Abstract
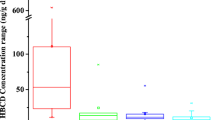
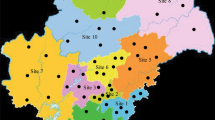
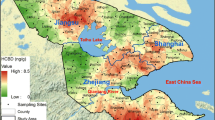
Contamination by hexabromocyclododecanes (HBCDDs) in the soil environment is an ongoing concern because of their “specific exemption” on the production and use in China. In this study, spatial distribution, temporal trend, and diastereoisomer profiles of HBCDDs were examined in surface soils collected in Jinan, China. Concentrations of ΣHBCDD (sum of α-, β-, and γ-HBCDDs) in soils ranged from 1.70 to 228 ng/g dry weight (dw), with a mean value of 26.1 ng/g dw. Soils collected from e-waste dismantling sites (mean 146 ng/g dw) contained significantly higher concentrations of ΣHBCDD than those of urban (15.5 ng/g dw) and farmland soils (3.86 ng/g dw) (p < 0.01). The temporal trend suggested that ΣHBCDD levels in the industrial area rose significantly between 2014 and 2019 (p < 0.05), with an annual increase of 12%. An increase in ΣHBCDD levels was also observed in urban and farmland soil samples during the study period, although it did not reach a significant level (p > 0.05). All surface soils were dominated by γ-HBCDD (mean 60.7% of total concentrations); however, the proportions of α-isomer increased from 28.7% in urban and rural soils to 43.4% in industrial soils. The calculated risk quotients of HBCDDs present in soils were at least 25-fold lower than the threshold limit value. The mean mass inventory of HBCDDs was approximately 2501 kg in the cultivated land of Jinan City; further studies are needed to discern the uptake of HBCDDs by crops and the fate of these chemicals in agricultural ecosystems.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Braune, B. M., Letcher, R. J., Gaston, A. J., & Mallory, M. L. (2015). Trends of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and hexabromocyclododecane in eggs of Canadian Arctic seabirds reflect changing use patterns. Environmental Research, 142, 651–661.
Cao, X., Lu, Y., Zhang, Y., Khan, K., Wang, C., & Baninla, Y. (2018). An overview of hexabromocyclododecane (HBCDDs) in environmental media with focus on their potential risk and management in China. Environmental Pollution, 236, 283–295.
Covaci, A., Gerecke, A. C., Law, R. J., Voorspoels, S., Kohler, M., Heeb, N. V., Leslie, H., Allchin, C. R., & Boer, J.d. (2006). Hexabromocyclododecanes (HBCDDs) in the environment and humans: a review. Environmental Science & Technology, 40, 3679–3688.
Drage, D., Mueller, J. F., Birch, G., Eaglesham, G., Hearn, L. K., & Harrad, S. (2015). Historical trends of PBDEs and HBCDDs in sediment cores from Sydney estuary, Australia. Science of the Total Environment, 512–513, 177–184.
Esslinger, S., Becker, R., Jung, C., Schröter-Kermani, C., Bremsera, W., & Nehls, I. (2011). Temporal trend (1988–2008) of hexabromocyclododecane enantiomers in herring gull eggs from the German coastal region. Chemosphere, 83, 161–167.
Fan, Y., Chen, S. J., Li, Q. Q., Zeng, Y., Yan, X., & Mai, B. X. (2020). Uptake of halogenated organic compounds (HOCs) into peanut and corn during the whole life cycle grown in an agricultural field. Environmental Pollution, 263, 114400.
Gao, C., Xia, L., Wu, C., Wong, C. S., & Guo, Y. (2019). The effects of prosperity indices and land use indicators of an urban conurbation on the occurrence of hexabromocyclododecanes and tetrabromobisphenol A in surface soil in South China. Environmental Pollution, 252, 1810–1818.
Gerecke, A. C., Giger, W., Hartmann, P. C., Heeb, N. V., Kohler, H. P. E., Schmid, P. P., Zennegg, M., & Kohler, M. (2006). Anaerobic degradation of brominated flame retardants in sewage sludge. Chemosphere, 64, 311–317.
Harrad, S. J., Abdallah, M. A. E., & Covaci, A. (2009). Causes of variability in concentrations and diasteromer patterns of hexabromocyclododecanes in indoor dust. Environment International, 35, 573–579.
