Abstract
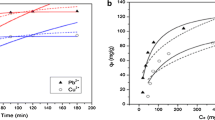
Biosorption of Cr(VI) on sulfuric and phosphoric acid–treated Datura stramonium fruit was investigated in batch mode. The various parameters that influence the biosorption process such as Cr(VI) initial concentration, biosorbent dosage, contact time, temperature, and pH value were optimized. Both linear and non-linear regression analysis of isotherm data suggest that Langmuir isotherm model mimics the behavior of Cr(VI) ion biosorption onto Datura stramonium fruit biosorbent. The maximum Cr(VI) ions adsorption capacity of 138.074 mg/g at pH 2 is achieved with phosphoric acid treated Datura stramonium (PDSF). The kinetics of adsorption process is well described by pseudo-second-order model with high R2 and low χ2 value. The estimated activation energy of < 8 kJ/mol obtained for both raw and chemically modified adsorbents suggests that the adsorption occurs mainly via physisorption. Besides, thermodynamic results reveal that biosorption of Cr(VI) on both treated and untreated Datura stramonium was endothermic, spontaneous, and randomness in nature.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Ghani, N. T., Hefny, M. M., & El-Chaghaby, G. A. (2008). Removal of metal ions from synthetic wastewater by adsorption onto eucalyptus camaldulenis tree leaves. Journal of the Chilean Chemical Society, 53, 1585–1587.
Ahluwalia, S. S., & Goyal, D. (2005). Removal of heavy metals by waste tea leaves from aqueous solution. Engineering in Life Sciences, 5, 158–162.
Ahmad, A., Ghazi, Z. A., Saeed, M., Ilyas, M., Ahmad, R., Khattak, A. M., & Iqbal, A. (2017). A comparative study of the removal of Cr(VI) from synthetic solution using natural biosorbents. New Journal of Chemistry, 41, 10799–10807.
Albadarin, A. B., Mangwandi, C., Al-Muhtaseb, A. H., Walker, G. M., Allen, S. J., & Ahmad, M. N. M. (2012). Kinetic and thermodynamics of chromium ions adsorption onto low-cost dolomite adsorbent. Chemical Engineering Journal, 179, 193–202.
Apiratikul, R., & Pavasant, P. (2008). Batch and column studies of biosorption of heavy metals by Caulerpa lentillifera. Bioresource Technology, 99, 2766–2777.
Argun, M. E., & Dursun, S. (2008). A new approach to modification of natural adsorbent for heavy metal adsorption. Bioresource Technology, 99, 2516–2527.
Ashraf, A., Bibi, I., Niazi, N. K., Ok, Y. S., Murtaza, G., Shahid, M., Kunhikrishnan, A., Li, D., & Mahmood, T. (2017). Chromium(VI) sorption efficiency of acid-activated banana peel over organo-montmorillonite in aqueous solutions. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 19, 605–613.
Attia, A. A., Khedr, S. A., & Elkholy, S. A. (2010). Adsorption of chromium ion (VI) by acid activated carbon. Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 27, 183–193.
Bansal, M., Singh, D., & Garg, V. K. (2009). A comparative study for the removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution by agriculture wastes’ carbons. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 171, 83–92.
Barakat, M. A. (2011). New trends in removing heavy metals from industrial wastewater. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 4, 361–377.
Bellu, S., García, S., González, J. C., Atria, A. M., Sala, L. F., & Signorella, S. (2008). Removal of chromium(VI) and chromium(III) from aqueous solution by grainless stalk of corn. Separation Science and Technology, 43, 3200–3220.
Blazquez, G., Hernáinz, F., Calero, M., Martín-Lara, M. A., & Tenorio, G. (2009). The effect of pH on the biosorption of Cr (III) and Cr (VI) with olive stone. Chemical Engineering Journal, 148, 473–479.
Chen, Z., Ma, W., & Han, M. (2008). Biosorption of nickel and copper onto treated alga (Undaria pinnatifida): application of isotherm and kinetic models. Journal of Hazard Materials, 155, 327–333.
Chen, Y., Tang, G., Yu, Q. J., Zhang, T., Chen, Y., & Gu, T. (2009). Biosorption properties of hexavalent chromium on to biomass of tobacco-leaf residues. Environmental Technology, 30, 1003–1010.
Dada, A. O., Olalekan, A. P., Olatunya, A. M., & Dada, O. (2012). Langmuir, Freundlich, Temkin and Dubinin–Radushkevich isotherms studies of equilibrium sorption of zn2+ unto phosphoric acid modified rice husk. IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry, 3(1), 38–45.
Dehghani, M. H., Sanaei, D., Ali, I., & Bhatnagar, A. (2016). Removal of chromium (VI) from aqueous solution using treated waste newspaper as a low-cost adsorbent: Kinetic modeling and isotherm studies. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 215, 671–679.
Etim, U. J., Umoren, S. A., & Eduok, U. M. (2016). Coconut coir dust as a low cost adsorbent for the removal of cationic dye from aqueous solution. Journal of Saudi Chemical Society, 20, S67–S76.
