Abstract
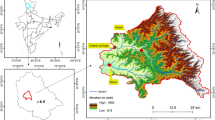
Changes to land use generate imbalances in the natural dynamics of aquatic ecosystems. These changes can vary according to the specific characteristics of each environment and due to seasonal factors, reinforcing the importance of studies in this area in different regions of the globe. Thus, the aim of this study was to analyze the effects of land use change on the rivers and streams of the Cachoeira River Basin in the Northeast of Brazil. Samples were collected bi-monthly at 16 points along the basin over 1 year and analyzed for physical and chemical parameters (temperature, pH, conductivity, and percentage saturation of dissolved oxygen), inorganic nutrients (NO3−, NO2−, NH4+/NH3, PO43−, SiO4) and dissolved major ions (Ca2+, K+, Mg2+, Na+, HCO3−). The highest concentrations of NO3−, NO2−, NH4+/NH3, and PO43− occurred at the points with the highest percentage of urban areas and population density. The major ions Ca2+, K+, Mg2+, Na+, and HCO3− were positively correlated with the percentage of pasture coverage; however, the high concentrations of these ions and the strong correlation between them revealed that other factors besides land use, such as soil cover, geological formation, and water deficit, may be jointly contributing to increases in their concentrations. Thus, the results show that urbanization represents the type of land use with the greatest negative effect on water quality since it alters the concentrations of inorganic nutrients dissolved in the Cachoeira River Basin.








Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Cultivation of cacao (Theobroma cacao) in the understorey, surrounded by natural vegetation.
Intrusive mass of plutonic igneous rock.
References
Adams, S., Titus, R., Pietersen, K., Tredoux, G., & Harris, C. (2001). Hydrochemical characteristics of aquifers near Sutherland in the Western Karoo, South Africa. Journal of Hydrology, 241, 91–103.
Alberts, J. M., Beaulieu, J. J., & Buffam, I. (2017). Watershed land use and seasonal variation constrain the influence of riparian canopy cover on stream ecosystem metabolism. Ecosystems, 20, 553–567.
Allan, J. D. (2004). Landscapes and riverscapes: the influence of land use on stream ecosystems. Annual Review of Ecology Evolution and Systematic, 35, 257–284.
ANA (2013). Atlas Esgotos: Despoluição de Bacias Hidrográficas. Agência Nacional de Águas. http://www.snirh.gov.br/portal/snirh/snirh-1/atlas-esgotos. Accessed 02 Dec 2019.
Andrade, T. M. B., Camargo, P. B., Silva, D. M. L., Piccolo, M. C., Vieira, S. A., Alves, L. F., Joly, C. A., & Martinelli, L. A. (2011). Dynamics of dissolved forms of carbon and inorganic nitrogen in small watersheds of the coastal Atlantic forest in Southeast Brazil. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 214, 393–408.
BAHIA. (2001). Programa de Recuperação das Bacias dos Rios Cachoeira e Almada - Diagnóstico Regional. Núcleo de Bacias Hidrográficas da UESC, Superintendência de Recursos Hídricos do Estado da Bahia.
Ballester, M. V. R., Victoria, D. C., Kruschea, A. V., Coburnb, R., Victoria, R. L., Richeyb, J. R., Logsdonb, M. G., Mayorgab, E., & Matricardic, E. (2003). A remote sensing/GIS-based physical template to understand the biogeochemistry of the Ji-Paraná river basin (Western Amazônia). Remote Sensing of Environment, 87, 429–445.
Barrenha, P. I. I., Tanaka, M. O., Hanai, F. Y., Pantano, G., Moraes, G. H., Xavier, C., Awan, A. T., Grosseli, G. M., Fadini, P. S., & Mozeto, A. A. (2018). Multivariate analyses of the effect of an urban wastewater treatment plant on spatial and temporal variation of water quality and nutrient distribution of a tropical mid-order river. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 190, 43–55.