Huang, H., Wang, D., Wan, W., & Wen, B. (2017). Hexabromocyclododecanes in soils and plants from a plastic waste treatment area in North China: occurrence, diastereomerand enantiomer-specific profiles, and metabolization. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24, 21625–21635.
Huang, M., Li, J., Xiao, Z., & Shi, Z. (2020). Tetrabromobisphenol A and hexabromocyclododecane isomers in breast milk from the general population in Beijing, China: contamination levels, temporal trends, nursing infant’s daily intake, and risk assessment. Chemosphere, 244, 125524.
Hunziker, R. W., Gonsior, S., MacGregor, J. A., Desjardins, D., Ariano, J., & Friederich, U. (2004). Fate and effect of hexabromocyclododecane in the environment. Organohalogen Compounds, 66, 2300–2305.
Kim, U. J., & Oh, J. E. (2014). Tetrabromobisphenol A and hexabromocyclododecane flame retardants in infant-mother paired serum samples, and their relationships with thyroid hormones and environmental factors. Environmental Pollution, 184, 193–200.
Law, R. J., Bersuder, P., Barry, J., Wilford, B. H., Allchin, C. R., & Jepson, P. D. (2008). A significant downturn in levels of hexabromocyclododecane in the blubber of harbor porpoises (Phocoena phocoena) stranded or bycaught in the UK: an update to 2006. Environmental Science & Technology, 42, 9104–9109.
Li, Y., Zhou, Q., Wang, Y., & Xie, X. (2011). Fate of tetrabromobisphenol A and hexabromocyclododecane brominated flame retardants in soil and uptake by plants. Chemosphere, 82, 204–209.
Li, F., Jin, J., Tan, D., Wang, L., Geng, N., Cao, R., Gao, Y., & Chen, J. (2016). Hexabromocyclododecane and tetrabromobisphenol A in sediments and paddy soils from Liaohe River Basin, China: levels, distribution and mass inventory. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 48, 209–217.
Lu, J. F., He, M. J., Yang, Z. H., & Wei, S. Q. (2018). Occurrence of tetrabromobisphenol a (TBBPA) and hexabromocyclododecane (HBCDD) in soil and road dust in Chongqing, western China, with emphasis on diastereoisomer profiles, particle size distribution, and human exposure. Environmental Pollution, 242, 219–228.
Lü, H., Ma, X. J., Huang, X. J., Lu, S., Huang, Y. H., Mo, C. H., Cai, Q. Y., & Wong, M. H. (2019). Distribution, diastereomer-specific accumulation and associated health risks of hexabromocyclododecanes (HBCDDs) in soil-vegetable system of the Pearl River Delta region, South China. Journal of Environmental Management, 248, 109321.
Marvin, C. H., Tomy, G. T., Armitage, J. M., Arnot, J. A., McCarty, L., Covaci, A., & Palace, V. (2011). Hexabromocyclododecane: current understanding of chemistry, environmental fate and toxicology and implications for global management. Environmental Science & Technology, 45, 8613–8623.
MEP (Ministry of Environmental Protection of China). (2016). The prohibition of production and use of hexabromocyclododecane in China. http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2016-12/29/content_5154160.htm. Accessed 5 Jun 2020.
Morf, L. S., Tremp, J., Gloor, R., Huber, Y., Stengele, M., & Zennegg, M. (2005). Brominated flame retardants in waste electrical and electronic equipment: substance flows in a recycling plant. Environmental Science & Technology, 39, 8691–8699.
Parvizian, B. A., Zhou, C., Fernando, S., Crimmins, B. S., Hopke, P. K., & Holsen, T. M. (2020). Concentrations and long-term temporal trends of hexabromocyclododecanes (HBCDDD) in lake trout and walleye from the Great Lakes. Environmental Science & Technology, 54, 6134–6141.
Ruan, Y., Lam, J. C. W., Zhang, X., & Lam, P. K. S. (2018). Temporal changes and stereoisomeric compositions of 1,2,5,6,9,10-hexabromocyclododecane and 1,2-dibromo-4-(1,2-dibromoethyl)cyclohexane in marine mammals from the South China Sea. Environmental Science & Technology, 52, 2517–2526.
