Abstract
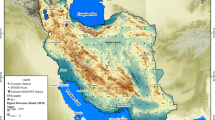
Central Asia has become a key node of the belt and road corridor. It is located in arid and semi-arid climate regions, and it is a region where the contribution of global aerosols of sand and dust is continuous. However, few studies have been conducted on the Central Asian aerosol optical depth. Therefore, this paper relied on the belt and road sustainable development dataset to analyze the spatial-temporal variations in the AOD in Central Asia and provide spatial-temporal characteristics of the AOD for environmental services. We analyzed the spatial and temporal variation in the aerosol optical depth (AOD) in Central Asia by using MODIS/AQUA C6 MYD08_M3 images from 2008 to 2017. The results showed that (1) the annual average AOD in Central Asia in the past decade varied from 0.183 to 0.232, which indicated a slow decline starting in 2014. The percentage of average annual decline was approximately 0.18%, and the regular distinct revealed the distribution characteristics of AOD. In different years, the Central Asian region exhibited the similar monthly change characteristics: from July to December, the AOD decreased, and from December to February, it increased. In different seasons, the Central Asian region exhibited the different seasonal change characteristics: the AOD value was higher in the spring and summer. The mean values in the spring, summer, autumn, and winter were 0.273, 0.240, 0.155, and 0.183, respectively, and the standard deviations were 0.036, 0.038, 0.025, and 0.048, respectively. (3) Based on spatial distribution characteristics, the Tarim Basin, Aral Sea region, and Ebinur Lake area were high value areas, and Kazakhstan was a low value area. The AOD of the surrounding area of the Aral Sea had increased in the last 5 years, while that of Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, and Turkmenistan had decreased. The AOD of the Taklamakan area exhibited an inter-annual change. Sand dust aerosols were the largest contributors to the AOD in the Taklamakan area. The rising trend of the AOD in the Aral Sea area was clear, with an average annual increase of 0.234%, and the contribution of salt dust aerosols to the AOD increased. The average annual AOD in the Ebinur Lake area remained stable.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, T. L., Charlson, R. J., Schwartz, S. E., Knutti, R., Boucher, O., Rodhe, H., & Heintzenberg, J. (2003). Climate forcing by aerosols: a hazy picture. Science, 300(5622), 1103–1104. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1084777.
Belle, J., & Liu, Y. (2016). Evaluation of Aqua MODIS Collection 6 AOD parameters for air quality research over the continental United States. Remote Sensing, 8(10), 815. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8100815.
Bennouna, Y. S., & Cachorro, V. E. (2013). Atmospheric turbidity determined by the annual cycle of the aerosol optical depth over north-center Spain from ground (AERONET) and satellite (MODIS). Atmospheric Environment, 67(2), 352–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.10.065.
Bilal, M., Nichol, J. E., & Nazeer, M. (2016). Validation of Aqua-MODIS C051 and C006 operational aerosol products using AERONET measurements over Pakistan. Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations & Remote Sensing, 9(5), 2074–2080. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2481460.
Bilal, M., Nazeer, M., & Nichol, J. E. (2017). Validation of MODIS and VIIRS derived aerosol optical depth over complex coastal waters. Atmospheric Research, 9(4), 43–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2016.11.009.
Butt, M. J., Assiri, M. E., & Ali, M. A. (2017). Assessment of AOD variability over Saudi Arabia using MODIS Deep Blue products. Environmental Pollution, 231(1), 143–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.07.104.
Chen, B, & Sverdlik, L. (2007). Optical and microphysical characteristics of aerosol structures in central asia. Proceedings of SPIE -The International Society for Optical Engineering, 67330S-67330S-7.
Chen, B. B., Sverdlik, L. G., Imashev, S. A., Solomon, P. A., Lantz, J., Schauer, J. J., et al. (2013). Empirical relationship between particulate matter and aerosol optical depth over northern Tien-Shan, Central Asia. Air Quality Atmosphere & Health, 6(2), 385–396.
Chen, S., Huang, J., Li, J., et al. (2017). Comparison of dust emissions, transport, and deposition between the Taklimakan Desert and Gobi Desert from 2007 to 2011. Science China-Earth Sciences, 60(1), 1338–1355 CNKI:SUN:JDXG.0.2017–07-011.
