Abstract
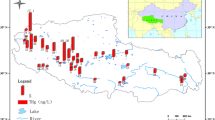
Mercury and its speciation in aquatic ecosystems have been assessed globally. Even though previous studies were limited to Arctic freshwater lakes, they are highly significant in the context of the changing climate. The present study is based on sediment samples collected from three Arctic freshwater lakes over a period of 4 years (2015–2018). The samples were analysed for total mercury (THg), methyl mercury (MHg), and various mercury fractions. The observed mean THg and MHg concentrations were 22.23 ng/g and 0.41 ng/g respectively; these values were comparable with those for other Arctic freshwater lakes. The mercury content significantly varied among the years as well as among the lakes. Changes in snowdrift and meltwater inputs, which are the major sources of water for the lakes, may have influenced the sediment mercury content along with geographical location and increased productivity. The results of MHg indicated the susceptibility of lake sediments to methylation. The major fractions observed were the organo-chelated form of mercury, followed by the elemental and water-soluble forms. These results indicate the availability of mercury for methylation. Hence, it is necessary to conduct more studies on the influence of climate change, mercury release through permafrost melting, and atmospheric deposition.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arctic Climate Impact Assessment. (2004). Impacts of a warming Arctic (pp. 1–140). Cambridge: Cambridge University.
Arctic Monitoring and Assessment Program (2011) Mercury in the Arctic. Oslo, Norway. xiv+193 pp.
Ariya, P. A., Dastoor, A. P., Amyot, M., Schroeder, W. H., Barrie, L., Anlauf, K., Raofie, F., Ryzhkov, A., Davignon, D., Lalonde, J., & Steffen, A. (2004). The Arctic: a sink for mercury. Tellus B., 56(5), 397–403.
Bacon, J. R., & Davidson, C. M. (2008). Is there a future for sequential chemical extraction? Analyst, 133(1), 25–46.
Bard, S. M. (1999). Global transport of anthropogenic contaminants and the consequences for the Arctic marine ecosystem. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 38(5), 356–379.
Bełdowski, J., Miotk, M., Zaborska, A., & Pempkowiak, J. (2015). Distribution of sedimentary mercury off Svalbard, European Arctic. Chemosphere., 122, 190–198.
Berg, T., Pfaffhuber, K. A., Cole, A. S., Engelsen, O., & Steffen, A. (2013). Ten-year trends in atmospheric mercury concentrations, meteorological effects and climate variables at Zeppelin, Ny-Ålesund. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 13(13), 6575–6586.
Bloom, N. S., Preus, E., Katon, J., & Hiltner, M. (2003). Selective extractions to assess the biogeochemically relevant fractionation of inorganic mercury in sediments and soils. Analytica Chimica Acta, 479(2), 233–248.
Cheng, M. D., & Schroeder, W. H. (2000). Potential atmospheric transport pathways for mercury measured in the Canadian high arctic. Journal of Atmospheric Chemistry, 35(1), 101–107.
Cole, A. S., Steffen, A., Pfaffhuber, K. A., Berg, T., Pilote, M., Poissant, L., Tordon, R., & Hung, H. (2013). Ten-year trends of atmospheric mercury in the high Arctic compared to Canadian sub-Arctic and mid-latitude sites. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 13(3), 1535–1545.
Dastoor, A. P., & Durnford, D. A. (2014). Arctic Ocean: is it a sink or a source of atmospheric mercury? Environmental Science & Technology, 48(3), 1707–1717.
Douglas TA, Blum JD (2019) Mercury isotopes reveal atmospheric gaseous mercury deposition directly to the Arctic coastal snowpack. Environmental Science & Technology Letters.
Douglas, T. A., Loseto, L. L., Macdonald, R. W., Outridge, P., Dommergue, A., Poulain, A., Amyot, M., Barkay, T., Berg, T., Chételat, J., & Constant, P. (2012). The fate of mercury in Arctic terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, a review. Environment and Chemistry, 9(4), 321–355.