Biggs, T. W., Dunne, T., & Martinelli, L. A. (2004). Natural controls and human impacts on stream nutrient concentrations in a deforested region of the Brazilian Amazon basin. Biogeochemistry, 68, 227–257.
Bossa, A. Y., Diekkrüger, B., & Agbossou, E. K. (2014). Scenario-based impacts of land use and climate change on land and water degradation from the meso to regional scale. Water, 6, 3152–3181.
Bustamante, M. M. C., Martinelli, L. A., Pérez, T., Rasse, R., Ometto, J. P. H. B., Pacheco, F. S., Lins, S. R. M., & Marquina, S. (2015). Nitrogen management challenges in major watersheds of South America. Environmental Research Letters. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/10/6/065007.
Butcher, J. B. (1995). Dissolved-oxygen analysis with temperature dependence. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 121, 756–759.
Cabrini, R., Canobbio, S., Sartori, L., Fornaroli, R., & Mezzanotte, V. (2013). Leaf packs in impaired streams: the influence of leaf type and environmental gradients on breakdown rate and invertebrate assemblage composition. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 224, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1697-8.
Capps, K. A., Bentsen, C. N., & Ramírez, A. (2016). Poverty urbanization and environmental degradation: urban streams in the developing world. Freshwater Science, 35, 429–435.
Carmouze JP (1994) O metabolismo dos ecossistemas aquáticos: fundamentos teóricos, métodos de estudo e análises químicas. Editora Edgar Blücher. São Paulo ed. Edgar Blücher.CEPLAC (1976) Comissão Execultiva do Plano da Lavoura cacaueira. Recursos Hídricos. 1976. Rio de Janeiro: IICA/CEPLAC.
CEPLAC. Cpmissão Executiva do Plano da Lavoura Cacaueira. (1976). Recursos Hidricos. Rio de Janeiro:IICA/CPLAC. 280p.
CEPTEC/INPE (2015) Centro de Previsão de Tempo e Estudos Climáticos/Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas Espaciais. Proclima – Programa de Monitoramento Climático em Tempo Real da região nordeste. http://proclima.cptec.inpe.br/ Accessed 02 Mar 2015.
Cetra, M., Sarmento-Soares, L. M., & Martins-Pinheiro, R. F. (2010). Peixes de riachos e novas Unidades de Conservação no sul da Bahia. Pan-American Journal of Aquatic Sciences, 5, 11–21.
Chaussê, T. C. C., Brandão, C. S., Silva, L. P., & Silva, D. M. L. (2016). Evaluation of nutrients and major ions in streams - implications of different timescale procedures. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 188, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-5034-0.
Correa-Gonzalez, J. C., Chavvez-Parga, M. C., Cortés, J. Á., & Pérez-Munguia, R. M. (2013). Photosynthesis, respiration and reaeration in a stream with complex dissolved oxygen pattern and temperature dependence. Ecological Modelling, 10, 220–227.
Dodds, W. K., & Smith, V. H. (2016). Nitrogen phosphorus and eutrophication in streams. Inland Waters, 6, 155–164.
EMBRAPA (2002) Solos da região Sudeste da Bahia: atualização da legenda de acordo com o sistema brasileiro de classificação de solos. Ilhéus: CEPLAC; Rio de Janeiro: Embrapa Solos. http://www.ceplac.gov.br/radar/Solos_Sudeste_Bahia.pdf. Accessed 16 Mar 2016.
EMBRAPA (2006) Centro Nacional de Pesquisa de Solos (Rio de Janeiro). Sistema brasileiro de classificação de solos. 2. ed. – Rio de Janeiro : EMBRAPA-SPI 2006.
Ficklin, D. L., Stewart, I. T., & Maurer, E. P. (2013). Effects of climate change on stream temperature, dissolved oxygen and sediment concentration in the Sierra Nevada in California. Water Resource Research, 49, 2765–2782.