Ruan, Y., Zhang, K., Wu, C., Wu, R., & Lam, P. K. S. (2019). A preliminary screening of HBCDD enantiomers transported by microplastics in wastewater treatment plants. Science of the Total Environment, 674, 171–178.
Rüdel, H., Müller, J., Nowak, J., Ricking, M., Klein, R., & Kotthoff, M. (2017). Hexabromocyclododecane diastereomers in fish and suspended particulate matter from selected European waters—trend monitoring and environmental quality standard compliance. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24, 18048–18062.
Shi, Y., Xu, X., Chen, J., Liang, R., Zheng, X., Shi, Y., & Wang, Y. (2018). Antioxidant gene expression and metabolic responses of earthworms (Eisenia fetida) after exposure to various concentrations of hexabromocyclododecane. Environmental Pollution, 232, 245–251.
Smythe, T. A., Loseto, L. L., Bignert, A., Rosenberg, B., Budakowski, W., Halldorson, T., Pleskach, K., & Tomy, G. T. (2018). Temporal trends of brominated and fluorinated contaminants in Canadian Arctic beluga (Delphinapterus leucas). Arctic Science, 4, 388–404.
Song, S. M., Duan, Y. S., Zhang, T., Zhang, B., Zhao, Z., Bai, X. Y., Xie, L., He, Y., Ouyang, J. P., Huang, X. F., & Sun, H. W. (2019). Serum concentrations of bisphenol A and its alternatives in elderly population living around e-waste recycling facilities in China: associations with fasting blood glucose. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 169, 822–828.
Song, S. M., He, Y., Zhang, T., Zhu, H. K., Huang, X. F., Bai, X. Y., Zhang, B., & Kannan, K. (2020). Profiles of parabens and their metabolites in paired maternal-fetal serum, urine and amniotic fluid and their implications for placental transfer. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 191, 110235.
Stockholm Convention. (2020). All POPs listed in the Stockholm Convention. http://chm.pops.int/TheConvention/ThePOPs/AllPOPs/tabid/2509/Default.aspx. Accessed 5 Jun 2020.
Sun, R., Luo, X., Zheng, X., Cao, K., Peng, P., Li, Q. X., & Mai, B. (2018). Hexabromocyclododecanes (HBCDDs) in fish: evidence of recent HBCDD input into the coastal environment. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 126, 357–362.
Swedish Chemicals Agency. (2008). Risk assessment-hexabromocyclododecane, final report. Swedish Chemicals Agency, Sundbyberg. https://echa.europa.eu/documents/10162/661bff17-dc0a-4475-9758-40bdd6198f82. Accessed 5 Jun 2020.
Tang, J., Feng, J., Lia, X., & Li, G. (2014). Levels of flame retardants HBCDD, TBBPA and TBC in surface soils from an industrialized region of East China. Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts, 16, 1015–1021.
Tomko, G., & McDonald, K. M. (2013). Environmental fate of hexabromocyclododecane from a new Canadian electronic recycling facility. Journal of Environmental Management, 114, 324–327.
Tue, N. M., Takahashi, S., Suzuki, G., Isobe, T., Viet, P. H., Kobara, Y., Seike, N., Zhang, G., Sudaryanto, A., & Tanabe, S. (2013). Contamination of indoor dust and air by polychlorinated biphenyls and brominated flame retardants and relevance of nondietary exposure in Vietnamese informal e-waste recycling sites. Environment International, 51, 160–167.
Wang, T., Han, S., Ruan, T., Wang, Y., Feng, J., & Jiang, G. (2013). Spatial distribution and inter-year variation of hexabromocyclododecane (HBCDD) and tris-(2,3-dibromopropyl) isocyanurate (TBC) in farm soils at a peri-urban region. Chemosphere, 90, 182–187.
Wang, Y., Sun, H. W., Zhu, H. K., Yao, Y. M., Chen, H., Ren, C., Wu, F. C., & Kannan, K. (2018). Occurrence and distribution of organophosphate flame retardants (OPFRs) in soil and outdoor settled dust from a multi-waste recycling area in China. Science of the Total Environment, 625, 1056–1064.
