Abstract
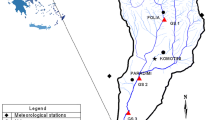
The assessment of surface water quality is often laborious, expensive and tedious, as well as impractical, especially for the developing and middle-income countries in the ASEAN region. The application of the water quality index (WQI), which depends on several independent key parameters, has great potential and is a useful tool in this region. Therefore, this study aims to find out the spatial variability of various water quality parameters in geographical information system (GIS) environment and perform a comparative study among the ASEAN WQI systems. At present, there are four ASEAN countries which have implemented the WQI system to evaluate their surface water quality, which are (i) Own WQI system—Malaysia, Thailand and Vietnam—and (ii) Adopted WQI system: Indonesia. A spatial distribution of 12 water quality parameters in the Selangor river basin, Malaysia, was plotted and then applied into the different ASEAN WQI systems. The WQI values obtained from the different WQI systems have an appreciable difference, even for the same water samples due to the disparity in the parameter selection and the standards among them. WQI systems which consider all biophysicochemical parameters provide a consistent evaluation (Very Poor), but the system which either considers physicochemical or biochemical parameters gives a relatively lenient evaluation (Fair–Poor). The Selangor river basin is stressed and impacted by all physical, biological and chemical parameters caused by both the aridity of the climate and anthropogenic activities. Therefore, it is crucial to include all these aspects into the evaluation and corresponding actions should be taken.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi, T., & Abbasi, S. A. (2012). Water quality indices: Elsevier Science.
Akkoyunlu, A., & Akiner, M. E. (2012). Pollution evaluation in streams using water quality indices: a case study from Turkey’s Sapanca Lake Basin. Ecological Indicators, 18, 501–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2011.12.018.
Ali, Z. M., Ibrahim, N. A., Mengersen, K., Shitan, M., & Juahir, H. (2014). Robust principal component analysis in water quality index development. In AIP Conference Proceedings 1602, 1091-1097, 1: AIP
Almeida, C., González, S. O., Mallea, M., & González, P. (2012). A recreational water quality index using chemical, physical and microbiological parameters. [journal article]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 19(8), 3400–3411. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-0865-5.
Alves, M. T. R., Teresa, F. B., & Nabout, J. C. (2014). A global scientific literature of research on water quality indices: trends, biases and future directions. Acta Limnologica Brasiliensia, 26(3), 245–253.
Aqeel Ashraf, M., Maah, M., Yusoff, I., Wajid, A., & Mahmood, K. (2011). Sand mining effects, causes and concerns: a case study from Bestari Jaya, Selangor, Peninsular Malaysia. Scientific Research and Essays, 6(6), 16. https://doi.org/10.5897/SRE10.690.
ASEAN Secretariat. (2017). Fifth ASEAN State of the Environment Report. Jakarta: Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN).
ASEAN Working Group on Water Resources Management (2012). ASEAN Water Data Management and Reporting System. http://rhn.water.gov.my/awgwrm/.. 23th March 2019.
Avvannavar, S. M., & Shrihari, S. (2008). Evaluation of water quality index for drinking purposes for river Netravathi, Mangalore, South India. [journal article]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 143(1), 279–290. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-9977-7.
Basheer, A. O., Hanafiah, M. M., & Abdulhasan, M. J. (2017). A study on water quality from Langat River, Selangor. Acta Scientifica Malaysia, 1(2), 4.
Bassi, N., & Kumar, M. D. (2017). Water quality index as a tool for wetland restoration. Water Policy, wp2017099.
Bharti, N., & Katyal, D. (2011). Water Quality Indices Used for Surface Water Vulnerability Assessment, 2.
Boyacioglu, H. (2007). Development of a water quality index based on a European classification scheme. Water Southern African, 33(1).
Brown, R. M., McClelland, N. I., Deininger, R. A., & Tozer, R. G. (1970). A water quality index - do we dare.
Canter, L. W. (1977). Environmental impact assessment. New York: McGraw-Hill.
CCME. (2001). Canadian water quality guidelines for the protection of aquatic life: CCME Water Quality Index 1.0 Technical Report Canadian Environmental Quality Guidelines, 1999. Winnipeg: Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment.