Frohne, T., Rinklebe, J., Langer, U., Du Laing, G., Mothes, S., & Wennrich, R. (2012). Biogeochemical factors affecting mercury methylation rate in two contaminated floodplain soils. Biogeosciences, 9(1), 493–507.
Gamberg, M., Chételat, J., Poulain, A. J., Zdanowicz, C., & Zheng, J. (2015). Mercury in the Canadian Arctic terrestrial environment: an update. The Science of the Total Environment, 509, 28–40.
Givelet, N., Roos-Barraclough, F., Goodsite, M. E., Cheburkin, A. K., & Shotyk, W. (2004). Atmospheric mercury accumulation rates between 5900 and 800 calibrated years BP in the High Arctic of Canada recorded by peat hummocks. Environmental Science & Technology, 38(19), 4964–4972.
Halbach, K., Mikkelsen, Ø., Berg, T., & Steinnes, E. (2017). The presence of mercury and other trace metals in surface soils in the Norwegian Arctic. Chemosphere., 188, 567–574.
Haldorsen, S., Heim, M., Lefauconnier, B., Pettersson, L. E., Røros, M., & Sandsbråten, K. (2002). The water balance of an arctic lake and its dependence on climate change: Tvillingvatnet in Ny-Ålesund, Svalbard. Norsk Geografisk Tidsskrift-Norwegian Journal of Geography, 56(2), 146–151.
Hammerschmidt, C. R., Fitzgerald, W. F., Lamborg, C. H., Balcom, P. H., & Tseng, C. M. (2006). Biogeochemical cycling of methylmercury in lakes and tundra watersheds of Arctic Alaska. Environmental Science & Technology, 40(4), 1204–1211.
Hudelson, K. E., Drevnick, P. E., Wang, F., Armstrong, D., & Fisk, A. T. (2020). Mercury methylation and demethylation potentials in Arctic lake sediments. Chemosphere, 248, 126001.
Jia, N., Sun, L., He, X., You, K., Zhou, X., & Long, N. (2012). Distributions and impact factors of antimony in topsoils and moss in Ny-Ålesund. Arctic. Environmental pollution., 171, 72–77.
Jiang, S., Liu, X., & Chen, Q. (2011). Distribution of total mercury and methylmercury in lake sediments in Arctic Ny-Ålesund. Chemosphere., 83(8), 1108–1116.
Jiao, L., Zheng, G. J., Minh, T. B., Richardson, B., Chen, L., Zhang, Y., Yeung, L. W., Lam, J. C., Yang, X., Lam, P. K., & Wong, M. H. (2009). Persistent toxic substances in remote lake and coastal sediments from Svalbard, Norwegian Arctic: levels, sources and fluxes. Environmental Pollution, 157(4), 13421351.
Kainz, M., Lucotte, M., & Parrish, C. C. (2003). Relationships between organic matter composition and methyl mercury content of offshore and carbon-rich littoral sediments in an oligotrophic lake. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 60(7), 888–896.
Klaminder J, Yoo K, Rydberg J, Giesler R (2008) An explorative study of mercury export from a thawing palsa mire. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences. 113(G4).
Korosi, J. B., Griffiths, K., Smol, J. P., & Blais, J. M. (2018). Trends in historical mercury deposition inferred from lake sediment cores across a climate gradient in the Canadian High Arctic. Environmental Pollution, 241, 459–467.
Larose, C., Dommergue, A., De Angelis, M., Cossa, D., Averty, B., Marusczak, N., Soumis, N., Schneider, D., & Ferrari, C. (2010). Springtime changes in snow chemistry lead to new insights into mercury methylation in the Arctic. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 74(22), 6263–6275.
Lindberg, S. E., Brooks, S., Lin, C. J., Scott, K. J., Landis, M. S., Stevens, R. K., Goodsite, M., & Richter, A. (2002). Dynamic oxidation of gaseous mercury in the Arctic troposphere at polar sunrise. Environmental Science & Technology, 36(6), 1245–1256.
Lindeberg, C., Bindler, R., Bigler, C., Rosén, P., & Renberg, I. (2007). Mercury pollution trends in subarctic lakes in the northern Swedish mountains. AMBIO: A Journal of the Human Environment., 36(5), 401–405.
