Abstract
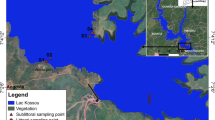
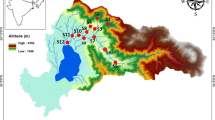
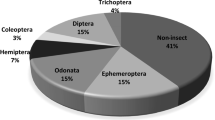
The accelerated development of industrial activities in Taza City implies the appearance of new sources of pollution that directly affect the quality of surface water. This is reflected in the structure and biodiversity of the city’s Oueds, particularly Oued Lârbaa, which receives the majority of the pollution load produced. Therefore, the study of the benthic fauna can be an effective tool to characterize the state of the waters of Oued Lârbaa. The objective of our study is to assess the impact of anthropogenic activities on Oued Lârbaa, through the monitoring of physicochemical parameters (hydrogen potential (pH), salinity, conductivity, total dissolved solids (TDS), and oxidation–reduction potential) and biological biodiversity represented by benthic macroinvertebrates at 10 stations, during two periods of the year: a wet period (December 2018) and a dry period (June 2019). The spatial variations of recorded physicochemical parameters, as well as the effect of anthropogenic activities, control the diversity of macroinvertebrates at Oued Lârbaa. In relation to these data, the first stations of our study (S1-S2-S3) are moderately polluted, characterized by an important biodiversity, which includes sensitive species (Crustacea, Trichoptera, Ephemeroptera), and other resistant species (Diptera). The stations S4-S5-S6-S7-S8-S9 and S10 are characterized by a low biodiversity represented mainly by macroinvertebrates that colonize waters of critical quality (Diptera). The statistical study by principal component analysis consisting of a projection of the biological (benthic macroinvertebrates) and physicochemical variables obtained from each of the two study periods on a two-dimensional factorial plane shows the existing correlations between these variables.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullah, A. R., Lim, R. P., & Chapman, J. C. (1993). Inhibition and recovery of acetylcholinesterase in Paratya australiensis exposed to the organophosphate insecticide chlorpyrifos. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 2, 752–757.
Agblonon Houelome, T. M., Adandejan, D., Chikou, A., ImorouToko, I., Bonou, C., Youssao, I., & Laleye, P. (2016). Evaluation de la qualité des eaux des ruisseaux du cours moyen de la rivière Alibori par l’étude des macroinvertébrés benthiques dans le bassin cotonnier du Bénin (Afrique de l’Ouest). International Journal of Biological and Chemical Sciences, 10(6), 2461–2476. (In French).
Alba-Tercedor, J. (1996). Macroinvertebrados acuáticos y calidad de las aguas de los ríos. Memorias del IV Simposio el agua en Andalucía. Siaga, Almeria, 2, 203–213. (In Spanish).
Alba-Tercedor, J., Jáimez-Cuéllar, P., Álvarez, M., Avilés, J., Bonada, N., Casas, J., et al. (2002). Caracterización del estado ecológico de ríos mediterráneos ibéricos mediante el índice IBMWP (antes BMWP’). Limnetica., 21(2), 175–185. (In Spanish).
Alhejoj, I., Salameh, E., & Bandel, K. (2014). Mayflies (order Ephemeroptera): An effective indicator of water bodies conditions in Jordan. International journal of scientific research in environmental sciences, 2(10), 361–370.
Arambourou, H., & Chenevoy, A. (2010). Mise en évidence des pressions toxiques exercées sur la rivière la Drouette grâce à l’analyse des déformations affectant le mentum des Chironominae (Diptères, Chironomidae). Bulletin des Laboratoires des Ponts et Chaussées., 276, 97–106. (In French).
Bekkoussa, B., Jourde, H., Batiot-Guilhe, C., Meddi, M., Khaldi, A., & Azzaz, H. (2013). Origine de la salinité et des principaux éléments majeurs des eaux de la nappe phréatique de la plaine de Ghriss. Nord-Ouest algérien. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 58(5), 1111–1127. (In French).
Bonada, N., Prat, N., Resh, V. H., & Statzner, B. (2006). Developments in aquatic insect biomonitoring: A comparative analysis of recent approaches. Annual Review of Entomology, 51, 495–523.
Bou, C., & Salomon, J. N. (1998). L’impact des aménagements anthropiques sur les cours moyen du Tarn. Sud-Ouest européen - questions à l’environnement, 3, 29–38. (In French).