Freundlich, H., & Heller, W. (1939). The adsorption of cis- and trans-Azobenzene. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 61, 2228–2230.
Gonzalez, M. H., Araújo, G. C. L., Pelizaro, C. B., Menezes, E. A., Lemos, S. G., de Sousa, G. B., & Nogueira, A. R. A. (2008). Coconut coir as biosorbent for Cr(VI) removal from laboratory wastewater. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 159, 252–256.
Gupta, V. K., & Rastogi, A. (2009). Biosorption of hexavalent chromium by raw and acid-treated green alga Oedogonium hatei from aqueous solutions. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 163, 396–402.
Gupta, V. K., Rastogi, A., & Nayak, A. (2010). Adsorption studies on the removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution using a low cost fertilizer industry waste material. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 342, 135–141.
Hasan, S. H., Singh, K. K., Prakash, O., Talat, M., & Ho, Y. S. (2008). Removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions using agricultural waste ‘maize bran. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 152, 356–365.
Ho Lee, S., Hun Jung, C., Chung, H., Yeal Lee, M., & Yang, J.-W. (1998). Removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution by apple residues. Process Biochemistry, 33, 205–211.
Ho, Y. S., & McKay, G. (1999). Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochemistry, 34, 451–465.
Jain, M., Garg, V. K., & Kadirvelu, K. (2009). Equilibrium and kinetic studies for sequestration of Cr(VI) from simulated wastewater using sunflower waste biomass. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 171, 328–334.
Jaina, M., Garga, V. K., & Kadirvelu, K. (2009). Chromium(VI) removal from aqueous system using Helianthus annuus (sunflower) stem waste. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 162, 365–372.
Khan, T. A., Mukhlif, A. A., Khan, E. A., & Sharma, D. K. (2016). Isotherm and kinetics modeling of Pb(II) and cd(II) adsorptive uptake from aqueous solution by chemically modified green algal biomass. Model Earth Syst. Environ, 2, 117.
Khoubestani, R. S., Mirghaffari, N., & Farhadian, O. (2015). Removal of three and hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions using a microalgae biomass-derived biosorbent. Environmental Progress & Sustainable Energy, 34, 949–956.
Kuppusamy, S., Thavamani, P., Megharaj, M., Venkateswarlu, K., Lee, Y. B., & Naidu, R. (2016). Potential of Melaleuca diosmifolia leaf as a low-cost adsorbent for hexavalent chromium removal from contaminated water bodies. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 100, 173–182.
Lagergren, S. (1898). About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances, Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption gelster stoffe. Kungliga Svenska Vetenskapsakademiens, Handlingar, Band, 24(1898), 1–39.
Langmuir, I. (1918). The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 40, 1361–1368.
Lodeiro, P., Barriada, J. L., Herrero, R., & Sastre de Vicente, M. E. (2006). The marine macroalga Cystoseira baccata as biosorbent for cadmium(II) and lead(II) removal: kinetic and equilibrium studies. Environmental Pollution, 142, 264–273.
Lv, L., Chen, N., Feng, C., Zhang, J., & Li, M. (2017). Heavy metal ions removal from aqueous solution by xanthate-modified cross-linked magnetic chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) particles. Royal Society of Chemistry Advances, 7, 27992–28000.
Ma, J., Qin, G., Zhang, Y., Sun, J., Wang, S., & Jiang, L. (2018). Heavy metal removal from aqueous solutions by calcium silicate powder from waste coal fly-ash. Journal of Cleaner Production, 182, 776–782.
Mahmoud, M. A. (2015). Thermodynamics and kinetics studies of Mn (II) removal from aqueous solution onto powder corn cobs (PCC). Chromatography Separation Techniques, 6(7), 301.
Mahmud, H. N. M. E., Huq, A. K. O., & Yahya, R. B. (2016). The removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater/aqueous solution using polypyrrole-based adsorbents: a review. Royal Society of Chemistry Advances, 6, 14778–14791.
Mondal, N. K., & Basu, S. (2019). Potentiality of waste human hair towards removal of chromium(VI) from solution: kinetic and equilibrium studies. Applied Water Science, 9(49).
Muthukumaran, K., & Beulah, S. (2011). Removal of chromium (VI) from wastewater using chemically activated Syzygium jambolanum nut carbon by batch studies. Procedia Environmental Sciences, Urban Environmental Pollution 2010, 4, 266–280.
Nakkeeran, E., & Selvaraju, N. (2017). Biosorption of chromium (VI) in aqueous solutions by chemically modified Strychnine tree fruit shell. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 19(12), 1065–1076.
Nameni, M., Moghadam, M. R. A., & Arami, M. (2008). Adsorption of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions by wheat bran. International Journal of Environmental Science & Technology, 5(2), 161–168.
Nasseh, N., Taghavi, L., Barikbin, B., & Harifi-Mood, A. R. (2017). The removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution by almond green hull waste material: kinetic and equilibrium studies. Journal of Water Reuse and Desalination, 7, 449–460.