Chubarova, N. Y., Poliukhov, A. A., & Gorlova, I. D. (2016). Long-term variability of aerosol optical thickness in Eastern Europe over 2001-2014 according to the measurements at the Moscow MSU MO AERONET site with additional cloud and NO2 correction. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 9(2), 313–334. https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-9-313-2016.
Deng, X. L., Pan, D. L., He, D. Y., et al. (2009). Anthropogenic and dust aerosol components estimated by satellite data over the China’s seas. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 31(4), 58–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-014-4045-z.
Deng, Y. J., Hu, M., Lin, C. Y., et al. (2016). Analysis of aerosol optical depth in Guangdong based on FY3A/MERSI data. Meteorological Monthly, 42(1), 61–66. https://doi.org/10.11834/jrs.20143274.
Dubovik, O., Smirnov, A., Holben, B. N., King, M. D., Kaufman, Y. J., Eck, T. F., & Slutsker, I. (2000). Accuracy assessments of aerosol optical properties retrieved from Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) Sun and sky radiance measurements. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 105(D8), 9791–9806. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000JD900040.
Eck, T. F., Holben, B. N., Dubovik, O., Smirnov, A., Goloub, P., Chen, H. B., Chatenet, B., Gomes, L., Zhang, X. Y., Tsay, S. C., Ji, Q., Giles, D., & Slutsker, I. (2005). Columnar aerosol optical properties at AERONET sites in central eastern Asia and aerosol transport to the tropical mid-Pacific. Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmospheres, 110(D06202), 887–908. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004JD005274.
Georgoulias, A. K., Alexandri, G., Kourtidis, K. A., Lelieveld, J., Zanis, P., & Amiridis, V. (2016). Differences between the MODIS Collection 6 and 5.1 aerosol datasets over the greater Mediterranean region. Atmospheric Environment, 147, 310–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2016.10.014.
Han, Y. X., Fang, X. M., Song, L. C., et al. (2005). A study of atmospheric circulation and dust storm causes of formation in the Tarim Basin — the restructured wind field by shapes of dune and observed prevailing wind. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 29(4), 627–635. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-004-0010-x.
Hänel, G. (1976). The properties of atmospheric aerosol particles as functions of the relative humidity at thermodynamic equilibrium with the surrounding moist air. Advances in Geophysics, 19C, 73–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2687(08)60142-9.
Hoelzemann, J. J., Longo, K. M., Fonseca, R. M., do Rosário, N. M. E., Elbern, H., Freitas, S. R., & Pires, C. (2009). Regional representativity of AERONET observation sites during the biomass burning season in South America determined by correlation studies with MODIS Aerosol Optical Depth. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 114(D13), D13301. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008JD010369.
Hsu, N. C., Tsay, S. C., King, M. D., et al. (2006). Deep blue retrievals of Asian aerosol properties during ACE-Asia. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 44(11), 3180–3195. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2006.879540.
Hsu, N. C., Bettenhausen, C., Sayer, A. M., et al. (2013). Enhanced Deep Blue aerosol retrieval algorithm, the second generation. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 118(16), 9296–9315. https://doi.org/10.1002/jgrd.50712.
Indoitu, R., Orlovsky, L., & Orlovsky, N. (2012). Dust storms in Central Asia: spatial and temporal variations. Journal of Arid Environments, 85(none), 62–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2012.03.018.
Kaiser, D. P., & Qian, Y. (2002). Decreasing trends in sunshine duration over China for 1954–1998, indication of increased haze pollution? Geophysical Research Letters, 9, 2042. https://doi.org/10.1016/10.1029/2002/GL016057.
Kaufman, Y. J., Tanre, D., & Boucher, O. (2002). A satellite view of aerosols in the climate system. Nature, 419(6903), 215–223. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01091.
Kim, M., Kim, J., Jeong, U., Kim, W., Holben, B., Eck, T. F., Lim, J. H., Song, C. K., & Lee, S. (2015). Improvements in AOD retrieval from geostationary measurements over Asia with aerosol optical properties derived from the DRAGON-Asia campaign. Atmospheric Chemistry & Physics, 15(7), 10773–10812. https://doi.org/10.5194/acpd-15-10773-2015.
