Abstract
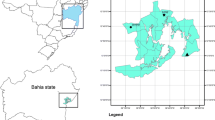
In order to estimate pollution impact in soil and plants by phosphates mining activities, three mining sites and one control site were selected around Metlaoui (phosphates basin of Gafsa, southern Tunisia) in March 2019. Heavy metal concentrations in soil and in two native plants (Moricandia arvensis and Diplotaxis harra: Brassicaceae) were measured using atomic absorption spectrometry. Development instability was estimated using leaf fluctuating asymmetry of the two plant species. The results showed that the soils of the Metlaoui sites contain higher levels of Cd, Ni, Zn, and Cr compared with control site (maximum of 33.225 ± 2.588; 100.86 ± 0.314; 180.267 ± 16.103; and 16.554 ± 0.313 ppm, respectively). These levels are higher than the maximal contents tolerated in soils. Heavy metals also occurred at high concentrations in plant organs in Metlaoui sites especially in leaves. Cadmium and Zn concentrations in these plants exceed the phytotoxic level (with maximum of 20.498 ± 0.627 ppm and maximum of 337.901 ± 16.686 ppm, respectively). Statistical analysis showed that fluctuating asymmetries (FA) of leaves of the two sampled plants are higher in mining sites compared with control. Pearson correlation and PCA analysis showed that FA is related to Cd, Ni, and Zn concentrations in soil. The results indicate that phosphate extraction and laundries in the mining sites caused heavy metal pollution in soil that accumulates in plant organs and caused also development instability. Our study showed that Moricandia arvensis may have the potential for phytoremediation.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acosta, J. A., Faz, A., Martinez-Martinez, S., Zornoza, R., Carmona, D. M., & Kabas, S. (2011). Multivariate statistical and GIS-based approach to evaluate heavy metals behavior in mine sites for future reclamation. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 109, 8–17.
Aggarwal, A., Sharma, I., Tripati, B. N., Munjal, A. K., Baunthiyal, M., & Sharma, V. (2012). Metal toxicity and photosynthesis. In Photosynthesis: overviews on recent progress & future perspectives. New Delhi: I K International Publishing House Pvt. Ltd.
Alkorta, I., Hernández-Allica, J., Becerril, J., Amezaga, I., Albizu, I., & Garbisu, C. (2004). Recent findings on the phytoremediation of soils contaminated with environmentally toxic heavy metals and metalloids such as zinc, cadmium, lead, and arsenic. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio/Technology, 3, 71–90.
Anciaes, M., & Marini, M. A. (2000). The effects of fragmentation on fluctuating asymmetry in passerine birds of Brazilian tropical forests. Journal of Applied Ecology, 37, 1013–1028.
Anjum, N. A., Ahmad, I., Pereira, M. E., Costa Duarte, A., Umar, S., & Khan, N. A. (2012). The plant family Brassicaceae. Contribution towards phytoremediation. Dordrecht: Springer.
Atafar, Z., Mesdaghinia, A., Nouri, J., Homaee, M., Yunesian, M., Ahmadimoghaddam, M., & Mahvi, A. H. (2010). Effect of fertilizer application on soil heavy metal concentration. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 160, 83–90.
Awofolu, O. (2005). A survey of trace metals in vegetation, soil and lower animal along some selected major roads in metropolitan city of Lagos. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 105, 431–447.
Benavides, M. P., Gallego, S. M., & Tomaro, M. L. (2005). Cadmium toxicity in plants. Brazilian Journal of Plant Physiology, 17, 21–34.
Bensalem, K., Bensalem, B. M., & Zouary, S. (2013). History vs. reality, mining industry diagnostic and environmental effects: illustration case in real size of Tunisian mining basin. Journal of Environmental Science, Toxicology and Food Technology, 4(2), 56–64.
Bjorksten, T. A., Fowler, K., & Pomiankowski, A. (2000). What does sexual trait FA tell us about stress? Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 15, 163–166.