Chowdhury, M. S., Othman, F., Wan Zurina Wan Jaafar, and Nuzaima Che Mood, & Ema, N. (2018). Assessment of pollution and improvement measure of water quality parameters using scenarios modeling for Sungai Selangor Basin. Sains Malaysiana, 47, doi:https://doi.org/10.17576/jsm-2018-4703-05.
Corcoran, E., Nellemann, C., Baker, E., Bos, R., Osborn, D., & Savelli, H. (2010). Sick water? The central role of wastewater management in sustainable development. A Rapid Response Assessment: United Nations Environment Programme, UN-HABITAT, GRID-Arendal.
Cude, C. G. (2001). Oregon Water Quality Index a tool for evaluating water quality management effectiveness. American Water Resources Association, 37(1), 125–137. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1752-1688.2001.tb05480.x.
Department of Environment (2008). Interim national water quality standards for Malaysia. Malaysia.
Department of Statistic (2016). Current population estimates, Malaysia, 2014-2016.
Dezfooli, D., Hosseini-Moghari, S.-M., Ebrahimi, K., Araghinejad, S. J. M. E. S., & Environment. (2018). Classification of water quality status based on minimum quality parameters: application of machine learning techniques. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, 4(1), 311–324. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-017-0406-9.
Dunnette, D. A. (1979). A geographically variable water quality index used in Oregon. Journal of the Water Pollution Control Federation, 51, 53–61.
Elmore, H., & Hayes, T. (1960) Solubility of atmospheric oxygen in water. In Proc. Am. Sot. Civil Engrs, 41-53)
Faridah Othman, M., Chowdhury, S., & Sakai, N. (2014). Assessment of microorganism pollution of Selangor River, Malaysia. Advances in Agricultural & Environmental Engineering, 1(2).
Fathi, E., Zamani-Ahmadmahmoodi, R., & Zare-Bidaki, R. J. A. W. S. (2018). Water quality evaluation using water quality index and multivariate methods, Beheshtabad River, Iran. Applied Water Science, 8(7), 210. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0859-7.
Fukushi, K., Kurisu, F., Oguma, K., Furumai, H., & Fontanos, P. (2010). Southeast Asian Water Environment 4: IWA Publishing, Southeast Asian Water Environment 4.
Gholizadeh, M. H., Melesse, A. M., & Reddi, L. (2016). A comprehensive review on water quality parameters estimation using remote sensing techniques. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland), 16(8), 1298. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16081298.
Gorde, S., & Jadhav, M. (2013). Assessment of water quality parameters: a review. Journal of Engineering Research Applications, 3(6), 2029–2035.
Gupta, A. (1996). Erosion and sediment yield in Southeast Asia: a regional perspective. IAHS Publications-Series of Proceedings Reports-Intern Assoc Hydrological Sciences, 236, 215–222.
Horton, R. K. (1965). An index number system for rating water quality. Journal - Water Pollution Control Federation, 37(3), 300–306.
Jing, C., Jianmin, Z., Zhongyu, W., Xiaohong, L., & Xiaolan, Z. (2007). Application of grey relational analysis in water quality evaluation Vol. 19.
Kannel, P. R., Lee, S., Kanel, S. R., Khan, S. P., & Lee, Y.-S. (2007). Spatial–temporal variation and comparative assessment of water qualities of urban river system: a case study of the river Bagmati (Nepal). [journal article]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 129(1), 433–459. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-9375-6.
Khan, F., Husain, T., & Lumb, A. (2003). Water quality evaluation and trend analysis in selected watersheds of the Atlantic Region of Canada. [journal article]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 88(1), 221–248. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1025573108513.
Khanna, D., Bhutiani, R., Tyagi, B., Tyagi, P. K., & Ruhela, M. (2013). Determination of water quality index for the evaluation of surface water quality for drinking purpose. International journal of Science and Engineering, 1(1), 9–14.
Khuong, P. M., McKenna, R., & Fichtner, W. (2019). Analyzing drivers of renewable energy development in Southeast Asia countries with correlation and decomposition methods. Journal of Cleaner Production, 213, 710–722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.12.192.
Koh, K.-L. (2009). ASEAN environmental law, policy, and governance. World Scientific.