Kulkarni, S., Sobhani, N., Millerschulze, J. P., et al. (2015). Source sector and region contributions to BC and PM2.5 in Central Asia. Atmospheric Chemistry & Physics Discussions, 14(4), 1683–1705. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-15-1683-2015.
Kumar, A. (2016). Spatio-temporal synoptic variability of aerosol optical depth and cloud properties over the Central North region of India through MODIS Collection V satellite sensors. Indian Journal of Physics, 90(6), 613–625. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-015-0783-8.
Kurmanalieva, E., & Parpiev, Z. (2011). Geography and trade in Central Asia. Social Science Electronic Publishing, 4(28), 36. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.1824933.
Lee, H. J., Liu, Y., Coull, B. A., et al. (2011). A novel calibration approach of MODIS AOD data to predict PM2.5 concentrations. Atmospheric Chemistry & Physics, 11(11), 9769–9795. https://doi.org/10.1097/EDE.027.
Levin, Z.,Cotton, W. R. (2008). Aerosol pollution impact on precipitation: a scientific review. Berlin:Springer-Verlag, 2(8):205–294.
Levy, R. C., Remer, L. A., Kleidman, R. G., et al. (2010). Global evaluation of the collection 5 MODIS dark-target aerosol products over land. Atmospheric Chemistry & Physics & Discussions, 10(6), 10399–10420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2014.10.016.
Levy, R. C., Mattoo, S., Munchak, L. A., Remer, L. A., Sayer, A. M., Patadia, F., & Hsu, N. C. (2013). The collection 6 MODIS aerosol products over land and ocean. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 6(11), 2989–3034. https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-6-2989-2013.
Lin, S., Sun, C. K., Liu, Q. H., et al. (2010). Aerosol optical depth retrieval by HJ-1/CCD supported by MODIS surface reflectance data. Science in China, 53(1), 74–80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-010-4134-5.
Lipponen, A., Mielonen, T., Pitkänen, M. R. A., et al. (2018). Bayesian aerosol retrieval algorithm for MODIS AOD retrieval over land. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 11(3), 1–27. https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-2017-359.
Liu, Y., Wu, C., Rui, J., et al. (2018). An overview of the influence of atmospheric circulation on the climate in arid and semi-arid region of Central and East Asia. Science China Earth Sciences, 61(9), 31–42 CNKI:SUN:JDXG.0.2018-09-003.
Lv, B., Hu, Y., Chang, H. H., Russell, A. G., Cai, J., Xu, B., & Bai, Y. (2017). Daily estimation of ground-level PM 2.5, concentrations at 4 km resolution over Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei by fusing MODIS AOD and ground observations. Science of the Total Environment, 580, 235–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.12.049.
Mallet, M., Dubovik, O., Nabat, P., et al. (2013). Absorption properties of Mediterranean aerosols obtained from multi-year ground-based and satellite remote sensing observations. Atmospheric Chemistry & Physics, 13(18), 9195–9210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2010.11.005.
Mcmillan, W. W., Warner, J. X., Comer, M. C., et al. (2008). AIRS views transport from 12 to 22 July 2004 Alaskan/Canadian fires, correlation of AIRS CO and MODIS AOD with forward trajectories and comparison of AIRS CO retrievals with DC-8 in situ measurements during INTEX-A/ICARTT. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 113(D20), 20301. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007jd009711.
Mu, G. J., Yan, S., Jilili, A., et al. (2002). Wind erosion at the dryup bottom of Ebinur Lake—a case study on the source of air dust. Science in China (Series D), 45(s1), 157–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02878403.
Namdari, S., Valizade, K. K., Rasuly, A. A., & Sari Sarraf, B. (2016). Spatio-temporal analysis of MODIS AOD over western part of Iran. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 9(3), 191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2029-7.
Ni, X., Cao, C., Zhou, Y., et al. (2018). Spatio-temporal pattern estimation of PM2.5 in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region based on MODIS AOD and meteorological data using the back propagation neural network. Atmosphere, 9(3), 105. https://doi.org/10.5194/isprsarchives-XLI-B2-721-2016.