Niazi, L., Lashanizadegan, A., & Sharififard, H. (2018). Chestnut oak shells activated carbon: Preparation, characterization and application for Cr (VI) removal from dilute aqueous solutions. Journal of Cleaner Production, 185, 554–561.
Olguin, M. T., López-González, H., & Serrano-Gómez, J. (2013). Hexavalent chromium removal from aqueous solutions by Fe-modified peanut husk. Water Air Soil Pollution, 224(1654).
Pandey, P. K., Sharma, S. K., & Sambi, S. S. (2010). Kinetics and equilibrium study of chromium adsorption on zeoliteNaX. International Journal of Environmental Science & Technology, 7, 395–404.
Parlayici, Ş., & Pehlivan, E. (2019). Comparative study of Cr(VI) removal by bio-waste adsorbents: equilibrium, kinetics, and thermodynamic. Journal of Analytical Science and Technology, 10(15).
Pourfadakari, S., Jorfi, S., Ahmadi, M., & Takdastan, A. (2017). Experimental data on adsorption of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution using nanosized cellulose fibers obtained from rice husk. Data in Brief, 15, 887–895.
Rangabhashiyam, S., & Selvaraju, N. (2015a). Evaluation of the biosorption potential of a novel Caryota urens inflorescence waste biomass for the removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 47, 59–70.
Rangabhashiyam, S., & Selvaraju, N. (2015b). Efficacy of unmodified and chemically modified Swietenia mahagoni shells for the removal of hexavalent chromium from simulated wastewater. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 209, 487–497.
Saha, R., Mukherjee, K., Saha, I., Ghosh, A., Ghosh, S. K., & Saha, B. (2013). Removal of hexavalent chromium from water by adsorption on mosambi (Citrus limetta) peel. Research on Chemical Intermediates, 39(5), 2245–2257.
Sari, A., & Tuzen, M. (2008). Biosorption of total chromium from aqueous solution by red algae (Ceramium virgatum): Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 160, 349–355.
Sathish, T., Vinithkumar, N. V., Dharani, G., & Kirubagaran, R. (2015). Efficacy of mangrove leaf powder for bioremediation of chromium (VI) from aqueous solutions: kinetic and thermodynamic evaluation. Applied Water Science, 5, 153–160.
Sharma, D. C., & Forster, C. F. (1994). A preliminary examination into the adsorption of hexavalent chromium using low-cost adsorbents. Bioresource Technology, 47, 257–264.
Shukla, S. S., Yu, L. J., Dorris, K. L., & Shukla, A. (2005). Removal of nickel from aqueous solutions by sawdust. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 121, 243–246.
Singh, K. K., Rastogi, R., & Hasan, S. H. (2005). Removal of Cr(VI) from wastewater using rice bran. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 290, 61–68.
Singha, B., & Das, S. K. (2011). Biosorption of Cr(VI) ions from aqueous solutions: kinetics, equilibrium, thermodynamics and desorption studies. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 84, 221–232.
Singha, B., Naiya, T. K., Bhattacharya, A. K., & Das, S. K. (2011). Cr(VI) ions removal from aqueous solutions using natural adsorbents – FTIR studies. Journal of Environmental Protection, 02, 729–735.
Sugashini, S., & Begum, K. M. M. S. (2013). Optimization using central composite design (CCD) for the biosorption of Cr(VI) ions by cross linked chitosan carbonized rice husk (CCACR). Clean Technology and Environmental Policy, 15, 293–302.
Vinodhini, V., & Das, N. (2010). Relevant approach to assess the performance of sawdust as adsorbent of chromium (VI) ions from aqueous solutions. International Journal of Environmental Science & Technology, 7, 85–92.
Weber, W. J., & Morris, J. C. (1963). Kinetics of adsorption of carbon from solution. Journal of the Sanitary Engineering Division. American Society of Civil Engineering, 89, 31–60.
Yang, L., & Chen, J. P. (2008). Biosorption of hexavalent chromium onto raw and chemically modified Sargassum sp. Bioresource Technology, 99, 297–307.
Yogeshwaran, V., & Ak, P. (2017). Removal of hexavalent chromium (Cr6+) using different natural adsorbents - a review. Journal of Chromatography & Separation Techniques, 8, 1–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Datura stramonium fruit was used as novel biosorbent for the biosorption of Cr(VI).
• The maximum Cr(VI) uptake on RDSF, SDSF, and PDSF biosorbents obtained was found to be 85.916, 119.632, and 138.074 mg/g respectively at optimum pH 2.0.
• The observed free energy (∆G° (kJ/mol)) values were − 0.249, − 0.026, and − 0.107 for RDSF, PDSF, and SDSF biosorbents respectively.
• The Langmuir isotherm and pseudo-second-order kinetics models mimic the biosorption behavior of Cr(VI).
• The activation energy onto RDSF, SDSF, and PDSF adsorbent was estimated to be 0.192, 7.632, and 7.794 kJ/mol respectively
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, S., Shahnaz, T., Selvaraju, N. et al. Kinetic and thermodynamic studies on biosorption of Cr(VI) on raw and chemically modified Datura stramonium fruit. Environ Monit Assess 192, 248 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-8181-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-8181-x