Figueirêdo, A. F. R., & Calasans, N. A. (2008). Risco de salinização dos solos da Bacia Hidrográfica do Rio Colônia - sudeste da Bahia/Brasil. Engevista, 10, 15–26.
Filho WP, Morais EML (2001) Relationships between land use and macrophyte infestation in the Tucurui reservoir - Para – Brazil. International Geosciences and Remote Sensing Symposium - IGARSS'01 Sydney - Australia. Anais. IEEE 2001 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. https://doi.org/10.1109/IGARSS.2001.978248.
Folke, C., Jansson, A., Larsson, J., & Costanza, R. (1997). Ecosystem appropriation by cities. Ambio, 26, 168–172.
Germer, S., Neill, C., Vetter, T., Chaves, J., Krusche, A. V., & Elsenbeer, H. (2009). Implications of long-term land-use change for the hydrology and solute budgets of small catchments in Amazonia. Journal of Hydrology, 364, 349–363.
Gibbs, R. J. (1970). Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. American Association for the Advancement of Science, 170, 1088–1090.
Gonçalves MGM (2016) Gênese de solos com horizonte Bt no domínio gnáissico da depressão semiárida do Vale do Jequitinhonha MG. Dissertation Universidade Federal de Viçosa. http://www.locus.ufv.br/bitstream/handle/123456789/10374/texto%20completo.pdf?sequence=5. Accessed 5 June 2017.
Grasshoff, K., Erhardt, M., & Kremling, K. (1983). Methods of seawater analysis. Verlag Chemie: Weinheim.
Gücker, B., Silva, R. C. S., Graeber, D., Monteiro, J. A. F., Brookshire, E. N. J., Chaves, R. C., & Boëchat, I. G. (2016). Dissolved nutrient exports from natural and human-impacted Neotropical catchments. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 25, 378–390.
Halstead, J. A., Kliman, S., Berheide, C. W., Chaucer, A., & Cock-Esteb, A. (2014). Urban stream syndrome in a small lightly developed watershed: a statistical analysis of water chemistry parameters land use patterns and natural sources. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 186, 3391–3414.
Harvey R, Lye L, Khan A, Paterson R (2011). The influence of air temperature on water temperature and the concentration of dissolved oxygen in Newfoundland rivers. Canadian Water Resource Journal 36.
Huang, J., Li, Q., Pontius, R. G., Klemas, V., & Hong, H. (2013). Detecting the dynamic linkage between landscape characteristics and water quality in a subtropical coastal watershed southeast China. Environmental Management, 51, 32–44.
IBGE (1999) Instituto Brasileiro De Geografia e Estatística: Projeto RADAM BRASIL. Folha SD24 Salvador – Potencial dos recursos Hídricos. Rio de Janeiro: IBGE.
IBGE (2010) Instituto Brasileiro De Geografia e Estatística: Censo Demográfico Características da população e dos domicílios: resultados do universo. Rio de Janeiro: IBGE 2011. Disponível em: http://www.ibge.gov.br/home/estatistica/populacao/condicaodevida/indicadoresminimos/tabela1.shtm.
ITB (2015) Instituto Trata Brasil: Ranking do Saneamento - 2015. Brasília. http://www.tratabrasil.org.br/ranking-do-saneamento-2015 Accessed 10 Sept 2015.
Jeffrey, S. W., & Humphrey, G. F. (1975). New spectrophotometric equations for determining chlorophylls a, b, c and c2 in higher plants algae and natural phytoplankton. Biochemie und Physiologie der Pflanzen, 167, 191–194.
Klumpp, A., Bauer, K., Franz-Gerstein, C., & Menezes, M. (2002). Variation of nutrient and metal concentrations in aquatic macrophytes along the Rio Cachoeira in Bahia (Brazil). Environment International, 28, 165–171.