Boubaker, S. & Hassen, M. (2016). La Compagnie des Phosphates de Gafsa (CPG) : État des lieux de la gouvernance et recommandations (in French), National Resource Governance Institute, https://resourcegovernance.org/sites/default/files/documents/la-compagnie-des-phosphates-de-gafsa.pdf (accessed 2019-08-06).
Chaffai, R., & Koyama, H. (2011). Heavy metal tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Advances in Botanical Research, 60, 1–49.
Chibuike, G. U., & Obiora, C. (2014). Heavy metal polluted soils: effect on plants and bioremediation methods. Applied and Environmental Soil Science, 2014, 12.
Choppala, G., Saifullah Bolan, N., Bibi, S., Iqbal, M., Rengel, Z., Kunhikrishnan, A., & Ok, Y. S. (2014). Cellular mechanisms in higher plants governing tolerance to cadmium toxicity. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 33, 374–391.
Concas, A., Ardau, C., Cristini, A., Zuddas, P., & Cao, G. (2006). Mobility of heavy metals from tailings to stream waters in a mining activity contaminated site. Chemosphere, 63, 244–253.
Cuevas-Reyes, P., Gilberti, L., González-Rodríguez, A., & Fernandes, G. W. (2013). Patterns of herbivory and fluctuating asymmetry in Solanum lycocarpum St. Hill (Solanaceae) along an urban gradient in Brazil. Ecological Indicators, 24, 557–561.
Ehsan, S., Ali, S., Noureen, S., Mahmood, K., Farid, M., Ishaque, W., Shakoor, M. B., & Rizwan, M. (2014). Citric acid assisted phytoremediation of cadmium by Brassica napus L. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 106, 164–172.
Fan, S. (2014). Assessment of spatial distribution and pollution with heavy metals in roadside soils along Xi’an-Baoji highway in northwest China. Environmental Engineering and Management Journal, 13(12), 3161–3171.
Fernandes, G. W., De Oliveira, S. C., Campos, I. R., Barbosa, M., Soares, L. A., & Cuevas-Reyes, P. (2016). Leaf fluctuating asymmetry and herbivory of Tibouchina heteromalla in restored and natural environments. Neotropical Entomology, 45, 44–49.
Fey, D. P., & Hare, J. A. (2008). Fluctuating asymmetry in the otoliths of larval Atlantic menhaden Brevoortia tyrannus (Latrobe) a condition indicator? Journal of Fish Biology, 72(1), 121–130.
Galfati, I., Essaïd, B., Beji Sassi, A., Abdallah, H., & Zaïer, A. (2011). Accumulation of heavy metals in native plants growing near the phosphate treatment industry, Tunisia. Carpathian Journal of Earth and Environmental Sciences, 6(2), 85–100.
Harmanescu, M., Alda, L. M., Bordean, D. M., Gogoasa, I., & Gergen, I. (2011). Heavy metals health risk assessment for population via consumption of vegetables grown in old mining area; a case study: Banat County, Romania. Chemistry Central Journal, 5(64), 1–10.
Hazrat, A., Khan, E., & Sajad, M. A. (2013). Phytoremediation of heavy metals—Concepts and applications. Chemosphere, 91, 869–881.
Henry, M. U., Ogenyi, R. A., Henry, U. I., & Dogun, O. (2018). Assessment of heavy metal concentration in water, soil and vegetable in ex-mining pond, Jos South L.G.A Plateau State, Nigeria. International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, 8(8), 840–845.
Jan, A. T., Singhal, P., & Haq, Q. M. R. (2013). Plant abiotic stress: deciphering remedial strategies for emerging problem. Journal of Plant Interactions, 8, 97–108.
Kabata-Pendias, A., & Pendias, H. (1986). Trace elements in soils and plants. Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Khan, S., Hesham, A.E.-L., Qiao, M., Rehman, S. & He, J.-Z. (2010). Effects of Cd and Pb on soil microbial community structure and activities. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 17, 288–296.
