Abstract
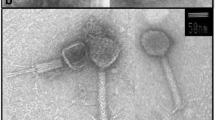
Marinobacter is an ecologically important genus of Gammaproteobacteria found in diverse marine habitats, many species of which are capable of degrading hydrocarbons. In this study, we isolated a Marinobacter phage-host system from the surface waters of the Arabian Sea using enrichment culture methods, studied their growth characteristics and investigated the effect of salinity and nitrate concentrations on phage-host interactions. The bacterial isolate had maximum identity to Marinobacter salsuginis based on 16S rRNA similarities and was termed as Marinobacter sp., strain D1S9. It could tolerate up to 14% of NaCl with maximum growth at 11% NaCl. The host grew optimally between 35 and 40 °C and at pH 8. It had a generation time of 3.7 h with a mean growth rate of 0.27 h−1. The phage infected the host forming clear, round plaques of 1–2 mm diameter. It had a narrow host range restricted to the strain Marinobacter D1S9. The latent period and burst size of the phage were estimated to be 30 min and 106 phages per infected cell, respectively. The phage had an adsorption rate of 3.4 × 10−8 ml min−1 and retained 40.4% of its adsorption efficiency at 16% NaCl with a maximum at 4% NaCl (76.1%). Inorganic nitrate was found to have a direct role in controlling host growth and phage burst size.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abedon, S. T. (1989). Selection for bacteriophage latent period length by bacterial density: a theoretical examination. Microbial Ecology, 18, 79–88.
Ackermann, H. W. (2006). Classification of bacteriophages. In R. Calendar (Ed.), The bacteriophages (pp. 8–16). New York: Oxford University Press.
Amann, R. I., Ludwig, W., & Schleifer, K. H. (1995). Phylogenetic identification and in situ detection of individual microbial cells without cultivation. Microbiological Reviews, 59, 143–169.
Aparna, S., Parvathi, A., Ram, A. P., & Sime-Ngando, T. (2019). Genome analysis of Marinobacter phage AS1 suggests its close interactions with host Marinobacter sp. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 83, 119–129.
Bergh, O., Borsheim, K. Y., Bratbak, G., & Heldal, M. (1989). High abundance of viruses found in aquatic environments. Nature, 340, 467–468.
Bratbak, G., Jacobsen, A., Heldal, M., Nagasaki, K., & Thingstad, F. (1998). Virus production in Phaeocystis pouchetii and its relation to host cell growth and nutrition. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 16, 1–9.
Cann, A. J. (2016). Particles. In A. J. Cann (Ed.), Principles of molecular virology (pp. 27–57). Cambridge: Academic.
Duran, R. (2010). Marinobacter. In K. N. Timmis (Ed.), Handbook of hydrocarbon and lipid microbiology (p. 1289). Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer.
Evans, C., Archer, S. D., Jacquet, S., & Wilson, W. H. (2003). Direct estimates of the contribution of viral lysis and microzooplankton grazing to the decline of a Micromonas spp. population. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 30, 207–219.
Evans, M. V., Panescu, J., Hanson, A. J., Welch, S. A., Sheets, J. M., Nastasi, N., et al. (2018). Members of Marinobacter and Arcobacter influence system biogeochemistry during early production of hydraulically fractured natural gas wells in the Appalachian basin. Frontiers in Microbiology, 9, 2646.
Finke, J., Hunt, B., Winter, C., Carmack, E., & Suttle, C. (2017). Nutrients and other environmental factors influence virus abundances across oxic and hypoxic marine environments. Viruses, 9, 152.
Handley, K. M., & Lloyd, J. R. (2013). Biogeochemical implications of the ubiquitous colonization of marine habitats and redox gradients by Marinobacter species. Frontiers in Microbiology, 4, 136. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2013.00136.
Huu, N. B., Denner, E. B., Ha, D. T., Wanner, G., & Stan-Lotter, H. (1999). Marinobacter aquaeolei sp. nov., a halophilic bacterium isolated from a Vietnamese oil-producing well. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 49, 367–375.