Wang, X., Sun, R., Chen, Y., Zhang, X., & Cui, Z. (2019). Temporal-spatial distribution and diastereoisomer pattern of hexabromocyclododecane in the vicinity of a chemical plant. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 82, 203–212.
Wu, T., Wang, S., Huang, H., & Zhang, S. (2012). Diastereomer-specific uptake, translocation, and toxicity of hexabromocyclododecane diastereoisomers to maize. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 60, 8528–8534.
Wu, M. H., Han, T., Xu, G., Zang, C., Li, Y. J., Sun, R., Xu, B. T., Sun, Y., Chen, F. F., & Tang, L. (2016b). Occurrence of hexabromocyclododecane in soil and road dust from mixed-land-use areas of Shanghai, China, and its implications for human exposure. Science of the Total Environment, 559, 282–290.
Wu, T., Huang, H., & Zhang, S. (2016a). Accumulation and phytotoxicity of technical hexabromocyclododecane in maize. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 42, 97–104.
Yi, S., Liu, J. G., Jin, J., & Zhu, J. (2016). Assessment of the occupational and environmental risks of hexabromocyclododecane (HBCDD) in China. Chemosphere, 150, 4431–4437.
Zhang, Y., Ruan, Y., Sun, H., Zhao, L., & Gan, Z. (2013). Hexabromocyclododecanes in surface sediments and a sediment core from rivers and harbor in the northern Chinese city of Tianjin. Chemosphere, 90, 1610–1616.
Zhang, Y., Li, Q., Lu, Y., Jones, K., & Sweetman, A. J. (2016). Hexabromocyclododecanes (HBCDDDs) in surface soils from coastal cities in North China: correlation between diastereoisomer profiles and industrial activities. Chemosphere, 148, 504–510.
Zhang, Y., Lu, Y., Wang, P., Li, Q., Zhang, M., & Johnson, A. C. (2018). Transport of Hexabromocyclododecane (HBCDD) into the soil, water and sediment from a large producer in China. Science of the Total Environment, 610–611, 94–100.
Zhang, B., He, Y., Zhu, H. K., Huang, X. F., Bai, X. Y., Kannan, K., & Zhang, T. (2020). Concentrations of bisphenol A and its alternatives in paired maternal-fetal urine, serum and amniotic fluid from an e-waste dismantling area in China. Environment International, 136, 1–7.
Zhu, H. K., & Kannan, K. (2018). Distribution profiles of melamine and its derivatives in indoor dust from twelve countries and the implications for human exposure. Environmental Science & Technology, 52, 12801–12808.
Zhu, H., Sun, H., Zhang, Y., Xu, J., Li, B., & Zhou, Q. (2016). Uptake pathway, translocation, and isomerization of hexabromocyclododecane diastereoisomers by wheat in closed chambers. Environmental Science & Technology, 50, 2652–2659.
Zhu, H., Sun, H., Yao, Y., Wang, F., Zhang, Y., & Liu, X. (2017a). Fate and adverse effects of hexabromocyclododecane diastereoisomers (HBCDDDs) in a soil-ryegrass pot system. Chemosphere, 184, 452–459.
Zhu, H., Zhang, K., Sun, H., Wang, F., & Yao, Y. (2017b). Spatial and temporal distributions of hexabromocyclododecanes in the vicinity of an expanded polystyrene material manufacturing plant in Tianjin, China. Environmental Pollution, 222, 338–347.
Zhu, H., Sun, H., Yao, Y., Gan, Z., Wang, Y., & Kannan, K. (2018). Legacy and alternative brominated flame retardants in outdoor dust and pine needles in mainland China: spatial trends, dust-plant partitioning and human exposure. Environmental Pollution, 243, 758–765.
Zhu, H. K., Wang, Y., Sun, H., & Kannan, K. (2019). Fertilizers as a source of melamine and cyanuric acid in soils: a nationwide survey in China. Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 6, 55–61.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Sun analyzed and interpreted the measured data regarding the occurrence of HBCDDs in soils, and was a major contributor in writing the manuscript. Zhu performed the project supervision, writing review, and editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Y., Zhu, H. Spatial and temporal distributions of hexabromocyclododecanes in surface soils of Jinan, China. Environ Monit Assess 192, 629 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08587-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08587-6