrospray ionisation tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A, 1218, 1620–1631.
Kosjek, T., & Heath, E. (2008). Applications of mass spectrometry to identifying pharmaceutical transformation products in water treatment. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 27(10), 807–820. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2008.08.014
Krizman-Matasic, I., Senta, I., Kostanjevecki, P., Ahel, M., & Terzic, S. (2019). Long-term monitoring of drug consumption patterns in a large-sized European city using wastewater-based epidemiology: Comparison of two sampling schemes for the assessment of multiannual trends. Science of the Total Environment, 647, 474–485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.441
Lai, F. Y., Bruno, R., Leung, H. W., Thai, P. K., Ort, C., Carter, S., Thompson, K., Lam, P. K. S., & Mueller, J. F. (2013). Estimating daily and diurnal variations of illicit drug use in Hong Kong: A pilot study of using wastewater analysis in an Asian metropolitan city. Forensic Science International, 233(1–3), 126–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2013.09.003
Li, J., Gao, J., Thai, P. K., Sun, X., Mueller, J. F., Yuan, Z., & Jiang, G. (2018). Stability of illicit drugs as biomarkers in sewers: From lab to reality. Environmental Science and Technology, 52(3), 1561–1570. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b05109
Mackul’ak, T., Škubák, J., Grabic, R., Drtil, M., & Bodík, I. . (2015). Comparison of illicit drug use in three selected towns in Slovakia by wastewater analysis. Urban Water Journal, 12(7), 519–524. https://doi.org/10.1080/1573062X.2014.949797
Metcalfe, C. D., Chu, S., Judt, C., Li, H., Oakes, K. D., Servos, M. R., & Andrews, D. M. (2010). Antidepressants and their metabolites in municipal wastewater, and downstream exposure in an urban watershed. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 29(1), 79–89.
Nassiri Koopaei, N., & Abdollahi, M. (2017). Health risks associated with the pharmaceuticals in wastewater. DARU Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 25, 9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40199-017-0176-y
Nefau, T., Karolak, S., Castillo, L., Boireau, V., & Levi, Y. (2013). Presence of illicit drugs and metabolites in influents and effluents of 25 sewage water treatment plants and map of drug consumption in France. Science of the Total Environment, 461–462, 712–722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.05.038
Nikolaou, A., & Meric, S. (2007). Occurrence patterns of pharmaceuticals in water and wastewater environments. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 387, 1225–1234.
Östman, M., Fick, J., Näsström, E., & Lindberg, R. H. (2014). A snapshot of illicit drug use in Sweden acquired through sewage water analysis. Science of the Total Environment, 472, 862–871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.11.081
Pal, R., Megharaj, M., Kirkbride, K. P., & Naidu, R. (2013). Illicit drugs and the environment—A review. Science of the Total Environment, 463–464, 1079–1092. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.05.086
Ramin, P., Polesel, F., Brock, A. L., & Plósz, B. G. (2018). The impact of temperature on the transformation of illicit drug biomarkers in wastewater. Science of the Total Environment, 644, 1612–1616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.307
Repice, C., Grande, M. D., Maggi, R., & Pedrazzani, R. (2013). Licit and illicit drugs in a wastewater treatment plant in Verona, Italy. Science of the Total Environment, 463–464, 27–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.05.045
Rodriguez-Mozaz, S., Lopez de Alda, M. J., & Barceló, D. (2007). Advantages and limitations of on-line solid phase extraction coupled to liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry technologies versus biosensors for monitoring of emerging contaminants in water. Journal of Chromatography A, 1152(1–2), 97–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2007.01.046
Skees, A. J., Foppe, K. S., Loganathan, B., & Subedi, B. (2018). Contamination profiles, mass loadings, and sewage epidemiology of neuropsychiatric and illicit drugs in wastewater and river waters from a community in the Midwestern United States. Science of the Total Environment, 631–632, 1457–1464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.060
Subedi, B., & Kannan, K. (2014). Mass loading and removal of select illicit drugs in two wastewater treatment plants in New York State and estimation of illicit drug usage in communities through wastewater analysis. Environmental Science and Technology, 48(12), 6661–6670. https://doi.org/10.1021/es501709a
Thomaidis, N. S., Gago-Ferrero, P., Ort, C., Maragou, N. C., Alygizakis, N. A., Borova, V. L., & Dasenaki, M. E. (2016). Reflection of Socioeconomic changes in wastewater: Licit and illicit drug use patterns. Environmental Science and Technology, 50(18), 10065–10072. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b02417
van Nuijs, A. L. N., Lai, F. Y., Been, F, Andres-Costa, M. J., Barron, L., Baz-Lomba, J. A., Berset, J.-D., Benaglia, L., Bijlsma, L., Burgard, D., Castiglioni, S., Christophoridis, C., Covaci, A., de Voogt, P., Emke, E., Fatta-Kassinos, D., Fick, J., Hernandez, F., Gerber, C., ... Ort, C. (2018). Multi-year inter-laboratory exercises for the analysis of illicit drugs and metabolites in wastewater: Development of a quality control system. TrAC - Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2018.03.009
van Nuijs, A. L. N., Mougel, J. F., Tarcomnicu, I., Bervoets, L., Blust, R., Jorens, P. G., Neels, H., & Covaci, A. (2011). Sewage epidemiology—A real-time approach to estimate the consumption of illicit drugs in Brussels. Belgium. Environment International, 37(3), 612–621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2010.12.006
vanNuijs, A. L. N., Pecceu, B., Theunis, L., Dubois, N., Charlier, C., Jorens, P. G., Bervoets, L., Blust, R., & Neels, H. (2009). Cocaine and metabolites in waste and surface water across Belgium. Environmental Pollution, 157, 123–129.
vanNuijs, A. L. N., & Tarcomnicu, I. (2011). Illicit drug consumption estimations derived from wastewater analysis: A critical review. Science of the Total Environment, 409(19), 3564–3577.
Yadav, M. K., Short, M. D., Aryal, R., Gerber, C., van den Akker, B., & Saint, C. P. (2017). Occurrence of illicit drugs in water and wastewater and their removal during wastewater treatment. Water Research, 124, 713–727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.07.068
Zervou, S.-K., Christophoridis, C., Kaloudis, T., Triantis, T. M., & Hiskia, A. (2017). New SPE-LC-MS/MS method for simultaneous determination of multi-class cyanobacterial and algal toxins. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 323, 56–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.07.020
Zuccato, E., & Castiglioni, S. (2009). Illicit drugs in the environment. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A, 367, 3965–3978.
Zuccato, E., Chiabrando, C., Castiglioni, S., Calamari, D., Bagnati, R., Schiarea, S., & Fanelli, R. (2005). Cocaine in surface waters: A new evidence-based tool to monitor community drug abuse. Environmental Health: A Global Access Science Source, 4, 14. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-069X-4-14
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank “Stavros Niarchos Foundation” for the provision and funding of the Waters Acquity UPLC-TQD MS/MS system.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Application of a validated LC-ESI-MS/MS method for the determination of illicit drugs/pharmaceuticals
• First-time analysis of WWTP samples from Thessaloniki, N. Greece
• Estimation of illicit drug consumption using sewage epidemiology approach
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Christophoridis, C., Veloutsou, S., Mitsika, E. et al. Determination of illicit drugs and psychoactive pharmaceuticals in wastewater from the area of Thessaloniki (Greece) using LC–MS/MS: estimation of drug consumption. Environ Monit Assess 193, 249 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09035-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09035-9