Bourassa, N. (1993). Effet de la trophie et de la taille du substrat sur le spectre de taille des invertébrés benthiques en ruisseaux. Thèse Doc. University of Ottawa, 67p. (In French).
Camargo, J. A., Alonso, A., & De La Puente, M. (2003). Multimetric assessement of nutriment enrichment in impounded rivers based on benthic macroinvertebrates. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 96, 233–249.
Chapeau, A., Pont, D., Gregoire, A., & Kerambrun, P. (1979). Les invertébrés indicateurs de la qualité des eaux en camargue. Rapport de la Commission Internationale de la Méditerrané. Centre d'Ecologie de Camargue et Université d'Aix-Marseille II, 157 p. (In French).
Délégation Provinciale du Commerce et de l'Industrie de Taza (DPCE). (2019). Enquête des industries installées au niveau de la province de Taza. (In French).
Derwich, E., Beziane, Z., Benaabidate, L., & Belghyti, D. (2008). Evaluation de la qualité des eaux de surface des Oueds Fès et Sebou utilisées en agriculture maraichère au Maroc. Larhyss Journal, 7, 59–77. (In French).
Fagrouch, A., Berrahou, A., & El Halouani, H. (2011). Impact d’un effluent urbain de la ville de Taourirt sur la structure des communautés de macroinvertébrés de l’Oued Za (Maroc oriental). Revue des sciences de l’eau, 24(2), 87–101. (In French).
Floury, M. (2013). Analyse des tendances d’évolution de peuplements de macroinvertébrés benthiques dans un contexte de réchauffement des eaux. Thèse Doc. Université Blaise Pascal, Clermont-Ferrand, 236p. (In French).
Gascoyne, M. (1997). Evolution of redox conditions and groundwater composition in recharge-discharge environments on the canadianshield. Hydrogeology Journal, 5(3), 4–18.
Hunte, W. (1977). Laborator yrearing of the Atyidshrimps Atyainnocus Herbst and Micratya Poeyi Guérin-Méneville (Decapoda, Atyidae). Aquaculture, 11(4), 373–378.
Iliopoulou Georgudaki, J., Kantzaris, V., Katharios, P., Kaspiris, P., Georgiadis, T., & Montesantou, B. (2003). An application of different bioindicators for assessing water quality: A case study in the rivers Alfeios and Pineios (Peloponnisos, Greece). Ecological Indicators, 2(4), 345–360.
Jacquemin, G. (2001). Les éphéméroptères en Lorraine: Etat de l’inventair e, utilisation comme bio-indicateurs Préservation. Bulletin de l’académie Lorraine des sciences, 40, 11–22. (In French).
Jáimez Cuéllar, P. (2004). Caracterización físico-química, macroinvertebrados acuáticos y valoración del estado ecológico de dos cuencas mediterráneas de influencia nival (ríosguadalfeo y adra), según los criterios de la directiva marco del agua. Phd thesis. Universidad de Granada, 226 p. (In Spanish).
Jáimez-Cuéllar, P., Vivas, S., Bonada, N., Robles, S., Mellado, A., Álvarez, M., et al. (2004). Protocolo Guadalmed (PRECE). Limnética, 21(2002), 187–204.
Kambiré, O., Adingra, A. A., Eblin, S. G., Aka, N., Kakou, A. C., & Koffi-Nevry, R. (2014). Caractérisation des eaux d’une lagune estuarienne de la Côte d’Ivoire : La Lagune Aby. Larhyss Journal, 20, 95–110. (In French).
Karrouch, L., & Chahlaoui, A. (2009). Bio-évaluation de la qualité des eaux de l’Oued Boufekrane (Meknès, MAROC). Biomatec Echo, 3(6), 6–17. (In French).
Klein, L. (1973)."River Pollution Il- causes and effects" (5th ed. 206 p) Butterwork and co. London.
Koumba, M., Hans, K. M., Aubin, A. K., Zinga Koumba, C. R., Mboye, B. R., Liwouwou, J. F., et al. (2017). Diversité familiale des macroinvertébrés et qualité des cours d’eau du Parc National de Moukalaba Doudou (sud-ouest du Gabon). Faunistic Entomology, 70, 107–120. (In French).
Kraïem, M. (1986). Contribution à l’étude hydrobiologique de trois cours d’eau du nord-ouest de la Tunisie, Présentation physico-chimie et aperçu faunistique. Publications de la Société Linnéenne de Lyon, 55(3), 96–104. (In French).