Koklu, R., Sengorur, B., & Topal, B. (2010). Water quality assessment using multivariate statistical methods—a case study: Melen River System (Turkey). [journal article]. Water Resources Management, 24(5), 959–978. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-009-9481-7.
Letchumanan, R. (2010). Climate change: is Southeast Asia up to the challenge?: is there an ASEAN policy on climate change? London: LSE IDEAS, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Li, R., Dong, M., Zhao, Y., Zhang, L., Cui, Q., & He, W. (2007). Assessment of water quality and identification of pollution sources of plateau lakes in Yunnan (China). Environmental Quality, 36(1), 291–297.
Lumb, A., C. Sharma, T. C. Sharma & Bibeault, J.-F. (2011). A review of genesis and evolution of water quality index (WQI) and some future directions Vol. 3.
Madhloom, H. M., Al-Ansari, N., Laue, J., & Chabuk, A. (2018). Modeling spatial distribution of some contamination within the lower reaches of Diyala River using IDW interpolation. Sustainability, 10(1), 22.
Magyar, N., Hatvani, I. G., Székely, I. K., Herzig, A., Dinka, M., & Kovács, J. (2013). Application of multivariate statistical methods in determining spatial changes in water quality in the Austrian part of Neusiedler See. Ecological Engineering, 55, 82–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2013.02.005.
Mahazar, A., Shuhaimi-Othman, M., Kutty, A., & Desa, M. (2013). Monitoring urban river water quality using macroinvertebrate and physicochemical parameters: case study of Penchala River, Malaysia. Journal of Biological Sciences, 13, 474–482. https://doi.org/10.3923/jbs.2013.474.482.
Mantzafleri, N., Psilovikos, A., & Blanta, A. (2009). Water quality monitoring and modeling in Lake Kastoria, using GIS. Assessment and Management of Pollution Sources. Water Resources Management, 23(15), 3221–3254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-009-9431-4.
Ministry of Environment and Forestry (2001). Government Regulation No. 82: water quality management and water pollution control
Ministry of Environment and Forestry (2003). Guidelines for determination of water quality status. In Ministry of Environment and Forestry (Ed.). Indonesia.
Ministry of Environment and Forestry (2018). Development of water quality index in Indonesia by Ministry of Environment and Forestry. http://www.menlhk.go.id/siaran-249-klhk-kembangkan-formula-pengukuran-kualitas-air-sungai-di-indonesia.html. 29th April 2019
Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment (2011). Guidelines and handbook for calculation of water quality index. Hanoi.
Mohamad, J., & Goh, H. C. (2015). Land use dynamics and governance in the Sungai Selangor Watershed: University of Malaya Press.
Mohamed, I., Othman, F., Ibrahim, A. I. N., Alaa-Eldin, M. E., & Yunus, R. M. (2014). Assessment of water quality parameters using multivariate analysis for Klang River basin, Malaysia. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187(1), 4182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-4182-y.
Mohd Ali, Z., Ibrahim, N. A., Mengersen, K., Shitan, M., & Juahir, H. (2013) The Langat River water quality index based on principal component analysis. In AIP Conference Proceedings, 1522, 1322-1336, Vol. 1: AIP
Nada, B., & Kirton, L. (2004). The secret life of fireflies. IRBM Updates, 3(December 2004), 2–4.
Nagels, J., Davies-Colley, R., & Smith, DG. (2001). A Water quality index for contact recreation in New Zealand, 43.
Nemerow, N., & Sumitomo, H. (1970). Benefits of water quality enhancement. New York: Syracuse University.
Noori, R., Berndtsson, R., Hosseinzadeh, M., Adamowski, J. F., & Abyaneh, M. R. (2019). A critical review on the application of the National Sanitation Foundation Water Quality Index. Environmental Pollution, 244, 575–587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.10.076.
Ogwueleka, T. C. (2015). Use of multivariate statistical techniques for the evaluation of temporal and spatial variations in water quality of the Kaduna River, Nigeria. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187(3), 137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4354-4.
Othman, F., Chowdhury, M. S., Sakai, N., Shaaban, M., & Shimizu, Y. (2014). Identification of pollution loading in a tropical river basin: a case study of Selangor River, Malaysia. Beijing: Paper presented at the International Conference on Environmental Science and Biological Engineering Beijing.