King, K.W., William, M.R., Johnson, L.T., Smith, D.R., Gregory, A.LaB., Fausey, N.R. (2017). Phosphorus Availability in Western Lake Erie Basin Drainage Waters: Legacy Evidence across Spatial Scales. Journal of Environmental Quality, 46, 466–469.
Lauerwald, R., Laruelle, G. G., Hartmann, J., Ciais, P., & Regnier, P. A. G. (2015). Spatial patterns in CO2 evasion from the global river network. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 29, 534–554.
Lewis E, Wallace DWR (1998) Program developed for CO2 system calculations. ORNL/CDIAC- 105. Oak Ridge Tennessee: Carbon Dioxide Information Analysis Center Oak Ridge National Laboratory U.S. Department of Energy .
Lucio MZTPQL, Santos SS, Silva DML (2012) Hydrochemistry of Cachoeira River (Bahia State Brazil). Acta Limnologica Brasiliensia, https://doi.org/10.1590/S2179-975X2012005000037.
Marchetti, M. P., Light, T., Moyle, P. B., & Viers, J. H. (2004). Fish invasions in California watersheds: testing hypotheses using landscape patterns. Ecological Applications, 14, 1507–1525.
Martinelli LA, Krusche AV, Vicgoria R L, Camargo PB, Bernardes M, Ferraz ES, Moraes JM, Ballester MV (1999) Effects of sewage on the chemical composition of Piracicaba river Brazil. Water Air & Soil Pollution, https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005052213652
Martins AAM, Santos RA (Orgs.) (1993) Folha Ibicaraí: SD.24-Y-B-V: Estado da Bahia. Brasília: CPRM 1993. Programa Levantamentos Geológicos Básicos do Brasil - PLGB. Brasília MME/SMM/CPRM. http://rigeo.cprm.gov.br/xmlui/handle/doc/ 8644?show=full. Acessed 23 June 2017.
Mazzetto, A. M., Feigl, B. J., Cerri, C. E. P., & Cerri, C. C. (2016). Comparing how land use change impacts soil microbial catabolic respiration in Southwestern Amazon. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjm.2015.11.025.
McDowell, W. H., Potter, J. D., & Ramirez, A. (2019). Nutrient export and elemental stoichiometry in an urban tropical river. Ecological Applications, 29, 1–13.
Meglioli, P. A., Aranibar, J. N., Villagra, P. E., & Riveros, C. V. (2017). Spatial patterns of soil resources under different land use in Prosopis woodlands of the Monte desert. Catena, 149, 86–97.
Melo CR, Melo SC, Silva JFR, Guedes PA, Luna DS (2014) Análise quali-quantitativa da Bacia do Rio Cachoeira (BA). XII Simpósio de Recursos Hídricos do Nordeste. http://www.abrh.org.br/xiisrhn/anais/papers/PAP018343.pdf. Acessed 15 Nov 2015.
Menezes, R. C. L., Conceição, H., Rosa, M. L. S., Galarza, M. A., Rios, D. C., & Macambira, M. J. B. (2012). O stock nefelina-sienítico rio Pardo província alcalina do sul do estado da Bahia. Geonomos, 20, 14–22.
Meyer, J. L., Paul, M. J., & Taulbee, W. K. (2005). Stream ecosystem function in urbanizing landscapes. Journal of the North American Benthological Society, 24, 602–612.
Millot, R., Gaillardet, J., Dupre, B., & Allegre, C. J. (2002). The global control of silicate weathering rates and the coupling with physical erosion: new insights from rivers of the Canadian Shield. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 196, 83–98.
Nacif PGS (2000) Ambientes naturais da Bacia Hidrográfica do Rio Cachoeira com ênfase nos Domínios Pedológicos. Thesis Universidade Federal de Viçosa. http://www.locus.ufv.br/handle/123456789/10732. Acessed 01 Jan 2016.