Opp, C., Groll, M., Aslanov, I., et al. (2016). Aeolian dust deposition in the southern Aral Sea region (Uzbekistan): ground-based monitoring results from the LUCA project. Quaternary International, S104061821600224X. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2015.12.103.
Qoraboyev, I., & Moldashev, K. (2018). The belt and road initiative and comprehensive regionalism in Central Asia. Social Science Electronic Publishing, 9(8), 115–130, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-5915-5_7.
Remer, L. A., Mattoo, S., Levy, R. C., et al. (2013). MODIS 3 km aerosol product, algorithm and global perspective. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 6(6), 69–112. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8040328.
Rosenfeld, D., Dai, J., Yu, X., Yao, Z., Xu, X., Yang, X., & du, C. (2007). Inverse relations between amounts of air pollution and orographic precipitation. Science, 315(5817), 1396–1398. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1137949.
Semenov, V. K., Alexander, S., Aref’ev V. N. et al. (2005). Aerosol optical depth over the mountainous region in Central Asia (Issyk-kul lake, Kyrgyzstan). Geophysical Research Letters.
Sherman, J. P., Gupta, P., Levy, R. C., et al. (2016). An evaluation of MODIS-retrieved aerosol optical depth over a mountainous AERONET site in the southeastern US. Aerosol & Air Quality Research, 16(12), 3243–3255. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006JD008175.
Shinozuka, Y., Redemann, J., Livingston, J. M., Russell, P. B., Clarke, A. D., Howell, S. G., Freitag, S., O'Neill, N. T., Reid, E. A., Johnson, R., Ramachandran, S., McNaughton, C. S., Kapustin, V. N., Brekhovskikh, V., Holben, B. N., & McArthur, L. J. B. (2010). Airborne observation of aerosol optical depth during ARCTAS: vertical profiles, inter-comparison, fine-mode fraction and horizontal variability. Atmospheric Chemistry & Physics Discussions, 10(8), 18315–11836. https://doi.org/10.5194/acpd-10-18315-2010.
Sitnov, S. A. (2011). Spatial-temporal variability of the aerosol optical thickness over the central part of European Russia from MODIS data. Izvestiya Atmospheric & Oceanic Physics, 47(5), 584–602. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0001433811050100.
Sockol, A., & Griswold, J. D. S. (2017). Inter-comparison between Cmip5 model and Modis satellite-retrieved data of aerosol optical depth, cloud fraction, and cloud-aerosol interactions, CMIP5 and MODIS AOD-CF interactions. Earth & Space Science, 4(8), 485–505. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017EA000288.
Song, J., Xia, X., Zhang, X., et al. (2017). Weekday AOD smaller than weekend AOD in eastern China on the basis of the MODIS AOD product. Theoretical & Applied Climatology, (Part B): 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-017-2142-5.
Stanhill, G. (2007). A perspective on global warming, dimming, and brightening. Eos Transactions American Geophysical Union, 88(5), 58–58. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007EO450011.
Tao, M., Chen, L., Wang, Z., Wang, J., Che, H., Xu, X., Wang, W., Tao, J., Zhu, H., & Hou, C. (2017a). Evaluation of MODIS Deep Blue aerosol algorithm in desert region of East Asia: ground validation and inter-comparison. Journal of Geophysical Research, 122(19), 10,357–10,368. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JD026976.
Tao, M., Wang, Z., Tao, J., Chen, L., Wang, J., Hou, C., Wang, L., Xu, X., & Zhu, H. (2017b). How do aerosol properties affect the temporal variation of MODIS AOD Bias in Eastern China? Remote Sensing, 9(8), 800. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080800.
Tomasi, C., Lupi, A., Mazzola, M., Stone, R. S., Dutton, E. G., Herber, A., Radionov, V. F., Holben, B. N., Sorokin, M. G., Sakerin, S. M., Terpugova, S. A., Sobolewski, P. S., Lanconelli, C., Petkov, B. H., Busetto, M., & Vitale, V. (2012). An update on POLAR aerosol optical properties using POLAR-AOD and other measurements performed during the International Polar Year. Atmospheric Environment, 52(5), 29–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.02.055.
Wang, K., Dickinson, R. E., & Liang, S. (2009). Clear sky visibility has decreased over land globally from 1973 to 2007. Science, 323(5920), 1468–1470. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1167549.