Lockhart, W. L., Wilkinson, P., Billeck, B. N., Danell, R. A., Hunt, R. V., Brunskill, G. J., Delaronde, J., & Louis, V. S. (1998). Fluxes of mercury to lake sediments in central and northern Canada inferred from dated sediment cores. Biogeochemistry., 40(2–3), 163–173.
Lu, Z., Cai, M., Wang, J., Yin, Z., & Yang, H. (2013). Levels and distribution of trace metals in surface sediments from Kongsfjorden, Svalbard, Norwegian Arctic. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 35(2), 257–269.
Macdonald, R. W., Barrie, L. A., Bidleman, T. F., Diamond, M. L., Gregor, D. J., Semkin, R. G., Strachan, W. M. J., Li, Y. F., Wania, F., Alaee, M., & Alexeeva, L. B. (2000). Contaminants in the Canadian Arctic: 5 years of progress in understanding sources, occurrence and pathways. The Science of the Total Environment, 254(2–3), 93–234.
Macdonald, R. W., Harner, T., & Fyfe, J. (2005). Recent climate change in the Arctic and its impact on contaminant pathways and interpretation of temporal trend data. The Science of the Total Environment, 342(1–3), 5–86.
Maggi, C., Berducci, M. T., Bianchi, J., Giani, M., & Campanella, L. (2009). Methylmercury determination in marine sediment and organisms by direct mercury analyser. Analytica Chimica Acta, 641(1–2), 32–36.
Maiti, S. K. (2003). Handbook of methods in environmental studies, vol. 2: Air, noise, soil, overburden, solid waste and ecology. Japur: ABD Publishers
Mason, R. P., Fitzgerald, W. F., & Morel, F. M. (1994). The biogeochemical cycling of elemental mercury: anthropogenic influences. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 58(15), 3191–3198.
Mason, R. P., Laporte, J. M., & Andres, S. (2000). Factors controlling the bioaccumulation of mercury, methylmercury, arsenic, selenium, and cadmium by freshwater invertebrates and fish. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 38(3), 283–297.
Mohan, M., Sreelakshmi, U., Sagar, M. V., Gopikrishna, V. G., Pandit, G. G., Sahu, S. K., Tiwari, M., Ajmal, P. Y., Kannan, V. M., Shukkur, M. A., & Krishnan, K. P. (2018). Rate of sediment accumulation and historic metal contamination in a tidewater glacier fjord. Svalbard. Marine pollution bulletin., 131, 453–459.
Mohan, M., KA, T. N., Kannan, V. M., Gopikrishna, V. G., Shukkur, A., Binish, M. B., Arunbabu, V., Rakesh, P. S., & Krishnan, K. P. (2019). Metal content in zooplanktons of two Arctic fjords, Ny-Ålesund, Svalbard. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring & Management, 12, 100251.
Møller, A. K., Barkay, T., Al-Soud, W. A., Sørensen, S. J., Skov, H., & Kroer, N. (2011). Diversity and characterization of mercury-resistant bacteria in snow, freshwater and sea-ice brine from the high Arctic. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 75(3), 390–401.
Morgan, H., De Búrca, R., Martin, J., & Jefries, J. (2009). Soil guideline values for mercury in soil. Bristol: Environment Agency.
Moskovchenko, D. V., Kurchatova, A. N., Fefilov, N. N., & Yurtaev, A. A. (2017). Concentrations of trace elements and iron in the Arctic soils of Belyi Island (the Kara Sea, Russia): patterns of variation across landscapes. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 189(5), 210.
O'Driscoll, N. J., Siciliano, S. D., Peak, D., Carignan, R., & Lean, D. R. S. (2006). The influence of forestry activity on the structure of dissolved organic matter in lakes: implications for mercury photoreactions. The Science of the Total Environment, 366(2–3), 880–893.