Nagy, R. C., Lockaby, B. G., Kalin, L., & Anderson, C. (2012). Effects of urbanization on stream hydrology and water quality: the Florida Gulf Coast. Hydrological Processes, 26, 2019–2030.
Neill, C., Deegan, L. A., Thomas, S. M., & Cerri, C. C. (2001). Deforestation for pasture alters nitrogen and phosphorus in small Amazonian streams. Ecological Applications, 11, 1817–1828.
O’Dricoll, C., O’Connor, M., Asam Zeyta, E., Brown, L. E., & Xiao, L. (2016). Forest clearfelling effects on dissolved oxygen and metabolism in petland stream. Journal of Environmental Management, 166, 250–259.
Ometto, J. P. H. B., Martinelli, L. A., Ballester, M. V., Gessner, A., Krusche, A. V., Victoria, R. L. E., & William, S. M. (2000). Effects of land use on water chemistry and macroinvertebrates in two streams of the piracicaba river basin south-east Brazil. Freshwater Biology, 44, 327–337.
Parsons TR, Maita Y, Lalli CM (1984) A manual of chemical and biological methods for seawater analysis. 2. ed. Oxford: New York: Pergamon Pres.
Patel, P., Raju, N. J., Reddy, B. C. S. R., Suresh, U., Gossel, W., & Wycisk, P. (2016). Geochemical processes and multivariate statistical analysis for the assessment of groundwater quality in the Swarnamukhi River basin Andhra Pradesh India. Environmental Earth Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5108-x.
Paula, F. C. F., Silva, D. M. L., & Souza, C. M. (2012). Tipologias Hidroquímicas das Bacias Hidrográficas do Leste da Bahia. Revista Virtual de Química, 4, 365–373.
Pereira, S. A., Trindade, C. R. T., Albertoni, E. F., & Palma-Silva, C. (2012). Aquatic macrophytes as indicators of water quality in subtropical shallow lakes, Southern Brazil. Acta Limnologica Brasiliensia, 24, 52–63.
Pompêo, M. (2008). Monitoramento e manejo de macrófitas aquáticas. Oecologia Brasiliensis, 12, 406–424.
Potter, J. D., McDowell, W. H., Helton, A. M., & Daley, M. L. (2014). Incorporating urban infrastructure into biogeochemical assessment of urban tropical stream in Puerto Rico. Biogeochemistry, 121, 272–286.
Powers, S. M., Bruulsema, T. W., Burt, T. P., Chan, N. L., Elser, J. J., Haygarth, P. M., Howden, J. N. K., Jarvie, H. P., Lyu, Y., Peterson, H. M., Sharpley, A. N., Shen, J., Worrall, F., & Zhang, F. (2016). Long-term accumulation and transport of anthropogenic phosphorus in three river basins. Nature Geoscience, 9, 353–356.
Prakash, K. L., Raghavendra, K., & Somashekar, R. K. (2009). Temporal-scale spectral variability analysis of water quality parameters to realize seasonal behaviour of a tropical river system-River Cauvery India. Journal of Environmental Biology, 30, 235–240.
Rajwa-Kuligiewicz, A., Bialik, R. J., & Rowinki, P. M. (2015). Dossilved oxygen and water temperature dynamics in lowland rivers over various timescale. Journal of Hydrology Hydromechanics, 63, 353–363.
Rosa, M. L. S., Conceição, H., Macambira, M. J. M., Marinho, M. M., & Marques, L. S. (2003). Idade (pb-pb) e aspectos petrográficos e litogeoquímicos do Complexo Alcalino Floresta Azul sul do Estado da Bahia. Revista Brasileira de Geociencias, 33, 13–20.
Salomão, M. S. M. B., Cole, J., Clemente, C. A., Silva, D. M. L., Camargo, P. B., Victoria, R. L., & Martinelli, L. A. (2008). CO2 and O2 dynamics in human-impacted watersheds in the state of São Paulo, Brazil. Biogeochemistry, 88, 271–283.