Kasana, R. C., Salwan, R., Dhar, H., Dutt, S., & Gulati, A. (2008). A rapid and easy method for the detection of microbial cellulases on agar plates using Gram’s iodine. Current Microbiology, 57, 503–507.
Koskella, B., & Meaden, S. (2013). Understanding bacteriophage specificity in natural microbial communities. Viruses, 5, 806–823.
Krieg, N. R., & Holt, J. G. (1984). Bergey's manual of systemic bacteriology. Baltimore: Wiliams & Wilkins.
Kropinski, A. M. (2009). Measurement of the rate of attachment of bacteriophage to cells. In M. R. Clokie & A. M. Kropinski (Eds.), Methods in molecular biology (pp. 151–155). New York: Humana Press.
Kukkaro, P., & Bamford, D. H. (2009). Virus–host interactions in environments with a wide range of ionic strengths. Environmental Microbiology Reports, 1, 71–77.
Kumar, S., & Khare, S. K. (2012). Purification and characterization of maltooligosaccharide-forming α-amylase from moderately halophilic Marinobacter sp. EMB8. Bioresource Technology, 116, 247–251.
Lal, D., Jindal, S., Kumari, H., Jit, S., Nigam, A., Sharma, P., Kumari, K., & Lal, R. (2015). Bacterial diversity and real-time PCR based assessment of linA and linB gene distribution at hexachlorocyclohexane contaminated sites. Journal of Basic Microbiology, 55, 363–373.
Lara, E., Vaqué, D., Sà, E. L., Boras, J. A., Gomes, A., Borrull, E., et al. (2017). Unveiling the role and life strategies of viruses from the surface to the dark ocean. Science Advances, 3, e1602565.
Li, R., Zi, X., Wang, X., Zhang, X., Gao, H., & Hu, N. (2013). Marinobacter hydrocarbonoclasticus NY-4, a novel denitrifying, moderately halophilic marine bacterium. SpringerPlus, 2, 1–9.
MacLeod, R. A. (1965). The question of the existence of specific marine bacteria. Bacteriological Reviews, 29, 9–23.
MacLeod, R. A. (1986). Salt requirements for membrane transport and solute retention in some moderate halophiles. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 2, 109–113.
Martin, S., Márquez, M. C., Sánchez-Porro, C., Mellado, E., Arahal, D. R., & Ventosa, A. (2003). Marinobacter lipolyticus sp. nov., a novel moderate halophile with lipolytic activity. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 53, 1383–1387.
Middelboe, M. (2000). Bacterial growth rate and marine virus–host dynamics. Microbial Ecology, 40, 114–124.
Middelboe, M., Chan, A., & Bertelsen, S. K. (2010). Isolation and life cycle characterization of lytic viruses infecting heterotrophic bacteria and cyanobacteria. In S. Wilhelm, M. Weinbauer, & C. Suttle (Eds.), Manual of aquatic viral ecology (pp. 118–133). Waco: American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc.
Moebus, K. (1996a). Marine bacteriophage reproduction under nutrient-limited growth of host bacteria. I. Investigations with six phage-host systems. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 144, 1–2.
Moebus, K. (1996b). Marine bacteriophage reproduction under nutrient-limited growth of host bacteria. II. Investigations with phage-host system [H3: H3/1]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 144, 13–22.
Moebus, K. (1997a). Investigations of the marine lysogenic bacterium H24. II. Development of pseudolysogeny in nutrient-rich broth culture. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 148, 229–240.
Moebus, K. (1997b). Investigations of the marine lysogenic bacterium H24. III. Growth of bacteria and production of phage under nutrient-limited conditions. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 148, 241–250.
Mojica, K. D., & Brussaard, C. P. (2014). Factors affecting virus dynamics and microbial host–virus interactions in marine environments. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 89, 495–515.
Mojica, K. D., Huisman, J., Wilhelm, S. W., & Brussaard, C. P. (2016). Latitudinal variation in virus-induced mortality of phytoplankton across the North Atlantic Ocean. The ISME Journal, 10, 500.
Montes, M. J., Bozal, N., & Mercade, E. (2008). Marinobacter guineae sp. nov., a novel moderately halophilic bacterium from an Antarctic environment. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 58, 1346–1349.