Khelifi, F., Besser, H., Ayadi, Y., Liu, G., Yousaf, B., Harabi, S., Bedoui, S., Zighmi, K., & Hamed, Y. (2019). Evaluation of potentially toxic elements’ (PTEs) vertical distribution in sediments of Gafsa–Metlaoui mining basin (southwestern Tunisia) using geochemical and multivariate statistical analysis approaches. Environmental Earth Sciences, 78, 53. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8048-z.
Kozlov, M. V. (2015). How reproducible are the measurements of leaf fluctuating asymmetry? PeerJ, 3, e1027. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.1027.
Kozlov, M. V., Wilsey, B. J., Koricheva, J., & Haukioja, E. (1996). Fluctuating asymmetry of birch leaves increases under pollution impact. Journal of Applied Ecology, 33, 1489–1495.
Kozlov, M. V., Zvereva, E. L., & Niemelä, P. (2001). Shoot fluctuating asymmetry: a new and objective stress index in Norway spruce (Picea abies). Revue Canadienne de recherche forestière, 31(7), 1289–1291.
Kozlov, M. V., Niemelä, P., & Mälkönen, E. (2002). Effects of compensatory fertilisation on pollution-induced stress in Scots pine. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 134, 307–318.
Kozlov, M. V., Cornelissen, T., Gavrikov, D. E., Kunavin, M. A., Lama, A. D., Milligan, J., et al. (2017). Reproducibility of fluctuating asymmetry measurements in plants: sources of variation and implications for study design. Ecological Indicators, 73, 733–740.
Kpomblekou, K., & Tabatabai, M. A. (1994). Metal content of phosphate rocks. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 25, 2871–2882.
Kuc, J. (1995). Phytoalexins, stress metabolism, and disease resistance in plants. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 33, 275–297.
Mabrouk, L., Guarred, T., Hamza, A., Messaoudi, I., & Hellal, A. N. (2014). Fluctuating asymmetry in grass goby Zosterisessor ophiocephalus Pallas, 1811 inhabiting polluted and unpolluted area in Tunisia. Marine pollution bulletin, 85(1), 248–251.
Markow, T. A. (1995). Evolutionary ecology and developmental instability. Annual Review of Entomology, 40, 105–120.
Mekki, A., & Sayadi, S. (2017). Study of heavy metal accumulation and residual toxicity in soil saturated with phosphate processing wastewater. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 2017, 215–228.
Mithofer, A., Schulze, B., & Boland, W. (2004). Biotic and heavy metal stress response in plants: evidence for common signals. FEBS Letters, 566, 1–5.
Mohamed, R., Taieb, D., & Ben Brahim, A. (2014). Chemical and mineralogy characteristics of dust collected near the phosphate mining basin of Gafsa (South-Western of Tunisia). Journal of Environmental & Analytical Toxicology, 4(6), 234.
Moradi, L., & Ehsanzadeh, P. (2015). Effects of Cd on photosynthesis and growth of safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) genotypes. Photosynthetica, 53, 506–518.
Mukhtar, N., Hameed, M., Ashraf, M., Ahmed, R. (2013). Modifications in stomatal structure and function in Cenchrus ciliaris L. and Cynodon dactylon (L.) Pers. in response to cadmium stress. Pakistan Journal of Botany, 45, 351–357.
Ounis, A. (2002). Caractérisation environnementale de la région de Mdhilla (Bassin Gafsa Sud). Etude des rejets de l’usine de Mdhilla et des laveries de la compagnie de phosphate de Gafsa ». Master thesis in Géologie Appliquée à l’Environnement. Tunis El Manar university, Faculté des Sciences de Tunis. Tunisia.
Palmer, A.R. (1994). Fluctuating asymmetry analysis: a primer. In: T.A. Markow (Ed.), Developmental Instability: Its Origins and Evolutionary Implications. pp. 335–364. Springer, Dordrecht.