Santana, L. M., Moraes, M. E. B., Silva, D. M. L., & Ferragut, C. (2016). Spatial and temporal variation of phytoplankton in a tropical eutrophic river. Brazilian Journal of Biology, 76, 600–610.
SEI - Sítio da Superintendência de Estudos Econômicos e Sociais da Bahia-SEI (1999) Série Estudos e Pesquisas 45. Balanço hídrico do estado da Bahia. Salvador 1999. http://www.sei.ba.gov.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=76&Itemid=284. Accessed 28 Apr 2016.
Seitzinger, S. P., Styles, R. V., Boyer, E. W., Alexander, R. B., Billen, G., Howarth, R. W., Mayer, B., & Breemen, N. (2002). Nitrogen retention in rivers: model development and application to watersheds in the northeastern U.S.A. Biogeochemistry. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015745629794.
Sferratore, A., Garnier, J., Billen, G., Conley, D. J., & Pinault, S. (2006). Diffuse and point sources of silica in the Seine River watershed. Environmental Science and Technology, 40, 6630–6635.
Silva Junior, L. G. A., Gheyi, H. R., & Medeiros, J. F. (1999). Composição química de águas do cristalino do nordeste brasileiro. Revista Brasileira de Engenharia Agrícola e Ambiental, 3, 11–17.
Silva, J. S. O., Bustamante, M. M. C., Markewitz, D., Krusche, A. V., & Ferreira, L. G. (2011a). Effects of land cover on chemical characteristics of streams in the Cerrado region of Brazil. Biogeochemistry, 105, 75–88.
Silva, V. A., Moreau, M. S., Moreau, A. M. S. S., & Rego, N. A. C. (2011b). Uso da terra e perda de solo na Bacia Hidrográfica do Rio Colônia Bahia. Revista Brasileira Engenharia Agrícola Ambiental, 15, 310–315.
Silva, D. M. L., Camargo, P. B., Mcdowell, W. H., Salomão, M. S. M. B., Vieira, I., & Martinelli, L. A. (2012). Influence of land use changes on water chemistry in streams in State of São Paulo southeast Brazil. Annals Brazilian Academy of Sciences, (Impress), 84, 919–930.
Tran, C. P., Bode, R. W., Smith, A. J., & Klepper, G. S. (2010). Land-use proximity as a basis for assessing stream water quality in New York State (USA). Ecological Indicators. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2009.12.002.
Trindade, M. E. J., Peressin, A., Cetra, M., & Jucá-Chagas, R. (2013). Variation in the diet of a small characin according to the riparian zone coverage in an Atlantic Forest stream northeastern Brazil. Acta Limnologica Brasiliensia, 25, 34–41.
Tromboni, F., & Dodds, W. K. (2017). Relationships between land use and stream nutrient concentrations in a highly urbanized tropical region of Brazil: thresholds and riparian zones. Environmental Management, 60, 30–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-017-0858-8.
UNFPA (2007) State of world population 2007: unleashing the potential of urban growth United Nations Population Fund. http://www.unfpaorg/swp/2007/presskit/pdf/sowp2007_engpdf
Walsh, C. J., Roy, A. H., Feminella, J. W., Cottingham, P. D., Groffman, P. M., & Morgan, R. P. (2005). The urban stream syndrome: current knowledge and the search for a cure. Journal of the North American Benthological Society, 24, 706–723.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the support provided from the FAPESB for the doctorate scholarship. We are grateful to all field volunteers who participated in the field collection and all the people who directly or indirectly contributed to this work.
Funding
This work received funding from the Universidade Estadual de Santa Cruz [Grant Number 0220.1100.1360].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cerqueira, T.C., Mendonça, R.L., Gomes, R.L. et al. Effects of urbanization on water quality in a watershed in northeastern Brazil. Environ Monit Assess 192, 65 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-8020-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-8020-0