Kumar, A., Correll, R., Grocke, S., & Bajet, C. (2010). Toxicity of selected pesticides to freshwatershrimp, Paratyaaustraliensis (Decapoda: Atyidae): Use of time series acute toxicity data to predictchroniclethality. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 73(3), 360–369.
Lamhasni, N., Chillasse, L., Abbai, H., El Haouat, S., & El Madani, M. (2013). Typologie des eaux de surface du bassin du Sebou par multi-approche : corrélation entre indice biologique global des réseaux de contrôle et de surveillance (IBG-RCS) et l’approche physicochimique et microbiologique. Afrique Science, 09(2), 35–49. (In French).
Lee Foote, A., & Rice, C. L. (2005). Odonates as biological indicators of grazing effects on Canadian prairie wetlands. Ecological Entomology, 30, 273–283.
Löwner, R. (2009). Recherches sédimentlogiques et structurales à l’articulation entre Haut et Moyen Atlas et la Haute Moulouya, Maroc. Thèse Doc. Technische Universitat Berlin, 201 p. (In French).
Makhoukh, M., Sbaa, M., Berrahou, A., & Van Clooster, M. (2011). Contribution à l’étude physico-chimique des eaux superficielles de l’Oued Moulouya (Maroc Oriental). Larhyss Journal, 9, 149–169. (In French).
Medupin, C. (2020). Spatial and temporal variation of benthic macroinvertebrate communities along an urban river in Greater Manchester. UK. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 192, 84.
Mherzi, N., Lamchouri, F., Khabbach, A., Boulfia, M., Zalaghi, A., & Toufik, H. (2020). Ecological types and bioindicator macrophyte species of pollution of riparian vegetation of Oued Lârbaa in Taza City of Morocco. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 192, 265.
Popović, N. Z., Đuknić, J. A., ČanakAtlagić, J. Ž, Raković, M. J., Tubić, B. P., Anđus, S. P., & Paunović, M. M. (2016). The relation between chironomid (Diptera: Chironomidae) assemblages and environmental variables: The Kolubara River case study. Archives of Biological Sciences, 68(2), 405–415.
Roback, S. S. (1974). Chapter 10: Insects (Anhropoda: Insecta) (pp. 313–376). Pollution Ecology of Freshwater Invertebrates. New York: Academic Press.
Rotheray, G. (1999). Phylogeny of Palaearctic Syrphidae (Diptera): evidence from larval stages. Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society, 127(1), 1–112.
Sadiki, S., Faleh, A., & Mesrar, H. (2011). Landslide susceptibility modelling using GIS and staticalméthod in the Oued Larbaa basin (Eastern Rif, Morocco). Journal of Materials and Environmental Science, 2(S1), 526–531.
Shen, Y., Yang, Y., Zhou, Y., Bian, B., & Zhang, L. (2020). Unraveling the nexus of multi-environmental factors and benthic macroinvertebrates in typical inflow river of Taihu Lake in China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 192, 137.
Siesa, M. E. (2010). Freshwater communities and biological invasions: Odonata, Amphibia and Procambarus clarkii. Phd thesis. Università de gli Studi, Milan, 211 p.
Tachet, H., Bournaud, M., & Richoux, P. (1991). Introduction à l'étude des macroinvertébrés des eaux douces : systématique élémentaire et aperçu écologique. (4th ed.151 p) Association française de limnologie-Villeurbanne: Université de Lyon I – Paris. (In French).
Vivier, P. (1972). Action de la pollution organique sur la faune aquatique d’eau douce. International Water Journal, 2(3), 149p. (In French).
Vuori, K. M., & Kukkonen, J. V. K. (2002). Hydropsychid (Trichoptera, Hydropsychidae) gill abnormalities as morphological biomarkersof stream pollution. Freshwater Biology, 47, 1297–1306.
World Health Organization (WHO). 2017. Guidelines for drinking water quality. (4th ed. 564 p), Geneva.
Yoboué, K. P., Ouattara, N. I., Berté, S., Aboua, B. R. D., Coulibaly, J. K., & Kouamélan, E. P. (2020). Structure of benthic macroinvertebrates population in an area of Mopoyem Bay (Ebrie Lagoon, Côte d’Ivoire) exposed to the discharge of a fish farm effluents. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 192, 203.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lakhloufi, M.Y., Lamchouri, F., El Haissoufi, M. et al. Evaluation of anthropic activities impact through the monitoring of aquatic fauna on Oued Lârbaa in Taza City of Morocco. Environ Monit Assess 193, 153 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-08938-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-08938-x