Palmer, A. R., & Strobeck, C. (2003). Fluctuating asymmetry analyses revisited. In M. Polak (Ed.), Developmental instability: causes and consequences (pp. 279–319). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Pottier-Alapetite, G. (1981). Flore de la Tunisie : Apétales – Dialypétales- Gamopétales. Tunisie: Publications scientifiques Tunisiennes.
Reta, G., Dong, X., Zhonghua, L., Bob, S., Xiaonong, H., Huijuan, B., et al. (2018). Environmental impact of phosphate mining and beneficiation: review. International Journal of Hydrology, 2(4), 424–431.
Salhi, B. (2017). Mutations socio-spatiales et environnementales du bassin minier de Gafsa (Sud-ouest de Tunisie) : Approche par les outils géomatiques. Master Thesis, Le Mans University and Université Bretagne Loire, France.
Sarwar, N., Malhi, S.S., Zia, M.H., Naeem, A., Bibi, S., & Farid, G. (2010). Role of mineral nutrition in minimizing cadmium accumulation by plants. Journal of the science of food and agriculture, 90(6), 925–37.
Sarwar, N., Ishaq, W., Farid, G., Shaheen, M. R., Imran, M., Geng, M., & Hussain, S. (2015). Zinc–cadmium interactions: impact on wheat physiology and mineral acquisition. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 122, 528–536.
Sarwar, N., Imran, M., Shaheen, M. R., Ishaque, W., Kamran, M. A., Matloob, A., Rehim, A., & Hussain, S. (2017). Phytoremediation strategies for soils contaminated with heavy metals: modifications and future perspectives. Chemosphere, 171, 710–721.
Sengar, R. S., Gautam, M., Sengar, R. S., Garg, S. K., Sengar, K., & Chaudhary, R. (2009). Lead stress effects on physiobiochemical activities of higher plants. Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 196, 1–21.
Sigfridsson, K. G., Bernat, G., Mamedov, F., & Styring, S. (2004). Molecular interference of Cd2+ with photosystem II. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta-Biomembranes, 1659, 19–31.
Srivastava, S., Tripathi, R. D., & Dwivedi, U. N. (2004). Synthesis of phytochelatins and modulation of antioxidants in response to cadmium stress in Cuscuta reflexa an angiospermic parasite. Journal of Plant Physiology, 161, 665–674.
Susarla, S., Medina, V. F., & McCutcheon, S. C. (2002). Phytoremediation: an ecological solution to organic chemical contamination. Ecological Engineering, 18(5), 647–658.
Tong, Y. P., Kneer, R., & Zhu, Y. G. (2004). Vacuolar compartmentalization: a second generation approach to engineering plants for phytoremediation. Trends in Plant Science, 9, 7–9.
Van Valen, L. (1962). A study of fluctuating asymmetry. Evolution, 16, 125–142.
Wauters, L. A., Dhondt, A. A., Knothe, H., & Parkin, D. T. (1996). Fluctuating asymmetry and body size as indicators of stress in red squirrel populations in woodland fragments. Journal of Applied Ecology, 33, 735–740.
Wojtaszek, P. (1997). Oxidative burst: an early plant response to pathogen infection. Biochemical Journal, 322(3), 681–692.
Zorina, A. A. & Korosov, A. V. (2009). Variation in parameters and indices of asymmetry in leaf characters in the crown of Betula pendula (Betulaceae), Botanicheskiĭ Zhurnal, 94 (8), 1172–1192.
Zvereva, E., Kozlov, M., & Haukioja, E. (1997). Stress responses of Salix borealis to pollution and defoliation. Journal of Applied Ecology, 34, 1387–1396.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the inhabitants of the city of Metlaoui for their assistance during sampling. They also thank Dr. Jose Alexander Elvir and the reviewers for their comments which improved the quality of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mabrouk, L., Mabrouk, W. & Mansour, H.B. High leaf fluctuating asymmetry in two native plants growing in heavy metal-contaminated soil: the case of Metlaoui phosphate mining basin (Gafsa, Tunisia). Environ Monit Assess 192, 406 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08385-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08385-0