Othman, F., Chowdhury, M. S. U., Wan Jaafar, W. Z., Faresh, E. M. M., & Shirazi, S. M. (2018). Assessing risk and sources of heavy metals in a tropical river basin: a case study of the Selangor River, Malaysia. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 27(4), 1659–1671. https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/76309.
Pham, H., Rahman, M. M., Nguyen, N. C., Vo, P., Le Van, T., & Ngo, H. (2017). Assessment of surface water quality using the water quality index and multivariate statistical techniques-a case study: the upper part of Dong Nai River Basin, Vietnam. 7.
Pollution Control Department (1994). Thailand national surface water quality standards.
Pollution Control Department (2016a). Water quality index calculation- manual.
Pollution Control Department (2016b). Thailand water quality index calculation- manual.
Rohmad Barokah, G., Ariyani, F., & Siregar, T. (2017). Comparison of Storet and pollution index method to assess the environmental pollution status: a case study from Lampung Bay, Indonesia. Squalen Bulletin of Marine and Fisheries Postharvest and Biotechnology, 12, 67–74. https://doi.org/10.15578/squalen.v12i2.287.
Saraswati, S., Sunyoto, B. A. K., & Ba, H. (2014). Assessment of the forms and sensitivity of the index formula PI, Storet, CCME for the determination of water quality status of a tropical stream in Indonesia. Human and Environmental, 21, 129–142.
Selvam, S., Manimaran, G., Sivasubramanian, P., Balasubramanian, N., & Seshunarayana, T. J. E. E. S. (2014). GIS-based evaluation of water quality index of groundwater resources around Tuticorin coastal city, south India. Environmental Earth Sciences, 71(6), 2847–2867. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2662-y.
Singh, R. P., Nath, S., Prasad, S. C., & Nema, A. K. (2008). Selection of suitable aggregation function for estimation of aggregate pollution index for river Ganges in India. Environmental Engineering, 134(8), 689–701.
Subramaniam, V. (2004). Managing water supply in Selangor and Kuala Lumpur. Buletin Ingenieur, 22, 9.
Sutadian, A. D., Muttil, N., Yilmaz, A. G., & Perera, B. (2016). Development of river water quality indices—a review. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 188(1), 58.
Suwandana, E., Kawamura, K., Tanaka, K., Sakuno, Y., & Raharjo, P. (2011). Escherichia coli and biophysicochemical relationships of seawater and water pollution index in the Jakarta Bay. American Journal of Environmental Sciences, 7(3), 12.
Tripathi, M., & Singal, S. K. (2019). Use of principal component analysis for parameter selection for development of a novel water quality index: a case study of river Ganga India. Ecological Indicators, 96, 430–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.09.025.
Tyagi, S., Sharma, B., Singh, P., & Dobhal, R. (2013). Water quality assessment in terms of water quality index. American Journal of Water Resources, 1(3), 34–38.
WWAP (United Nations World Water Assessment Programme). (2015). The United Nations world water development report 2015: water for a sustainable world. Paris: UNESCO.
Xu, G., Jiao, L., Liu, J., Shi, Z., Zeng, C., & Liu, Y. (2019). Understanding urban expansion combining macro patterns and micro dynamics in three Southeast Asian megacities. Science of the Total Environment, 660, 375–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.039.
Zhila, H., Mahmood, H., & Rozainah, M. Z. (2014). Biodiversity and biomass of a natural and degraded mangrove forest of Peninsular Malaysia. Journal Environmental Earth Sciences, 71(11), 4629–4635. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2853-6.
Zhu, C., & Hao, Z. (2009). Application of grey relation analysis in evaluation of water quality.
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to express their deepest gratitude to the Department of Environment, Malaysia, for permitting the use of the Selangor river basin water quality data for this study. We thank the two anonymous reviewers and the associate editor Prof. Andrew S. Hursthouse for their constructive comments which helped in improving the article significantly.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wong, Y.J., Shimizu, Y., He, K. et al. Comparison among different ASEAN water quality indices for the assessment of the spatial variation of surface water quality in the Selangor river basin, Malaysia. Environ Monit Assess 192, 644 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08543-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08543-4