Outridge, P. M., Stern, G. A., Hamilton, P. B., Percival, J. B., McNeely, R., & Lockhart, W. L. (2005). Trace metal profiles in the varved sediment of an Arctic lake. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 69(20), 4881–4894.
Outridge, P. M., Sanei, H., Stern, G. A., Hamilton, P. B., & Goodarzi, F. (2007). Evidence for control of mercury accumulation rates in Canadian High Arctic lake sediments by variations of aquatic primary productivity. Environmental Science & Technology, 41(15), 5259–5265.
Poissant, L., Zhang, H. H., Canario, J., & Constant, P. (2008). Critical review of mercury fates and contamination in the arctic tundra ecosystem. The Science of the Total Environment, 400(1–3), 173–211.
Poulain, A. J., Garcia, E., Amyot, M., Campbell, P. G., & Ariya, P. A. (2007). Mercury distribution, partitioning and speciation in coastal vs. inland high Arctic snow. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 71(14), 3419–3431.
Ramasamy, E. V., Toms, A., Shylesh, C. M. S., Jayasooryan, K. K., & Mahesh, M. (2012). Mercury fractionation in the sediments of Vembanad wetland, west coast of India. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 34(5), 575–586.
Ruus, A., Øverjordet, I. B., Braaten, H. F. V., Evenset, A., Christensen, G., Heimstad, E. S., Gabrielsen, G. W., & Borgå, K. (2015). Methylmercury biomagnification in an Arctic pelagic food web. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 34(11), 2636–2643.
Schroeder, W. H., Anlauf, K. G., Barrie, L. A., Lu, J. Y., Steffen, A., Schneeberger, D. R., & Berg, T. (1998). Arctic springtime depletion of mercury. Nature., 394(6691), 331–332.
St. Pierre, K. A., St. Louis, V. L., Kirk, J. L., Lehnherr, I., Wang, S., & La Farge, C. (2015). Importance of open marine waters to the enrichment of total mercury and monomethylmercury in lichens in the Canadian High Arctic. Environmental Science & Technology, 49(10), 5930–5938.
Stern, G. A., Sanei, H., Roach, P., Delaronde, J., & Outridge, P. M. (2009). Historical interrelated variations of mercury and aquatic organic matter in lake sediment cores from a subarctic lake in Yukon, Canada: further evidence toward the algal-mercury scavenging hypothesis. Environmental Science & Technology, 43(20), 7684–7690.
Tseng, C. M., Lamborg, C., Fitzgerald, W. F., & Engstrom, D. R. (2004). Cycling of dissolved elemental mercury in Arctic Alaskan lakes. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 68(6), 1173–1184.
Ullrich, S. M., Tanton, T. W., & Abdrashitova, S. A. (2001). Mercury in the aquatic environment: a review of factors affecting methylation. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 31(3), 241–293.
Zaborska, A., Beszczyńska-Möller, A., & Włodarska-Kowalczuk, M. (2017). History of heavy metal accumulation in the Svalbard area: distribution, origin and transport pathways. Environmental Pollution, 231, 437–450.
Zdanowicz, C., Krümmel, E. M., Lean, D., Poulain, A. J., Yumvihoze, E., Chen, J., & Hintelmann, H. (2013). Accumulation, storage and release of atmospheric mercury in a glaciated Arctic catchment, Baffin Island, Canada. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 107, 316–335.
Zhang, Y., Jacob, D. J., Dutkiewicz, S., Amos, H. M., Long, M. S., & Sunderland, E. M. (2015). Biogeochemical drivers of the fate of riverine mercury discharged to the global and Arctic oceans. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 29(6), 854–864.
Funding
We would like to thank the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES), Department of Science and Technology (DST) PURSE & FIST programs for their financial support to our work and DST-INSPIRE for the research fellowship to the first author. Moreover, we are grateful to the National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR), MoES, Government of India for its logistical and financial support through Arctic Expedition and PACER-POP Project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 35 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gopikrishna, V.G., Kannan, V.M., Binish, M.B. et al. Mercury in the sediments of freshwater lakes in Ny-Ålesund, Arctic. Environ Monit Assess 192, 538 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08511-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08511-y