Motegi, C., & Nagata, T. (2007). Enhancement of viral production by addition of nitrogen or nitrogen plus carbon in subtropical surface waters of the South Pacific. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 48, 27–34.
Motegi, C., Nagata, T., Miki, T., Weinbauer, M. G., Legendre, L., & Rassoulzadegand, F. (2009). Viral control of bacterial growth efficiency in marine pelagic environments. Limnology and Oceanography, 54, 1901–1910.
Nabergoj, D., Modic, P., & Podgornik, A. (2018). Effect of bacterial growth rate on bacteriophage population growth rate. MicrobiologyOpen, 7, e00558.
Parsons, R. J., Breitbart, M., Lomas, M. W., & Carlson, C. A. (2012). Ocean time-series reveals recurring seasonal patterns of virioplankton dynamics in the northwestern Sargasso Sea. The ISME Journal, 6, 273.
Payet, J. P., & Suttle, C. A. (2013). To kill or not to kill: the balance between lytic and lysogenic viral infection is driven by trophic status. Limnology and Oceanography, 58, 465–474.
Rosenberg, E., Bittan-Banin, G., Sharon, G., Shon, A., Hershko, G., Levy, I., & Ron, E. Z. (2010). The phage-driven microbial loop in petroleum bioremediation. Microbial Biotechnology, 3, 467–472.
Sánchez-Porro, C., Martin, S., Mellado, E., & Ventosa, A. (2003). Diversity of moderately halophilic bacteria producing extracellular hydrolytic enzymes. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 94, 295–300.
Suttle, C. A. (2007). Marine viruses—major players in the global ecosystem. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 5, 801–812.
Torrella, F., & Morita, R. Y. (1979). Evidence by electron micrographs for a high incidence of bacteriophage particles in the waters of Yaquina Bay, Oregon: ecological and taxonomical implications. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 37, 774–778.
Williamson, S. J., & Paul, J. H. (2004). Nutrient stimulation of lytic phage production in bacterial populations of the Gulf of Mexico. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 36, 9–17.
Wolf, A., Zheng, T., Witzel, K. P., & Jost, G. (2004). Impact of initial phage/host ratio and nutrient addition on coexistence in a phage-host system. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 35, 131–139.
Wommack, K. E., Hill, R. T., Kessel, M., Russek-Cohen, E., & Colwell, R. R. (1992). Distribution of viruses in the Chesapeake Bay. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 58, 2965–2970.
Yang, Y., Motegi, C., Yokokawa, T., & Nagata, T. (2010). Large-scale distribution patterns of virioplankton in the upper ocean. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 60, 233–246.
Yoon, J. H., Shin, D. Y., Kim, I. G., Kang, K. H., & Park, Y. H. (2003). Marinobacter litoralis sp. nov., a moderately halophilic bacterium isolated from sea water from the East Sea in Korea. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 53, 563–568.
Zhu, M., Wang, M., Jiang, Y., You, S., Zhao, G., Liu, Y., Yang, Q., Liu, Q., Liu, Z., Gong, Z., & Shao, H. (2018). Isolation and complete genome sequence of a novel Marinobacter phage B23. Current Microbiology, 75, 1619–1625.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Dr. Sunil Kumar Singh, the Director, CSIR-NIO, Goa and Dr. T. Pankajakshan, the Scientist-in-Charge, NIO (RC), Cochin for their support and advice. Authors are grateful to the Director, Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services, Hyderabad and Dr. Jyothibabu R, Principal Scientist, for the funding through grant-in aid project, GAP 2807. AS is grateful to University Grants Commission (UGC), New Delhi, India for financial support for senior research fellowship grant. The authors are grateful to Dr. Sandhya S. V., ICAR-Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute, Cochin for providing Marinobacter and Alteromonas cultures.
Funding
This work was supported by the Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services through grant-in-aid project [NIO GAP 2807].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aparna, S., Parvathi, A. & Kaniyassery, A. Isolation and characterization of a moderately halophilic Marinobacter phage-host system from the Arabian Sea. Environ Monit Assess 192, 199 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-8166-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-8166-9