Wang, W., Mao, F., Pan, Z., du, L., & Gong, W. (2017). Validation of VIIRS AOD through a comparison with a Sun photometer and MODIS AODs over Wuhan. Remote Sensing, 9(5), 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9050403.
Wei, J., Huang, B., Sun, L., Zhang, Z., Wang, L., & Bilal, M. (2017). A simple and universal aerosol retrieval algorithm for Landsat series images over complex surfaces. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 122(24), 13338–13355. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JD026922.
Wolff, C., Plessen, B., Dudashvilli, A. S., Breitenbach, S. F. M., Cheng, H., Edwards, L. R., & Strecker, M. R. (2017). Precipitation evolution of Central Asia during the last 5000 years. Holocene, 27(1), 0959683616652711. https://doi.org/10.1177/0959683616652711.
Xiao, Q., Zhang, H., Choi, M., Li, S., Kondragunta, S., Kim, J., Holben, B., Levy, R. C., & Liu, Y. (2016). Evaluation of VIIRS, GOCI, and MODIS Collection 6 AOD retrievals against ground sunphotometer observations over East Asia. Atmospheric Chemistry & Physics, 16(3), 20709–20741. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-16-1255-2016.
Xie, Y., Xue, Y., Jie, G., et al. (2017). Image fusion of MODIS AOD (collection 6) in China based on uncertainty. IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, 7(6), 3365–3368. https://doi.org/10.1109/IGARSS.2017.8127719.
Yang, S., Shi, G. Y., Chen, L., et al. (2011). Evaluation of moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) deep blue aerosol products using ground-based measurements over Beijing. Scientific Online Letters on the Atmosphere Sola, 7(1), 133–136. https://doi.org/10.2151/sola.2011-034.
Zhang, X. L., Xia, X. A., Che, H. Z., et al. (2014). Observation study on aerosol optical properties and radiative forcing using the ground-based and satellite remote sensing at background station during the regional pollution episodes. Environmental Science, 35(7), 2439–2448. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-015-0367-3.
Zhang, S., Wang, M., Ghan, S. J., et al. (2016a). On the characteristics of aerosol indirect effect based on dynamic regimes in global climate models. Atmospheric Chemistry & Physics Discussions, 15(17), 23683–23729. https://doi.org/10.5194/acpd-15-23683-2015.
Zhang, W., Gu, X., Xu, H., Yu, T., & Zheng, F. (2016b). Assessment of omi near-uv aerosol optical depth over central and East Asia. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 121(1), 382–398.
Zhang, T., Zeng, C., Gong, W., Wang, L., Sun, K., Shen, H., Zhu, Z., & Zhu, Z. (2017a). Improving spatial coverage for Aqua MODIS AOD using NDVI-based multi-temporal regression analysis. Remote Sensing, 9(4), 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9040340.
Zhang, Z., Ding, J., & Wang, J. (2017b). Spatio-temporal variations and potential diffusion characteristics of dust aerosol originating from Central Asia. Acta Geographica Sinica, 72(3), 507–520. https://doi.org/10.11821/dlxb20103011.
Zheng, X. B., Kang, W. M., & Zhao, T. L. (2008). Long-term trends in sunshine duration over Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau in Southwest China for 1961–2005. Geophysical Research Letters, 35(15), 386–390. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008GL034482.
Zhu, T., Weng, F. Z., Liu, H. X., John, D. (2010). Improvement of the use of MSG and GOES data in the NCEP GDAS, Proc. SPIE 7811, Atmospheric and Environmental Remote Sensing Data Processing and Utilization VI: Readiness for GEOSS IV, 781103. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.860090.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank everyone for providing helpful suggestions to improve this manuscript. MODIS aerosol product is provided by the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC).
Funding
This research was carried out with financial support provided by the Strategic Priority Research Program of the CAS, Pan-Third Pole Environment Study for a Green Silk Road (No. XDA20040400).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, D., Zhang, F., Yang, S. et al. Exploring the spatial-temporal characteristics of the aerosol optical depth (AOD) in Central Asia based on the moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS). Environ Monit Assess 192, 383 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08299-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08299-x